Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A Professional Accountant in Public Practice Shall Not Knowingly Engage in Any Business
Hochgeladen von
sana ol0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
27 Ansichten3 SeitenOriginaltitel
A professional accountant in public practice shall not knowingly engage in any business.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
27 Ansichten3 SeitenA Professional Accountant in Public Practice Shall Not Knowingly Engage in Any Business
Hochgeladen von
sana olCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
A professional accountant in public practice
shall not knowingly engage in any business,
occupation, or activity that impairs or might
impair integrity, objectivity or the good
reputation of the profession and as a result
would be incompatible with the fundamental
principles.
Self-interest
Self-review
Familiarity
Advocacy
Intimidation.
Safeguards that may eliminate or reduce
threats to an acceptable level fall into two
broad categories:
Safeguards created by the
profession, legislation or regulation;
and
Safeguards in the work environment.
Client Acceptance- Before accepting a new
client relationship, a professional accountant
in public practice shall determine whether
acceptance would create any threats to
compliance with the fundamental principles.
A professional accountant in public practice
shall evaluate the significance of any threats
and apply safeguards when necessary to
eliminate them or reduce them to an
acceptable level.
Professional accountants in business may be
solely or jointly responsible for the
preparation and reporting of financial and
other information. They may also be
responsible for providing effective financial
management and competent advice on a
variety of business-related matters.
A professional accountant in business may
hold a senior position within an organization.
A professional accountant in business shall
not knowingly engage in any business,
occupation, or activity that impairs or might
impair integrity, objectivity or the good
reputation of the profession and as a result
would be incompatible with the fundamental
principles.
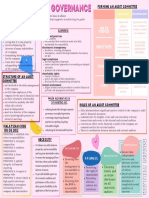
be well-informed about the b. Corporate Governance - refers to a
company and the external system whereby shareholders,
environment in which it operates creditors and other stakeholders of a
have a strong command of issues corporation ensure that management
relevant to the business enhances the value of the corporation
insist on a comprehensive, formal as it competes in an increasingly
and tailored induction, continually global market place.cralaw
develop and refresh their
knowledge and skills to ensure c. Independent Director - refers to a
that their contribution to the board person other than an officer or
remains informed and relevant employee of the corporation, its
ensure that information is parent or subsidiaries, or any other
provided sufficiently in advance of individual having any relationship with
meetings to enable thorough the corporation, which would interfere
consideration of the issues facing with the exercise of independent
the board judgment in carrying out the
insist that information is sufficient, responsibilities of a director. This
accurate, clear and timely means that apart from the directors'
uphold the highest ethical fees and shareholdings, he should be
standards of integrity and probity independent of management and free
question intelligently, debate from any business or other
constructively, challenge relationship which could materially
rigorously and decide interfere with the exercise of his
dispassionately independent judgment.cralaw
promote the highest standards of
d. Public Company - refers to any
corporate governance and seek
corporation with a class of equity
compliance with the provisions of
securities listed in an Exchange or
the Combined Code wherever
with assets in excess of Fifty Million
possible.
Pesos (P50,000,000.00) and having
two hundred (200) or more
NEDs on the board
stockholders each holding at least one
hundred (100) shares of a class of its
Advantages securities.cralaw
Monitoring: they offer a clear e. Management - refers to the body
monitoring role, particularly on given the authority to implement the
remuneration committees to policies determined by the Board in
dampen the excesses of directing the course/business
executives. activity/ies of the corporation.cralaw
Expertise: to expand this resource
available for management to use. f. Executive Director - refers to a
Perception: institutional and director who is at the same time
watchdog perception is enhanced appointed to head a department/unit
because of their presence. within the corporate
Communication: the implied organization.cralaw
improvement in communication
KEY ROLES of NED’s between shareholders' interests g. Non-executive Director - refers to a
and the company. Board member with non-executive
Strategy role: this recognises that NEDs Discipline: NEDs may have a functions.cralaw
have the right and responsibility to positive influence on the success
contribute to strategic success, or otherwise of takeovers. h. Non-audit Work - refers to other
challenging strategy and offering advice services offered by the external
on direction. auditor to a corporation that are not
Disadvantages
directly related and relevant to its
Scrutinising role: NEDs are required to statutory audit function. Examples
Unity: lack of trust and needless include accounting, payroll,
hold executive colleagues to account for
input can affect board operations. bookkeeping, reconciliation, computer
decisions taken and results obtained.
