Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Maths Project
Hochgeladen von
Aaditya Walake0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
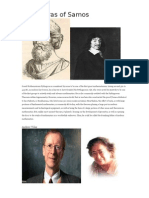
61 Ansichten7 Seiten1) Pythagoras was an ancient Greek mathematician and philosopher born in 570 BC in Samos, Greece. He is best known for the Pythagorean theorem regarding right triangles and founded a religious group called the Pythagoreans who studied mathematics and lived like monks.
2) Richard Dedekind was a German mathematician born in 1831 who made important contributions to abstract algebra, the foundations of numbers, algebraic number theory, and defined the real numbers. While teaching calculus, he developed the concept now known as a Dedekind cut to define irrational numbers.
3) Georg Cantor was a German mathematician born in 1845 who created set theory, a fundamental theory in mathematics. He established the one
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Maths Project.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1) Pythagoras was an ancient Greek mathematician and philosopher born in 570 BC in Samos, Greece. He is best known for the Pythagorean theorem regarding right triangles and founded a religious group called the Pythagoreans who studied mathematics and lived like monks.
2) Richard Dedekind was a German mathematician born in 1831 who made important contributions to abstract algebra, the foundations of numbers, algebraic number theory, and defined the real numbers. While teaching calculus, he developed the concept now known as a Dedekind cut to define irrational numbers.
3) Georg Cantor was a German mathematician born in 1845 who created set theory, a fundamental theory in mathematics. He established the one
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
61 Ansichten7 SeitenMaths Project
Hochgeladen von
Aaditya Walake1) Pythagoras was an ancient Greek mathematician and philosopher born in 570 BC in Samos, Greece. He is best known for the Pythagorean theorem regarding right triangles and founded a religious group called the Pythagoreans who studied mathematics and lived like monks.
2) Richard Dedekind was a German mathematician born in 1831 who made important contributions to abstract algebra, the foundations of numbers, algebraic number theory, and defined the real numbers. While teaching calculus, he developed the concept now known as a Dedekind cut to define irrational numbers.
3) Georg Cantor was a German mathematician born in 1845 who created set theory, a fundamental theory in mathematics. He established the one
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 7
Great Mathematicians
1}Pythagoras :Pythagoras of Samos was a
famous Greek mathematician and philosopher. He was born in 570
Bc. He is known best for the proof of the important Pythagorean
theorem, which is about right angle triangles. He started a group
of mathematicians, called the Pythagoreans, who
worshiped numbers and lived like monks. He had a great impact
on mathematics, theory of music and astronomy. His theories are
still used in mathematics today. He was one of the greatest
thinkers of his time.
Pythagoras was born in Samos, a little island off the western
coast of Asia Minor. There is not much information about his life.
He was said to have had a good childhood. Growing up with two
or three brothers, he was well educated. Some say he was the
first person to use the term philosophy.
Pythagoras is most famous for his theorem to do with right
triangles. He said that the length of the longest side of the right
angled triangle called the hypotenuse (C) squared would equal
the area of the other sides squared. A(c x c) was born. There are
many different proofs for this Pythagorean theorem. nd so (a x a)
+ (b x b) = (c x c) was born. There are many different proofs for
this Pythagorean theorem. And so (a x a) + (b x b) = (c x c) was
born. There are many different proofs for this Pythagorean
theorem.
2} R . Dedekind : Julius Wilhelm Richard Dedekind
was a German mathematician who made important
contributions to abstract algebra (particularly ring
theory), axiomatic foundation for the natural
numbers, algebraic number theory and the definition of
the real numbers. He was born on 6 October 1831 and
died on 12 February1916. Dedekind's father was Julius
Levin Ulrich Dedekind, an administrator of Collegium
Carolinum in Braunschweig. Dedekind had three older
siblings. As an adult, he never used the names Julius
Wilhelm. He was born, lived most of his life, and died in
Braunschweig.
While teaching calculus for the first time at
the Polytechnic school, Dedekind developed the notion
now known as a Dedekind cut (German: Schnitt), now a
standard definition of the real numbers. The idea of a cut
is that an irrational number divides the rational
numbers into two classes (sets), with all the numbers of
one class (greater) being strictly greater than all the
numbers of the other (lesser) class.
3} G . Cantor : Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp
Cantor was a German mathematician. He was born on 3rd
March 1845 and died on January 6 1918. He created set
theory, which has become a fundamental theory in
mathematics. Cantor established the importance of one-
to-one correspondence between the members of two sets,
defined infinite and well-ordered sets, and proved that
the real numbers are more numerous than the natural
numbers.
