Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Aniline 1
Hochgeladen von
Arljayn Cuachon0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
51 Ansichten2 SeitenAniline as parent drug
Originaltitel
ANILINE 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenAniline as parent drug
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
51 Ansichten2 SeitenAniline 1
Hochgeladen von
Arljayn CuachonAniline as parent drug
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
a.
Anilines are used in the rubber industry for the
processing of rubber chemicals and products
Intro: Blue jeans - have you ever wondered about the such as car tyres, balloons, gloves, etc.
dye used to give them their color? One of the
b. It is used as a dyeing agent in the manufacture
chemicals that is used to make the indigo dye used
of clothes such as jeans, etc
for our jeans is a substance called aniline.
c. It is employed in the production of drugs such
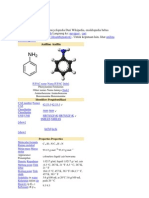
ANILINE- C6H7N or C6H5NH2 as paracetamol, Tylenol, acetaminophen.
d. It is used as a pesticide and fungicides in the
- Anilines are the organic compounds which are agricultural industry
also called as aminobenzene or phenylamine.
- The aniline compounds are said to have the Natural Sources:
formula C6H5NH2 wherein the amino group is
Small amounts of aniline may be found in some
supposed to be attached to the Phenyl group. foods, such as corn, grains, rhubarb, apples,
beans. Aniline has also been found as a volatile
Synonyms:
component of black tea.
Benzenamine Chemical sources
A. Preparation of aniline from benzene
Phenylamine
There are two steps to prepare aniline from benzene.
Aminobenzene
1. Benzene to nitrobenzene- Benzene reacts with
concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid
on heating about 400C and give nitrobenzene. A -
Physical properties
NO2 group is substituted to the benzene ring.
Aniline is a colourless to brown, oily liquid which
darkens on exposure to air and light. It has a 2. Nitrobenzene to aniline- Aniline is prepared by the
characteristic amine odour, Hedonic tone; pungent reaction of nitrobenzene and Sn / concentrated HCl /
excess NaOH with nitrobenzene. In this reaction,
(detectable at 0.6 to 10 ppm ) and burning taste.
Hygroscopic. Moderately soluble in water. Aniline is nitrobenzene is reduced to aniline salt by Sn /
miscible with alcohol, benzene, chloroform, carbon concentrated HCl. Then aniline is recovered by adding
NaOH.
tetrachloride, acetone, and most organic solvents.
a. Melting Point: -6.2°C
b. Boiling Point: 184°C
c. Specific Gravity: 1.0217
Chemical properties
Hazards
a. Combustible.
b. Darkens on exposure to air and light.
c. The substance is a weak base.
d. Reacts with metals such as sodium, potassium,
and calcium, producing flammable hydrogen
gas.
Physiological use and chemical use
a. Toxic if swallowed
b. Toxic in contact with skin
c. Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious
eye damage/eye irritation]
d. Toxic if inhaled
e. Suspected of causing genetic defects
f. Suspected of causing cancer
g. Causes damage to organs through prolonged
or repeated exposure
h. Very toxic to aquatic life
Precaution
a. Follow good hygiene procedures when
handling chemical material
b. Do not eat, drink, smoke or use
products when handling chemical
substance.
c. Follow chemical hygiene plan.
d. Use only in well ventilated areas
e. Avoid splashes or spray in enclosed
areas
f. Avoid open flames, heat sources or
hot surfaces
g. Do not breathe vapour or aerosols.
h. Stor e n a cool location. Provide
ventilation for containers.
i. Store away from oxidizing agents
j. Protect from sunlight
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Production of Aniline From Ammonolysis of Phenol - 2010-CH-09,61,65,87Dokument17 SeitenProduction of Aniline From Ammonolysis of Phenol - 2010-CH-09,61,65,87Shiraz Daud100% (3)
- Synthesis of para Red Dye SubmissionDokument6 SeitenSynthesis of para Red Dye SubmissionMuhammad Hazim TararNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo 'Sudan 1'Dokument5 SeitenSynthesis of 1-Phenylazo 'Sudan 1'seryuyuyu100% (2)
- Lab No.1 - Preparation of Organic CompoundsDokument6 SeitenLab No.1 - Preparation of Organic CompoundsJin-Woo SungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitro BenzeneDokument1 SeiteNitro Benzenezelec991178Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 - Quarter 2 - Week 5 1Dokument24 SeitenScience 9 - Quarter 2 - Week 5 1Marian TimbrezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- David FR16Dokument7 SeitenDavid FR16FrettyDavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDokument3 SeitenAromatic Hydrocarbonsmihai_bors_01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aniline DefinitionDokument2 SeitenAniline DefinitionBadder DanbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties of PhenolDokument2 SeitenPhysical Properties of Phenoldanica100% (1)
- Chemistry Module 10 GeroDokument4 SeitenChemistry Module 10 Geroangelo aquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Module 3Dokument8 SeitenChemistry Module 3angelo aquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-NaphtholDokument4 SeitenSynthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-NaphtholEdric RaguindinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Pahs)Dokument17 SeitenPolynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Pahs)Yumna zaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethyl Benzene and CumeneDokument26 SeitenEthyl Benzene and CumeneRelaxation MasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aniline Project 1234Dokument6 SeitenAniline Project 1234kareem100% (1)
- Ascorbic Acid Promoted (4 + 2) Benzannulation: A Mild, Operationally Simple Approach To The Synthesis of PhenanthrenesDokument5 SeitenAscorbic Acid Promoted (4 + 2) Benzannulation: A Mild, Operationally Simple Approach To The Synthesis of PhenanthrenesThạnh Hưng HồngNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnilinDokument18 SeitenAnilinM Septian PrasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Module 3 FinalDokument7 SeitenChemistry Module 3 Finalangelo aquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol Product/ Synonyms IUPAC Name Method of Preparation Classification/Properti Es Uses 1. Methyl Alcohol - Wood SpiritDokument8 SeitenAlcohol Product/ Synonyms IUPAC Name Method of Preparation Classification/Properti Es Uses 1. Methyl Alcohol - Wood SpiritJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicinal Chemistry 8th Semester PracticalDokument11 SeitenMedicinal Chemistry 8th Semester PracticalMohammad Nasim AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Benomyl From 2-ButeneDokument14 SeitenSynthesis of Benomyl From 2-ButeneSophia Chua MelotindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparation of Aniline Yellow - CBSE Chemistry Practicals Class 12Dokument1 SeitePreparation of Aniline Yellow - CBSE Chemistry Practicals Class 12tmqj5qxvykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condensed Azines. Quinoline. Isoquinoline. Acridine. Diazines. Purine.Dokument151 SeitenCondensed Azines. Quinoline. Isoquinoline. Acridine. Diazines. Purine.Rajesh Kumar0% (2)
- Condensed Azines. Quinoline. Isoquinoline. Acridine. Diazines. Purine.Dokument151 SeitenCondensed Azines. Quinoline. Isoquinoline. Acridine. Diazines. Purine.omansuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 10 ChemistryDokument2 SeitenModule 10 Chemistryangelo aquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnilineDokument20 SeitenAnilineRicardo KakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhenolDokument20 SeitenPhenolUmar TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS ApChem Q4 MELC 1 EditedDokument15 SeitenLAS ApChem Q4 MELC 1 EditedElla de la Cruz GulanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amination: Amination Is The Process of Introducing The Amino Group (Dokument9 SeitenAmination: Amination Is The Process of Introducing The Amino Group (Riva Nur ArofahNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Basra For Oil and Gas: 1-Chapter OneDokument11 SeitenUniversity of Basra For Oil and Gas: 1-Chapter Onekareem100% (1)
- Experiment 16: Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-Napthol: Pre-Lab and Post-Lab Discussion + Experimental ResultsDokument32 SeitenExperiment 16: Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-Napthol: Pre-Lab and Post-Lab Discussion + Experimental ResultsBianca VirtudasoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aniline From Nitrobenzene 1Dokument11 SeitenAniline From Nitrobenzene 1Neha MiracleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review in Azo Compounds and Its Biological Activity 2161 1009 1000169Dokument4 SeitenReview in Azo Compounds and Its Biological Activity 2161 1009 1000169Christa-Gay CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehydes and KetonesDokument6 SeitenAldehydes and KetonesayayayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Pengertian BenzenaDokument7 SeitenA. Pengertian BenzenaNova RefinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AkyneDokument6 SeitenAkyneRaymund CalanayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A02 037Dokument21 SeitenA02 037jaimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Quarter Applied Chemistry 1Dokument10 Seiten4th Quarter Applied Chemistry 1Jasmine Anne LapizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol Product/synonyms Iupac Name/structural Formula Method of Preparation Classification/Propertie S UsesDokument2 SeitenAlcohol Product/synonyms Iupac Name/structural Formula Method of Preparation Classification/Propertie S UsesNera AyonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samiksha Indurkar - Class12 - Chemistry Investigatory Project-1Dokument16 SeitenSamiksha Indurkar - Class12 - Chemistry Investigatory Project-1Aryan BhujbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitro BenzeneDokument7 SeitenNitro Benzenewasay0% (1)
- KIMOR Anilin YellowDokument12 SeitenKIMOR Anilin YellowWigati Nuraeni0% (1)
- Molecular ProfileDokument7 SeitenMolecular ProfileSherly ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Compounds CARBON Its Nature and DerivativeDokument2 SeitenOrganic Compounds CARBON Its Nature and DerivativeVirsol JaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geranyl Pyrophosphate LinaloylDokument6 SeitenGeranyl Pyrophosphate LinaloylSalis Iqbal MazariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aniline Formaldehyde ResinsDokument4 SeitenAniline Formaldehyde ResinsAbu Asim50% (2)
- Synthesis of AcetanilideDokument4 SeitenSynthesis of AcetanilideMyla ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Acetanilide Synthesis of AcetanilideDokument4 SeitenSynthesis of Acetanilide Synthesis of AcetanilideRachael LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- T1 - AR - Stage 4 - FQEDokument7 SeitenT1 - AR - Stage 4 - FQEAmi ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 14 - Preparation of Sudan I, An Azo DyeDokument9 SeitenExercise 14 - Preparation of Sudan I, An Azo DyeAki FujikawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co and CohDokument22 SeitenCo and Cohapi-289060519Noch keine Bewertungen
- AnilineDokument57 SeitenAnilineShivam PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis Organic CompoundDokument11 SeitenSynthesis Organic CompoundricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 PhenylpropanoidsDokument15 Seiten6 Phenylpropanoidskusum AkkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Research 2019) .Dokument29 Seiten(Research 2019) .Jo Che RenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enantioselective Synthesis of Beta-Amino AcidsVon EverandEnantioselective Synthesis of Beta-Amino AcidsEusebio JuaristiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Part Four Dictionary: Grow Your Vocabulary, #31Von EverandChemistry Part Four Dictionary: Grow Your Vocabulary, #31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Group Chemistry: From Synthesis to the Life SciencesVon EverandAmino Group Chemistry: From Synthesis to the Life SciencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjugate Acid Base Pairs WorksheetDokument1 SeiteConjugate Acid Base Pairs WorksheetFrank Massiah100% (3)
- 3.3.2 Co-25Cr-10Ni-7.5W-B AlloyDokument4 Seiten3.3.2 Co-25Cr-10Ni-7.5W-B Alloyqueno1Noch keine Bewertungen
- FloatingDokument12 SeitenFloatingrobson2015Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dielectric Strength of Transformer OilDokument2 SeitenDielectric Strength of Transformer OilAnil VarriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bs en 357 - 2004 Glass-Frp ClassDokument16 SeitenBs en 357 - 2004 Glass-Frp ClassKwong chi hoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NuclearDokument10 SeitenNuclearUsman MunirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 15 - Effects of Catalyst On Reaction RateDokument2 SeitenLab 15 - Effects of Catalyst On Reaction Ratealextzhao1996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cummins SB 4022060-Oil Analysis Techniques For High Horsepower Diesel Engines-UpdateDokument34 SeitenCummins SB 4022060-Oil Analysis Techniques For High Horsepower Diesel Engines-Updategilar herliana putraNoch keine Bewertungen
- For NAT Review Earth and Life ScienceDokument2 SeitenFor NAT Review Earth and Life ScienceKier CorbitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petroleum Dissertation TopicsDokument7 SeitenPetroleum Dissertation TopicsEnglishPaperHelpCanada100% (1)
- LET FOODS Review MaterialsDokument10 SeitenLET FOODS Review MaterialsNix RobertsNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Core Manual - Chapter 5 Pesticide Hazards and First AidDokument55 SeitenNational Core Manual - Chapter 5 Pesticide Hazards and First AidMarvinGarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectureone Introduction To BioChE - 2Dokument20 SeitenLectureone Introduction To BioChE - 2desalegn abera100% (1)
- Bab 4 ObjektifDokument9 SeitenBab 4 ObjektifFida NordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DesalinationTechnologiesforDevelopingCountriesAReview PDFDokument22 SeitenDesalinationTechnologiesforDevelopingCountriesAReview PDFlebob12Noch keine Bewertungen
- E Grout Mc050Dokument2 SeitenE Grout Mc050Tori SmallNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAMG-PA3 5052 Aluminum Honeycomb: DescriptionDokument2 SeitenPAMG-PA3 5052 Aluminum Honeycomb: Descriptionsahiljain_146Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Microalgae Application To Bone Repairing Process - A ReviewDokument19 Seiten2023 Microalgae Application To Bone Repairing Process - A ReviewvirgiparedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular SpectrosDokument4 SeitenSpectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular SpectrosSyafrian AzmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oisd 142Dokument55 SeitenOisd 142sandeep MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo General de Valvulas KSB (Aplicaciones)Dokument7 SeitenCatalogo General de Valvulas KSB (Aplicaciones)Leandro AguiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Shield6421 Datasheet PDFDokument1 SeiteE Shield6421 Datasheet PDFYo ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading TOEFLDokument13 SeitenReading TOEFLwelnitesiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embuild BrochureDokument38 SeitenEmbuild BrochureKawish TamourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Tumbuhan: Ihsan Tria Pramanda, M.SDokument19 SeitenAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Tumbuhan: Ihsan Tria Pramanda, M.SReva RahmafitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sofw Thickening AgentsDokument8 SeitenSofw Thickening AgentsPulbere NeagraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Systems Worksheet 7-12: Summary QuestionsDokument2 SeitenEnergy Systems Worksheet 7-12: Summary Questionsapi-341899824Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiments 11 15 NotesDokument16 SeitenExperiments 11 15 Notesforisko05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Book by MontogomeryDokument10 SeitenBook by MontogomerySubba PappuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramabulana Et Al. 2021 MN and MetPA - Chemical Space of Four Momordica Plant SpeciesDokument15 SeitenRamabulana Et Al. 2021 MN and MetPA - Chemical Space of Four Momordica Plant SpeciesFernanda SantosNoch keine Bewertungen