Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Face and Text Recognition For Visually Impaired Person Based On Raspberrypi-IJAERDVO5I0389731
Hochgeladen von
fawadn_84Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Face and Text Recognition For Visually Impaired Person Based On Raspberrypi-IJAERDVO5I0389731
Hochgeladen von
fawadn_84Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
e-ISSN (O): 2348-4470
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 5.71
p-ISSN (P): 2348-6406
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research
Development
Volume 5, Issue 03, March -2018
Face and Text Recognition for Visually Impaired Person Based On Raspberrypi
Dr.R.Naveen1, S.A.Sivakumar2, M.Cholavendan3, S.Satheesh kumar4,
A.Sivanesh Kumar Singh5, S.Thilak6, C.Arunkumar7
1
Associate Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering Info Institute of Engineering, Tamilnadu
2,3
Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering Info Institute of Engineering, Tamilnadu
4,5,6,7
UG Scholar, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Info Institute of Engineering, Tamilnadu
Abstract — Independent travel is a well known challenge for blind or visually impaired persons and also the increasing
availability of cost efficiency, high performance and portable digital imaging devices has created a tremendous
opportunity for supplementing traditional scanning for document image acquisition. We propose a camera based visual
assistance framework for text reading, motion of objects and the feelings of persons etc.. It converts into a voice output to
help blind peoples. Thus we propose this system from a single camera-captured image as well as more number of frames
and highlight some sample applications under development and feasible ideas for future development.
Keywords- Raspberrypi, blind people, sign recognition, digital imaging devices, visual assistance.
I. INTRODUCTION
To improve the ability of people who are blind or have significant visual impairments to independently access,
understand, and explore unfamiliar indoor and outdoor environments, we propose a new framework using a single
camera to detect and recognize the signs, text and obstacles to give audio as an output. we extract and recognize the text
information associated with the detected objects. We first extract text regions from indoor signs with multiple colors.
Then text character localization and layout analysis of text strings are applied to filter out background interference.
The object type, orientation, and location can be displayed as speech for blind travelers. To improve the ability of people
who are blind or have significant visual impairments to independently access, understand, and explore unfamiliar indoor
environments, we propose a new framework using a single camera to detect and recognize the face, obstacles, signs
incorporating text information associated with the detected object. In order to discriminate similar objects in indoor
environments, the text information associated with the detected objects is extracted.
This paper is organized as follows: section II. existing methods, section III proposed methods, section IV materials and
methods, followed by result in section V and conclusion in section VI.
II. EXISTING AGRICULTURAL AUTOMATION SYSTEM
This part illustrates the present method of monitoring and controlling agricultural fields.
2.1 Camera-based analysis of text and documents
Here they proposed a camera-based assistive framework to help blind persons to read text labels from cylinder objects in
their daily life. First, the object is detected from the background or other surrounding objects in the camera view
by shaking the object. Then we propose a mosaic model to unwrap the text label on the cylinder object surface and
reconstruct the whole label for recognizing text information. This model can handle cylinder objects in any orientations
and scales. The text information is then extracted from the unwrapped and flatted labels. The recognized text codes are
then output to blind users in speech. Experimental results demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed
framework from different cylinder objects with complex backgrounds.
2.2 Context-based Indoor Object Detection as an Aid to Blind Persons Accessing Unfamiliar Environments
In order to find different rooms (i.e. an office, a lab, or a bathroom) and other building amenities (i.e. an exit or an
elevator), they incorporated this door detection with text recognition. First they developed a robust and efficient
algorithm to detect doors and elevators based on general geometric shape, by combining edges and corners. The
algorithm is generic enough to handle large intra-class variations of the object model among different indoor
environments, as well as small inter-class differences between different objects such as doors and elevators.
Next, to distinguish an office door from a bathroom door, they extracted and recognize the text information associated
with the detected objects. Here first text regions from indoor signs with multiple colours were extracted. Then text
character localization and layout analysis of text strings are applied to filter out background interference. The extracted
text is recognized by using off-the-shelf optical character recognition (OCR) software products. The object type,
orientation, and location can be displayed as speech for blind travelers.
