Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
S Block, P Block Practice Sheet
Hochgeladen von
jayeshOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
S Block, P Block Practice Sheet
Hochgeladen von
jayeshCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 10
S -BLOCK ELEMENTS
1. What are s- block elements? Name the elements present in the 1st Group of the Periodic
Table. Why I group elements are called alkali metals?
2. What is the reason for the diagonal relationship?
3. How the ionization enthalpy varies in alkali metals?
4. Arrange the first group elements in the decreasing order of Hydration
Enthalpy. Why Li salts are hydrated?
5. Give reason for the higher melting point and boiling point of alkali earth metals than alkali
metals.
6. Give reason for the colour imparted to the flame by alkali metals. Why Be and Mg do not
impart colour to the flame?
7. The compounds of alkaline earth metals are less ionic than alkali metals.Why?
8. Why are Cs and K used as electrodes in photoelectric cells?
9. Name the most power full reducing agent among alkali metals & give reason for it.
10. Give reason for the low solubility of LiF & CsI in water.
11. How does the of Hydration Enthalpy of alkaline earth metals vary & compare it with alkali
metals
12. What is the colour imparted to the flame by Ca,Sr and Ba?
13. How does alkali metals react with halogens?
14. Explain the formation of oxide ,peroxide and superoxide by alkali metals.
15. When alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia, the solution can acquire different colours.
Explain the reason.
16. What is polarization? Discuss it by taking example of lithium halide.
17. Although IE1 values of alkaline earth metals are higher than those of alkali metals, the IE2
values of alkaline earth metals are much smaller than those of alkali metals why?
18. The hydroxides of alkali metals are strongly basic why?
19. lithium is strongest reducing agent. Why ?
p-Block Elements
1. Why atomic radii of 'Ga' is smaller than 'Al'?
2. BCl3 is known but Tl Cl3 is not known. Why?
3. The metallic character increases from boron to aluminium and then decreases from
aluminium to thallium. Explain.
4. What is inert pair effect?
7. BCl3 acts as a lewis acid. How?
5. BCl3 exists as a monomer where as AlCl3 exists as a dimer. Why ?
6. Why anhydrous aluminium chloride has a lower melting point than anhydrous
aluminium flouride?
7. Why boron and thallium does not form B3+ and Tl3+ ions?
8. (i) Why ionisation enthalpy of 'Ga' is higher than that of 'Al'?
(ii) Thallous compounds (Tl+) are more stable than thallic (Tl3+) compounds. Why?
Tin and lead show '+2' and '+4' oxidation states but for lead compounds +2 oxidation
state is more stable. Why?
9. [SiF6]2- is possible where as [CF6]-2 is not possible. Why?
Tin (II) is a reducing agent, whereas, lead (II) is not. Why ?
10. The ionization enthalpy of lead is more than tin. Why?
11. SiCl4 is hydrolysed by water while CCl4 does not. Why ?
12. CO2 is a gas SiO2 is solid . Why?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions on s-Block ElementsDokument11 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions on s-Block ElementsNitish MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 The S-Block Elements PDFDokument11 SeitenChapter 10 The S-Block Elements PDFNitish MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Jan11 Chapter 10 The S Block ElementsDokument16 SeitenNcert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Jan11 Chapter 10 The S Block Elementserfgtrgv vfvvvNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Textbook Solved QuestionsDokument3 SeitenNCERT Class 11 Chemistry Textbook Solved QuestionsSri DharshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - P Block ElementsDokument2 SeitenAssignment - P Block ElementsYash KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkali Metals Properties and CharacteristicsDokument30 SeitenAlkali Metals Properties and Characteristicsbhupesh mahapatroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The S Block Elements - 0Dokument21 SeitenNcert Solutions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The S Block Elements - 0Raghav VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 - The S-Block Elements Important Questions 2022-23Dokument14 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 - The S-Block Elements Important Questions 2022-23Geljlk kljNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Part 2 - Previous Board QuestionDokument13 SeitenChemistry Part 2 - Previous Board QuestionSay2LearnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd YEAR Short Question RedDokument9 Seiten2nd YEAR Short Question RedNosha FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 The S-Block ElementsDokument18 SeitenChapter 10 The S-Block ElementsYash PlayNoch keine Bewertungen
- S BlockDokument6 SeitenS BlockSora RoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- S - Block Elements, Class 11Dokument13 SeitenS - Block Elements, Class 11Ashish kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Year Chemistry Questions Bank: Concordia College KasurDokument9 Seiten2 Year Chemistry Questions Bank: Concordia College KasurNosha FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of S block elementsDokument32 SeitenCharacteristics of S block elementsjhapindra adhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 ExerciseDokument24 SeitenCH 10 ExerciseTr Mazhar PunjabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- S - Block ElementsDokument23 SeitenS - Block ElementsAnand MurugananthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Chemistry Notes Unit 8 NewDokument6 Seiten9 Chemistry Notes Unit 8 NewR.S.HNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year Chemistry Chapter 1 NOTESPKDokument5 Seiten2nd Year Chemistry Chapter 1 NOTESPKFaisal RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- S BLOCK TESTDokument1 SeiteS BLOCK TESTRavinder singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 S Block Elements NCERT Class 11 SolutionsDokument20 SeitenChapter 10 S Block Elements NCERT Class 11 SolutionsZagreus OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12TH Class Chemistry Guess PaperDokument22 Seiten12TH Class Chemistry Guess PaperMugal HanzalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class10 Science Notes Chapte3Dokument9 SeitenClass10 Science Notes Chapte3PallaviGupta100% (1)
- 11 Chemistry Notes - The S-Block ElementsDokument21 Seiten11 Chemistry Notes - The S-Block ElementsAishwary yadav100% (1)
- Electrolysis and Electroplating QuestionsDokument6 SeitenElectrolysis and Electroplating QuestionsManash SinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 14 ELEMENTS (IVA Group Elements)Dokument8 SeitenGROUP 14 ELEMENTS (IVA Group Elements)Premangshu GhoshalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The S-Block Elements - Shobhit NirwanDokument14 SeitenThe S-Block Elements - Shobhit NirwanAadarsh PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 1-ADokument14 SeitenGroup 1-AShivam GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shapes of Molecules & Ions: SolubilityDokument2 SeitenShapes of Molecules & Ions: SolubilitycomplinotionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write Answers To All NCERT Intext Solved & Unsolved Problems. 2. Write Answers To All NCERT Questions in ExercisesDokument2 SeitenWrite Answers To All NCERT Intext Solved & Unsolved Problems. 2. Write Answers To All NCERT Questions in ExercisesJagriti DaryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Chemistry Assignment on Surface Chemistry and Extraction of MetalsDokument4 SeitenClass 12 Chemistry Assignment on Surface Chemistry and Extraction of MetalsSumathi SrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals and Non Metals QuestionsDokument2 SeitenMetals and Non Metals QuestionsraghavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry HW S and P BlockDokument1 SeiteChemistry HW S and P BlockrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 13Dokument2 SeitenCH 13usmanrathore784Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metals and Non MetalsDokument4 SeitenMetals and Non MetalsMohita RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reaction and EquationsDokument3 SeitenChapter 1 Chemical Reaction and EquationsAbabeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Block 11Dokument28 SeitenS Block 11Simranpreet Singh KhalsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Chemistry A - Notes Chapter 9 - The Periodic TableDokument28 SeitenIGCSE Chemistry A - Notes Chapter 9 - The Periodic TableShadman RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: The S-Block Elements Top ConceptsDokument10 SeitenSubject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: The S-Block Elements Top ConceptsRISHI KEJRIWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year Chemistry Guess Paper 2022Dokument6 Seiten2nd Year Chemistry Guess Paper 2022SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Block ADokument5 SeitenS Block AMr BurgerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit1 Mod 3 Group IV ElementsDokument9 SeitenUnit1 Mod 3 Group IV ElementsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes The S-Block ElementsDokument40 SeitenClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes The S-Block ElementsNair SidharthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XI Chemistry Assignment On S and P - Block Elements PDFDokument4 SeitenClass XI Chemistry Assignment On S and P - Block Elements PDFSadiq JavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERTSolutions Class11 Chemistry s-BlockElements PDFDokument19 SeitenNCERTSolutions Class11 Chemistry s-BlockElements PDFNACHAMMAI PRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Worksheet Unit 10: The S-Block ElementsDokument1 SeiteChemistry Worksheet Unit 10: The S-Block ElementsDark DevilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Question PaperDokument1 SeiteChemistry Question PaperAt TanwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- group-1-elementsDokument11 Seitengroup-1-elementsKIRAN ALLUNoch keine Bewertungen
- P BlockDokument29 SeitenP BlockVishal SNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB 10 Chapter 5&6Dokument4 SeitenQB 10 Chapter 5&6Nitin SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyDokument4 SeitenClass X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyToshiGMaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- S-Block Elements 2Dokument28 SeitenS-Block Elements 2Aman SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals: Properties and ReactivityDokument20 SeitenMetals: Properties and ReactivityKivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S - BlockDokument8 SeitenS - BlockKartik ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- S - Block - Alkali Metals - Rapid Revision - 1st JanDokument48 SeitenS - Block - Alkali Metals - Rapid Revision - 1st JanAryan WaghavekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technique of Answering SPM Chemistry: Disediakan Oleh Chong Pei SiDokument8 SeitenTechnique of Answering SPM Chemistry: Disediakan Oleh Chong Pei SichongpeisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- S BlockDokument53 SeitenS BlockhappyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 136-LAB EDokument5 SeitenChem 136-LAB Esidro12382% (11)
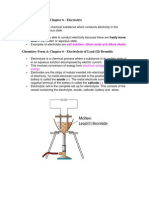