Quality: there may be a poor gene project management, data processing
pool of NEDs willing to serve. or information technology outsourcing
Risk role: NEDs ensure the company has
Liability: the poor remuneration services, internal auditing, and
an adequate system of internal
with the suggested (Higgs) services that may compromise the
controls and systems of risk
removal of stock options from the independence and objectivity of the
management in place.
package coupled with the equal external audit.cralaw
liability in law for company
People role: NEDs oversee a range of operations might lead some to I. Internal Control - refers to the
responsibilities with regard to the question whether they want the process effected by a company's
appointment and remuneration of job or not. Board of Directors, management and
executives and will be involved in other personnel, designed to provide
contractual and disciplinary issues. a. Board of Directors - refers to the reasonable assurance regarding the
collegial body that exercises the achievement of objectives in the
To be effective, a NED needs to: corporate powers of all corporations effectiveness and efficiency of
formed under the Corporation Code. It operations, the reliability of financial
build a recognition by executives conducts all business and controls or reporting, and compliance with
of their contribution in order to holds all property of such applicable laws, regulations, and
promote openness and trust corporations. internal policies.cralaw
j. Internal Control Environment - refers It involves the problem of directors and firms make independent
to the framework under which internal controlling a company whilst shareholders decisions that are guided and
controls are developed, implemented, own the company. In the past, a problem coordinated by market prices).
alone or in concert with other policies was identified whereby the directors might
or procedures, to manage and control not act in the shareholders (or other The decision is based on a comparison of
a particular risk or business activity, or stakeholders) best interests. Agency the "transaction costs" of the two
combination of risks or business theory considers this problem and what approaches. Transaction costs are the
activities, to which the company is could be done to prevent it. indirect costs (i.e. non production costs)
exposed.cralaw incurred in performing a particular activity,
An agent is employed by for example the expenses incurred
k. Internal Auditing - refers to an a principal to carry out a task on through outsourcing.
independent, objective assurance and their behalf.
consulting activity designed to add Agency refers to the relationship When outsourcing, transaction costs arise
value and improve an organization's between a principal and their from the effort that must be put into
operations. It helps an organization agent. specifying what is required and
accomplish its objectives by bringing Agency costs are incurred by subsequently coordinating delivery and
a systematic, disciplined approach to principals in monitoring agency monitoring quality.
evaluate and improve the behaviour because of a lack of
effectiveness of risk management, trust in the good faith of agents.
control, and governance High transaction costs for outsourcing
By accepting to undertake a task may suggest an in-house solution
processes.cralaw
on their behalf, an agent becomes whereas low transaction costs for
accountable to the principal by outsourcing would support the argument
l. Internal Audit Department - refers to
whom they are employed. The to outsource.
a department, division, team of
agent is accountable to that
consultants, or other practitioner(s)
principal. POSSIBLE CONCLUSIONS
that provide independent, objective
assurance and consulting services
designed to add value and improve an Opportunistic behaviour could
organization's operations.cralaw have dire consequences on
financing and strategy of
m. Chief Audit Executive - refers to the businesses, hence discouraging
top position within the organization potential investors. Businesses
responsible for internal audit activities. therefore organise themselves to
In a traditional internal audit activity, minimise the impact of bounded
this would be the internal audit rationality and opportunism as
director. In the case where internal much as possible.
audit activities are obtained from Governance costs build up
outside service providers, the chief including internal controls to
audit executive is the person monitor management.
responsible for overseeing the service Managers become more risk
contract and the overall quality averse seeking the safe ground of
assurance of these activities, and easily governed markets.
follow-up of engagement results. The
term also includes such titles as
TCS VS. AT
general auditor, chief internal auditor,
and inspector general.cralaw
Transaction cost theory and agency
n. Independence - refers to that theory essentially deal with the same
environment which allows the person issues and problems. Where agency
to carry out his/her work freely and Transaction cost theory can be viewed as theory focuses on the individual agent,
objectively.cralaw part of transaction cost theory focuses on the
corporate governance and agency theory individual transaction.
o. Objectivity - refers to unbiased . It is based on the principle that costs will
mental attitude that requires the arise when you get someone else to do Agency theory looks at the
person to carry out his/her work in something for you .e.g. directors to run the tendency of directors to act in their
such a manner that he/she has an business you own. own best interests, pursuing
honest belief in his/her work product salary and status. Transaction
and that no significant quality CONTEXT- “MAKE OR BUY” DECISION cost theory considers that
compromises are made. Objectivity managers (or directors) may
requires the person not to subordinate Transaction cost theory (Wiliamson) was arrange transactions in an
his/her judgment to that of first discussed in the context of the opportunistic way.
others.cralaw decision by a firm whether to do The corporate governance
something in-house or to outsource. problem of transaction cost theory
p. Standards for the Professional is, however, not the protection of
Practice of Internal Auditing (SPPIA) - ownership rights of shareholders
Organisations choose between two
refers to the criteria by which the (as is the agency theory focus),
methods of obtaining control over
operations of an internal auditing rather the effective and efficient
resources:
department are evaluated and accomplishment of transactions
measured. They are intended to by firms.
represent the practice of internal the ownership of assets
auditing as it should be, provide a (hierarchy solutions – decisions
framework for performing and over production, supply, and the
promoting a broad range of value- purchases of inputs are made by
added internal audit activities and managers and imposed through
foster improved organizational hierarchies) and
processes and operations.cralaw buying in the use of assets (the
market solution – individuals
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Controlling the Costs of Conflict: How to Design a System for Your OrganizationVon EverandControlling the Costs of Conflict: How to Design a System for Your OrganizationNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES - GOVBUSMAN - Chapter 1Dokument2 SeitenNOTES - GOVBUSMAN - Chapter 1Bundalian, Louisse Nicole A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDokument9 SeitenLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoChristian Grace ManatadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Effective Corporate GovernanceDokument3 SeitenBasic Principles of Effective Corporate GovernanceLovely Mae LacasteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer To Audi312 Gov (Prelim)Dokument3 SeitenReviewer To Audi312 Gov (Prelim)alaine daphneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Competency Framework 1697547786Dokument13 SeitenThe Competency Framework 1697547786montaserangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Corporate Governance: The Board'S Governance ResponsibilitiesDokument12 SeitenCode of Corporate Governance: The Board'S Governance ResponsibilitiesMartha TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1sec Code of Corporate GovernanceDokument8 Seiten1sec Code of Corporate Governancegfyyyvbwz8Noch keine Bewertungen
- SEC Memorandum Circular No. 6 Series of 2009: Revised Code of Corporate GovernanceDokument13 SeitenSEC Memorandum Circular No. 6 Series of 2009: Revised Code of Corporate GovernanceJames FigueroaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 - Corporate Performance-Governance-Business EthicsDokument3 SeitenChapter 11 - Corporate Performance-Governance-Business Ethicsjane garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The New Internal Audit Charter: Defining The Next Generation CaesDokument11 SeitenThe New Internal Audit Charter: Defining The Next Generation Caesarfian yuddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec Code of Corporate GovernanceDokument10 SeitenSec Code of Corporate GovernanceMary Antonette MulingtapangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meaning and Definitions of Corporate GovernanceDokument6 SeitenMeaning and Definitions of Corporate GovernanceBhargaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gbri NotesDokument19 SeitenGbri NotesJaylou AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in GBRC PRELIMDokument2 SeitenReviewer in GBRC PRELIMJhernel SuaverdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bussiness Ethics Chapter 12Dokument3 SeitenBussiness Ethics Chapter 12Ian Farouk Ahmad EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance MIND MAPDokument1 SeiteCorporate Governance MIND MAPnormalasaliminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Governance Chapter 2Dokument4 SeitenGovernance Chapter 2Tiffany CenizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Practice IoDDokument8 SeitenCode of Practice IoDjunaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance in The Boardroom: A Practical PerspectiveDokument36 SeitenCorporate Governance in The Boardroom: A Practical PerspectiveArmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate GovernanceDokument5 SeitenCorporate GovernanceMj PacunayenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate GovernanceDokument5 SeitenCorporate Governancezyvencaviliza656Noch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance TemplateDokument20 SeitenCorporate Governance TemplateAbs PangaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES - GOVBUSMAN - Chapter 2Dokument3 SeitenNOTES - GOVBUSMAN - Chapter 2Bundalian, Louisse Nicole A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Goodgov Chapter 3Dokument12 SeitenGoodgov Chapter 3Johnmon Mabulis EscoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in MGT3Dokument5 SeitenReviewer in MGT3Dave ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSR ReviewerDokument9 SeitenBSR Reviewerst4bb8r09y0uNoch keine Bewertungen
- CG Guidelines For Listed Companies Nov2010Dokument13 SeitenCG Guidelines For Listed Companies Nov2010Raymond ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate GovernanceDokument1 SeiteCorporate GovernanceJessa RomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Mgt. 21Dokument12 SeitenLesson 1 - Mgt. 21Sofia Lynn Rico RebancosNoch keine Bewertungen
- UK MaihanDokument17 SeitenUK Maihannhan leNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance 08Dokument17 SeitenCorporate Governance 08Gaurav SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Govbusman - Midterm ReviewerDokument9 SeitenGovbusman - Midterm Reviewercheeniecunanan04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Long-Term Investment, Financial Stability and Business IntegrityDokument4 SeitenLong-Term Investment, Financial Stability and Business IntegrityLee TeukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Corporate Governance Practice in IndiaDokument15 SeitenEvolution of Corporate Governance Practice in IndiaAniket ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GGSR ReviewerDokument5 SeitenGGSR ReviewerTrisha mae CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of GovernanceDokument10 SeitenCode of GovernanceCarlo ImperialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hedge Fund AdministrationDokument3 SeitenHedge Fund AdministrationRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Corporate StrategyDokument4 SeitenComponents of Corporate StrategyKy CuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Ethics: Code of Ethics For Executive Directors and Senior Financial Officers Key RequirementsDokument1 SeiteCode of Ethics: Code of Ethics For Executive Directors and Senior Financial Officers Key RequirementsMarinette Valencia MedranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The New Four Pillars of CFO SuccessDokument15 SeitenThe New Four Pillars of CFO Successanver2679Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 E3Dokument7 SeitenChapter 3 E3mkoenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CII Ethics MeeDokument26 SeitenCII Ethics MeeDivyangi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in CORPORATE GOVERNANCE-singsonDokument5 SeitenReviewer in CORPORATE GOVERNANCE-singsonDonna Mae SingsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gerente Module 1 Activity (Governance)Dokument2 SeitenGerente Module 1 Activity (Governance)Aldrin GerenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6: Corporate-Level Strategy Diversification: Pooled Negotiating Power: ImprovementDokument2 SeitenChapter 6: Corporate-Level Strategy Diversification: Pooled Negotiating Power: ImprovementcaicaiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11Dokument14 SeitenChapter 11Willma PaladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Styles Governance Improved Outcomes May 2016 PDFDokument5 SeitenLeadership Styles Governance Improved Outcomes May 2016 PDFbabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenifer Basalo, CpaDokument12 SeitenJenifer Basalo, CpaJenifer BasaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 Corporate Governance - Responsibilities and AccountabilitiesDokument3 SeitenLesson 2 Corporate Governance - Responsibilities and AccountabilitiesKen Ivan HervasNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOVERNANCE ReviewerDokument12 SeitenGOVERNANCE ReviewerPrincess SagunNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOVERNANCE ReviewerDokument8 SeitenGOVERNANCE ReviewerPrincess SagunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Conduct - Specifies How A Business IsDokument8 SeitenCode of Conduct - Specifies How A Business IsYuuna HoshinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finals ReviewerDokument6 SeitenFinals ReviewerDharnel Jude EpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Four Pillars of CFO SuccessDokument7 SeitenThe Four Pillars of CFO Successanand1kumar-31Noch keine Bewertungen
- GovbusmanDokument30 SeitenGovbusmanDUNGCA, Regina T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- World-Class Controllership: Charting Your Course To SuccessDokument4 SeitenWorld-Class Controllership: Charting Your Course To Successmasterjugasan6974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance Publicly Listed CompaniesDokument21 SeitenCorporate Governance Publicly Listed CompaniesCzarina JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- AA 3 Corporate GovernanceDokument17 SeitenAA 3 Corporate Governanceleo MessiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Director Duties Appointment and RemovalDokument6 SeitenCompany Director Duties Appointment and Removallindamirembe07Noch keine Bewertungen