2.3 Eyes of Things
Responsible Research and Innovation (RRI) is an approach that anticipates and assesses potential implications and
@IJAERD-2018, All rights Reserved 90
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development (IJAERD)
Volume 5, Issue 03, March-2018, e-ISSN: 2348 - 4470, print-ISSN: 2348-6406
societal expectations with regard to research and innovation, with the aim to foster the design of inclusive and sustainable
research and innovation. While RRI includes many aspects, in certain types of projects ethics and particularly privacy, is
arguably the most sensitive topic. The objective in Horizon 2020 innovation project Eyes of Things (EoT) is to build a
small high performance, low-power, computer vision platform (similar to a smart camera) that can work independently
and also embedded into all types of artifacts. In this paper, we describe the actions taken within the project related to
ethics and privacy. A privacy by- design approach has been followed, and work continues now in four platform
demonstrators.
2.4 Blind people guidance system
This paper describes a guidance system for blind and partially sighted people with the aim of coping in the known and
unknown internal and external spaces without the assistance of human guides. This work represents a significant step
forward in the application of innovative technological solutions to increase independence and improve the quality of life
for people with disabilities. This paper describes the technical and functional architecture of the system for orientation
and guidance of a blind person using available modern technology. The described system consists of a digital sensor for
determining the location by dead reckoning technique, infrared marks in space and handheld device that provides voice
guidance instructions.
2.5 Reading Labels of Cylinder objects for blind
Here they proposed a camera-based assistive framework to help blind persons to read text labels from cylinder objects in
their daily life. First, the object is detected from the background or other surrounding objects in the camera view by
shaking the object. Then they proposed a mosaic model to unwarp the text label on the cylinder object surface and
reconstruct the whole label for recognizing text information. This model can handle cylinder objects in any orientations
and scales. The text information is then extracted from the unwarped and flatted labels. The recognized text codes are
then output to blind users in speech. Experimental results demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed
framework from different cylinder objects with 3rcomplex backgrounds.
III. PROPOSED METHOD WORKING METHODOLOGY
In all the above previous system we had found some errors which affects the efficiency of the system and its code. So, we
had done very efficient coding in python script which makes the coding side as simple as possible, we also used jessay
OS & open cv lib file to make thing more easy.
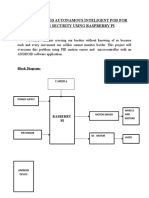
Visual assistance Head set
Raspberrypi
B+module
Blind person
objects
Voice output
Fig 1 Block Diagram of the Proposed Method
The main purpose of this model is to help blind persons by guiding them using this system design. It recognizes the face,
signs, obstacles, humans such as known and unknown persons will be identified using face and text recognition features.
It gives the scanned and recognized images in the form of audio output to help and guide the blind person. It is specially
designed to blind navigation purpose.
@IJAERD-2018, All rights Reserved 91
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development (IJAERD)
Volume 5, Issue 03, March-2018, e-ISSN: 2348 - 4470, print-ISSN: 2348-6406
Fig 2 Example showing road signs
IV. MATERIALS & METHODS
4.1 RASPBERRY PI
The Raspberry Pi 3 Model B is the third generation Raspberry Pi. This powerful credit-card sized single board computer
can be used for many applications and supersedes the original Raspberry Pi Model B+ and Raspberry Pi 2 Model B.
Whilst maintaining the popular board format the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B brings you a more powerful processer, 10x
faster than the first generation Raspberry Pi. Additionally it adds wireless LAN & Bluetooth connectivity making it the
ideal solution for powerful connected designs.
