Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A Primer On Colostral Immunoglobulins
Hochgeladen von
Ioana PipirigOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A Primer On Colostral Immunoglobulins
Hochgeladen von
Ioana PipirigCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Calf Note #03 – A primer on colostral immunoglobulins
Introduction
Differences from whole milk. Colostrum is the secretion from the mammary gland for the first 24 hours
after parturition. It differs markedly from milk in composition, physical properties, and function.
Transition milk is the secretion from the mammary gland from 24 to 72 hours after calving. The
composition of transition milk changes to that of milk by 72 hours after calving. Colostrum differs
from transition milk (see Table 1) as colostrum contains much larger amounts of solids, protein, and
immunoglobulins (Ig). It is also more important in providing passive immunity to the calf during the
first 24 hours after birth.
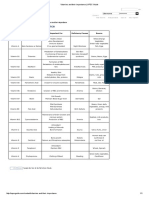
Milking Number
Item 1 2 3 Milk
Colostral Immunoglobulins.
Immunoglobulins (or antibodies) are Specific Gravity 1.056 1.040 1.035 1.032
Solids, % 23.9 17.9 14.1 12.9
proteins critical to the identifying and
Protein, % 14.0 8.4 5.1 3.1
destroying pathogens in the animal. Casein, % 4.8 4.3 3.8 2.5
There are three types of Ig in colostrum IgG, g/L 48 25 15 0.6
of cattle: IgG, IgM, and IgA. Fat, % 6.7 5.4 3.9 3.5
Additionally, there are two isotypes of Lactose, % 2.7 3.9 4.4 5.0
IgG: IgG1 and IgG2. These Ig work Table 1. Composition of bovine colostrum and transition milk.
together to provide the calf with passive From: Foley and Otterby, 1978, J. of Dairy Science 61:1033.
immunity (immunity provided by the dam
and not synthesized by the calf) until the calf's own active immunity develops. Colostrum contains 70-
80% IgG, 10-15% IgM and 10-15% IgA. Most of the IgG in bovine colostrum is IgG1.
IgG1 and IgG2 are transported from the blood of the cow into colostrum by a highly specific
transport mechanism. This mechanism moves large amounts of IgG (particularly IgG1) from blood
into the udder. Consequently, serum IgG concentrations of the dam decline precipitously, beginning
about 2 to 3 weeks prior to calving. Cows require several weeks to resynthesize the lost IgG. IgM
and IgA are synthesized by the plasmacytes in the mammary gland.
What do they do?
Each Ig has a different role in the animal. IgG is the most prevalent in colostrum and serum. Its
primary role is to identify and help destroy invading pathogens. Because it is smaller than other Ig, it
can move out of the blood stream and make its way into other body pools where it helps identify
pathogens. IgM is the antibody that serves as a first line of defense in cases of septicemia. IgM is a
large molecule that stays in the blood and protects against bacterial invasion. IgA protects mucosal
surfaces such as the intestine. It attaches to the intestinal lining and prevents pathogens from
Calf Notes.com © 2001 by Dr. Jim Quigley Page 1
attaching and causing disease. Feeding colostrum for 3 days after birth is a good idea - that provides
IgA to bathe the gut and protect against pathogens.
Colostrum contains large amounts of IgG and smaller amounts of IgM and IgA. All three Ig are
important to the calf, and are necessary to minimize the chance of disease or death. However, it is
important to remember that Ig are only one part of the calf's immune system. Proper nutrition,
minimal stress and a clean environment also help keep calves health
N N
N N J-chain
L L
i i
s s
C C
IgM
IgG C C
molecule
IgM
IgA molecule
molecule (pentameric
form)
Written by Dr. Jim Quigley (17 February 1997).
©2001 by Dr. Jim Quigley
Calf Notes.com (http://www.calfnotes.com)
Calf Notes.com © 2001 by Dr. Jim Quigley Page 2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Determination of Passive Immunity in CalvesDokument3 SeitenDetermination of Passive Immunity in CalvesIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- An Update On Colostral IgGDokument2 SeitenAn Update On Colostral IgGIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Biochemical and Antibacterial Properties of Bovine Mammary SecretionDokument10 SeitenBiochemical and Antibacterial Properties of Bovine Mammary SecretionIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Adaptive Immune Response, Survival, and Somatic Cell Score Between Postpartum Holstein and Norwegian Red × Holstein First-Calf HeifersDokument9 SeitenAdaptive Immune Response, Survival, and Somatic Cell Score Between Postpartum Holstein and Norwegian Red × Holstein First-Calf HeifersIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- An Overview of Calf DiarrheaDokument17 SeitenAn Overview of Calf DiarrheaIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Vet Clin Food Anim Colostrum Dairy CalvesDokument21 SeitenVet Clin Food Anim Colostrum Dairy CalvessandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- A New Passive Immune StrategyDokument9 SeitenA New Passive Immune StrategyIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Improving Passive Transfer of Immunoglobulins in CalvesDokument7 SeitenImproving Passive Transfer of Immunoglobulins in CalvesIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- An Overview of Calf DiarrheaDokument17 SeitenAn Overview of Calf DiarrheaIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structura ADN Si PCRDokument28 SeitenStructura ADN Si PCRIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Calf ImmunologyDokument6 SeitenCalf ImmunologyIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention and Control of Foot Problems in Dairy CowsDokument20 SeitenPrevention and Control of Foot Problems in Dairy CowsIoana PipirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Medical Lab Questions & AnswersDokument85 SeitenMedical Lab Questions & Answersyasser95% (20)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFDokument8 SeitenHemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFjenn1722Noch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- 22.3 Anatomy Study Resources - A PDFDokument3 Seiten22.3 Anatomy Study Resources - A PDFNothingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- ECG WorldDokument139 SeitenECG WorldsatyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- KIT CD117 A Review On Expression in Normal and Neoplastic TissuesDokument16 SeitenKIT CD117 A Review On Expression in Normal and Neoplastic TissuesVlado VladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- Chapter 013Dokument4 SeitenChapter 013Nusa Koj100% (1)
- Antifungal Task Involving Punicalagin Nystatin Combinations Towards Vaginal Yeast InfectionsqnidvDokument1 SeiteAntifungal Task Involving Punicalagin Nystatin Combinations Towards Vaginal Yeast Infectionsqnidvhoursail5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heinamaa - Beauvoir and Husserl - An Unorthodox Approach To The Second SexDokument29 SeitenHeinamaa - Beauvoir and Husserl - An Unorthodox Approach To The Second SexJacky TaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charnley Ankle ArthrodesisDokument12 SeitenCharnley Ankle Arthrodesisdr_s_ganeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Digestive SystemDokument95 SeitenPhysiology of Digestive SystemEsha KumavatNoch keine Bewertungen
- GyyggDokument11 SeitenGyyggYaumil AqsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Biological Effects of Microwaves and Radio Frequency RadiationDokument25 SeitenBiological Effects of Microwaves and Radio Frequency RadiationMichael Janitch100% (2)
- Course Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersDokument2 SeitenCourse Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersbillNoch keine Bewertungen
- StudyDokument23 SeitenStudyJose Paul RaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paget Disease Causes Excessive Bone Formation and DeformationDokument14 SeitenPaget Disease Causes Excessive Bone Formation and DeformationOrson SimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidance Foundations: Three Kinds of LearningDokument11 SeitenGuidance Foundations: Three Kinds of LearningJOEVY P. DE LIMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Nervous SystemDokument63 SeitenOverview of Nervous SystemMAHARANI100% (1)
- PNTD 0005534 s001Dokument22 SeitenPNTD 0005534 s001Paolo VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Placenta DeliveryDokument3 SeitenReview of Placenta DeliverygitapramodhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- E147 Full PDFDokument21 SeitenE147 Full PDFcahyatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 7Dokument32 SeitenBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 7Shephard Png85% (13)
- Sleep Studies: in The Sleep Laboratory and in The Home: Patient EducationDokument2 SeitenSleep Studies: in The Sleep Laboratory and in The Home: Patient EducationALINoch keine Bewertungen
- P.E 2nd Quarter ExamDokument2 SeitenP.E 2nd Quarter ExamCherry Vhim Flores Lanurias100% (3)
- TonsillectomyDokument27 SeitenTonsillectomyRho Vince Caño MalagueñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamins and Their Importance - UPSC Guide PDFDokument1 SeiteVitamins and Their Importance - UPSC Guide PDFRajesh ManjhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- English: Yusran 909312906105.274Dokument6 SeitenEnglish: Yusran 909312906105.274Rachmat MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level ExaminationDokument20 SeitenGeneral Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level ExaminationMaggie NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Reveiw Electrolyte Acid Base MCQ and AnswerDokument15 SeitenBoard Reveiw Electrolyte Acid Base MCQ and AnswerEma100% (8)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 10th SCERT KeralaDokument72 Seiten10th SCERT KeralaArun KNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiobutanolDokument11 SeitenBiobutanolPabloDoriaNoch keine Bewertungen