Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Q&A Pressure
Hochgeladen von
Zenif Fatkhur Rohman0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
35 Ansichten3 SeitenAbsolute pressure is the force exerted by a fluid per unit area, while gauge pressure is the difference between absolute and atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pressure is the amount atmospheric pressure exceeds absolute pressure. Common pressure units include the Pascal, psi, kg/cm2, and bar. Common pressure measurement devices include U-tube, well-type, inclined, ring balance, and micro manometers. Bourdon tubes, bellows, and diaphragms are common elastic pressure gauges that sense pressure and convert it to displacement or deflection proportional to the applied pressure. Capacitive, piezoresistive, and thermal conductivity pressure transducers also measure pressure based on changes in their electrical properties in response to applied pressure
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Q&A Pressure.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenAbsolute pressure is the force exerted by a fluid per unit area, while gauge pressure is the difference between absolute and atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pressure is the amount atmospheric pressure exceeds absolute pressure. Common pressure units include the Pascal, psi, kg/cm2, and bar. Common pressure measurement devices include U-tube, well-type, inclined, ring balance, and micro manometers. Bourdon tubes, bellows, and diaphragms are common elastic pressure gauges that sense pressure and convert it to displacement or deflection proportional to the applied pressure. Capacitive, piezoresistive, and thermal conductivity pressure transducers also measure pressure based on changes in their electrical properties in response to applied pressure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
35 Ansichten3 SeitenQ&A Pressure
Hochgeladen von
Zenif Fatkhur RohmanAbsolute pressure is the force exerted by a fluid per unit area, while gauge pressure is the difference between absolute and atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pressure is the amount atmospheric pressure exceeds absolute pressure. Common pressure units include the Pascal, psi, kg/cm2, and bar. Common pressure measurement devices include U-tube, well-type, inclined, ring balance, and micro manometers. Bourdon tubes, bellows, and diaphragms are common elastic pressure gauges that sense pressure and convert it to displacement or deflection proportional to the applied pressure. Capacitive, piezoresistive, and thermal conductivity pressure transducers also measure pressure based on changes in their electrical properties in response to applied pressure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Question and Answer
Subject: Instrumentation
1. Define Absolute pressure
The force exerted by the fluid per unit area of the wall of the container is called the absolute
pressure.
2. Define Gauge pressure
It is the difference between the absolute and the local atmospheric pressure.
3. Define vacuum pressure
Vacuum pressure is the amount by which atmospheric pressure exceeds the absolute pressure.
4. Give some units of pressure
Pascal,
psi,
kg/cm2,
bar etc.
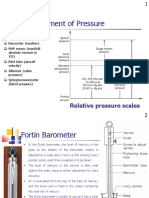
5. What are the types of manometers?
U – tube manometer
Well type manometer
Inclined type manometer
Ring balance manometer
Micro manometer
6. State the principle of U- tube manometer
The U-tube manometer is the simplest measuring instrument used for gauge pressure
measurement by balancing the pressure against the weight of a column of liquid.
7. What are the types of elastic pressure gauges?
Bourdon tubes
Bellows
Diaphragms
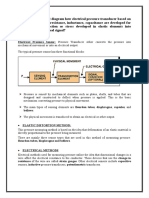
8. Explain the principle of Bourdon tube pressure gauge
Bourdon tube is a device that senses pressure and converts the pressure into displacement.
Since the bourdon tube displacement is a function of the applied pressure it may be amplified
and indicated by a pointer.
9. What are the advantages and disadvantages of bellows?
Advantages:
1. Simple construction
2. Moderate price
3. Useful for measurement of low, medium, high pressures.
4. Used to measure absolute, gauge, differential pressures
Disadvantages:
1. Not suited for dynamic measurements.
2. Errors will occur
10. State the principle of Diaphragms
The pressure to be measured is applied to the diaphragm, causing it to deflect. That deflection
is being proportional to the applied pressure.
11. What are the types of diaphragms?
Flat type
Corrugated type
12. State the principle of LVDT and STRAIN GAUGE
LVDT:
The differential output voltage of the secondary winding of the LVDT is proportional to the
displacement experienced by the mass caused due to acceleration on the Core; the differential
output voltage becomes a measure of acceleration.
Strain Gauge:
When the strain gauge is stretched or compressed, its resistance changes on the account of the
fact that both length and diameter of the strain gauge changes. This change in resistance will be
proportional to the torque in the shaft.
13. State the principle of capacitive pressure transducer
The output of a parallel plate capacitor depends on the gap between its movable and fixed
plates. Due to pressure, if the gap between the plates is altered, its capacitance also changes.
This change in capacitance becomes a measure of pressure.
14. Write the advantages and disadvantages of capacitive pressure transducer
Advantages:
Simple construction
Useful for measurement of low, medium, high pressures.
Used to measure absolute, gauge, differential pressures
Disadvantages:
Errors will occur
15. State the principle of piezo-resistive pressure sensor
When a wire is subjected to pressure from all sides its electrical resistance changes. This change
in resistance occurs due to the distortion produced in the crystal when subjected to external
pressure.
16. What are the applications of piezoresistive pressure sensor?
Household appliances – washing machine, vacuum cleaner
Automotive appliances – oil level, gas level
Biomedical appliances – blood pressure measurement
17. State the principle of Mc leod gauge
Compression of a sample of the low pressure gas to a level which is sufficiently high so that it
can be read with the use of a simple manometer.
18. What are the advantages and limitations of Mc leod gauge
Advantages:
Independent of gas composition
Linear relationship exists
Disadvantages:
It should obey boyle‘s law.
It cannot give a continuous output.
19. State the principle of thermal conductivity gauges
When a conductivity wire gets heated electric current flows through it. The rate at which heat is
dissipated from this wire depends on the conductivity of the surrounding media.
20. What are the types of thermal conductivity gauge?
Pirani gauge
Thermocouple type conductivity gauge
Ionization gauge
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures ClassificationDokument8 SeitenElements, Compounds and Mixtures ClassificationMinorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and InstrumentationDokument4 SeitenMeasurement and InstrumentationAbirami RajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radar PlottingDokument23 SeitenRadar Plottingthugsdei100% (2)
- 1-Sheet 4 Measure AnswerDokument17 Seiten1-Sheet 4 Measure AnswerBahaa EmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5Dokument29 SeitenUnit 5rajamanickam sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Media8092592512293728315Dokument8 SeitenLocal Media8092592512293728315Bowie S. PascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Measurement Part 3 of 3 PDFDokument37 SeitenPressure Measurement Part 3 of 3 PDFSimanjuntak JulpianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and Process Control: Khalid NawazDokument19 SeitenInstrumentation and Process Control: Khalid NawazAizen SousukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2. Preasure and Flow MeausrementDokument16 Seiten3.2. Preasure and Flow MeausrementAbeyu AssefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4156342Dokument19 Seiten4156342Th GmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ans: Electrical Pressure Sensor: Pressure Transducer Either Converts The Pressure IntoDokument6 SeitenAns: Electrical Pressure Sensor: Pressure Transducer Either Converts The Pressure IntoSpryknterNoch keine Bewertungen
- FME Notes Unit5Dokument16 SeitenFME Notes Unit5vishal shuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL (Presentation)Dokument33 SeitenINSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL (Presentation)Abdul RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Najva s5 PDFDokument7 SeitenNajva s5 PDFUwaiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain Bernoulli's Theorem. State Its ApplicationDokument4 SeitenExplain Bernoulli's Theorem. State Its ApplicationQamar Hassan IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Pressure Sensors Learning Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDokument4 SeitenMechanical Pressure Sensors Learning Instrumentation and Control EngineeringNGASSAKI ATONGUI Christ HubertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strain GaugeDokument28 SeitenStrain Gaugekanye trikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation Lab: Malla Reddy Engineering College (Autonomous) Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument34 SeitenInstrumentation Lab: Malla Reddy Engineering College (Autonomous) Department of Mechanical EngineeringRavi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Pressure and Vacuum with TransducersDokument16 SeitenMeasure Pressure and Vacuum with Transducerssukriti dhauniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure MeasurementDokument28 SeitenPressure MeasurementbcramcNoch keine Bewertungen
- (I) Resistive, (Ii) Inductive, (Iii) Capacitive, (Iv) Piezo-Electric TransducersDokument4 Seiten(I) Resistive, (Ii) Inductive, (Iii) Capacitive, (Iv) Piezo-Electric Transducersamritsaikias4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ics Manual PDFDokument47 SeitenIcs Manual PDFSurya RawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibrating Pressure SensorsDokument10 SeitenCalibrating Pressure SensorsromasokyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Pressure MeasurementDokument28 Seiten5 Pressure MeasurementMorshedul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summ Mid SemDokument9 SeitenSumm Mid Semhadeed shaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental PhysicsDokument7 SeitenExperimental PhysicsIthnaini KamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Measuring Instruments: Dr. Fahad Rehman CUI, Lahore CampusDokument69 SeitenPressure Measuring Instruments: Dr. Fahad Rehman CUI, Lahore CampusAhmed Mustafa100% (1)
- Pressure and Tempreture MeasurementDokument61 SeitenPressure and Tempreture MeasurementVarad DateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Portfolio Capstone ProjectDokument36 SeitenAuto Portfolio Capstone ProjectJohn wilbert CeprezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NI Tutorial 3639 enDokument4 SeitenNI Tutorial 3639 enNishanthini SuppiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bourdon GageDokument5 SeitenBourdon GageMark Aldaba ReytiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument48 SeitenChapter 5Endalk SimegnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Instrumentation - Module 3Dokument100 SeitenProcess Instrumentation - Module 3ibuddhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure SensingDokument8 SeitenPressure Sensingteacher9999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and P&ID - QuestionDokument6 SeitenInstrumentation and P&ID - QuestionSharath KotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module v. Calibration and Uses of Pressure & Temperature Measuring InstrumentsDokument25 SeitenModule v. Calibration and Uses of Pressure & Temperature Measuring InstrumentsDomingo NoverasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics Micro-Project: Topic: Study of Pressure Measuring DevicesDokument18 SeitenHydraulics Micro-Project: Topic: Study of Pressure Measuring DevicesGvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMDokument18 SeitenEMSuprava GhoshPaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- INinDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION Pewssure SensorDokument53 SeitenINinDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION Pewssure SensorAmna EhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Control System CompressDokument116 SeitenAutomatic Control System Compressswapnil28.08 k100% (1)
- Electronic Pressure SensorsDokument5 SeitenElectronic Pressure Sensorsmcbmcb159Noch keine Bewertungen
- Two Mark Question Answer: Unit I Measurement of Voltage and CurrentDokument8 SeitenTwo Mark Question Answer: Unit I Measurement of Voltage and CurrentPraveen Chandran C RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure & Temperature Gause NotesDokument9 SeitenPressure & Temperature Gause NotesNazimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure TransducerDokument12 SeitenPressure TransducerAsif BhatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Sensor: Class: III B.SC (Electronics) Subject: Sensor TechnologyDokument16 SeitenPressure Sensor: Class: III B.SC (Electronics) Subject: Sensor TechnologyThilaga KaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Instrumentation Ch.E-401: Muhammad Rashed JavedDokument22 SeitenIndustrial Instrumentation Ch.E-401: Muhammad Rashed JavedAqib LatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bourdon Tube-Type DetectorsDokument6 SeitenBourdon Tube-Type Detectorsputra sandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MELABDokument5 SeitenMELABKristoff GermainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transducers U2Dokument64 SeitenTransducers U2R NAVEEN KUMAR MECHNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSDFJSDDokument26 SeitenJSDFJSDJeremy CatallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation & Process ControlDokument51 SeitenInstrumentation & Process ControlChiến Phan Công100% (1)
- Summer Training Project Report: "Overview and Role of C & I in Thermal Power Plant"Dokument109 SeitenSummer Training Project Report: "Overview and Role of C & I in Thermal Power Plant"ysr3ee6926Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecourses - Ndri.res - in Moodle File - PHP 92 Lesson 16Dokument5 SeitenEcourses - Ndri.res - in Moodle File - PHP 92 Lesson 16Amit Kr GodaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurements: Part 2d: Measurement of PressureDokument15 SeitenMeasurements: Part 2d: Measurement of Pressureviswa37Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Ee ViiiDokument43 SeitenManual Ee ViiiAkhilesh Kumar MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Gauge and Transmitter GuideDokument35 SeitenPressure Gauge and Transmitter GuideTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Wire Pressure Transducers 2020uch1937 and 2020uch1936Dokument16 SeitenHigh Wire Pressure Transducers 2020uch1937 and 2020uch1936nishantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesta, Martinez (Sensors Pressure and Temperature)Dokument30 SeitenDiesta, Martinez (Sensors Pressure and Temperature)Rodolfo Rey TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Pressure: Static and Dynamic PressureDokument10 SeitenMeasurement of Pressure: Static and Dynamic PressureTarun VarshneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Is It Important?: Pressure MeasurementDokument28 SeitenWhy Is It Important?: Pressure MeasurementMd MohinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure SensorsDokument20 SeitenPressure Sensorshitesh bhoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Effective Surface Areas of Random PackingsDokument10 SeitenComparing Effective Surface Areas of Random PackingsAntonio MezzopreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diketopiperazines RevDokument27 SeitenDiketopiperazines RevIsaí MillánNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjoint Rans With Filtered Shape Derivatives For Hydrodynamic OptimisationDokument11 SeitenAdjoint Rans With Filtered Shape Derivatives For Hydrodynamic Optimisationvolo87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applying IGBTs - 5SYA 2053-04 PDFDokument22 SeitenApplying IGBTs - 5SYA 2053-04 PDFbacuoc.nguyen356Noch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Beams & Columns To Eurocode 4Dokument155 SeitenComposite Beams & Columns To Eurocode 4dfdfdfasd324sad100% (2)
- Audio Processing Quiz 1Dokument2 SeitenAudio Processing Quiz 1Tony BrooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Chemical Kinetics and Charge Transfer Based On Nonequilibrium ThermodynamicsDokument17 SeitenTheory of Chemical Kinetics and Charge Transfer Based On Nonequilibrium ThermodynamicsYoana Yoa YoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cati Pakistan Training Course - MechanicalDokument13 SeitenCati Pakistan Training Course - MechanicalImam Haryadi WibowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH20005-Chemical Reaction Engineering:) C C CRDokument2 SeitenCH20005-Chemical Reaction Engineering:) C C CRSunny KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- 85 Describing Motion OrganizerDokument10 Seiten85 Describing Motion OrganizerFernando Sorto50% (2)
- Chapter 22 Thermal Expansion: EXERCISE 122, Page 266Dokument9 SeitenChapter 22 Thermal Expansion: EXERCISE 122, Page 266NurulAinMatAron0% (1)
- Tutorial Chapter 1 2018Dokument3 SeitenTutorial Chapter 1 2018Ain Syahira0% (1)
- Submodular Set Function - WikipediaDokument5 SeitenSubmodular Set Function - WikipedianmahsevNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersDokument1 SeiteRCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersArwin VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDokument6 Seiten4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Numerical Programming I (For CSE) : Final ExamDokument7 SeitenNumerical Programming I (For CSE) : Final ExamhisuinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Differential Equations Standard Form and Operator FormDokument10 SeitenLinear Differential Equations Standard Form and Operator FormJoSaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Vapour Pressure of Hydrocarbon LiquidsDokument3 SeitenMeasuring Vapour Pressure of Hydrocarbon LiquidsAnnelzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curtain Wall System From Technal - Geode-BrochureDokument38 SeitenCurtain Wall System From Technal - Geode-BrochurebatteekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University KakinadaDokument4 SeitenJawaharlal Nehru Technological University KakinadaVenkat ChadalavadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 WS3Dokument2 SeitenUnit 6 WS3Kaitlyn TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum Material Boundary (MMB) and Its Advantages in GD&T Analysis PDFDokument6 SeitenMaximum Material Boundary (MMB) and Its Advantages in GD&T Analysis PDFSangeethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jar TestDokument1 SeiteJar TestEduardo Tonino Chavez GaytanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics PDFDokument51 SeitenElectrostatics PDFSaksham GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Electrical Induction Near Power LinesDokument22 SeitenCalculation of Electrical Induction Near Power LinesalpcruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Optical ProThe Optical Properties of Lung As A Function of Respirationperties of Lung As A Function ofDokument11 SeitenThe Optical ProThe Optical Properties of Lung As A Function of Respirationperties of Lung As A Function ofAgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interference PatternsDokument8 SeitenInterference PatternsAsa mathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearings ShaftsDokument74 SeitenBearings ShaftsCik MinnNoch keine Bewertungen