Specifications:
Processor :Broadcom BCM2387 chipset. 1.2GHz Quad-Core ARM Cortex-A53 802.11 b/g/n Wireless LAN and
GPU :Dual Core VideoCore IV® Multimedia Co-Processor. Provides Open GL. It is ES 2.0, hardware-
accelerated OpenVG, and 1080p30 H.264 high-profile decode. Capable of 1Gpixel/s, 1.5Gtexel/s or
24GFLOPs with texture filtering and DMA infrastructure
Memory :1GB LPDDR2
OS :Boots from Micro SD card, running a version of the Linux operating system or Windows 10 IoT
Dimensions :85 x 56 x 17mm
Power : Micro USB socket 5V1, 2.5A
Connectors : Ethernet10/100 BaseT Ethernet socket
Video Output :HDMI (rev 1.3 & 1.4Composite RCA (PAL and NTSC)
Audio Output :Audio Output 3.5mm jack, HDMIUSB 4 x USB 2.0 Connector
GPIO Connector :40-pin 2.54 mm (100 mil) expansion header: 2x20 strip Providing 27 GPIO pins as well as +3.3 V,
+5 V
and GND supply lines
Camera Connector:15-pin MIPI Camera Serial Interface (CSI-2)
Display Connector :Display Serial Interface (DSI) 15 way flat flex cable connector with two data lanes and a clock lane
Memory Card Slot :Push/pull Micro SDIO
Fig 3: Raspberypi B+ module
@IJAERD-2018, All rights Reserved 92
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development (IJAERD)
Volume 5, Issue 03, March-2018, e-ISSN: 2348 - 4470, print-ISSN: 2348-6406
Key Benefits:
• Low cost
• Consistent board format &10x faster processing
The main advantage of the raspberry pi module over another processor is raspberry pi is a fully functional linux computer
and also compact in size.
4.2 LOGITECH CAMERA :
System Requirements is 1GHz = CPU Minimum in which 1.6GHz is CPU Recommended. The Minimum RAM is 1gb
whereas the recommended RAM is 2gband also 2.4 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo CPU is Recommended and 2 GB RAM. The
Software Support (at release), Logitech Webcam Software 2.0 (LWS).
Camera Specifications:
The Optical Resolution (True) 1280 x 960 1.2MP
Image Capture (4:3 SD) 320x240, 640x480 1.2 MP, 3.0 MP
Image Capture (16:9 W) 360p, 480p, 720p
Video Capture (4:3 SD) 320x240, 640x480, 800x600
Video Capture (16:9 W) 360p, 480p, 720p,
Frame Rate (max) 30fps @ 640x480
Fig 4: Logitech camera
4.3 HEAD SET
It converts into a voice output to help blind peoples. Its Audio input is 3.5mmjack. This gets the result from the
raspberrypi module and convey to the receiver.
Fig 5: Head set
@IJAERD-2018, All rights Reserved 93
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development (IJAERD)
Volume 5, Issue 03, March-2018, e-ISSN: 2348 - 4470, print-ISSN: 2348-6406
V. HARDWARE RESULT
By the efficient programming in the module it recognizes the feeded obstacles, faces , signs and gave it as a required
audio output through the earphone. The main purpose of this model is to help blind persons by guiding them using this
system design. It recognizes the face, signs, obstacles, humans such as known and unknown persons will be identified
using face and text recognition features. It gives the scanned and recognized images in the form of audio output to help
and guide the blind person. It is specially designed to blind navigation purpose.
Fig 6 Hardware output
VI. CONCLUSIONS & FUTURE ENHANCEMENTS
We have proposed a design on face and text recognition based on raspberry pi which is mainly designed for the purpose
of blind navigation. Our future work will focus on detecting the emotions of the persons and recognizing more types of
indoor objects and icons on signage in addition to text for indoor wayfinding aid to assist blind people travel
independently. We will also study the significant human interface issues including auditory output and spatial updating of
object location, orientation, and distance. With real-time updates, blind users will be able to better use spatial memory to
understand the surrounding environment, obstacles and signs.
The future enhancements are given below:
Human emotions can be preprogrammed in order to guide blind peoples.
Unknown persons can be identified to great extent.
REFERENCES
[1] Eyes of things(IEEE 2017) by Noelia Vallez ,THALES Communications & Security, 4 Avenue des Louvresses,
92230 Gennevilliers, France
[2] Camera based analysis of text and documents by Jian Liang, David Doermann . In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2004.
[3] Context-based Indoor Object Detection as an Aid to Blind Persons Accessing Unfamiliar Environments by Xiaodong
Yang, Yingli Tian from The city of newyork, USA. . IEEE Trans PAMI 24(9):1167–1183.
[4] Reading labels of cylinder objects for blind persons by Ze Ye, Chucai Yi and Yingli Tian. Dept. of Electrical
Engineering, The City College of New York,The City University of New York, USA.e-mail: zye01@ccny.cuny.edu.
[5] Blind people guidance system by Ljupko simunovic,Velimir Andelic, Ivan Pavlinusic at Central European conference
on information and intelligent system.
[6] Auditory Feedback and Sensory Substitution During Teleoperated Navigation by Rong Liu, Member, IEEE, and
Yong-Xuan Wang.
@IJAERD-2018, All rights Reserved 94
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Face Recognition For PDFDokument104 SeitenFace Recognition For PDFfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Face Recognition For PDFDokument104 SeitenFace Recognition For PDFfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- STEM EducationDokument32 SeitenSTEM Educationfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Kids Wear Store Business PlanDokument44 SeitenRetail Kids Wear Store Business PlanMirza Shakeel76% (17)
- Zara Abbasi KidswearDokument44 SeitenZara Abbasi Kidswearfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scratch2Cards PDFDokument12 SeitenScratch2Cards PDFdeep_p69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 01Dokument18 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 01fawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Example How To Write A ProposalDokument9 SeitenExample How To Write A ProposalSpoorthi PoojariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27012-Forces and GravityDokument35 Seiten27012-Forces and Gravityfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trans Benchmark SurveyDokument27 SeitenTrans Benchmark Surveyfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing The Customer PreferenceDokument30 SeitenAnalyzing The Customer Preferencefawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing The Customer PreferenceDokument30 SeitenAnalyzing The Customer Preferencefawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statcom FullDokument89 SeitenStatcom Fullfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Basic Concepts of FEMDokument35 SeitenLecture 1 Basic Concepts of FEMfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- MPCEPAChp50 63Dokument73 SeitenMPCEPAChp50 63fawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- RESEARCH AT UTTDokument27 SeitenRESEARCH AT UTTfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To ApplicationDokument6 SeitenGuide To Applicationfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Performance Static CompensDokument6 SeitenDynamic Performance Static Compensfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- RESEARCH AT UTTDokument27 SeitenRESEARCH AT UTTfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Serial WinDokument4 SeitenSerial WinFrancisco Ochoa Bueno100% (1)
- Serial ProgrammingDokument7 SeitenSerial ProgrammingDanny FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Performance Static CompensDokument6 SeitenDynamic Performance Static Compensfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Inverted Pendulum Benchmark in Nonlinear Control Theory - A Survey PDFDokument9 SeitenThe Inverted Pendulum Benchmark in Nonlinear Control Theory - A Survey PDFLuis Felipe Antunes R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Layoffs, Outsourcing, Offshoring Impact Employee ReactionsDokument11 SeitenLayoffs, Outsourcing, Offshoring Impact Employee Reactionsfawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Entrepreneurship Project: " The Café Coffee Day"Dokument13 SeitenEntrepreneurship Project: " The Café Coffee Day"fawadn_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparison of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Compensation Instruments in The Banking Sector of PakistanDokument11 SeitenA Comparison of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Compensation Instruments in The Banking Sector of PakistanmansoorzunairaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- ManualDokument72 SeitenManualj00000000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smart ATM Using Facial Recognition (Smart ATM)Dokument4 SeitenSmart ATM Using Facial Recognition (Smart ATM)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7CS4-21 IoT Lab ManualDokument80 Seiten7CS4-21 IoT Lab ManualGravityboiNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Iot Based Air Pollution Monitoring System For Smart CitiesDokument5 SeitenAn Iot Based Air Pollution Monitoring System For Smart CitiesNimai ChaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Manufacture of Underwater Rov (Remotely Operated Vehicle)Dokument25 SeitenDesign and Manufacture of Underwater Rov (Remotely Operated Vehicle)Albert TomyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Raspberry PiDokument20 SeitenIntroduction To Raspberry PiKohilan VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IoT Hardware 2016 Prototyping Boards and Development KitsDokument53 SeitenIoT Hardware 2016 Prototyping Boards and Development KitsPinder KhahraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raspberry Pi 4 Beginner's Guide PDFDokument169 SeitenRaspberry Pi 4 Beginner's Guide PDFsorin61100% (1)
- R22 - IT - Internet of ThingsDokument36 SeitenR22 - IT - Internet of ThingsJasmitha BompellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Baby Cradle Using Sensor TechnologyDokument7 SeitenSmart Baby Cradle Using Sensor TechnologyIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raspberry Pi & IOT Industrial Training ReportDokument110 SeitenRaspberry Pi & IOT Industrial Training ReportParminder ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analogue Sensors On The Raspberry Pi Using An MCP3008Dokument9 SeitenAnalogue Sensors On The Raspberry Pi Using An MCP3008Tatenda BizureNoch keine Bewertungen
- An 221 Adding An ADC To A Raspberry PiDokument11 SeitenAn 221 Adding An ADC To A Raspberry PialesysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iot Unit6Dokument35 SeitenIot Unit6Krishna DolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8 (1) IotDokument12 SeitenLab 8 (1) IotNAUTASH KHAN100% (1)
- Physical Computing and IoT ProgrammingDokument197 SeitenPhysical Computing and IoT Programmingamishagupta2908Noch keine Bewertungen
- Openmediavault Readthedocs Io en 5.xDokument167 SeitenOpenmediavault Readthedocs Io en 5.xTony NGUYENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthcare Monitoring System and Transforming Monitored Data Into Real Time Clinical Feedback Based On Iot Using Raspberry PiDokument7 SeitenHealthcare Monitoring System and Transforming Monitored Data Into Real Time Clinical Feedback Based On Iot Using Raspberry Pimikko intalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT LabprogramsDokument20 SeitenIOT LabprogramsSushant PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 A Brief History of Ultra-Cheap and Small ComputersDokument7 Seiten2.1 A Brief History of Ultra-Cheap and Small ComputersBharathi SidhireddiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feature Satip4Dokument6 SeitenFeature Satip4Alexander WieseNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT Madras Thesis Synopsis Template 3Dokument31 SeitenIIT Madras Thesis Synopsis Template 3SAGAR RATHEENoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Based Smart Mirror: A Project Report OnDokument71 SeitenIOT Based Smart Mirror: A Project Report OnBHAKTI VIBHANDIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hello World 17Dokument100 SeitenHello World 17Nfa HereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digit1 Vol 15 Issue 06 June 2015Dokument126 SeitenDigit1 Vol 15 Issue 06 June 2015Sailesh100% (1)
- Firealarm System Using IotDokument22 SeitenFirealarm System Using IotAbhijeet DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiate Between Microprocessor and Microcontrollers? AnswerDokument7 SeitenDifferentiate Between Microprocessor and Microcontrollers? AnswerRajkumar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android Based Autonamous Inteligent Pod For Border Security Using Raspberry PiDokument3 SeitenAndroid Based Autonamous Inteligent Pod For Border Security Using Raspberry PiAmbareeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHC0002 Diverse IoT Based Gadgets To Update A Moderate Condition of Farmers in IndiaDokument5 SeitenCHC0002 Diverse IoT Based Gadgets To Update A Moderate Condition of Farmers in IndiaCrispNoch keine Bewertungen
- IoT-Based Water Monitoring SystemDokument5 SeitenIoT-Based Water Monitoring SystemManuel Luis Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen