Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Grade 4 - Science Notes - Interactions in A Community
Hochgeladen von
marieanas trenchOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Grade 4 - Science Notes - Interactions in A Community
Hochgeladen von
marieanas trenchCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NAME:
Science - Grade 4/ Third Quarter/ S.Y. 2017-2018/Notes in Lesson 8.2: Interactions in a Community
FORMS OF INTERACTIONS IN A COMMUNITY
1. PREDATION – two organisms do not live together, where predator (an organism that hunts,
attacks or kills) feed on its prey (an organism that is attacked or killed)
FROG and CRICKET. Frog (predator) is fed on small insects like cricket (prey).
LION and BUFFALO. Lion (predator) attacks and kills buffalo (prey) for food.
2. COMPETITION – organisms in same or different species do not live together, competing for
limited resources like food, water, space or even mate.
PLANTS. Plant roots growing close together compete for nutrients, water and space.
LIONS and TIGERS. Both lions and tigers fight for the same food resources and even
territory.
3. SYMBIOSIS – relationship between two or more organisms that live closely together
a. Mutualism – is a relationship where two organisms benefit or help each other
FLOWER and BEES. Flowers provide nectar to bees and the bees help flowers
spread their pollen for reproduction
FUNGI and ANTS. Fungi grow on wastes of ants. Once the fungi grow, the ants eat it.
b. Commensalism – one organism benefits while the other organism is neither helped nor
harmed
SMALL FISHES and SEA ANEMONE. Small fishes stay in the sea anemone to protect
themselves from big fishes while the sea anemone has not benefited nor harmed by
the fishes.
MOSS and TREES. The moss receives more sunlight for photosynthesis if the moss
grows high on tree branches rather than close to the ground. The tree is not affected
at all.
c. Parasitism – one organism (parasite) while the other is harmed (host). The host is rarely
killed but the health is greatly affected.
MOSQUITO and HUMAN or ANIMALS. Mosquito (parasite) that is fed by sucking
blood on human or animals (hosts).
BACTERIA and HUMAN. Bacteria (parasite) use the body of human for
nourishment and reproduction while the human (host) gets sick.
*See the back of this page for more examples.
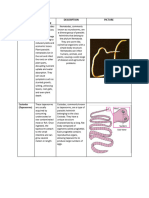
ORGANISMS INVOLVED RELATIONSHIP
FUNGUS & ALGAE
Fungus provides nutrients to algae MUTUALISM
Algae provides food to fungus
TICK & FLEAS
Flea gets nourishment from dog.
PARASITISM
Dog is harmed… may become sick from bites/diseases
transmitted by the parasite.
CLOWN FISH & SEA ANEMONE
Clown fish get protection from the anemone MUTUALISM
Sea anemone get cleaned of parasites from the clown fish
INSECTS & OAK TREES
Insects form a nursery called a gall on the leaf/branch of
COMMENSALISM
a tree. Insects have a safe place to develop.
Tree us not helped or harmed by the presence of the galls
MISTLETOE & TREE THAT IT ATTACHED TO
Mistletoe gets food and water from the tree
PARASITISM
Tree loses food and water that it needs… eventually will
die.
SHARK & REMORA FISH
Remora fish get free food by hanging out with sharks COMMENSALISM
Sharks are not affected by the presence of fish
EAGLE & FISH
Eagles can spot fish swimming in a lake from high
altitudes. They swoop down, and grab fish to feed their PREDATION
young back in the nest.
The fish instantly dies and is eaten by eagles
COW & INTESTINAL BACTERIA
Bacteria live in the intestines of cows and other
MUTUALISM
organisms. They help to digest food for the cow.
The cow provides a warm, moist environment to live.
TWO MALE BIGHORN SHEEPS
Male bighorn sheep, called rams butt heads to see which
one is dominant. COMPETITION
The dominant male can mate with more females than the
non-dominant male sheep
ATHLETE’S FOOT: RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TOES &
FUNGUS
Athlete’s food is a fungus growing between and around
human toes. PARASITISM
The fungus gets nutrients from the human skin
Athlete’s foot causes dry, scaly, itching, inflammation and
even blisters
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Good Buddies - Symbiotic RelationshipsDokument1 SeiteGood Buddies - Symbiotic Relationshipsapi-95178008Noch keine Bewertungen
- MontesorryDokument11 SeitenMontesorrymvmbappleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation and Protection of Estuaries Andmintertidal Zones Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenConservation and Protection of Estuaries Andmintertidal Zones Lesson PlanPaciano Cansing100% (1)
- Clinical ParasitologyDokument404 SeitenClinical ParasitologyDrMohamedBenrashed100% (2)
- Jay Davidson Symptoms of A Parasitic InfectionDokument4 SeitenJay Davidson Symptoms of A Parasitic InfectionNaga BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainable EcosystemsDokument5 SeitenSustainable EcosystemsbobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes - MEDICAL PARASITOLOGYDokument12 SeitenLecture Notes - MEDICAL PARASITOLOGYAngelica Marzo67% (3)
- Symbiotic Relationships PracticeDokument2 SeitenSymbiotic Relationships Practiceapi-264004571Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body Parts Clip CardsDokument6 SeitenBody Parts Clip Cardscat7mnmnNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Five SensesDokument4 SeitenThe Five Sensesapi-307358504Noch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid: 15 Minutes Presentation at Ald Ersgate CollegeDokument19 SeitenFirst Aid: 15 Minutes Presentation at Ald Ersgate CollegeEmmanuel John Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of A Plant Worksheets PDFDokument7 SeitenParts of A Plant Worksheets PDFNathalie Villanueva PueblosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Paper For Science Month Earth Savers Club 1Dokument14 SeitenConcept Paper For Science Month Earth Savers Club 1Aaron Manuel MunarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading MaterialsDokument62 SeitenReading MaterialsJoules Laureta Fabros GaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fun With Common and Proper Nouns WorksheetDokument2 SeitenFun With Common and Proper Nouns Worksheetany nameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuller Lessons With Modification Lesson 4Dokument4 SeitenFuller Lessons With Modification Lesson 4chong chojun balsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Degrees of AdjectivesDokument17 SeitenDegrees of AdjectivesBilly Rhay Villareal100% (1)
- Assessment in Science Vi-Q2 m3Dokument2 SeitenAssessment in Science Vi-Q2 m3Fritzy PremaylonNoch keine Bewertungen
- I.Objective:: Teacher's Activity Student's ActivityDokument5 SeitenI.Objective:: Teacher's Activity Student's ActivityShin MonleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Vowel SoundsDokument20 SeitenLong Vowel SoundsMher RiveroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affidavit of Loss (Driver's License)Dokument1 SeiteAffidavit of Loss (Driver's License)aprilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crayon Color Flashcards PDFDokument3 SeitenCrayon Color Flashcards PDFRonnie De Vera Uno100% (1)
- NewspaperDokument4 SeitenNewspaperMatthew Alison ApostolNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ugly Duckling StoryDokument5 SeitenThe Ugly Duckling StoryNatalia Soledad RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inadequate Resources Difficult Work Assignments Unclear Expectations A Sink-Or-Swim Mentality, and Reality ShockDokument3 SeitenInadequate Resources Difficult Work Assignments Unclear Expectations A Sink-Or-Swim Mentality, and Reality ShockdoloresfilipinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Parts of Land AnimalsDokument15 SeitenBody Parts of Land AnimalsJoice Dela cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 4 English Quarter 2 Week 1 Context Clues: Teacher IrishDokument40 SeitenGrade 4 English Quarter 2 Week 1 Context Clues: Teacher IrishTeacher Irish LaquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative Report OrientationDokument5 SeitenNarrative Report OrientationSHAINA ELOISA CAUNINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compound and Complex SentencesDokument12 SeitenCompound and Complex Sentencesanon_180142914Noch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate Recognition QuarterlyDokument1 SeiteCertificate Recognition QuarterlyGe PebresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng6 q2 Module 7 Week7 Analyzing The Characters and Setting Used in Printnon Print and Digital Materials RemovedDokument14 SeitenEng6 q2 Module 7 Week7 Analyzing The Characters and Setting Used in Printnon Print and Digital Materials RemovedAngie AltoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5: Day 1Dokument31 SeitenWeek 5: Day 1bessie lorzanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of A Story (Grade 4)Dokument8 SeitenElements of A Story (Grade 4)Mai Mai BallanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint English 3 Week 4Dokument70 SeitenPowerpoint English 3 Week 4Sharon Panganiban - Gomez100% (1)
- Fun With Common and Proper Nouns WorksheetDokument2 SeitenFun With Common and Proper Nouns WorksheetThevika Periyasamy100% (1)
- Vowels LPDokument6 SeitenVowels LPShalla Anne GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Struggles of Our Life (TugasDokument1 SeiteThe Struggles of Our Life (TugasKusmanto KTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative Report On Handwashing Area For Grade FourDokument7 SeitenNarrative Report On Handwashing Area For Grade FourEfra SageNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Month MatrixDokument1 SeiteEnglish Month MatrixEdgar GorgonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 3C - TEST 1Dokument2 SeitenScience 3C - TEST 1Phạm Thị Tiền100% (1)
- Body Structures of Animals For Adaptation and Survival 2nd Grading Week 3Dokument33 SeitenBody Structures of Animals For Adaptation and Survival 2nd Grading Week 3daitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 3 LM Quarter 3 Final PDFDokument85 SeitenEnglish 3 LM Quarter 3 Final PDFJocelyn Pedro82% (11)
- Mini LessonsDokument10 SeitenMini Lessonsapi-302405971Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fuller Workbook ColoredDokument386 SeitenFuller Workbook ColoredFaye Dusayen - EsclamadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in English Iii: Time Duration: 1 Day Content StandardDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan in English Iii: Time Duration: 1 Day Content StandardJazzy ToqueroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pink Scheme Word ListDokument12 SeitenPink Scheme Word Listshaliniverma83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stages in The Life Cycle of OrganismsDokument44 SeitenStages in The Life Cycle of OrganismsCatherine Renante100% (1)
- Basic Research ProposalDokument21 SeitenBasic Research ProposalDennis Corsino RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beginning Blends 1: FR CL GR BL SC FL CR PLDokument1 SeiteBeginning Blends 1: FR CL GR BL SC FL CR PLKesanam SpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading MatrixDokument7 SeitenReading MatrixMacharisse Joanne Jumoc LabadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertebrates and Invertebrates With InteractiveDokument44 SeitenVertebrates and Invertebrates With InteractiveMelxie DeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL English Q2 W1Dokument4 SeitenDLL English Q2 W1Wiljohn ComendadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Periodical Test in English VIDokument5 Seiten1st Periodical Test in English VIrubieann_danzalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Grades and General Average: Names of LearnersDokument2 SeitenFinal Grades and General Average: Names of LearnersAnna KarinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English q2 w1 Day 2 Noting DetailDokument5 SeitenEnglish q2 w1 Day 2 Noting DetailElsbeth CañadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP Science 5 1ST-4THDokument344 SeitenLP Science 5 1ST-4THLeonardo Valle Taboy100% (2)
- Eng 6 Q 1 WK 8 Day 1-4Dokument58 SeitenEng 6 Q 1 WK 8 Day 1-4Verah LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polygon ReviewerDokument16 SeitenPolygon ReviewerEmanuel Tomas RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adverbs Worksheet 3Dokument2 SeitenAdverbs Worksheet 3pramod76Noch keine Bewertungen
- Communicable DiseaseDokument27 SeitenCommunicable DiseasePearl & Xenna PinanonangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet - Parts of A Plant - Answer KeyDokument2 SeitenWorksheet - Parts of A Plant - Answer Keycoolandcrazy44Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ms. Irish Lyn T. Alolod Vi-AdviserDokument17 SeitenMs. Irish Lyn T. Alolod Vi-AdviserIrish Lyn Alolod Cabilogan100% (1)
- EcologicalDokument27 SeitenEcologicalChonalyn LorenzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SymbiosisDokument1 SeiteSymbiosisJonalvin KENoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Community InteractionsDokument95 SeitenLecture Community Interactionsrkv100% (1)
- In Vivo Comparative Efficacy of Indigenous Plants Against Trichostrongylus of Sheep in District Zhob, BalochistanDokument8 SeitenIn Vivo Comparative Efficacy of Indigenous Plants Against Trichostrongylus of Sheep in District Zhob, BalochistanOpenaccess Research paperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiparasitics:: Ectoparasiticides, Endoparasiticides and Anti-Protozoal AgentsDokument26 SeitenAntiparasitics:: Ectoparasiticides, Endoparasiticides and Anti-Protozoal AgentsRISHIKANoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 JCE Agri LoyolaDokument12 Seiten2021 JCE Agri LoyolaMalack ChagwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasites PDFDokument6 SeitenParasites PDFDorcas ChinkuteleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2ND CotDokument5 Seiten2ND CotAko Si CrokieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Quarterly Examination in Science 4Dokument4 SeitenSecond Quarterly Examination in Science 4Māku KichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yuri Anthony D. Sucgang Bmls-2A Types of Symbiotic AssociationsDokument6 SeitenYuri Anthony D. Sucgang Bmls-2A Types of Symbiotic AssociationsYuri SucgangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Biology ch-8 Q BankDokument4 Seiten12 Biology ch-8 Q BankBhuvaneswari SenthilkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Year Zoology Paper-I PDFDokument2 Seiten1st Year Zoology Paper-I PDFAditi GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spatial EssayDokument5 SeitenSpatial Essayafhbgrgbi100% (2)
- m1 - Helminthic InfectionDokument9 Seitenm1 - Helminthic Infectionthe greatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Grade 7 Q 2 WK 7Dokument32 SeitenScience Grade 7 Q 2 WK 7ANGELICA A. VALDEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avian Brood Parasitism (PDFDrive)Dokument566 SeitenAvian Brood Parasitism (PDFDrive)Jessica RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitic Diseases Low Resolution 7th EditDokument616 SeitenParasitic Diseases Low Resolution 7th EditLusungu S. LupenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Veterinary Clinical ParasitologyDokument215 SeitenVeterinary Clinical ParasitologyGermano NetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ON CLASS 12 ON Mutualism, Commensalism and PredationDokument37 SeitenON CLASS 12 ON Mutualism, Commensalism and PredationifatimashekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- HelmithsDokument4 SeitenHelmithsTracy Del CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasite and Communicable Disease PDFDokument58 SeitenParasite and Communicable Disease PDFDr Dhruva PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of FishcultureDokument33 SeitenDiseases of FishcultureSiva SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Full Moon Parasite Cleanse ProtocolDokument49 SeitenThe Full Moon Parasite Cleanse ProtocolparthvarandaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symbiotic Relationships (Final) 1Dokument14 SeitenSymbiotic Relationships (Final) 1Jane PaguiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form Two Agriculture NotesDokument94 SeitenForm Two Agriculture NotesVennancia MukiwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasite Control For GoatsDokument40 SeitenParasite Control For GoatsCalvin ThorntonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community EcologyDokument93 SeitenCommunity Ecologysaksham111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fajfer 2012Dokument22 SeitenFajfer 2012Monika FajferNoch keine Bewertungen