Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Good Gov Midterms Reviewer
Hochgeladen von
celOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Good Gov Midterms Reviewer
Hochgeladen von
celCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Good Gov Chapter 2 (Bus.
Ethics & CSR compared)
Chapter 1 (Bus. Ethics as foundation for CSR)
CSR- sense of responsibility towards community & environment in
Good governance- process for making & implementing decisions w/c it operates
Seal of Good Housekeeping- good performance in internal Similarities between CSR & Bus. Ethics
housekeeping, in areas of: 1. Beyond profit- address common public good beyond of
Local legislation corporate interest
Development planning 2. Beyond compliance- responds to higher standards &
Resource generation principles beyond mere obedience to law
Resource allocation 3. Beyond form- beyond public relations & image building
Assessment areas: Similarities existing between CSR & Bus. Ethics
Disaster preparedness Beyond compliance w/ law
Social protection Not tantamount w/ relativism
Business friendliness & competitiveness Born w/ universal values
Peace & order Not utilitarian
Environmental mgmt. Pragmatic & practical
Financial administration About firm conviction
Beyond public relations
Main characteristics of Good gov Centered on total human development
1. Accountable- fundamental requirement
-obligation to report, explain & be answerable for The true, the just, the fair, & the good- only 1 universal language for
consequences of decisions all business pratitioners
2. Transparent- able to clearly see how & why decision was
made Evolution of bus. Ethics
3. Responsive- serve needs of entire community while 1. 1st phase- sees profit & only profit
balancing competing interests 2. 2nd phase- complies w/ laws & regulations
4. Equitable & inclusive- feeling their interests have been 3. 3rd phase- conforms to ethical requirements to build its
considered by council in decision-making process image
-opportunities to participate in process 4. Ultimate phase- CSR & ethical mgmt. because it is the right
5. Effective & efficient- implement decisions & follow thing to do
processes that make best use of available people,
resources & time Chapter 3 (Ethical mgmt. of profit)
6. Participatory- have opportunity to participate in process
for making that decisions People go into business :
7. Follows rule of law- consistent w/ relevant legislation or Personal satisfaction
common law Earn livelihood
Serve society through goods & services they offer to
Ethics/ Moral philosophy- study of morality customers
Morality- beliefs about right & wrong, good & evil Make profit
Beliefs- set of values, rules, principles & theories of morality
Business ethics- moral principles act as guidelines for way a business Profit-Latin “pro” w/c means forward & “facere” w/c means to make
conducts -to make progress, advance, to move
-oxymoron or self-contradiction -residual between value of output & other costs
-measured in terms of money equivalent
Ethical management- basic behavioral principles of business ethics
that corp must comply Good sides of profit-motive
-relevant to business survival & corporate reputation Motivates people to do something meaningful
Bio-prospecting- looks for useful products in nature to create Promotes ingenuity & cleverness
pharmaceutical products Makes people productive
Bio-piracy- development of these pharmaceutical products w/o Generates potential capital for business
giving compensation to community
Bioprospect- search for substances produced by living organisms Bad sides of profit-motive
Promotes rivalry among competitors
Role of ethics in management Makes people focus only on making money
1. EM in workplace Turns businessman from being reflective & questioning
2. EM regarding intellectual property rights person
3. EM in sales, ads & marketing- issue on pricing & price
Promotes self-interest rather common good
4. EM in Production- ensure that products & production
processes do not cause harm
Chapter 4 (Business ethics is not Utilitarianism)
5. EM in finance, acctg, & auditing- manipulation of financial
markets, bribery
Utilitarianism- moral or good when it produces greatest result for
greatest number of people
-actions are right in proportion as they tend to promote Homo Economicus- equal only to his qualified materiality
happiness, wrong as they tend to to produce reverse of happiness Imago Dei- we are all created in image & likeness of God
Human labor- free, conscious & intelligent subj. of work
Jeremy Bentham- most moral thing to do is the thing provides
greatest benefit to greatest no. of people Chapter 8 (MP2)
-all pleasure are the same Respect for Fundamental Human rights
John Stuart Mill- happiness, not pleasure, should be standard of Universal declaration of Human rights- civil, political, economic,
utility social & cultural rights
-have higher & lower class
Rights that can never be suspended:
Chapter 5 (Business ethics is not Relativism) Right to life
Recognition as person before law
Relativism- belief that there’s no absolute truth, only truths that Freedom from thought, conscience & religion
particular individual happen to believe Freedom from torture
Freedom from slavery
Guanxi- Chinese term meaning “relationships” or “connections” Freedom from imprisonment for debt or from retroactive
-it’s not what you know, but who you know that’s important penal legislation