In fact, Cantor's method of proof of this theorem implies
the existence of an "infinity of infinities". He defined
the cardinal and ordinal numbers and their arithmetic.
Cantor's work is of great philosophical interest, a fact he
was well aware of.
Cantor’s theory became a whole new subject of
research concerning the mathematics of the infinite (e.g.,
an endless series, as 1, 2, 3,…, and even more
complicated sets), and his theory was heavily dependent
on the device of the one-to-one correspondence. In thus
developing new ways of asking questions
concerning continuity and infinity, Cantor quickly became
controversial.
4} Archimedes : Archimedes of Syracuse was
a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor,
and astronomer.[3] Although few details of his life are
known, he is regarded as one of the
leading scientists in classical antiquity. Generally
considered the greatest mathematician of antiquity and
one of the greatest of all time.
Archimedes anticipated
modern calculus and analysis by applying concepts
of infinitesimals and the method of exhaustion to derive
and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems,
including the area of a circle, the surface
area and volume of a sphere, and the area under
a parabola. He was the first to compute digits in the decimal
expansion of Pie .
5} Rene Descartes : René Descartes was a
French philosopher, mathematician, and scientist. A native
of the Kingdom of France, he spent about 20 years (1629–
1649) of his life in the Dutch Republic after serving for a
while in the Dutch States Army of Maurice of
Nassau, Prince of Orange and the Stadtholder of
the United Provinces. One of the most notable intellectual
figures of the Dutch Golden Age,[19] Descartes is also
widely regarded as one of the founders of modern
philosophy. He was born on 31st March 1596 and died on
11th February 1650.
A native of the Kingdom of France, he spent about 20
years (1629–1649) of his life in the Dutch Republic after
serving for a while in the Dutch States Army of Maurice of
Nassau, Prince of Orange and the Stadtholder of
the United Provinces. One of the most notable intellectual
figures of the Dutch Golden Age,[19] Descartes is also
widely regarded as one of the founders of modern
philosophy.
5} Euclid : Euclid sometimes called Euclid of
Alexandria[1] to distinguish him from Euclid of Megara,
was a Greek mathematician, often referred to as the
"founder of geometry"[1] or the "father of geometry". He
was active in Alexandria during the reign
of Ptolemy I (323–283 BC). His Elements is one of the
most influential works in the history of mathematics,
serving as the main textbook for
teaching mathematics (especially geometry) from the time
of its publication until the late 19th or early 20th century.
In the Elements, Euclid deduced the theorems of what
is now called Euclidean geometry from a small set
of axioms. Euclid also wrote works on perspective, conic
sections, spherical geometry, number theory,
and mathematical rigor. Very few original references to
Euclid survive, so little is known about his life. He was
likely born c. 325 BC
7} thales : Thales of Miletus was
a Greek mathematician, astronomer and pre-Socratic
philosopher from Miletus in ancient Greek Ionia. He was
one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most
notably Aristotle, regarded him as the first philosopher in
the Greek tradition,[1][2] and he is otherwise historically
recognized as the first individual in Western
civilization known to have entertained and engaged
in scientific philosophy.
Thales is recognized for breaking from the use
of mythology to explain the world and the universe, and
instead explaining natural objects and phenomena
by theories and hypotheses, in a precursor to
modern science. Almost all the other pre-Socratic
philosophers followed him in explaining nature as deriving
from a unity of everything based on the existence of a
single ultimate substance, instead of using mythological
explanations.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fundamental Descartes: A Practical Guide to the Method and MeditationsVon EverandFundamental Descartes: A Practical Guide to the Method and MeditationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zeno of Elea: Philosophic Naturalism Principia Mathematical (Usually Called The Principia) Is Considered ToDokument4 SeitenZeno of Elea: Philosophic Naturalism Principia Mathematical (Usually Called The Principia) Is Considered ToVijay PeriyasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Great Mathematician 2Dokument3 SeitenGreat Mathematician 2Moreno NorbylynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Not Real Rene A Giant Historical FraudDokument5 SeitenNot Real Rene A Giant Historical FraudSot SyrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Famous Greek Mathematicians and Their ContributionsDokument16 Seiten15 Famous Greek Mathematicians and Their ContributionsMallari MarjorieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pythagoras of Samos: Dy/dxDokument14 SeitenPythagoras of Samos: Dy/dxCheryl JhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- An KitDokument3 SeitenAn KitankitthenewtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted By: Crystal Angela A. Naval Submitted To: Prof. Jerson JalaniDokument15 SeitenSubmitted By: Crystal Angela A. Naval Submitted To: Prof. Jerson JalaniSamantha Clarin SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pythagoras of Samos (Dokument14 SeitenPythagoras of Samos (Om Prakash SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Famous MathematicianDokument5 SeitenWorld Famous MathematicianSrini VasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math HHHDokument3 SeitenMath HHHLj SoquiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 Greatest MathematiciansDokument14 SeitenTop 10 Greatest MathematiciansIP GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medieval Mathematics PPT ReportDokument20 SeitenMedieval Mathematics PPT ReportJemuel VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euclid: Geometry Deduced The Euclidean Geometry. The Name Has It All, Which in GreekDokument6 SeitenEuclid: Geometry Deduced The Euclidean Geometry. The Name Has It All, Which in GreekHelen SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Scientific Revolution at Its Zenith 1620 1720Dokument13 SeitenThe Scientific Revolution at Its Zenith 1620 1720illumin24Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Greatest MathematiciansDokument5 Seiten10 Greatest MathematiciansJez VillaflorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Lecture 2023 8 MathematicsDokument23 SeitenLight Lecture 2023 8 MathematicsTianTianNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Great MathematiciansDokument5 SeitenThe Great Mathematicianssajkalif100% (1)
- Famous MathematiciansDokument15 SeitenFamous Mathematiciansshiela mae ucangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rene Descartes EngDokument2 SeitenRene Descartes Engzaknjige122Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Greatest Mathematicians by Group 2Dokument7 SeitenThe Greatest Mathematicians by Group 2Jaymar JaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDokument42 SeitenMathematics in The Modern WorldApril Dian Rudan PalattaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematician-WPS OfficeDokument8 SeitenMathematician-WPS OfficeKemalyn NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- GREECEDokument20 SeitenGREECErhea perezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 Greatest MathematiciansDokument5 SeitenTop 10 Greatest Mathematiciansapi-238348956Noch keine Bewertungen
- Filipino and Math AssignmentDokument7 SeitenFilipino and Math AssignmentAbbygale MalagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12-15 - Famous Greek MathematiciansDokument58 Seiten12-15 - Famous Greek MathematiciansGenelyn Mar LumacangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bip Kel 4Dokument18 SeitenBip Kel 4Nur RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FattyDokument28 SeitenFattyNorsaibah MANIRINoch keine Bewertungen
- Math SearchDokument10 SeitenMath Searchanne sanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Leonhard EulerDokument6 Seiten1 Leonhard EulerTon TonNoch keine Bewertungen
- GreekDokument1 SeiteGreekMerryshyra MisagalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famous MathematiciansDokument3 SeitenFamous MathematiciansHyacinth Sui SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Exponent: Rule #1: Multiplying Exponents With The Same Base A M X A N A (M+N)Dokument9 SeitenLaws of Exponent: Rule #1: Multiplying Exponents With The Same Base A M X A N A (M+N)Ako Si BensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematic's Form 1 ProjectDokument15 SeitenMathematic's Form 1 ProjectBrandon Gamer TaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prehistoric Mathematics: Plimpton 322 Rhind Mathematical Papyrus Moscow Mathematical PapyrusDokument3 SeitenPrehistoric Mathematics: Plimpton 322 Rhind Mathematical Papyrus Moscow Mathematical Papyruswenny capplemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir Isaac Newton PRS (25 December 1642 - 20 March 1727 (NS: 4 JanuaryDokument6 SeitenSir Isaac Newton PRS (25 December 1642 - 20 March 1727 (NS: 4 JanuaryLaarnie Pesic PantinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aryabhata: Aryabhata (IAST: Āryabha A, SanskritDokument3 SeitenAryabhata: Aryabhata (IAST: Āryabha A, SanskritManash ProtimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Club 2022 Draft Rane EnglishDokument14 SeitenMath Club 2022 Draft Rane EnglishThou Rane ធូ រ៉ាណេNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesopotamia: Ancient Greek Herodianic NumeralsDokument4 SeitenMesopotamia: Ancient Greek Herodianic NumeralsShailanie Valle Rivera0% (1)
- Lecture 4 Fall of Greece and The Rise of RomeDokument41 SeitenLecture 4 Fall of Greece and The Rise of Romekaijun.cheahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hellenistic Mathematics: Euclid Archimedes DiophantusDokument22 SeitenHellenistic Mathematics: Euclid Archimedes Diophantusrgeraldine_16100% (2)
- EuclidDokument1 SeiteEuclidrockeygreatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pythagoras of SamosDokument8 SeitenPythagoras of SamosDaler SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- HandoutDokument3 SeitenHandoutkimhanna0708Noch keine Bewertungen
- Leonhard EulerDokument10 SeitenLeonhard EulerHakim S MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greek MathemaDokument6 SeitenGreek MathemaSebastian GhermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC NO. 1 - Overview of MathematicsDokument5 SeitenTOPIC NO. 1 - Overview of MathematicsJeffrey RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astronomo - European Math&17th CenturyDokument34 SeitenAstronomo - European Math&17th CenturyGladys Galorport AstronomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of GeometryDokument14 SeitenHistory of GeometryKeppy AricangoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hellenistic Mathematics - Euclid: Euclid (c.330-275 BCE, Fl. c.300 Bce)Dokument6 SeitenHellenistic Mathematics - Euclid: Euclid (c.330-275 BCE, Fl. c.300 Bce)Van Gile EcleoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hellenistic Mathematics: Sagales, Mae Christian, VDokument25 SeitenHellenistic Mathematics: Sagales, Mae Christian, VJemuel VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of MathematicsDokument32 SeitenNature of MathematicsKashmir DelacroixNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Origins of Greek MathematicsDokument15 SeitenThe Origins of Greek MathematicslvminhtrietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen, Donald - The Origin of Greek MathematicsDokument159 SeitenAllen, Donald - The Origin of Greek Mathematicsjsyrris@hotmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famous MathematiciansDokument4 SeitenFamous MathematiciansJon Salditos-SilvelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greek Mathematics Is Divided Into Two Periods - Classical and HellenisticDokument3 SeitenGreek Mathematics Is Divided Into Two Periods - Classical and HellenisticShambhavi VarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pythagoras of Samos (Ancient Greek: Πσθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος Pythagóras ho Sámios "PythagorasDokument8 SeitenPythagoras of Samos (Ancient Greek: Πσθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος Pythagóras ho Sámios "PythagorasHeidi RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greek Mathematics and MathematicianDokument34 SeitenGreek Mathematics and MathematicianMONHANNAH RAMADEAH LIMBUTUNGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Signal & Power Signal: Work Force × Displacement Power Work / TimeDokument4 SeitenEnergy Signal & Power Signal: Work Force × Displacement Power Work / TimeNoraesyah KamaruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 ACOUSTICS 2 Acoustics SimulationsDokument33 Seiten7 ACOUSTICS 2 Acoustics SimulationsTech MitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find A Formula or Conjecture For Each of The Patterns Shown Below, and Give The Next Three Terms of Each PatternDokument48 SeitenFind A Formula or Conjecture For Each of The Patterns Shown Below, and Give The Next Three Terms of Each PatternDineo MasipaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDokument1 SeiteCountable and Uncountable NounsTrex DragonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 With TOS 1st Quarter ExamDokument6 SeitenGrade 10 With TOS 1st Quarter ExamCharles Gonzales91% (96)
- Grant - Much Ado About NothingDokument471 SeitenGrant - Much Ado About NothingJuan Salto100% (1)
- A Critical Examination of The Kalam Cosmological ArgumentDokument14 SeitenA Critical Examination of The Kalam Cosmological ArgumentdeeperknowledgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Degree: Bachelor of Science MathematicsDokument22 SeitenDegree: Bachelor of Science Mathematicssteven7 IsaacsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch01-Calculus 9E LimitsDokument34 SeitenCh01-Calculus 9E Limitsrofi modiNoch keine Bewertungen
- StewartCalcET7e 02 02MDokument29 SeitenStewartCalcET7e 02 02MsilviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clifford A. Pickover Keys To InfinityDokument357 SeitenClifford A. Pickover Keys To InfinityTimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cantor Set FunctionDokument15 SeitenCantor Set FunctionRenato GaloisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2 Uniform Infinite Line ChargeDokument2 SeitenExample 2 Uniform Infinite Line ChargeBill WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giordano Bruno - On The Infinite UniverseDokument13 SeitenGiordano Bruno - On The Infinite UniverseAnda IonescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0809.2135v1 (1) Cantor ParadoxDokument29 Seiten0809.2135v1 (1) Cantor ParadoxtevyionelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10724-The Seminar of JacquesDokument79 Seiten10724-The Seminar of Jacquesdanguba69100% (1)
- Semantic Shifts and The Concept of InfinityDokument7 SeitenSemantic Shifts and The Concept of InfinityDaniel ReifmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 011 13EG2001 Lecture Notes - Second Shifting TheoremDokument10 Seiten011 13EG2001 Lecture Notes - Second Shifting TheoremQy LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract Set Theory (Skolem)Dokument74 SeitenAbstract Set Theory (Skolem)germankrebsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PostulatesDokument36 SeitenPostulatesRajat PatodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPE262 - Tutorial 2 - L3 - L4-L5 - 1445-IDokument9 SeitenCPE262 - Tutorial 2 - L3 - L4-L5 - 1445-IAhmed SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 06: Zeros and Singularities: MA201 Mathematics IIIDokument28 SeitenTopic 06: Zeros and Singularities: MA201 Mathematics IIIDeepanshu RewariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics HL - OPTION 9 Calculus - Fannon, Kadelburg, Woolley and Ward - Cambridge 2012 PDFDokument188 SeitenMathematics HL - OPTION 9 Calculus - Fannon, Kadelburg, Woolley and Ward - Cambridge 2012 PDFginotrucheli100% (4)
- CS 4850-Lecture 1Dokument3 SeitenCS 4850-Lecture 1Sean LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nine Laws of The Dark Triad Man Official Release 20151231Dokument52 SeitenThe Nine Laws of The Dark Triad Man Official Release 20151231Cousscous Klan89% (18)
- Dorin David Life Is Not A Fractal in Hilbert SpaceDokument6 SeitenDorin David Life Is Not A Fractal in Hilbert SpacedorinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derrida and DeconstructionDokument51 SeitenDerrida and DeconstructionNagendra Rai100% (2)
- Aldo in Wonder-Land Remarks On The Houses of Aldo Van Eyck: Joost MeuwissenDokument11 SeitenAldo in Wonder-Land Remarks On The Houses of Aldo Van Eyck: Joost MeuwissenazimkhtrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applying Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development To Mathematics InstructionDokument8 SeitenApplying Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development To Mathematics InstructionAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhA 067 - Cleary - Aristotle and Mathematics - Aporetic Method in Cosmology and Metaphysics 1995 PDFDokument597 SeitenPhA 067 - Cleary - Aristotle and Mathematics - Aporetic Method in Cosmology and Metaphysics 1995 PDFPhilosophvs AntiqvvsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (30)
- Stoicism: How to Use Stoic Philosophy to Find Inner Peace and HappinessVon EverandStoicism: How to Use Stoic Philosophy to Find Inner Peace and HappinessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (86)
- Stoicism The Art of Happiness: How the Stoic Philosophy Works, Living a Good Life, Finding Calm and Managing Your Emotions in a Turbulent World. New VersionVon EverandStoicism The Art of Happiness: How the Stoic Philosophy Works, Living a Good Life, Finding Calm and Managing Your Emotions in a Turbulent World. New VersionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (51)
- The Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismVon EverandThe Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- How States Think: The Rationality of Foreign PolicyVon EverandHow States Think: The Rationality of Foreign PolicyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (7)
- The Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYVon EverandThe Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Jungian Archetypes, Audio CourseVon EverandJungian Archetypes, Audio CourseBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (124)
- The Three Waves of Volunteers & The New EarthVon EverandThe Three Waves of Volunteers & The New EarthBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (179)
- The Story of Philosophy: The Lives and Opinions of the Greater PhilosophersVon EverandThe Story of Philosophy: The Lives and Opinions of the Greater PhilosophersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- The Emperor's Handbook: A New Translation of The MeditationsVon EverandThe Emperor's Handbook: A New Translation of The MeditationsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- How to Destroy America in Three Easy StepsVon EverandHow to Destroy America in Three Easy StepsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosVon Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (207)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldVon EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (64)
- This Is It: and Other Essays on Zen and Spiritual ExperienceVon EverandThis Is It: and Other Essays on Zen and Spiritual ExperienceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (94)
- The Authoritarian Moment: How the Left Weaponized America's Institutions Against DissentVon EverandThe Authoritarian Moment: How the Left Weaponized America's Institutions Against DissentBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (17)
- Machinery of the Mind (An Interview)Von EverandMachinery of the Mind (An Interview)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (28)
- It's Easier Than You Think: The Buddhist Way to HappinessVon EverandIt's Easier Than You Think: The Buddhist Way to HappinessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (60)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesVon EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceVon EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (51)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingVon EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- The Socrates Express: In Search of Life Lessons from Dead PhilosophersVon EverandThe Socrates Express: In Search of Life Lessons from Dead PhilosophersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (79)
- Summary of Man's Search for Meaning by Viktor E. FranklVon EverandSummary of Man's Search for Meaning by Viktor E. FranklBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (101)