Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assignment
Hochgeladen von
Solly Fils De Marier0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
57 Ansichten4 Seitenthis is assignment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenthis is assignment
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
57 Ansichten4 SeitenAssignment
Hochgeladen von
Solly Fils De Marierthis is assignment
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle
Mekelle University
Mechanical engineering Department
Strength of Material I
Assignment Two
nd
2 Year Regular Mechanical Engineering Students
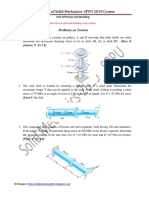
1. Determine the critical load on a steel column having a rectangular cross section, 12mm by
18mm, and a length of 280mm. the lower end of the column is inserted into a close fitting
socket and is welded securely. The upper end is pinned as shown in fig below. Reflected
your reaction is the column long or short?
2. Repeat problem 1, both end is pinned
3. Repeat problem 1, both end of the column is fixed
4. Repeat problem 1, lower end of the column is fixed and the upper is free
5. A steel pipe (outside diameter = 130 mm; wall thickness = 12.5 mm) supports an axial load
of P = 25 kN, which is applied at an eccentricity of e = 175 mm from the pipe centerline
(Fig below). The column is fixed at its base, free at its upper end, and its length is L = 4.0
m. Determine (a) the lateral deflection at the upper end of the column and (b) the maximum
stress in the pipe. Use E = 200 GPa.
SMD/SMIE/EiT-M/Mekelle University Page 1 of 2
Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle
Mekelle University
Mechanical engineering Department
6. Repeat problem 5, for the remained three end connection.
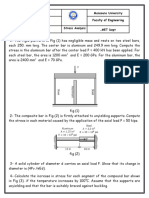
7. The uniform brass bar AB shown in Figure below has a rectangular cross section. The bar
is supported by pins and brackets at its ends. The pins permit rotation about a horizontal
axis (i.e., the strong axis of the rectangular cross section) but the brackets prevent rotation
about a vertical axis (i.e., the weak axis).
(a) Determine the critical buckling load of the assembly for the following parameters: L =
400 mm, b = 6 mm, h = 14 mm, and E = 100 GPa.
(b) Determine the ratio b/h for which the critical buckling load about both the strong and
weak axes is the same.
SMD/SMIE/EiT-M/Mekelle University Page 2 of 2
Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle
Mekelle University
Mechanical engineering Department
8. Rigid beam ABC is supported by a pinned connection at C and by an inclined strut that is
pin connected at B and D, as shown in Figure below. The strut is fabricated from two steel
[E = 200 GPa] bars, which are each 70 mm wide and 15 mm thick. Between B and D, the
bars are separated and connected by two spacer blocks, which are 25 mm thick. The strut
cross section is shown in Figure below. Determine:
(a) the compression force in strut BD that is created by the loads acting on the rigid beam.
(b) the slenderness ratios for the strut about its strong and weak axes.
(c) the minimum factor of safety in the strut with respect to buckling
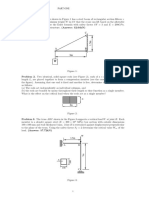
9. Rigid beam ABC is supported by a pinned connection at A and by a 180 mm by 180 mm
square timber post that is pin-connected at B and D, as shown in Figure below. The length
dimensions of the beam are x1 = 3.6 m and x2 = 2.8 m. The timber post has a length of L
= 4 m and an elastic modulus of E = 12 GPa. If a factor of safety of 2.0 with respect to
buckling is specified, determine the magnitude of the maximum distributed load w that
may be supported by the beam.
