Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SOKO Case Notes
Hochgeladen von
Chelsea Dela Torre0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
258 Ansichten4 SeitenThe document discusses Porter's five forces model as it applies to Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory. It analyzes the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products, the bargaining power of buyers, and the bargaining power of suppliers. For each force, it identifies relevant factors like barriers to entry, switching costs, product differentiation, and the number of suppliers. It also provides suggestions on how Soko Jewelry can address challenges from each of the five competitive forces.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document discusses Porter's five forces model as it applies to Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory. It analyzes the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products, the bargaining power of buyers, and the bargaining power of suppliers. For each force, it identifies relevant factors like barriers to entry, switching costs, product differentiation, and the number of suppliers. It also provides suggestions on how Soko Jewelry can address challenges from each of the five competitive forces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
258 Ansichten4 SeitenSOKO Case Notes
Hochgeladen von
Chelsea Dela TorreThe document discusses Porter's five forces model as it applies to Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory. It analyzes the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products, the bargaining power of buyers, and the bargaining power of suppliers. For each force, it identifies relevant factors like barriers to entry, switching costs, product differentiation, and the number of suppliers. It also provides suggestions on how Soko Jewelry can address challenges from each of the five competitive forces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
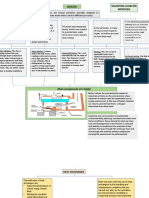
3.2.
Porter’s five forces
The five forces identified in Porter's model can effect Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual
Factory ’s ability to serve its clients and make a profit.
A change in any of the five forces may regularly require a business unit from Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and
Building a Virtual Factory to reassess the market place given the general change in industry data and
dynamics. The general industry appeal and attractiveness.
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory should apply and centre their skills, plan of action
or business models to accomplish profits above the business average. This may be done in multiple ways,
each distinguished in their application to the forces individually as is elaborated below:
3.2.1. The threat of new entrants
3.2.1.1. Market and industry share
New entrants to an industry bring new potential and a choice to increase the market share and overall share
of the pie that puts pressure on price, costs, and the investment price essential to compete.
For Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory, particularly while new entrants are
diversifying from different markets into the chief industry, they will be able to leverage existing talents and
cash flows to shake up the opposition.
3.2.1.2. Limitation on earning expectation and capability of firms in an industry
The threat of entry in the industry, consequently, puts a cap at the earning capacity and profit capability for
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory.
While the threat of new entreaty is high, Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory should
maintain their prices or increase funding and investment to discourage new competition.
3.2.1.3. The risk to new entrants because of high entry barriers
The risk of entry in an industry depends upon on the peak of entry barriers and limitations that are a blessing
for players such as Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory and on the response that new
entrants can count on from existing players.
If entry barriers are low and novices count on little retaliation from the entrenched competition, the chance of
entry is high, and profitability for Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory will be
moderated.
It is the danger of entry, not whether the entry of new players takes place that holds down profitability.
3.2.1.4. Some barriers to entry for new entrants in favour of Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory
:
Capital requirements: a strong barrier to entry as new entrants will require strong financial and resource
cushioning for operations to take off and be sustained.
Economies of scale: a strong barrier to entry as existing players in the industry operate with high economies
of scale, which new entrants will take time to achieve.
Product differentiation: the strong barrier of entry if products within the industry have high levels of
differentiation on which they operate and approach customers.
Access to distribution: a standard barrier to entry since new entrants will have equal access to the retailers
and distributing agents within the industry.
Customer loyalty to established brands: a strong barrier to entry since customer loyalties and perceptions
are emotionally built and strongly enforced as long as the brand continues to deliver on its core promise and
quality.
3.2.1.5. What can Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory do to face this challenge?
Build and invest in marketing to distinctly establish a point of differentiation in customer perception as well as
strengthen customer loyalty.
Invest in research and development to make sure that it continues to have competitive differentiation from
other players at all times.
Focus on building economies of scale in production and sales.
3.2.2. The threat of substitute products or services
3.2.2.1. Substitute form
There are always different alternatives or substitutes for various products that lead an industry.
These substitutes may be direct or indirect– the direct substitutes are the same category products. produced
by different players; indirect substitutes are the ones from different product categories that can replace the
product for Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory.
3.2.2.2. Switching cost to substitutes for consumers
Switching costs for direct substitutes is not very high for consumers.
The per-unit-volume prices may be higher or lower.
This makes the threat of substitute high.
3.2.2.3. Substitute and product benefit
Alternatives to the product or substitutes may not be able to provide the same benefits
May often lead to additional costs incurred.
Switching costs towards alternatives becomes higher, and consumers may not switch to substitutes.
This, in turn, will make the threat of substitutes low.
3.2.2.4. Substitutes and consumer behaviour
From the point of view of the consumer, there are some differences between the ways different products of
the same or similar category are used, but many consumption decisions are a matter of personal taste - this
makes products vulnerable to the threat of other substitutes.
Overall, the threat of substitutes is assessed to be moderately high.
3.2.2.5. How can Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory combat the threat from substitute
products?
Focus on delivering consistently high quality.
Focus on maintaining strong consumer relationships.
Integrate strategic marketing to form an emotional connection with the consumers and strengthen consumer
loyalty.
Invest in pop up stores owned by the company to stock the Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a
Virtual Factory brand exclusively, and integrate it with brand characteristics and personality to attract
consumers.
3.2.3. Bargaining Power of Buyers
3.2.3.1. Who is the buyer?
The buyer for Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory is not necessarily the group that
consumes the product – but rather refers to the group of customers that purchases the product from Soko
Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory to either distribute further, retail it, or even consume it.
Hypermarkets and supermarkets, as well as independent retailers and distribution agents to end consumers,
are the core buyers for Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory that make up the market’s
volume.
Supermarkets and hypermarkets, along with many food chains that are concentrated, which increases the
buyer power.
Products are stocked with buyers and retailers by Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory
based on consumer demand.
3.2.3.2. Buyer power and costs
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory will not experience switching costs for switching
buyers.
Multiple product offerings by buyers also increase buyer power.
3.2.3.3. Retail product differentiation
Products offered by retailers are differentiated based on several characteristics – not only reliant upon
product characteristics but also consumer segment characteristics. Because of this, retailers are expected to
offer a wide range of the same product category. This works towards negating and weakening the overall
buyer power.
Buyer power is assessed to be moderate to high.
3.2.3.4. What can Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory do to ensure risks against high buyer
power?
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory can focus on differentiating its product and
increasing its demand with the end consumers through different marketing tactics, this will increase the
demand of the product with different buyers, and will work towards moderating buyer power.
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory should employ economies of scale to manage
costs of production. If it offers products at moderate prices to buyers, it will again be able to attract a large
number of buyers for its product, and in this way, will be able to break off the high bargaining power.
3.2.4. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
3.2.4.1. Who is the supplier?
Supplier power refers to the power that is held by the suppliers in terms of pricing of the raw materials and
inputs used for the business.
3.2.4.2. Sources of production for Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory
The main sources for production are the following:
Supplies from vendors – sourcing from independent suppliers.
Own manufactured equipment and resources: this model is practised by companies that are well integrated
backwards and forwards.
3.2.4.3. Independent suppliers
For Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory, there are numerous independent suppliers
within the industry, and all comprise of a few pretty small operations that lead to weakened overall supplier
power.
Independent sellers and suppliers, however, can locate different opportunities and invest in alternative
markets – which can be a challenge for Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory.
3.2.4.4. Supply quality and business dynamics
Suppliers can integrate forward into the decision making and business dynamics themselves as well.
Also, to the buyers, the quality of the supplies and the raw materials is of utmost importance.
However, in an industry with a high number of suppliers, Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual
Factory can switch to different suppliers at any time without experiencing any costs of the business.
Overall bargaining power of suppliers is assessed to be moderate.
3.2.4.5. How can Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory deal with the challenge?
Get contracts with multiple suppliers and get resources and raw materials from them accordingly.
Invest in manufacturer controlled production facility to maintain consistency in quality.
3.2.5. Competitive Rivalry among Existing Firms.
3.2.5.1. Nature of fragmentation
The market is highly fragmented, which makes it more competitive.
The market is never too concentrated, and as a result, it has players of varying size of operation – from very
small to big players.
3.2.5.2. Brand management
Producers have begun to make use of brand management techniques and contemporary merchandising by
launching bold brands, label designs and marketing campaigns to become more identifiable to the public.
3.2.5.3. Diversification
Purchasers and buyers have a wide range of products to choose from, with relatively low switching costs.
These factors tend to intensify rivalry.
Though players in the industry may off niche or premium products, they also continue to operate in the mass
markets at large, which again leads to high competition.
3.2.5.4. High business costs
The high fixed cost and the high bargaining power of the buyers, which can lead to the lowering of the prices
from manufacturers add to the highly competitive nature of the industry.
The overall rivalry is assessed to be high.
3.2.5.5. How can Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory combat rivalry and competitive forces of
the industry?
Focus on research and development to identify market niche as well as to be able to add differentiating
factors t its products. This will increase its shield against influence from competitive forces and their actions.
Build a strong and loyal consumer base by focusing on quality and marketing strategies.
Focus on capturing new markets – in the same region as well as new regions to avoid saturation of
resources in one market only.
3.4.4. Maturity stage
3.4.4.1. Sales and growth
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory will experience slowing growth during this stage of
the industry life cycle.
Sales will be expanding, and earning will be growing – however, the rate will be slower than the growth
stage.
Competition from late entrants will be present, and obvious during this stage – who will all try to fight for
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory ’s share of the market.
3.4.4.2. Strategic Marketing
The marketing strategies must now focus on building loyalty.
Marketing tactics must be strong and should focus on the uniqueness of the product. Increasingly emotional
appeals may be used.
3.4.4.3. Firm size
Firm size is generally larger and is more dominant over players if successful- compared to growth stage.
Innovations continue but are stable and not radical.
5.2.4. Opportunities for Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory (External Strategic Factors)
This section of the SWOT analysis and strategic model focuses on external components that opportunities for
business development and advancement. For this situation, the key opportunities accessible to Soko Jewelry Fast
Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory are:
5.2.4.1. Green business products
With an increased focus and awareness of health and wellness lifestyles by consumers, it is important that
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory recognizes this as a viable business opportunity.
Increased numbers of consumers are shifting to the green lifestyle of consuming environmentally friendly
and organic products.
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory should focus on the expansion of the product
portfolio: inclusion of green products and environmentally sustainable services are suggested.
5.2.4.2. Expansion in emerging markets
Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory can expand its income streams through expansion
and developing presence in emerging markets – such as Brazil, China and India.
This opportunity draws consideration far from the U.S. region, where the majority of the organization's
incomes are created.
5.2.4.3. Business enhancement
Likewise noteworthy in this SWOT analysis of opportunities is the opportunity of business enhancement and
further business development.
This can help improve the long term position of Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory.
For instance, through higher diversification of the portfolio and the overall business, the Soko Jewelry Fast
Fashion and Building a Virtual Factory organization can diminish its reliance on its present enterprises, and
along these lines work towards improving its general income development.
5.2.4.4. Partnerships with different firms
5.2.4.4.1. Diversification through Partnerships
Diversification is right now a minor strategy as can be observed from Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion and
Building a Virtual Factory ’s competitive strategy and its overall directive strategy as well.
The business environments likewise display the chance to enhance the organization's competencies and
strengths
This will also increase its share of the overall industry through the association’s s with different firms. For
example, a partnership with real retailers improves dispersion.
5.2.4.4.2. Development of corporate clientele
The company can also formulate new B2B relations and contracts with other companies and corporate
entities.
The external key factors in this section of the SWOT analysis demonstrate that Soko Jewelry Fast Fashion
and Building a Virtual Factory can improve its industry position by building up its activities to make use of the
opportunities in the international business markets.
5.5.2.3.1. Market research and financial cushioning
This strategy is highly feasible.
This is because the company already operates along with this mission, and has high levels of market
research and information regarding high-income groups.
This information could be utilized for creating a suitable menu for high-income groups.
At the same time, the company also has the financial power to introduce premium menu items for the higher
class – to expand its menu accordingly.
5.5.3. Creation of a healthy menu for existing target consumer groups
5.5.3.1. Suitability
5.5.3.1.1. Diversification of product portfolio
This strategy would require a high diversification of the product portfolio.
This is suitable because the company has the resources and the information to make strategic decisions
about diversification.
builds partnerships with luxury fashion houses
This kind of collaboration can be analyzed from two different points of view. For fast fashion retailers it’s a way to spread
a very powerful image since they have the opportunity to sell clothes and/or accessories branded by famous stylists in
their stores. It is also a key point of differentiation from other retailers and gives consumers a new reason to visit stores. ]
designers get more visibility and it’s a perfect occasion to extend their brand to new areas or to reach new customers
5.5.3.1.2. Innovation
Moreover, the company also innovates regularly, which can be an added benefit for the suitability of the
strategy.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Industrial Organization FinalDokument12 SeitenIndustrial Organization FinalShakil Mustafa100% (1)
- The Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDokument5 SeitenThe Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyAmol Deherkar67% (3)
- Notice of RegistrationDokument1 SeiteNotice of Registrationbra9tee9tini100% (1)
- Lab 5 Post-Lab: Systems and Industrial Engineering University of ArizonaDokument6 SeitenLab 5 Post-Lab: Systems and Industrial Engineering University of Arizonairfanil100% (1)
- Under Irrevocable Confirmation Corporate Pay Order (Iccpo) : Payment Guarantee Letter (PGL) of UndertakingDokument9 SeitenUnder Irrevocable Confirmation Corporate Pay Order (Iccpo) : Payment Guarantee Letter (PGL) of UndertakingEsteban Enrique Posan Balcazar100% (1)
- Mid Term November 6 2020Dokument6 SeitenMid Term November 6 2020old times0% (1)
- The Budvar Company Sells Parts To A Foreign Customer OnDokument1 SeiteThe Budvar Company Sells Parts To A Foreign Customer OnTaimur TechnologistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Economics For Business by Group 2 MMB28BDokument15 SeitenPaper Economics For Business by Group 2 MMB28BLesmanaBotaxxIndraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Northern Napa Valley WineryDokument5 SeitenNorthern Napa Valley WinerySamantha HazellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Compettive StartegiesDokument6 SeitenNotes On Compettive Startegiesdivya8955Noch keine Bewertungen
- Finlatics Investment Banking Experience Program Project 2 Sustainable Fashion CompanyDokument6 SeitenFinlatics Investment Banking Experience Program Project 2 Sustainable Fashion CompanySaransh Thahrani100% (1)
- History of Schneider ElectricDokument12 SeitenHistory of Schneider ElectricKerin BerlianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix in ComputingDokument33 SeitenMatrix in ComputingmisteryfollowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Science Team 4Dokument12 SeitenManagement Science Team 4John Dave JavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Chapter 7 Overcome Key Organizational HurdlesDokument4 SeitenSummary Chapter 7 Overcome Key Organizational Hurdlesabd.mirza2627Noch keine Bewertungen
- International FinanceDokument206 SeitenInternational FinanceAbigail StaffordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lakewood Laser Skincare S Ending Cash Balance As of January 31Dokument1 SeiteLakewood Laser Skincare S Ending Cash Balance As of January 31Let's Talk With HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1.5 The Four Towns A, B, C, and D Are Connected ...Dokument3 Seiten4.1.5 The Four Towns A, B, C, and D Are Connected ...Yessy Dwi RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 13Dokument12 SeitenPresentation 13Parmeshwar KhendkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MM5006 Business Ecognomic 51BDokument12 SeitenMM5006 Business Ecognomic 51Bnicasavio2725Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hindustan Motors' Struggle For Survival:: Troubled Waters?Dokument6 SeitenHindustan Motors' Struggle For Survival:: Troubled Waters?Ramraj Ronil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Personal Class Notes, Videos, Resources, Homework, LabsDokument10 SeitenYour Personal Class Notes, Videos, Resources, Homework, LabsirfanilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untuk Mahasiswa, CVP AnalysisDokument60 SeitenUntuk Mahasiswa, CVP AnalysisErick JonathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE 5.1 PANERA BREAD: Occupying A Favourable Position in A Highly Competitive IndustryDokument25 SeitenCASE 5.1 PANERA BREAD: Occupying A Favourable Position in A Highly Competitive IndustrySujit Kumar ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18Dokument20 SeitenChapter 18Bo ZydarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- via.comDokument65 Seitenvia.comgoswamiphotostatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whiz Calculator CompanyDokument18 SeitenWhiz Calculator CompanyAsibur Rahman100% (1)
