Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Table 6 2 Robbins
Hochgeladen von
Jessica Bittar CamargoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Table 6 2 Robbins
Hochgeladen von
Jessica Bittar CamargoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
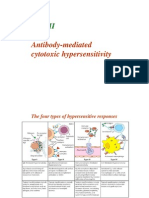
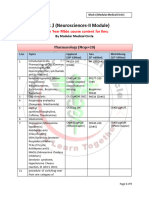
TABLE 6-2 MECHANISMS OF IMMUNOLOGICALLY MEDIATED HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS
TYPE OF REACTION PROTOTYPIC DISORDER IMMUNE MECHANISMS PATHOLOGIC LESIONS
Immediate (Type I) Hypersensitivity Anaphylaxis; allergies, bronchial Production of IgE antibody --> immediate release of Vascular dilation, edema, smooth
asthma (atopic forms) vasoactive amines and other mediateors from muscle contraction, mucus production,
mastclls; later recruitment of inflammatorycells tissue injury, inflammation
Antibody-mediated (Type II) Autoimmune hemolytic anemia; Production of IgG, IgM --> binds to antigen on Phagocytosis and lysis of cells;
Hypersensitivity Goodpasture syndrome target cell or tissue --> phagocytosis or lysis of inflammation; in some diseases,
target cell by activated complement of Fc functional derangements without cell
receptors; recuitment of leukocytes or tissue injury
Immune complex-mediated (Type III) Systemic lupus erythematosus Deposition of antigen-antibody complexes --> Inflammation, necrotizing vasculitis
Hypersensitivity (SLE); some forms of complement activation --> recruitment of (fibrinoid necrosis)
glomerulonephritis; serum leukocytes by complement products and Fc
sickness; Arthus reaction receptors --> release of enzymes and other toxic
molecules
Cell-mediated (Type IV) Contact dermatitis; multiple Activated T lymphocytes --> (i) release of cytokines Pericascular cellular infiltrates; edema;
Hypersensitivity sclerosis; type I diabetes; --> inflammation and macrophage activation; (ii) T granuloma formation; cell destruction
rheumatoid arthritis; cell-mediated cytotoxicity
inflammatory bowel disease;
tuberculosis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DR - Tjok. Istri Anom Saturti, Sppd. MarsDokument16 SeitenDR - Tjok. Istri Anom Saturti, Sppd. MarsYogiswara KarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 6-2 RobbinsDokument1 SeiteTable 6-2 RobbinsPA2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDokument25 SeitenHypersensitivity Reactionsbpt2100% (3)
- Disorders of Immunity Hypersensitivity Reactions: Dr. Mehzabin AhmedDokument25 SeitenDisorders of Immunity Hypersensitivity Reactions: Dr. Mehzabin AhmedFrances FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitive Reactions 2-4Dokument29 SeitenHypersensitive Reactions 2-4Ammara ZulqarnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument49 SeitenHypersensitivityAkanksha MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type of Hypersensitivity Immune Cells Involved (Mediators) Mechanism of Activation Onset Example of ReactionDokument5 SeitenType of Hypersensitivity Immune Cells Involved (Mediators) Mechanism of Activation Onset Example of ReactionJiezl Abellano AfinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11 Hypersensitivity ReactionsDokument41 SeitenLecture 11 Hypersensitivity ReactionsAakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMMUNOPATHOLOGYDokument78 SeitenIMMUNOPATHOLOGYсветлый попов100% (2)
- RX HIPERSENSITIVITYDokument34 SeitenRX HIPERSENSITIVITYEvie WulansariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergy and HypersensitivityDokument49 SeitenAllergy and HypersensitivityMoshe Cohen'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immuno PathologyDokument71 SeitenImmuno Pathologyb9p6vmfnc4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemDokument12 SeitenChapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemAgnieszka WisniewskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Fallujah Dr. Ahmed Sami Jarad College of Vet. Medicine Ph.D. (Pathology)Dokument7 SeitenUniversity of Fallujah Dr. Ahmed Sami Jarad College of Vet. Medicine Ph.D. (Pathology)Ab AbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology of The Pathology of The Immune System Immune SystemDokument12 SeitenPathology of The Pathology of The Immune System Immune SystemHeru HanantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On Immunology-HypersensitivityDokument45 SeitenSeminar On Immunology-HypersensitivitySalman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument37 SeitenHypersensitivitykiguzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaksi HipersensitivitasDokument28 SeitenReaksi HipersensitivitasLita AdharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument49 SeitenHypersensitivityayeasha siddika0% (1)
- Khan Hypersensitivity Reactions Final 2011Dokument56 SeitenKhan Hypersensitivity Reactions Final 2011Poptarts83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology. 10. Allergy-1Dokument40 SeitenImmunology. 10. Allergy-1safildhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 HypersensitivityDokument21 SeitenChapter 12 HypersensitivityJalil HaddadinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type III and IV Hypersensitivity Rev. 02Dokument31 SeitenType III and IV Hypersensitivity Rev. 02Alvin ValgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammation & Immune-Mediated Diseases: Introduction of Biomedical ScienceDokument30 SeitenInflammation & Immune-Mediated Diseases: Introduction of Biomedical SciencekimmyrereNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 HypersensitivityDokument63 Seiten9 Hypersensitivitymohammed barwaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument17 SeitenHypersensitivityihtishamulhaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity Innate Immunity: When The Going Gets Tough, The Tough Gets Going...Dokument7 SeitenImmunity Innate Immunity: When The Going Gets Tough, The Tough Gets Going...dtimtimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 超敏反应Dokument32 Seiten14 超敏反应Jennifer DixonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.hypersensitivity Reactions 2Dokument32 Seiten6.hypersensitivity Reactions 2عوض الكريمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of The Immune Response and Inflammation 3Dokument47 SeitenDisorders of The Immune Response and Inflammation 3Cres Padua QuinzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Hypersensitive ReactionsDokument32 Seiten14 Hypersensitive ReactionsrahuldhodapkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDokument11 SeitenHypersensitivity ReactionsMenly SusadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hipersensitivity 200111Dokument67 SeitenHipersensitivity 200111Aris BayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology of The Pathology of The Immune System Immune SystemDokument11 SeitenPathology of The Pathology of The Immune System Immune SystemHeru HanantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity ReactionDokument36 SeitenHypersensitivity ReactionMohana Sundaram100% (1)
- BBS2-MB-K26 RX Hypersensitivity 1-4Dokument36 SeitenBBS2-MB-K26 RX Hypersensitivity 1-4Paul Behring ManurungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karaganda State Medical University: Department of Pathological PhysiologyDokument23 SeitenKaraganda State Medical University: Department of Pathological PhysiologyPraveen NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity PDFDokument9 SeitenHypersensitivity PDFAisyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDokument3 SeitenHypersensitivity ReactionsAndrabi Muzzamil100% (1)
- HypersensitivityDokument30 SeitenHypersensitivityShweta Mittal100% (1)
- Imunologi Kulit DahDokument17 SeitenImunologi Kulit DahSayyid Muzahar AL-idruzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Question: What Happens When Immune System Overreacts?Dokument42 SeitenBig Question: What Happens When Immune System Overreacts?Louloun MoussignacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity Reaction TypesDokument1 SeiteHypersensitivity Reaction TypesTom MallinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune Hypersensitivity: Self-Test QuestionsDokument13 SeitenImmune Hypersensitivity: Self-Test QuestionszaheerbdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument20 SeitenHypersensitivityJAIRA RIEYELLE LIPANANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic InflammationDokument17 SeitenChronic InflammationMuhammad FaheemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Undisarable and Alterd ImmunotyDokument81 SeitenChapter 11 Undisarable and Alterd ImmunotyTofikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity StatesDokument40 SeitenHypersensitivity StatesMorrison NjageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitive Reactions 2-060806 (REPORT)Dokument35 SeitenHypersensitive Reactions 2-060806 (REPORT)Frances Joy Gines - LinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alteration in Immune ResponseDokument29 SeitenAlteration in Immune ResponsePachita AlexandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 5 Hypersesitivity Fall 2023Dokument13 SeitenLec 5 Hypersesitivity Fall 2023lara.kharroubi33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic InflammationDokument46 SeitenChronic Inflammationفاطمه علي رسولNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument28 SeitenHypersensitivityFrank Walt15Noch keine Bewertungen
- University of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Pharmacy - Department of Medical TechnologyDokument7 SeitenUniversity of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Pharmacy - Department of Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell-Mediated & Humoral Immunity PathologyDokument65 SeitenCell-Mediated & Humoral Immunity PathologyCrystal GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of The Immune SystemDokument3 SeitenDiseases of The Immune SystemTwinkle SalongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument85 SeitenHypersensitivityasad bashir94% (16)
- Presentation 3 2010 01 16Dokument22 SeitenPresentation 3 2010 01 16Muhammad Shafiqullah AsadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mosaic of Autoimmunity: The Novel Factors of Autoimmune DiseasesVon EverandMosaic of Autoimmunity: The Novel Factors of Autoimmune DiseasesCarlo PerriconeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Biology and Clinical Aspects of InflammationVon EverandBasic Biology and Clinical Aspects of InflammationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Inflammation PDFDokument18 SeitenAcute Inflammation PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thioredoxin-Dependent Regulation of AIF-mediated DNA Damage PDFDokument13 SeitenThioredoxin-Dependent Regulation of AIF-mediated DNA Damage PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glutathione Redox Potential in The Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space Is Linked To The Cytosol and Impacts The Mia40 Redox State PDFDokument14 SeitenGlutathione Redox Potential in The Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space Is Linked To The Cytosol and Impacts The Mia40 Redox State PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Inflammation Robbins Basic Pathology Inflammation Repair PDFDokument24 SeitenAcute Inflammation Robbins Basic Pathology Inflammation Repair PDFJessica Bittar Camargo100% (1)
- AIF Inhibits Tumor Metastasis by Protecting PTEN From Oxidation PDFDokument18 SeitenAIF Inhibits Tumor Metastasis by Protecting PTEN From Oxidation PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mia Pathway A Key Regulator of MT Oxidative Protein Folding and Biogenesis PDFDokument9 SeitenMia Pathway A Key Regulator of MT Oxidative Protein Folding and Biogenesis PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Redox Environment in The Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space Is Maintained Separately From The Cytosol and Matrix PDFDokument9 SeitenThe Redox Environment in The Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space Is Maintained Separately From The Cytosol and Matrix PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox Regulation of Protein Folding in The Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space PDFDokument7 SeitenRedox Regulation of Protein Folding in The Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nakao JBC2015 PDFDokument12 SeitenNakao JBC2015 PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aging-Dependent Changes in Rat Heart Mitochondrial Glutaredoxins-Implications For Redox RegulationDokument13 SeitenAging-Dependent Changes in Rat Heart Mitochondrial Glutaredoxins-Implications For Redox RegulationJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The MIA System For Protein Import Into The Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space PDFDokument8 SeitenThe MIA System For Protein Import Into The Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytosolic Thioredoxin System Facilitates The Import of Mitochondrial Small Tim Proteins PDFDokument7 SeitenCytosolic Thioredoxin System Facilitates The Import of Mitochondrial Small Tim Proteins PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanistic and Kinetic Details of Catalysis of Thiol-Disulfide Exchange by Glutaredoxins and Potential Mechanisms of Regulation PDFDokument24 SeitenMechanistic and Kinetic Details of Catalysis of Thiol-Disulfide Exchange by Glutaredoxins and Potential Mechanisms of Regulation PDFJessica Bittar CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akbarzadeh 2007 Induksi STZ Diabetic PDFDokument5 SeitenAkbarzadeh 2007 Induksi STZ Diabetic PDFPutri MauraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDokument6 SeitenPolycystic Kidney DiseaseRimsha Khan100% (1)
- Case Study Chronic CholecystitisDokument24 SeitenCase Study Chronic CholecystitisShehada Marcos BondadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart FailureDokument4 SeitenHeart FailureDane WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurotransmitter ChartDokument1 SeiteNeurotransmitter Chartmonster40lbs100% (2)
- Fluid Electrolyte Acid-Base BalanceDokument16 SeitenFluid Electrolyte Acid-Base BalanceAsif AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDokument52 SeitenRheumatoid ArthritisArun NingarajappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPC First TestDokument102 SeitenCPC First TestChinnammal M100% (2)
- Phenotype and Risk Factors of Venom-Induced Anaphylaxis: A Case-Control Study of The European Anaphylaxis RegistryDokument19 SeitenPhenotype and Risk Factors of Venom-Induced Anaphylaxis: A Case-Control Study of The European Anaphylaxis Registrydesta widayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Dr. Habibah S. Muhiddin, SP.M (K) : Departement of Ophthalmology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin UniversityDokument31 SeitenDr. Dr. Habibah S. Muhiddin, SP.M (K) : Departement of Ophthalmology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin UniversityRey AlwiwikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam ChecklistDokument13 SeitenExam Checklistmahmoud selimNoch keine Bewertungen
- DUMMYZ005 : LPL - Production Test Collection Centre Sector - 18, Block-E Rohini DELHI 110085Dokument2 SeitenDUMMYZ005 : LPL - Production Test Collection Centre Sector - 18, Block-E Rohini DELHI 110085Yatin VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet On Exercise 6 Case Study On Peptic Ulcer DiseasesDokument10 SeitenWorksheet On Exercise 6 Case Study On Peptic Ulcer DiseasesShannen Costo50% (2)
- Radiologic Contrast ExaminationDokument9 SeitenRadiologic Contrast ExaminationAnneCarla PuzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 ELSO Meeting Abstracts.1Dokument109 Seiten2019 ELSO Meeting Abstracts.1Luis Rubén MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casos Clínicos UDokument12 SeitenCasos Clínicos USARA DANIELA RIOS RIVEROSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutaneous Manifestations of Juvenile Onset Lupus Erythematosus: A Clinical StudyDokument5 SeitenCutaneous Manifestations of Juvenile Onset Lupus Erythematosus: A Clinical StudyMaya SusantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perception DisordersDokument4 SeitenPerception DisordersSabi HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Book of TherapeuticsDokument28 SeitenPractical Book of TherapeuticsSara AbdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated 4th Year MBBS CourseDokument30 SeitenUpdated 4th Year MBBS CourseAbdurehman ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- PN Nclex ComprehensiveDokument52 SeitenPN Nclex ComprehensiveVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (1)
- Ecgds 09 00916Dokument4 SeitenEcgds 09 00916Houda El MoufidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled DocumentDokument16 SeitenUntitled Documentrobymuiruri42Noch keine Bewertungen
- H1 AntihistaminesDokument17 SeitenH1 AntihistaminesRoppeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kode Diagnosa Icd 10Dokument5 SeitenKode Diagnosa Icd 10Heri SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefixime: Suprax Class and CategoryDokument3 SeitenCefixime: Suprax Class and CategoryArianne Joy SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part2MICRO (COMPILED)Dokument9 SeitenPart2MICRO (COMPILED)Thea GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenosine Life MedicalDokument20 SeitenAdenosine Life MedicalLaura ZahariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatitis 10Dokument28 SeitenHepatitis 10Matto RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bulletproof MindDokument7 SeitenBulletproof MindAdrian StanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Pankaj R BodadeDokument8 Seiten2013 Pankaj R BodadeGeorge StoicaNoch keine Bewertungen