SMD/SMIE/EiT-M/Mekelle University Page 3 of 2
Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle
Mekelle University
Mechanical engineering Department
SMD/SMIE/EiT-M/Mekelle University Page 4 of 2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesVon EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define Factor of SafetyDokument3 SeitenDefine Factor of SafetySunil AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahmedabad Center-9Dokument3 SeitenAhmedabad Center-9RenieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Design 1 EBME1021 January 2015 Semester Final ExaminationDokument8 SeitenMechanical Engineering Design 1 EBME1021 January 2015 Semester Final ExaminationAnonymous 5YMOxVQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation of Solid Mechanics: C D 50 KNDokument12 SeitenFoundation of Solid Mechanics: C D 50 KNLata SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameDokument2 SeitenAnswer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameavinashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsDokument5 Seiten7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsSrikant Potluri100% (1)
- Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameDokument10 SeitenAnswer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NamegalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDokument5 SeitenUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEC 409 EXAMi 2022Dokument5 SeitenCEC 409 EXAMi 2022Abdullahi MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Solids March 2021Dokument8 SeitenMechanics of Solids March 2021LuckyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Used Papers SEP 2021: (Civil Engineering)Dokument3 SeitenUsed Papers SEP 2021: (Civil Engineering)AYRUSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDokument4 Seiten9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahmedabad Center-7Dokument2 SeitenAhmedabad Center-7RenieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDokument11 SeitenAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Sheet - 1Dokument2 SeitenSheet - 1Abdel Hamied EbrahemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mec32 CPR3 ValezaDokument3 SeitenMec32 CPR3 ValezaAngelo ValezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument3 SeitenUntitleddivyen gamitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Concept of StressDokument3 SeitenAssignment Concept of StressYasser ZubaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahmedabad Center-12Dokument2 SeitenAhmedabad Center-12RenieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buckling TutorialsDokument10 SeitenBuckling TutorialsNkanyiso MsweliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 ME Som Model Examination 2013Dokument3 Seiten4 ME Som Model Examination 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 10 08SupplementaryCE304CE304 G Ktu QbankDokument2 Seiten2020 10 08SupplementaryCE304CE304 G Ktu QbankAa AaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 1 SOM 2019-20Dokument1 SeiteAssignment - 1 SOM 2019-20Prince SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestressed ConcreteDokument2 SeitenPrestressed ConcreteAmit ThoriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Solids PDFDokument8 SeitenMechanics of Solids PDFprashanthreddy26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument4 SeitenDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringAshok DaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 2Dechas Mohammed100% (2)
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringDokument2 SeitenFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringpranithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Score 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerDokument5 SeitenScore 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerChristian M. MortelNoch keine Bewertungen
- I I I I I I I I I I I: Design of Pre-Stressed Concrete StructuresDokument13 SeitenI I I I I I I I I I I: Design of Pre-Stressed Concrete StructuresSuryakant MangajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestress ConcreteDokument19 SeitenPrestress ConcreteAbdulrhman Abduelgassim OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological Universityharnishtanna21285Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Common To CE, CEE) : 0 S - 5 0 C - 5 0 S 5 2 C 5 2Dokument2 Seiten(Common To CE, CEE) : 0 S - 5 0 C - 5 0 S 5 2 C 5 2AYRUSNoch keine Bewertungen
- EURME 504 Ok PDFDokument3 SeitenEURME 504 Ok PDFkohli kingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDokument8 Seiten9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mem-402-Mos Final QB-2015Dokument9 SeitenMem-402-Mos Final QB-2015Rohit DiwakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 10 28SupplementaryCE201CE201 I Ktu QbankDokument3 Seiten2020 10 28SupplementaryCE201CE201 I Ktu Qbankprasidh msNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVL Final Exam Past YearDokument3 SeitenCVL Final Exam Past YearApril SkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zadaca ImfDokument3 SeitenZadaca ImfAzra HumićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column Buckling (Sheet)Dokument10 SeitenColumn Buckling (Sheet)Ahmed NabilNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021Dokument3 SeitenEnd Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021FelishiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OctoberNovember 2021Dokument2 SeitenOctoberNovember 2021anil kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Columns Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3Dokument1 SeiteColumns Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3berto2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1Cağdaş AydınNoch keine Bewertungen