- ArtappzDokument3 SeitenArtappzsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- TodayDokument1 SeiteTodaysana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec Code PDFDokument30 SeitenSec Code PDFsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYMBOLXDokument3 SeitenSYMBOLXsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax 3.0Dokument16 SeitenTax 3.0sana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Professional Accountant in Public Practice Shall Not Knowingly Engage in Any BusinessDokument3 SeitenA Professional Accountant in Public Practice Shall Not Knowingly Engage in Any Businesssana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Event Vendor ContractDokument2 SeitenEvent Vendor Contractsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- THEATREDokument6 SeitenTHEATREsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- EUNICEDokument3 SeitenEUNICEsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax 3.0Dokument16 SeitenTax 3.0sana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionnaerDokument2 SeitenQuestionnaersana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- THEATREDokument6 SeitenTHEATREsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathfit Contract WorkDokument2 SeitenPathfit Contract Worksana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 1Dokument3 SeitenQuestion 1sana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlatesDokument1 SeitePlatessana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Bar Q - MERCANTILE LAWDokument16 Seiten2015 Bar Q - MERCANTILE LAWLimVianesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 1Dokument3 SeitenQuestion 1sana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- TodayDokument1 SeiteTodaysana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- EuniceDokument3 SeitenEunicesana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- TPM Applicants FormDokument1 SeiteTPM Applicants Formsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- TodayDokument1 SeiteTodaysana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- TodayDokument1 SeiteTodaysana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- CnsdbygcsdDokument7 SeitenCnsdbygcsdsana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Bar Q - MERCANTILE LAWDokument16 Seiten2015 Bar Q - MERCANTILE LAWLimVianesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attestation Services 2Dokument8 SeitenAttestation Services 2sana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attestation Services 2Dokument8 SeitenAttestation Services 2sana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attestation Services 2Dokument8 SeitenAttestation Services 2sana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathfit Contract WorkDokument2 SeitenPathfit Contract Worksana olNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Sheet Substantive TestingDokument12 SeitenBalance Sheet Substantive TestingangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item7 KPMG Audit Strategy Planning MemorandumDokument14 SeitenItem7 KPMG Audit Strategy Planning Memorandumshane natividad100% (3)
- Consolidated County Governments - Financial Statements Template FY 2017-18 Amended May 2018Dokument49 SeitenConsolidated County Governments - Financial Statements Template FY 2017-18 Amended May 2018Calvin kamothoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suhana - Sem I ActivityDokument70 SeitenSuhana - Sem I Activityidfclogin7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 1-Audit Approach P.pointDokument17 SeitenBab 1-Audit Approach P.pointAslamaitulakma MohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit Sampling (Test of Control)Dokument17 SeitenAudit Sampling (Test of Control)MasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume PauloHenriqueDeMenezesAlbuquerque 2023Dokument3 SeitenResume PauloHenriqueDeMenezesAlbuquerque 2023Paulo AlbuquerqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Let's Check - Answer KeyDokument29 SeitenLet's Check - Answer KeyKaila CuestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance Assessment TemplateDokument42 SeitenCorporate Governance Assessment TemplateAnonymous mXJXLu7vLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 SolutionsDokument58 SeitenChapter 8 SolutionsLy VõNoch keine Bewertungen
- MindMap For COBIT 4.1Dokument1 SeiteMindMap For COBIT 4.1muraliduraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C.v... - Eman MahmoudDokument5 SeitenC.v... - Eman Mahmoudeman mahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Task 1Dokument17 SeitenAssessment Task 1besk0200% (3)
- Annual Report - Nesco Limited - 2019-20 PDFDokument170 SeitenAnnual Report - Nesco Limited - 2019-20 PDFAvinash PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Commissions Review Audit ReportDokument30 SeitenSales Commissions Review Audit ReportAdnan MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who FinalDokument27 SeitenWho FinalAnonymous 97dbabE5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Audit Responsibilities and Objectives: Auditing and Assurance Services, 15e (Arens)Dokument43 SeitenChapter 6 Audit Responsibilities and Objectives: Auditing and Assurance Services, 15e (Arens)GuinevereNoch keine Bewertungen
- De La Salle University: MODAUDP Syllabus - Full Online 1 of 14Dokument14 SeitenDe La Salle University: MODAUDP Syllabus - Full Online 1 of 14RedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Slavery Statement FY2021Dokument8 SeitenModern Slavery Statement FY2021AN0YM0us3Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Laws and Rules On Expenditures and Disbursements (ATA)Dokument52 SeitenNew Laws and Rules On Expenditures and Disbursements (ATA)Maria Julieta Stephanie TacogueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interloop Financials 2023Dokument31 SeitenInterloop Financials 2023Ghulam MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wsu Fbs Prospectus 2022Dokument272 SeitenWsu Fbs Prospectus 2022Asiphe BiyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRSG Dictionary Overview ListDokument18 SeitenHRSG Dictionary Overview ListWilliam AndersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit NotesDokument6 SeitenAudit NotesJesnyfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Germic I 1Dokument52 SeitenGermic I 1Raejayne IllesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Accounting Information SystemDokument26 SeitenEffect of Accounting Information SystemTilahun MikiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit of Plant Property and EquipmentDokument17 SeitenAudit of Plant Property and EquipmentChristian Lim0% (1)
- Prelim Operation AuditingDokument4 SeitenPrelim Operation AuditingHammar BokingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens Internship ReportDokument171 SeitenSiemens Internship ReportK.K.71% (7)
- Braskem S.A. - 2020 Financial StatementsDokument135 SeitenBraskem S.A. - 2020 Financial StatementsTheodore H. CallisterNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideVon Everand(ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideBewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (2)
- A Pocket Guide to Risk Mathematics: Key Concepts Every Auditor Should KnowVon EverandA Pocket Guide to Risk Mathematics: Key Concepts Every Auditor Should KnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionVon EverandBusiness Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Internal Audit Checklists: Guide to Effective AuditingVon EverandInternal Audit Checklists: Guide to Effective AuditingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Layman's Guide GDPR Compliance for Small Medium BusinessVon EverandThe Layman's Guide GDPR Compliance for Small Medium BusinessBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Bribery and Corruption Casebook: The View from Under the TableVon EverandBribery and Corruption Casebook: The View from Under the TableNoch keine Bewertungen
- GDPR-standard data protection staff training: What employees & associates need to know by Dr Paweł MielniczekVon EverandGDPR-standard data protection staff training: What employees & associates need to know by Dr Paweł MielniczekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrum Certification: All In One, The Ultimate Guide To Prepare For Scrum Exams And Get Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsVon EverandScrum Certification: All In One, The Ultimate Guide To Prepare For Scrum Exams And Get Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide: SOC 2 Reporting on an Examination of Controls at a Service Organization Relevant to Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, or PrivacyVon EverandGuide: SOC 2 Reporting on an Examination of Controls at a Service Organization Relevant to Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, or PrivacyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building a World-Class Compliance Program: Best Practices and Strategies for SuccessVon EverandBuilding a World-Class Compliance Program: Best Practices and Strategies for SuccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequently Asked Questions in International Standards on AuditingVon EverandFrequently Asked Questions in International Standards on AuditingBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Financial Statement Fraud: Prevention and DetectionVon EverandFinancial Statement Fraud: Prevention and DetectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement Fraud Casebook: Baking the Ledgers and Cooking the BooksVon EverandFinancial Statement Fraud Casebook: Baking the Ledgers and Cooking the BooksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- A Step By Step Guide: How to Perform Risk Based Internal Auditing for Internal Audit BeginnersVon EverandA Step By Step Guide: How to Perform Risk Based Internal Auditing for Internal Audit BeginnersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (11)
- Musings on Internal Quality Audits: Having a Greater ImpactVon EverandMusings on Internal Quality Audits: Having a Greater ImpactNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit. Review. Compilation. What's the Difference?Von EverandAudit. Review. Compilation. What's the Difference?Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- GDPR for DevOp(Sec) - The laws, Controls and solutionsVon EverandGDPR for DevOp(Sec) - The laws, Controls and solutionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Mastering Internal Audit Fundamentals A Step-by-Step ApproachVon EverandMastering Internal Audit Fundamentals A Step-by-Step ApproachBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Mistakes in Quality Statistics: and How to Fix ThemVon EverandMistakes in Quality Statistics: and How to Fix ThemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit and Assurance Essentials: For Professional Accountancy ExamsVon EverandAudit and Assurance Essentials: For Professional Accountancy ExamsNoch keine Bewertungen