Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hospt Equip 10 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Mohammed Al-shamiriOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hospt Equip 10 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Mohammed Al-shamiriCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
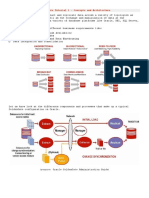
Hospital medical equipment - general information Computed radiography (CR) systems
UMDNS GMDN
17904 Digital imaging systems, computed radiography 35928 Digital imaging scanner, computed radiography
Other common names:
Computed radiographic systems; cassette digital x-ray; digital radiography systems
Health problem addressed
This device is an image digitization system designed to acquire
and digitize x-ray images from image storage phosphor plates.
The patient positioning and imaging techniques used in CR
imaging are identical to those used in conventional radiography.
Clinical applications include all radiographic examinations
performed by conventional table systems (e.g., pediatric,
skeletal, abdominal, urologic imaging) and portable systems.
Product description
A CR system consists of an image reader/digitizer, cassettes
containing imaging receptors (photostimulable-phosphor
plates), a computer console or workstation, software,
monitors, and a printer. Single-plate readers (each cassette
is loaded manually and read separately) and multiple-plate
readers (multiple plates—up to 10—can be stacked and loaded
Use and maintenance
User(s): Radiologist; radiology technician;
automatically) are available.
other medical staff
Principles of operation Maintenance: Biomedical engineering staff
Imaging plates are inserted in a radiographic table’s cassette and/or service contract with the manufacturer
holder and images are acquired using the x-ray system. When or third-party organization
exposed to x-rays, electrons in the phosphor plate are excited Training: Initial training by manufacturer;
into a higher energy state, forming a latent image. An image operator’s manuals; user’s guide
reader scans the phosphor plate with a laser spot. When the
trapped electrons absorb the laser energy, they emit light as Environment of use
2012
they return to their ground state. This light is collected by a light Settings of use: General radiology department;
guide and transmitted to a photomultiplier tube, which produces pediatric, orthopedic, or other hospital
an analog electrical signal that is amplified, converted to a departments; clinic; dental office
digital signal, and digitally stored. The plate can be reused after Requirements: Stable power source
it is exposed to an erasing light that removes residual radiation.
Product specifications
Operating steps Approx. dimensions (mm): 800 x 600 x 700
• After the image has been captured on an image plate by a for single-plate reader; 1300 x 600 x 800 for
standard x-ray system, the technologist takes the plate to an multi-plate reader
image-plate reader to extract the image.
Approx. weight (kg): 20-400 (100 typical) for
• The cassette is loaded (manually or automatically) into the
single-plate reader; 200 for multi-plate reader
reader.
• The digital image is produced in 30-120 seconds and Consumables: Photostimulable-phosphor
downloaded to an image-processing system, usually a imaging plate(s) housed in cassette(s)
computer workstation, for display and manipulation. Price range (USD): 27,000-209,000 (80,000
• The plate is erased for reuse. typical) for single-plate reader; 120,000-
230,000 (170,000 typical) for multi-plate
Reported problems reader
Most reported problems involve the condition of imaging plates Typical product life time: 7 years
and pose little to no direct danger to the patient. Plates can
Shelf life (consumables): No expiration date if
be damaged by careless handling and are expensive to replace.
kept under optimal storage conditions
Some readers have brushes or fans that automatically clear
dust off plates, which helps to prevent scratches. Cracks or
Types and variations
scratches would render the plate unusable for imaging. The light
• Single-plate reader/digitizer
guide should be cleaned as part of routine maintenance (dirt
• Multi-plate reader/digitizer
accumulation can affect image quality).
© Copyright ECRI Institute 2012 (not including GMDN codes and device names).
UMDNS codes and devices names: © Copyright ECRI Institute 2012.
Reproduced with Permission from ECRI Institute’s Healthcare Product Comparison System.
http://www.who.int/medical_devices GMDN Codes and Term Names: © Copyright and database rights: GMDN Agency Ltd 2005-2012. All rights reserved.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Radiographic Systems, Film DigitalDokument53 SeitenRadiographic Systems, Film Digitalkrimo biomédical100% (1)
- Digital Imaging Systems, PDFDokument37 SeitenDigital Imaging Systems, PDFJonathan DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Gas AnalyzerDokument1 SeiteBlood Gas Analyzerleo chiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whole Blood Coagulation Analyzer PDFDokument1 SeiteWhole Blood Coagulation Analyzer PDFmorton1472Noch keine Bewertungen
- Health Problem Addressed: Umdns GMDNDokument1 SeiteHealth Problem Addressed: Umdns GMDNYechale TafereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomedical Instruments Classification GuideDokument53 SeitenBiomedical Instruments Classification GuideSujith SurendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSB Human Humalyzer Calibration Toolset 001 PDFDokument2 SeitenHSB Human Humalyzer Calibration Toolset 001 PDFluisoft88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Whatdoyouknowhba1c PDFDokument20 SeitenWhatdoyouknowhba1c PDFahmet keserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmic LasersDokument44 SeitenOphthalmic LasersMarcela OviedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Operation Manual Manual: SA-232 & SA-202 SA-232 & SA-202Dokument16 SeitenOperation Operation Manual Manual: SA-232 & SA-202 SA-232 & SA-202tvmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diamedica Glostavent Helix Anaesthesia System - User ManualDokument30 SeitenDiamedica Glostavent Helix Anaesthesia System - User ManualAhmed El-AdawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Safety CabinetsDokument4 SeitenBiological Safety CabinetsHedy Mae Bautista100% (1)
- The Mechanics of HearingDokument13 SeitenThe Mechanics of HearingDustin NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of AutoclaveDokument53 SeitenBasics of AutoclaveWallace GualandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The A1C Test and SMBG: Understanding Your Diabetes Control NumbersDokument2 SeitenThe A1C Test and SMBG: Understanding Your Diabetes Control NumberseliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3Dokument42 Seiten3Dewina RamadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treadmill Service GuideDokument9 SeitenTreadmill Service GuidejoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bon Slitlamp SL-72, SL-75 - User Und Service ManualDokument21 SeitenBon Slitlamp SL-72, SL-75 - User Und Service ManualRobertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heracell VIOS CO2 Incubator User Manual 50144132 A enDokument200 SeitenHeracell VIOS CO2 Incubator User Manual 50144132 A enPriyankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corneal Topography SystemsDokument11 SeitenCorneal Topography SystemsMarcela Oviedo100% (1)
- Biological Safety Cabinet SC2 - ADokument4 SeitenBiological Safety Cabinet SC2 - AlucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Service ManualDokument19 SeitenMicro Service ManualalemanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haier Hrf-329aa 349aa 369aaDokument32 SeitenHaier Hrf-329aa 349aa 369aaDmitriy BalabashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Safety Cabinet SafesolDokument9 SeitenBiological Safety Cabinet SafesolnatrajangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifuges, Blood Bank: June 2003Dokument24 SeitenCentrifuges, Blood Bank: June 2003muhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquilion Lightning Clinical Image Gallery MCACT0276EADokument13 SeitenAquilion Lightning Clinical Image Gallery MCACT0276EAArbi RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas SterilizerDokument19 SeitenGas Sterilizerkevin. mitnickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifuges Training GuideDokument19 SeitenCentrifuges Training GuideMoe MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 2252.1-2002 Biological Safety Cabinets Biological Safety Cabinets (Class I) For Personnel and EnvironmentDokument10 SeitenAs 2252.1-2002 Biological Safety Cabinets Biological Safety Cabinets (Class I) For Personnel and EnvironmentSAI Global - APACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure On Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Device ClosureDokument9 SeitenProcedure On Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Device ClosurejaganjaggiNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-Ray Basics: A Concise Guide to X-Ray Production and Image FormationDokument43 SeitenX-Ray Basics: A Concise Guide to X-Ray Production and Image Formationakshaykohli7890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medidores de RadiacionDokument27 SeitenMedidores de RadiacionMarleneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigid Endoscope User ManualDokument2 SeitenRigid Endoscope User Manualأحمد العريقيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pointe II Servicio PDFDokument142 SeitenPointe II Servicio PDFAlex SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datex Ohmeda Excel 210 Anesthesia Machine - User Manual PDFDokument54 SeitenDatex Ohmeda Excel 210 Anesthesia Machine - User Manual PDFtallraj0% (1)
- ARI-8200 Installation Instruction (18042)Dokument36 SeitenARI-8200 Installation Instruction (18042)Neyda Salas100% (1)