- Chemistry Form 4: Chapter 6 - Electrolyte: Ions in The Molten or Aqueous StateDokument16 SeitenChemistry Form 4: Chapter 6 - Electrolyte: Ions in The Molten or Aqueous StateVinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrodes for Li-ion Batteries: Materials, Mechanisms and PerformanceVon EverandElectrodes for Li-ion Batteries: Materials, Mechanisms and PerformanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid & Basic Radicals Xi - 1Dokument16 SeitenAcid & Basic Radicals Xi - 1jayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid & Basic Radicals Xi - 1Dokument16 SeitenAcid & Basic Radicals Xi - 1jayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Material-ClassXI (Phy) Unit 1-2Dokument27 SeitenStudy Material-ClassXI (Phy) Unit 1-2harshal talwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution of Triangles FormulaeDokument1 SeiteSolution of Triangles FormulaejayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution of Triangles FormulaeDokument1 SeiteSolution of Triangles FormulaejayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
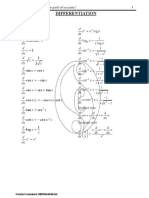
- Differentiation PDFDokument1 SeiteDifferentiation PDFjayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation PDFDokument1 SeiteDifferentiation PDFjayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation PDFDokument1 SeiteDifferentiation PDFjayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- DifferentiationDokument1 SeiteDifferentiationjayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigo FormulaeDokument2 SeitenTrigo Formulaejayesh100% (1)
- Clay Chemistry and Drilling FluidsDokument16 SeitenClay Chemistry and Drilling FluidsDoni Aditya SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Phosphono-Butane-1,2,3,4-Tetracarboxylic Acids SynthesisDokument5 Seiten2-Phosphono-Butane-1,2,3,4-Tetracarboxylic Acids SynthesisVenu KavetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizing the ElementsDokument50 SeitenOrganizing the ElementsLENETTE ALAGONNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM 303 March 2021Dokument154 SeitenCHM 303 March 2021Osei ebenezerNoch keine Bewertungen
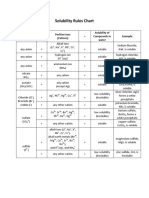
- Solubility Rules ChartDokument2 SeitenSolubility Rules ChartLumwanga MukadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Block QuestionsDokument9 SeitenS Block QuestionsZaid KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UK's Top Science and Tech AdvancesDokument18 SeitenUK's Top Science and Tech AdvancesLuis RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- JR VSA Q and A Wtih Star Marks (2023) PDFDokument42 SeitenJR VSA Q and A Wtih Star Marks (2023) PDFShaik irfan basha Shaik irfan bashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - Inorganic Chemistry and The Periodic TableDokument2 SeitenTopic 4 - Inorganic Chemistry and The Periodic TableSam ShohetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Properties: 1.alkali MetalsDokument5 SeitenBasic Properties: 1.alkali MetalsGanesh sargarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet 134a - SolchemDokument8 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet 134a - SolchemvictorlawNoch keine Bewertungen
- STSE Syllabus Class 12Dokument42 SeitenSTSE Syllabus Class 12Shivji RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Value Based Questions Class Xi ChemDokument15 SeitenValue Based Questions Class Xi ChemAnonymous KlaHb8tgOpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reasons Xii ChemistryDokument4 SeitenReasons Xii ChemistryManahil PariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved Problems: Problem-1Dokument23 SeitenSolved Problems: Problem-1Tushif RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Test BankDokument35 SeitenFull Download Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Test Bankwendelngosseuk100% (24)
- Pta 19 - QPDokument23 SeitenPta 19 - QPManas mittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusDokument17 SeitenAP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusbbbbbbbbbbbbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10: The S-Block ElementsDokument13 SeitenChapter 10: The S-Block Elementsgyogi1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- S-Block ElementsDokument17 SeitenS-Block ElementsPiggu SurfersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic-Table-Groups B v6 Anm s1Dokument31 SeitenPeriodic-Table-Groups B v6 Anm s1Sophi VijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Baharu Chemistry SyllabusDokument145 SeitenSTPM Baharu Chemistry SyllabusChung Chee YuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year Mcqs (Full Book)Dokument69 Seiten2nd Year Mcqs (Full Book)M Anas AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- US8034246 PatentDokument9 SeitenUS8034246 PatentCatalina SarriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 1A and 2A ChemistryDokument16 SeitenGroup 1A and 2A ChemistryDeandra WhitelyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM 105 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Autosaved)Dokument59 SeitenCHM 105 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Autosaved)Daniel DominicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part7 Imdg CodeDokument32 SeitenPart7 Imdg CodeJavier PenanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table of ElementsDokument5 SeitenPeriodic Table of Elementsmichael tenajerosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2.2Dokument8 SeitenExperiment 2.2BenjaminLauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Chemistry of S&P Block Elements Including Noble GasesDokument75 SeitenRevised Chemistry of S&P Block Elements Including Noble GasesKommraju Sravan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen