Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tut Sheet 2
Hochgeladen von
Anandu KBOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tut Sheet 2
Hochgeladen von
Anandu KBCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
Centre for Energy Studies
2019 – 2020 (II Semester)
ESL 710: Energy, Ecology and Environment
Tutorial Sheet - 2
1. A stream flowing at a rate of 10.0 m3/s has a tributary feeding into it with a flow of 5.0 m3/s.
The stream's concentration of chloride upstream of the junction is 20.0 mg/lt, and the
tributary chloride concentration is 40 mg/lt. Treating chloride as a conservative substance and
assuming complete mixing of the two streams, find the downstream chloride concentration.
2. Every year, herons, seagulls, eagles and other birds mass along a 4.75 km stretch of stream
connecting a lake to the ocean to catch the fingerling salmon as they migrate downstream to
the sea. The birds are efficient fishermen and will consume 10,000 fingerlings per kilometre
of stream each hour regardless of the number of salmon in the stream. In other words, there
are enough salmon; the birds are only limiter by how fast they can catch and eat the fish, The
stream's average cross-sectional area is 20 m2, and the salmon move downstream with the
stream's flow rate of 700 m3/min. If there are 7 fingerlings per m3 in the water entering the
stream, what is the concentration of salmon that reach the ocean when the birds are feeding?
3. A lagoon is designed to accommodate an input flow of 0. 1 m3/s of a non-conservative
pollutant with concentration 30 mg/lt. and reaction rate constant of 0.2 per day. The effluent
from the lagoon must have a pollutant concentration of less than l0 mg/lt. assuming that
complete mixing takes place, how large must the lagoon be?
4. A two-pond system, given in the figure below, is fed by a stream with flow rate of 1 million
gallons per day (MGD) and a non-conservative pollutant (BOD) with a concentration 20 mg/lt.
The rate of decay of the BOD is 0.3 per day. The volume of the first pond is 5 million gallons
(MG) and the second is 3 million gallons. Assuming complete mixing within each pond, find
the BOD concentration leaving each pond.
5. A creek carries 5.0 m3/s of water with a selenium (Se) concentration of 0.0015 mg/L. A farmer starts
withdrawing 1 .0 m3/s of the creek-water to irrigate the land. During irrigation, the wafer picks up
selenium from the salts in the soil. One half of the irrigation water is lost to the ground and plants and
the other half is returned to the creek. The irrigation runoff to the creek contains 1 mg/L. Selenium is a
conservative non-reactive substance and the stream does not pick up more selenium from any other
source.
i. If the farmer irrigates continuously, what will be the steady state concentration of selenium in
the stream downstream from the farm (after the irrigation run-off returns to the stream)?
ii. Fish are sensitive to selenium levels over 0.04 mg/L. The farmer agrees not to use more water than
will keep the stream selenium level below this critical concentration. How much water can the
farmer withdraw from the stream to use for irrigation?
6. Your stomach is a chemical reactor. When you devour a fast food special hamburger in about
a minute, it acts like an instantaneous input of 325 gms of fast food entering the stomach. In
response the stomach starts producing gastric liquids (acids), which are continuously excreted
into the stomach at a rate of l2 mL/min as the hamburger is digested. The fluid also leaves the
stomach to the small intestine at a flow rate of 12 mL/min, so the volume of liquid in the
stomach stays constant at 1.15 L, the hamburger digestion rate is 1.33 per hour. What fraction
of the hamburger's mass will remain undigested in your stomach one hour after you eat the
ham burger?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Problems Mass BalanceDokument2 SeitenProblems Mass BalanceKofi DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engineering QuizDokument1 SeiteEnvironmental Engineering QuizAbegail GarcimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceng5404 Assignment 1 Envrtl EngDokument1 SeiteCeng5404 Assignment 1 Envrtl Engashe zinabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Resource Management: D.HarshaDokument60 SeitenWater Resource Management: D.HarshaSenthil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4Dokument79 SeitenUnit 4pankajNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2Dokument2 SeitenA2akshayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 322 2014 HW1 PDFDokument2 Seiten322 2014 HW1 PDFmihrican302Noch keine Bewertungen
- River Cleaning ProjectDokument10 SeitenRiver Cleaning Projectcoepcesa100% (1)
- Oxidationponds 160122070624Dokument20 SeitenOxidationponds 160122070624Diwakar GurramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancaman Mangrove BuktiDokument1 SeiteAncaman Mangrove BuktiKamal Idris Switch-onNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER-1 FinalisedDokument19 SeitenCHAPTER-1 FinalisedShyam SundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOD CalculationDokument1 SeiteBOD CalculationGbenga AdewumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One: IntroductionDokument4 SeitenChapter One: IntroductionManandhar SomeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- River Water Pollution: A Challenge For Riverine Country - BangladeshDokument3 SeitenRiver Water Pollution: A Challenge For Riverine Country - BangladeshToufik AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthetic Detergents (Surfactants) and Organochlorine Pesticide Signatures in Surface Water and Groundwater of Greater Kolkata, IndiaDokument9 SeitenSynthetic Detergents (Surfactants) and Organochlorine Pesticide Signatures in Surface Water and Groundwater of Greater Kolkata, IndiamagdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.tech I Yr Environment and Ecology Unit 2 Detail NotesDokument18 SeitenB.tech I Yr Environment and Ecology Unit 2 Detail Notesbhaivarun65Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sales, Judayarose Bsce GEC 01 (Environmental Engineering) Assignment No. 1Dokument7 SeitenSales, Judayarose Bsce GEC 01 (Environmental Engineering) Assignment No. 1Kim Book JooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infiltration Galleries PDFDokument5 SeitenInfiltration Galleries PDFmuhardionoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infiltration Galleries:-A Solution To Drinking Water Supply For Urban Areas Near Rivers."Dokument5 SeitenInfiltration Galleries:-A Solution To Drinking Water Supply For Urban Areas Near Rivers."Prasenjit DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 SEWAGE EFFLUENT DISPOSAL TECHNIQUES Jen 2019 MtuDokument21 SeitenChapter 5 SEWAGE EFFLUENT DISPOSAL TECHNIQUES Jen 2019 MtuANDLENATU0% (1)
- Waste Stabilisation Pond Design - ManualDokument21 SeitenWaste Stabilisation Pond Design - ManualAchala NavaratneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dal Lake: Issues and Management StrategiesDokument5 SeitenDal Lake: Issues and Management StrategiesImtiyaz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS 0008 12 Final Addendum PDFDokument14 SeitenMS 0008 12 Final Addendum PDFGeorge_Wabag_2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pamba River and Its Risk AssessmentDokument6 SeitenPamba River and Its Risk AssessmentThasneem K. SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater Production, Treatment, and Use in Sri Lanka: AbstractDokument7 SeitenWastewater Production, Treatment, and Use in Sri Lanka: AbstractDhananjani DissanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 1SITI NADHIRAH AzmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Pollution ReportDokument12 SeitenWater Pollution ReportjEmAhLiCiOuSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 Water Pollution and ManagementDokument69 SeitenLesson 4 Water Pollution and ManagementRoge MonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- WASH Cluster Guidelines For Water Treatment in SomaliaDokument3 SeitenWASH Cluster Guidelines For Water Treatment in SomaliaAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part Ii. Thailand Catfish Mortalities in Farm Ponds: 1. Background InformationDokument5 SeitenPart Ii. Thailand Catfish Mortalities in Farm Ponds: 1. Background InformationaneeshmscNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infiltration Gallery Yamna PDFDokument5 SeitenInfiltration Gallery Yamna PDFshamoojeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Resource Management: D.HarshaDokument59 SeitenWater Resource Management: D.HarshaRonny RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waste TreatmentDokument9 SeitenWaste TreatmentGideon Abbey Commey100% (1)
- Organic Inggris EditDokument13 SeitenOrganic Inggris EditSarah AyundaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sea Water ChlorinationDokument2 SeitenSea Water ChlorinationE.C.MADHUDUDHANA REDDYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Pollution ControlVon EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Lake TerminologyDokument5 SeitenGlossary of Lake Terminologyapi-140528149Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rhizosolenia Bergonii, Dactyliosolen Mediteranius, Rhizosolenia Calcar Avis, and Guinardia Flacida. With The Abundance of That in Can NamelyDokument1 SeiteRhizosolenia Bergonii, Dactyliosolen Mediteranius, Rhizosolenia Calcar Avis, and Guinardia Flacida. With The Abundance of That in Can NamelyraisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Quality Management For Catfish CultureDokument5 SeitenWater Quality Management For Catfish Cultureapi-3803371100% (2)
- Bio Drainage - IcarDokument8 SeitenBio Drainage - IcarnheckmaierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Review of The Related LiteratureDokument12 SeitenChapter 2 Review of The Related Literaturewindow painNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecology Tutorials PDFDokument4 SeitenEcology Tutorials PDFSandeep MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecology Tutorials PDFDokument4 SeitenEcology Tutorials PDFSandeep MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecology Tutorials PDFDokument4 SeitenEcology Tutorials PDFSandeep Mehta100% (1)
- Chapter 4Dokument40 SeitenChapter 4ashuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carp Culture: Icar-Krishi Vigyan Kendra (Card), PathanamthittaDokument2 SeitenCarp Culture: Icar-Krishi Vigyan Kendra (Card), Pathanamthittajohnstruct archNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Trip To La Fish Breeding Centre and Kahandamodara Shrimp Breeding CentreDokument12 SeitenField Trip To La Fish Breeding Centre and Kahandamodara Shrimp Breeding CentreDimuthu DaluwatteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Pollution and PreventionDokument6 SeitenWater Pollution and PreventionjayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquatic EcosystemsDokument2 SeitenAquatic EcosystemsJonas ColipanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimum Condition of Water For AquacultureDokument5 SeitenOptimum Condition of Water For AquacultureBold PersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- River Water Quality and PollutionDokument20 SeitenRiver Water Quality and PollutionDaryl BartolomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrefaceDokument23 SeitenPrefaceManav GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partex Denims LTD.: Operation & Maintenance ManualDokument43 SeitenPartex Denims LTD.: Operation & Maintenance ManualSarang BondeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hw3 Solutions 2012Dokument15 SeitenHw3 Solutions 2012karthikeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Quality ParametersDokument4 SeitenWater Quality ParametersAmit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DhruviPareek 21060222093 DivA ILCDokument12 SeitenDhruviPareek 21060222093 DivA ILCLuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dissolved Oxygen DiscussionDokument4 SeitenThe Dissolved Oxygen Discussionneriansmith100% (1)
- Water Purification in Natural SystemsDokument3 SeitenWater Purification in Natural SystemsColdWinterKid100% (1)
- Did Your Can of Soda Kill A Whale? Water Pollution for Kids | Children's Environment BooksVon EverandDid Your Can of Soda Kill A Whale? Water Pollution for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
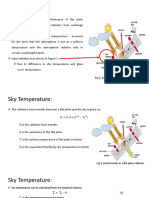
- Sky Temperature:: Fig 1. Heat Transfer in A Flat Plate CollectorDokument4 SeitenSky Temperature:: Fig 1. Heat Transfer in A Flat Plate CollectorAnandu KBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ku - S8 - Eee 2013Dokument34 SeitenKu - S8 - Eee 2013Anandu KBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Library Management Robot: Bomble Pranit R. G. Dipika Dr. ShaikhmeeravaliDokument4 SeitenLibrary Management Robot: Bomble Pranit R. G. Dipika Dr. ShaikhmeeravaliAnandu KBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stock Price Prediction Using LSTM On Indian Share MarketDokument10 SeitenStock Price Prediction Using LSTM On Indian Share MarketAnandu KBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iot Around: Linux EnvironmentDokument4 SeitenIot Around: Linux EnvironmentAnandu KBNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Des IIT Delhi Brochure PDFDokument22 SeitenM.Des IIT Delhi Brochure PDFAnandu KBNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaitlistsDokument17 SeitenWaitlistsAnandu KBNoch keine Bewertungen
- G CLIMATE OF PAKISTAN Key PointsDokument11 SeitenG CLIMATE OF PAKISTAN Key PointsTalha AfzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factory Act 1948Dokument27 SeitenFactory Act 1948priya singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Borne DiseasesDokument34 SeitenWater Borne DiseasesAra ArvinthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Balances Design Problem - Acrylic Acid Production: Process StreamsDokument39 SeitenMaterial Balances Design Problem - Acrylic Acid Production: Process StreamsmoheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Paes Part 2 SummaryDokument3 Seiten5 - Paes Part 2 SummaryCherry Mae Arado CervantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q-Ans-Chapter 17 Spontaneity Entropy and Free Energy 1Dokument40 SeitenQ-Ans-Chapter 17 Spontaneity Entropy and Free Energy 1Janzelle BorbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Moisture Swing Sorbent For Direct Air Capture of Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic and Kinetic AnalysisDokument9 SeitenA Moisture Swing Sorbent For Direct Air Capture of Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic and Kinetic AnalysisY BermainNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Education Reviewer (PRC)Dokument44 SeitenGeneral Education Reviewer (PRC)Ara HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calentador SolarDokument6 SeitenCalentador SolarMario ValentiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Troublshooting For PET PreformDokument5 SeitenTroublshooting For PET PreformSteven Cheng75% (4)
- MANUAL Vertical - Multi Stage - Jockey - Pump FMF 03 313 PVM - SeriesDokument20 SeitenMANUAL Vertical - Multi Stage - Jockey - Pump FMF 03 313 PVM - Seriessivan ebdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Fair ResearchDokument4 SeitenScience Fair Researchapi-537176699Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regional Plan For Goa Interim Report by The Task Force Government of GoaDokument67 SeitenRegional Plan For Goa Interim Report by The Task Force Government of Goajim mehta100% (1)
- Abstraction: Amount of Rainfall That Doesn't Turn Into RunoffDokument8 SeitenAbstraction: Amount of Rainfall That Doesn't Turn Into RunoffyomifNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDS For FPSC (Pakmcqs)Dokument352 SeitenEDS For FPSC (Pakmcqs)Muhammad IlyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrients and Gas RequirementsDokument12 SeitenNutrients and Gas Requirementsapi-616066735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Employees State Insurance Corporation Vs Bhag Singp890001COM630880Dokument8 SeitenEmployees State Insurance Corporation Vs Bhag Singp890001COM630880manraj pataudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CES ProfileDokument12 SeitenCES ProfileGanesh VijaykumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WL1 and AF1 Virginia Form P-378 Product BulletinDokument2 SeitenWL1 and AF1 Virginia Form P-378 Product BulletinTwisty OliverNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeneratorDokument9 SeitenGeneratorSooraj Surendran SugathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goal 6: Clean Water and SanitationDokument3 SeitenGoal 6: Clean Water and SanitationNazakat HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method StatementDokument9 SeitenMethod StatementUmpahPah75Noch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Cambridge Geography - CoastsDokument17 SeitenIGCSE Cambridge Geography - CoastsCrystal Berry100% (1)
- Williams-Evans CUI Paper, NACE-Calgary 2010Dokument23 SeitenWilliams-Evans CUI Paper, NACE-Calgary 2010John Williams100% (1)
- Fmea PosDokument8 SeitenFmea PosGeovin Dexter Uy100% (1)
- DLP in Science 3 Day 1Dokument6 SeitenDLP in Science 3 Day 1Wilmar MondidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim Exam EssayDokument1 SeitePrelim Exam EssayKeanu PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV - Kassim - GUECHI - 6 YEARS - EXPDokument2 SeitenCV - Kassim - GUECHI - 6 YEARS - EXPKassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ekelemu 16. A Review of Aquaculture Production in NigeriaDokument10 SeitenEkelemu 16. A Review of Aquaculture Production in Nigeriascribd52389122Noch keine Bewertungen
- KayserDokument7 SeitenKayseruretenaliNoch keine Bewertungen