- Infunsion Pump 707 V Service ManualDokument28 SeitenInfunsion Pump 707 V Service ManualJulio RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyonics Electroblade ResectorDokument68 SeitenDyonics Electroblade ResectorJeanfreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugation GuideDokument2 SeitenCentrifugation GuideBMTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gamma CameraDokument48 SeitenGamma CameraMarcela OviedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE Cardioserv - User ManualDokument126 SeitenGE Cardioserv - User ManualJavier Martinez Zamora100% (1)
- M A I N T e N A N C e M A N U A L F o R La B o R at o R y e Q U I P M e N TDokument77 SeitenM A I N T e N A N C e M A N U A L F o R La B o R at o R y e Q U I P M e N TBMTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspirators Emergency PDFDokument39 SeitenAspirators Emergency PDFAdriana FerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smith & Nephew Dyonics™ Power Ii Footswitch: Instructions For UseDokument36 SeitenSmith & Nephew Dyonics™ Power Ii Footswitch: Instructions For Useأحمد العريقيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gel Phantom in Ultrasound DosimetryDokument7 SeitenGel Phantom in Ultrasound DosimetrytomgrgicNoch keine Bewertungen
- ServiceManualM22 Rev3Dokument190 SeitenServiceManualM22 Rev3luisoft88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilator PortableDokument1 SeiteVentilator PortableAamer MumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eightcheck-3Wp Assay Sheet: Low LevelDokument5 SeitenEightcheck-3Wp Assay Sheet: Low LevelLeonard OnsikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Familiar. Reliable. Affordable.: GE HealthcareDokument6 SeitenFamiliar. Reliable. Affordable.: GE Healthcarecheng fengNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSIST Magazine Image Based FFR With QFRDokument9 SeitenASSIST Magazine Image Based FFR With QFRAsim AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxylog 2000 Plus PDFDokument128 SeitenOxylog 2000 Plus PDFRoberto CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1007-009-002A Stretcher PDFDokument168 Seiten1007-009-002A Stretcher PDFJuanAguileraOlivoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1603 ECUBEi7 Web Catalogue ENG Low Sheet PDFDokument7 Seiten1603 ECUBEi7 Web Catalogue ENG Low Sheet PDFeduardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beta Manual PDFDokument15 SeitenBeta Manual PDFTatiana Rosoga100% (1)
- Rev. KRDokument154 SeitenRev. KRAMINE AHMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiographs, Multichannel Interpretive: Scope of This Product ComparisonDokument83 SeitenElectrocardiographs, Multichannel Interpretive: Scope of This Product ComparisonchanlalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CathDokument12 SeitenCathbashir019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operation and Technical Manual: Model 233 Hyper-Hypothermia SystemDokument124 SeitenOperation and Technical Manual: Model 233 Hyper-Hypothermia SystemMarcelo PirizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Problem Addressed: Use and MaintenanceDokument1 SeiteHealth Problem Addressed: Use and MaintenanceKumar SuryavanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Transtibial PDFDokument52 SeitenEng Transtibial PDFRudi NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Modern Vehicle Design: List of ChaptersDokument2 SeitenAn Introduction To Modern Vehicle Design: List of ChaptersMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steeper Prosthetic Best Practice GuidelinesDokument67 SeitenSteeper Prosthetic Best Practice GuidelinesMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEG Signal Classification For Brain Computer Interface ApplicationsDokument72 SeitenEEG Signal Classification For Brain Computer Interface Applicationsiolandadumitrescu4365Noch keine Bewertungen
- EcgDokument16 SeitenEcgFrank FosterNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 2050 Bendable Resistance Thermometer ME 2060 General Purpose Resistance Thermometer With Flying LeadsDokument5 SeitenME 2050 Bendable Resistance Thermometer ME 2060 General Purpose Resistance Thermometer With Flying LeadsMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRANSFEMORAL GUIDEDokument3 SeitenTRANSFEMORAL GUIDEMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- RUF Status 2015Dokument46 SeitenRUF Status 2015AungThawNyeinChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datex-Ohmeda Tec7 - Service ManualDokument48 SeitenDatex-Ohmeda Tec7 - Service ManualCarlos Alberto SacsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 368 - Gas Anesthesia Vaporizer MaintenanceDokument4 Seiten368 - Gas Anesthesia Vaporizer MaintenanceMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens Fremtidens CTDokument95 SeitenSiemens Fremtidens CTMohammed Al-shamiri100% (1)
- The Prosthetic Limb Service: Information For PatientsDokument24 SeitenThe Prosthetic Limb Service: Information For PatientsMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Chart UKM Vice Chancellor ScholarshipDokument1 SeiteFlow Chart UKM Vice Chancellor ScholarshipMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drypix Smart 6000 Product SpecificationsDokument12 SeitenDrypix Smart 6000 Product SpecificationsMohammed Al-shamiri100% (1)
- Hospt Equip 10 PDFDokument1 SeiteHospt Equip 10 PDFMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMG Analysis PDFDokument9 SeitenEMG Analysis PDFlazarosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speedia 170920Dokument7 SeitenSpeedia 170920Mohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSRT 13nov2010 Radiation Exposure For CRDokument70 SeitenCSRT 13nov2010 Radiation Exposure For CRMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens Fremtidens CTDokument95 SeitenSiemens Fremtidens CTMohammed Al-shamiri100% (1)
- XL 2 DatasheetDokument2 SeitenXL 2 DatasheetHousam SoudanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datex-Ohmeda Tec7 - Service ManualDokument48 SeitenDatex-Ohmeda Tec7 - Service ManualCarlos Alberto SacsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRYPIX Smart Reference GuideDokument80 SeitenDRYPIX Smart Reference GuideHugo78% (32)
- Datex-Ohmeda Tec7 - Service ManualDokument48 SeitenDatex-Ohmeda Tec7 - Service ManualCarlos Alberto SacsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aun Perfusor Compact - Service ManualDokument82 SeitenAun Perfusor Compact - Service ManualMina Nassif100% (5)
- 368 - Gas Anesthesia Vaporizer MaintenanceDokument4 Seiten368 - Gas Anesthesia Vaporizer MaintenanceMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drypix Smart 6000 Product SpecificationsDokument12 SeitenDrypix Smart 6000 Product SpecificationsMohammed Al-shamiri100% (1)
- Ak 200sDokument336 SeitenAk 200sMohammed Ali Al-ShamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 368 - Gas Anesthesia Vaporizer MaintenanceDokument4 Seiten368 - Gas Anesthesia Vaporizer MaintenanceMohammed Al-shamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotic Grasping and Manipulation of Objects: András Fekete University of New HampshireDokument5 SeitenRobotic Grasping and Manipulation of Objects: András Fekete University of New HampshirerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Golden Gate TutorialDokument26 SeitenGolden Gate TutorialVimlendu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Find Oracle Database Patches InstalledDokument2 SeitenHow To Find Oracle Database Patches InstalledAnonymous 8RhRm6Eo7hNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comsale Inventory Canada 20191107Dokument231 SeitenComsale Inventory Canada 20191107Mahesh SkyzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Fabric 1200 Launch SlidesDokument10 SeitenOpen Fabric 1200 Launch SlidesLaboriosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: Understanding Local NetworksDokument12 SeitenUnit 2: Understanding Local Networksglenn.tabucanonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlador CQ 2001Dokument156 SeitenControlador CQ 2001Martin Raynoldi GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Without ComputersDokument14 SeitenLife Without Computersapi-488738864Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cd00020086 Sensorless BLDC Motor Control and Bemf Sampling Methods With St7mc StmicroelectronicsDokument35 SeitenCd00020086 Sensorless BLDC Motor Control and Bemf Sampling Methods With St7mc StmicroelectronicsmortezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNF CVDokument4 SeitenCNF CVJnz OlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JBase Env Variables, Tools, UsersDokument30 SeitenJBase Env Variables, Tools, UsersRaquel Peña SilverioNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.No: 1 Exp. Name: DateDokument3 SeitenS.No: 1 Exp. Name: DateSai KiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bbek4203 - Principles of MacroeconomicsDokument9 SeitenBbek4203 - Principles of MacroeconomicsSimon RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Improve Swap DCRDokument6 SeitenHow to Improve Swap DCRWANKHAMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Amplitude Modulation Fundamental - Take Home Quiz 2Dokument3 SeitenAmplitude Modulation Fundamental - Take Home Quiz 2Janica Rheanne JapsayNoch keine Bewertungen
- YMA (Penetration Methods of Hackers and Preventing Hacking)Dokument326 SeitenYMA (Penetration Methods of Hackers and Preventing Hacking)zawlwin oo100% (1)
- PS1Dokument1 SeitePS1shivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full paper-ICVEASTDokument5 SeitenFull paper-ICVEASTReza EbookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Panel Setting Instruction ManualDokument16 SeitenOperation Panel Setting Instruction ManualDinh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Security ArchitectureDokument6 SeitenDesign of Security ArchitectureAnusha KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Systems Btcse-Oe43: By: Naved Alam Assistant Professor (ECE) SEST, Jamia HamdardDokument42 SeitenEmbedded Systems Btcse-Oe43: By: Naved Alam Assistant Professor (ECE) SEST, Jamia Hamdardanon_947471502Noch keine Bewertungen
- SIMATIC S7 Connector Configurator enUS en-USDokument104 SeitenSIMATIC S7 Connector Configurator enUS en-USnemarc08Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0580 m22 Ms 22 PDFDokument8 Seiten0580 m22 Ms 22 PDFNameer omarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating GUIs with Java Swing ComponentsDokument51 SeitenCreating GUIs with Java Swing ComponentsRisa ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection System Fundamentals and ApplicationsDokument27 SeitenProtection System Fundamentals and ApplicationsHEMANT RAMJINoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 1 (It208)Dokument3 SeitenQuiz 1 (It208)Glaiza Angel MacapagalNoch keine Bewertungen
- LOEWE Certos Service ManualDokument79 SeitenLOEWE Certos Service Manualroberto100% (6)
- From Mental Maps To Geoparticipation: Jir ̌Í PánekDokument8 SeitenFrom Mental Maps To Geoparticipation: Jir ̌Í PánekWilliam BrandtNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS8492-Database Management SystemsDokument15 SeitenCS8492-Database Management SystemsChellamuthu HaripriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gis DatabasesDokument27 SeitenGis Databasessenwelo gulubaneNoch keine Bewertungen