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Dokument3 SeitenEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE8301-Strength of Materials IDokument4 SeitenCE8301-Strength of Materials Isyed1188Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling of Welded Connections in SolidWDokument5 SeitenModeling of Welded Connections in SolidWCleyton L. AlvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST7008 Prestressed StructuresDokument15 SeitenST7008 Prestressed StructuresSethuraman SundararajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Ramakrishna Engineering CollegeDokument3 SeitenSri Ramakrishna Engineering CollegeBharathi RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Simple StrainDokument24 Seiten4 - Simple StrainLorene Ropeta.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1-pscDokument2 SeitenAssignment 1-pscDhanalakshmi KiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reg No.: - NameDokument3 SeitenReg No.: - NameSijuKalladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L8 Statically Indeterminate BeamsDokument6 SeitenL8 Statically Indeterminate BeamsAngelica Shane A. SaludoNoch keine Bewertungen
- December - 2018-January - 2019Dokument2 SeitenDecember - 2018-January - 2019anil kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel and Timber StructuresDokument2 SeitenDesign of Steel and Timber StructuresAdhikari SushilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Mechanics: Instructions To CandidatesDokument2 SeitenSolid Mechanics: Instructions To CandidatesZamaan JanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presstres MidDokument2 SeitenPresstres MidTarun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set No. 7 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem Set No. 7 PDFKent Lawrence LordanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRC Unit WiseDokument12 SeitenDRC Unit WiseSasikumar Viswanathan100% (1)
- Learning Outcome of Mechanical Exit Exam CoursesDokument4 SeitenLearning Outcome of Mechanical Exit Exam CoursesNurhussen Nure0% (1)
- 3.2 - Analysis of Singly Reinforced Beams 2Dokument27 Seiten3.2 - Analysis of Singly Reinforced Beams 2Marcelo AbreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- El-Shnawy Commercial Mall: P A G e - 1 o F 4 1Dokument41 SeitenEl-Shnawy Commercial Mall: P A G e - 1 o F 4 1saly123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aerospace Engineering Sample Report PDFDokument4 SeitenAerospace Engineering Sample Report PDFDuncan LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProfQuiz Structural 04Dokument40 SeitenProfQuiz Structural 04Lloyd AnchetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1443purl ME ESE-II 1995-1999Dokument155 Seiten1443purl ME ESE-II 1995-1999TirunamalaPhanimohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Download Template (Free) 2 Start Download - View PDF: American Standard Steel ChannelsDokument7 Seiten1 Download Template (Free) 2 Start Download - View PDF: American Standard Steel ChannelsHiongyiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforced Concrete Design by Computer - 297 PDFDokument297 SeitenReinforced Concrete Design by Computer - 297 PDFRafael GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABSDokument3 SeitenETABSNancy BhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20220902-Structural Drawing For 40'x30', EAST KYISU, DAGONSEIKKANDokument29 Seiten20220902-Structural Drawing For 40'x30', EAST KYISU, DAGONSEIKKANhein htet zawNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERSS-Lecture 2 (ChiewSP 5mar20)Dokument30 SeitenERSS-Lecture 2 (ChiewSP 5mar20)sunilarunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample For Solution Manual Dynamics of Structures 5th SI Edition by Anil ChopraDokument20 SeitenSample For Solution Manual Dynamics of Structures 5th SI Edition by Anil ChopraAbdeta DendanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Vibration Chapter03Dokument130 SeitenAdvanced Vibration Chapter03Alooy MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Study On Dynamic Behavior of Multi-Story Reinforced Concrete Frames With Non-Seismic DetailingDokument11 SeitenExperimental Study On Dynamic Behavior of Multi-Story Reinforced Concrete Frames With Non-Seismic DetailingAmnart KhampanitNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Short NotesDokument5 SeitenRCC Short Notesashok pradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of BeamsDokument1 SeiteTypes of BeamsNerinel Coronado0% (1)
- 3 - CompTJ TypicalDetailsDokument8 Seiten3 - CompTJ TypicalDetailsdougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Simulation-Ii Lab (Type Text) Page 0Dokument43 SeitenDigital Simulation-Ii Lab (Type Text) Page 0Rahul ChowdariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is-13920 1Dokument22 SeitenIs-13920 1Shekhar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Use of Ductility in Nuclear Facilities: Paul DoyleDokument10 SeitenThe Use of Ductility in Nuclear Facilities: Paul DoylelsaishankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1Dokument18 SeitenActivity 1zyx xyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD-761 644 Structural and Force Diagrams of The Landing Gear V. L. Belskii, Et AlDokument42 SeitenAD-761 644 Structural and Force Diagrams of The Landing Gear V. L. Belskii, Et Alebooks list1Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Conical Beam Finite Element For Rotor Dynamics Analysis: L. M.GreenhillDokument10 SeitenA Conical Beam Finite Element For Rotor Dynamics Analysis: L. M.GreenhillPhuor TyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report and DesignDokument53 SeitenReport and DesignRK PROJECT CONSULTANTSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem AsDokument12 SeitenProblem AsRonal SalvatierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 220kV Beam - 1Dokument3 Seiten220kV Beam - 1k_arindam1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 PPT 1 Design ConceptsDokument33 Seiten2 PPT 1 Design ConceptsLuis Hernán Guillén CardonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ls DynaDokument33 SeitenLs DynaRajNoch keine Bewertungen