4 notions comprises relativism In’t labor organization conventions- concerned w/ human rights
1. Ethical- right or wrong depends on moral norms of society Right- personal entitlement to something
2. Situational – right or wrong based on particular situation Moral right- universal, inviolable & inalienable rights derived from
3. Cognitive- truth itself has no objective standard moral system
4. Cultural- we must understand individuals in context of -personal right that connect creator of work to their work
their own culture -begin when work is created, continue for lifetime & 70 yrs after
death
Chapter 6 (Business ethics is beyond Legal Compliance) Right of attribution- name is always shown w/ your work
Right of integrity- work is not treated in way that hurts your
Law- ordinance of reason promulgated by someone in authority reputation
-by nature, both persuasive & coercive Moral rights infringement- not have been properly named or
credited
Important features of law Derogatory treatment- treated your work in way that hurts
1. Must be morally acceptable reputation
2. Must be just
3. Precepts of law must be physically & morally possible Employment- labor conditions, recruiting & laying off employees
4. Must be ordained for common good Security- ensuring security of facilities & personnel
Economic dev’t- deciding w/c countries they are going to invest &
3 points of convergence operate
1. Coincidence Environment- identifying & managing environmental risk
2. Legal is the minimum requirement of ethics Community/ Social Responsibilities- making positive contribution to
3. Legal is not acceptable to ethics societies
Ethical Mgmt. mean going beyond legal compliance Chapter 9 (MP3)
1. Beyond profit Respect for Basic employee rights
2. Beyond compliance
3. Beyond form Right to work- part & parcel of right to life & duty to sustain
-fundamental right
Chapter 7 (MP1) People work to survive
Human dignity in priority of labor over capital Natural obligation to support out dependents
Psychological
Man above other M’s- above materials, machines, methods, mgmt.
money 1. Right to equal employment opportunities- embraces all
w/o discrimination
Human capital-human resource 2. Right to just wage & compensation- not only enable
Intellectual capital- human knowledge worker meet cost of living, but also provide means of
desirable improvements
Abraham Lincoln- capital is the fruit of labor 3. Right to security of tenure- services of workers cannot just
-16th president of USA be terminated except for just cause
-preserved Union, abolished slavery, strengthened federal Govt. & 4. Right to due process & grievance procedure
modernized economy -objective evaluation of case
-fair hearing & chance to appeal
John paul II in Centessimus Annus- priority of ethics over things &
superiority of spirit over matter Due process- plea for fair treatment
Homo Sapiens- thinking being Grievance machinery- alternative dispute settlement mechanism
Homo Politicus- equal to his being in society or involvement in
political party 5. Right to collective bargaining- right to have organizations
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Gov EthicsDokument10 SeitenGov Ethicsnarisalvador09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics RevisionDokument6 SeitenBusiness Ethics RevisionK57 PHAN QUOC THANHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Business EthicsDokument5 SeitenChapter 4 - Business EthicsRavindra ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics 2023 Ethics and EnvironmentDokument5 SeitenEthics 2023 Ethics and EnvironmentPauleene Mae McGuireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics: Members: Ngo Thu Dung Pham Van Anh Pham Thi Hong NhungDokument49 SeitenBusiness Ethics: Members: Ngo Thu Dung Pham Van Anh Pham Thi Hong NhungDo Kieu LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical DelimaDokument10 SeitenEthical Delimaaditir.khandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics Mba NotesDokument6 SeitenBusiness Ethics Mba NotesJebin James67% (3)
- Introduction To Business Ethics and Social ResponsibilityDokument23 SeitenIntroduction To Business Ethics and Social ResponsibilityJojo De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orgnizational Management: The Firm and Its EnvironmentDokument5 SeitenOrgnizational Management: The Firm and Its EnvironmentOSHIENoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Business EthicsDokument19 SeitenSummary of Business EthicsRemrose DechillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics, Fraud, and Internal Control (Chapter 3)Dokument6 SeitenEthics, Fraud, and Internal Control (Chapter 3)Mary Claudette UnabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business EthicsDokument53 SeitenBusiness EthicsEdwin Lopez100% (3)
- Introduction GGCSRDokument9 SeitenIntroduction GGCSRhenry siyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics, Social Responsibilty, and Stakeholders NotesDokument7 SeitenEthics, Social Responsibilty, and Stakeholders NotesMa.Edarlee RaccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Decision Making Unit 1Dokument15 SeitenEthical Decision Making Unit 1Gayatri ChopraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Pointers of EthicsDokument14 SeitenKey Pointers of EthicsSsneha DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics and CSR Presentation RevisedDokument84 SeitenBusiness Ethics and CSR Presentation RevisedJuvi CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Governance and Social Responsibility ReviewerDokument5 SeitenGood Governance and Social Responsibility ReviewerDe Villa, Ivy JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics QASMSDokument43 SeitenBusiness Ethics QASMSUltimate MemerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.principles of Business EthicsDokument7 Seiten1.principles of Business Ethicslegacy guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics & Corporate GovernanceDokument55 SeitenBusiness Ethics & Corporate Governancegau7766Noch keine Bewertungen
- GovernanceDokument5 SeitenGovernanceKRISTINA CASSANDRA CUEVASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics ReviewerDokument4 SeitenEthics ReviewerMaye PilapilNoch keine Bewertungen
- GGSR ReviewerDokument10 SeitenGGSR ReviewerFan GhoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Ethics: "Doing What Is Right"Dokument11 SeitenProfessional Ethics: "Doing What Is Right"harpominderNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRG650 Notes 2Dokument9 SeitenCRG650 Notes 22022919913Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theory Text - SEP 19Dokument7 SeitenTheory Text - SEP 19Nitin DhantoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout 3Dokument5 SeitenHandout 3DiemXieNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 02 Ethical Problems of OrganizationDokument25 SeitenCH 02 Ethical Problems of Organizationwestern111Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Ethics SampleDokument31 Seiten5 Ethics SampleAruna RajappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics and Social ResponibilitiesDokument18 SeitenEthics and Social ResponibilitiesAnup ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 9 - Ethics and CSRDokument28 SeitenWEEK 9 - Ethics and CSRomer1234viralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smith and Robersons Business Law 15th Edition Mann Solutions ManualDokument25 SeitenSmith and Robersons Business Law 15th Edition Mann Solutions ManualBriannaWashingtonpoyb100% (38)
- Corporate Culture and Ethical Climate: By: Debashree DasDokument25 SeitenCorporate Culture and Ethical Climate: By: Debashree DasNavneet MayankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics HandoutsDokument4 SeitenBusiness Ethics HandoutsAsterCauliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business EthicsDokument5 SeitenBusiness EthicsIan Paolo EspanolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics and Corporate GovernanaceDokument21 SeitenBusiness Ethics and Corporate GovernanaceShivam KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ba 203 Social PhilosophyDokument24 SeitenBa 203 Social PhilosophyKath HidalgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics in International BusinessDokument16 SeitenEthics in International BusinessBemnetNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Importance of Ethics in BusinessDokument27 SeitenThe Importance of Ethics in BusinessSederiku KabaruzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in EntrepreneurshipDokument2 SeitenReviewer in EntrepreneurshipRoselyn AnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch1.Vela Business Ethics OverviewDokument14 SeitenCh1.Vela Business Ethics Overviewvikasgoyal86Noch keine Bewertungen
- EthicsDokument38 SeitenEthicsavinash35Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics: Felix M. Del Rosario, Cpa, MbaDokument38 SeitenBusiness Ethics: Felix M. Del Rosario, Cpa, Mbafelix madayag del rosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Choices in Business (Modified)Dokument20 SeitenEthical Choices in Business (Modified)megha angadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics and GovernanceDokument5 SeitenEthics and GovernanceChinmay PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUSINESS ETHICS 3rd - 033045Dokument4 SeitenBUSINESS ETHICS 3rd - 033045Arnel DelingonNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Ethics of Principles and RightsDokument14 SeitenAn Ethics of Principles and RightsAllan GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics and BusinessDokument8 SeitenEthics and BusinesspjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business EthicsDokument26 SeitenBusiness EthicsDwight Jenna de MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics, The Changing Environment, and Stakeholder ManagementDokument26 SeitenBusiness Ethics, The Changing Environment, and Stakeholder ManagementDwight Jenna de MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 11 - SustainabilityDokument5 SeitenTopic 11 - SustainabilityCalvin YaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics ReviewerDokument1 SeiteBusiness Ethics ReviewerBea Dela PeniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics NoteDokument54 SeitenBusiness Ethics NoteSheetal Karmacharya100% (1)
- Module 3Dokument8 SeitenModule 3Mary Joy GeronaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1-3Dokument10 SeitenChapter 1-3GWYNETH SYBIL BATACANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7: Introduction To Ethics Business EthicsDokument8 Seiten7: Introduction To Ethics Business EthicsEll VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Issues in Management - LDDokument4 SeitenEthical Issues in Management - LDpriyanshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To EthicsDokument26 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction To EthicsAshleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filipino Ballet ProductionsDokument2 SeitenFilipino Ballet ProductionscelNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Financial Environment: © 2008 John Wiley and SonsDokument39 SeitenThe Financial Environment: © 2008 John Wiley and SonscelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Validating/Qualifying Exam For Far 3Dokument9 SeitenValidating/Qualifying Exam For Far 3celNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive Research Embraces A Large Proportion of Research. It Is Preplanned and Structured in DesignDokument6 SeitenDescriptive Research Embraces A Large Proportion of Research. It Is Preplanned and Structured in DesigncelNoch keine Bewertungen
- StatisticsDokument8 SeitenStatisticscelNoch keine Bewertungen
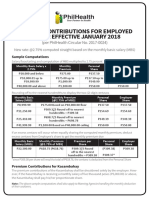
- PremiumContributionTable PDFDokument1 SeitePremiumContributionTable PDFcelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Ethics As Foundation For CSRDokument46 SeitenBus Ethics As Foundation For CSRcelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psy 370Dokument5 SeitenPsy 370ZoePhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Legal Logic and Legal RhetoricDokument10 SeitenDifference Between Legal Logic and Legal Rhetoricgagan deepNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Handbook of Existential TherapyDokument10 SeitenWorld Handbook of Existential TherapyFaten SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Researc Methodology FinalDokument18 SeitenResearc Methodology FinalKamya ChandokNoch keine Bewertungen
- PoliticaDokument301 SeitenPoliticaIsaúl FerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey - Qualtrics Survey SoftwareDokument5 SeitenSurvey - Qualtrics Survey SoftwaredavidmbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- LeadershipDokument8 SeitenLeadershipehm-ar. SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 7 - Analects of ConfuciusDokument6 SeitenLESSON 7 - Analects of ConfuciusKhristel AlcaydeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Studies On Leadership in Improving The Quality of Performance and Institutional ImageDokument7 SeitenEthical Studies On Leadership in Improving The Quality of Performance and Institutional ImageInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Themes of Realism and Its Implication To Educ.Dokument26 SeitenKey Themes of Realism and Its Implication To Educ.fikru terfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wordsworth's Attitude To Nature and Man As Revealed in Tintern AbbeyDokument2 SeitenWordsworth's Attitude To Nature and Man As Revealed in Tintern AbbeyAly FahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- الظاهراتية والظاهراتية التأويلية رؤية في المفاهيم والعلاقاتDokument20 Seitenالظاهراتية والظاهراتية التأويلية رؤية في المفاهيم والعلاقاتlamia alliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal & Ethical IssuesDokument13 SeitenLegal & Ethical IssuesAnusha Verghese50% (2)
- RetributionDokument5 SeitenRetributiongraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Does Everybody Have A TwinDokument4 SeitenDoes Everybody Have A TwinJoshua Sygnal GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICB Cultural Dilemma 6Dokument2 SeitenICB Cultural Dilemma 6Mahamud AbdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oedipus Rex As A Prominent TragedyDokument3 SeitenOedipus Rex As A Prominent TragedyGlory ChrysoliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Political Theory - An IntroductionDokument3 SeitenPolitical Theory - An IntroductionyashichauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Theories FinalDokument5 SeitenLearning Theories FinalJeo CapianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - God His Character and AttributesDokument7 SeitenLesson 3 - God His Character and AttributesgkeministryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antonio GramciDokument9 SeitenAntonio GramciIrene JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Polysphere BOOK #ONEDokument63 SeitenThe Polysphere BOOK #ONECGBENJNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Reflection On Feminism and The Post-Colonial Conception of Gender in The Philippine ContextDokument4 SeitenA Reflection On Feminism and The Post-Colonial Conception of Gender in The Philippine ContextJoms AltomeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BFM 3A978 1 4419 1428 6 2F1Dokument106 SeitenBFM 3A978 1 4419 1428 6 2F1Andi Putra NainggolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SociologyDokument5 SeitenSociologyjani_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lectures 3 To 8 Trolley Problem and Ethics, Utilitarianism and DeontologyDokument27 SeitenLectures 3 To 8 Trolley Problem and Ethics, Utilitarianism and DeontologysidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Validity in Evaluation - EPP - Manuscript - Accepted Manuscript For Preprint v3Dokument33 SeitenValidity in Evaluation - EPP - Manuscript - Accepted Manuscript For Preprint v32056160075Noch keine Bewertungen
- Weighted Hinge QuestionsDokument10 SeitenWeighted Hinge QuestionsBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purpose and Function of LawDokument13 SeitenPurpose and Function of Lawnagendra yanamala100% (1)
- 2023 - Feb-Reg - Filsafat Hukum-Sap TerperinciDokument1 Seite2023 - Feb-Reg - Filsafat Hukum-Sap TerperinciKeziaNoch keine Bewertungen