- Ikea Group Yearly Summary Fy14Dokument43 SeitenIkea Group Yearly Summary Fy14ArraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bradmark Questions CH 10 AnswerDokument10 SeitenBradmark Questions CH 10 AnswermaspnsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Puji WibowoDokument30 Seiten3-Puji Wibowojoko1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pak Taufikur CH 11 Financial Management BrighamDokument69 SeitenPak Taufikur CH 11 Financial Management BrighamRidhoVerianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team 4 - The GM BailoutDokument4 SeitenTeam 4 - The GM BailoutmpisgantengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quietly Brilliant HTCDokument2 SeitenQuietly Brilliant HTCOxky Setiawan WibisonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory in Action 6.2 Dan 5.2Dokument2 SeitenTheory in Action 6.2 Dan 5.2zahra zhafiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch07 Kecurangan, Pengendalian Internal, Dan KasDokument72 Seitench07 Kecurangan, Pengendalian Internal, Dan KasEnsy QuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas or Grouse AnswersDokument6 SeitenGas or Grouse AnswersSatrio Haryoseno100% (1)
- Pre Test FIRE D KEMNAKERDokument9 SeitenPre Test FIRE D KEMNAKERIGN Rai SuryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 7Dokument2 SeitenCase Study 7Mythes JicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case SolutionDokument44 SeitenCase Solution2rmj100% (1)
- 5762 10964 IM FinancialManagementandPolicy12e HorneDhamija 9788131754467Dokument152 Seiten5762 10964 IM FinancialManagementandPolicy12e HorneDhamija 9788131754467sukriti2812Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCS 14.1 O Reilley Associates 1Dokument10 SeitenMCS 14.1 O Reilley Associates 1Parth Shah100% (1)
- Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Keunggulan Bersaing Pada Maskapai PenerbanganDokument64 SeitenFaktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Keunggulan Bersaing Pada Maskapai PenerbanganBeni BeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Questions 2018Dokument6 SeitenCase Study Questions 2018ari0% (2)
- Porter Five Forces AnalysisDokument6 SeitenPorter Five Forces Analysisnaseeb_kakar_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 06-07. Facility Location ModelsDokument48 Seiten06-07. Facility Location ModelsMuhamad RidzwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Analysis of SubwayDokument13 SeitenEnvironmental Analysis of SubwayannetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rising or Emerging Industry/Maturing Industry/DecliningDokument6 SeitenRising or Emerging Industry/Maturing Industry/Decliningঅর্থী ইয়াসমিনNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1.6.2. Discrimination LawDokument41 Seiten3.1.6.2. Discrimination LawSaadAminNoch keine Bewertungen
- JYm RGR Vu VDGQ 1661365650550Dokument6 SeitenJYm RGR Vu VDGQ 1661365650550sagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysing The Indian Super Market Using Porter'S Five Forces ModelDokument5 SeitenAnalysing The Indian Super Market Using Porter'S Five Forces ModelDewang BaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic MGT Assignment 03Dokument9 SeitenStrategic MGT Assignment 03Abdullah Al Aziz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive Summary ... .. 3 1.0 Industry, Customer, and Competitor Analysis .. . ... 4Dokument49 SeitenExecutive Summary ... .. 3 1.0 Industry, Customer, and Competitor Analysis .. . ... 4mohamad hafizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acs 17Dokument41 SeitenAcs 17SaadAminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finlatics IBEP Project 2Dokument5 SeitenFinlatics IBEP Project 2Angel AliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 2Dokument6 SeitenProject 2Tanmay ChhikaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Industrial Marketing Definition of Industrial MarketingDokument5 SeitenConcept of Industrial Marketing Definition of Industrial MarketingAnwulika Joy Ogolime100% (1)
- ADL 04 Managerial Economics V3Dokument23 SeitenADL 04 Managerial Economics V3Amit100% (8)
- Marketing - CHPTR 6 - Case Cisco - 6-18,21,22Dokument3 SeitenMarketing - CHPTR 6 - Case Cisco - 6-18,21,22Benedictus Kevin RNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1.6.1. Labour LawDokument41 Seiten3.1.6.1. Labour LawSaadAminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Selecting Channel PartnersDokument98 SeitenChapter 7 Selecting Channel PartnersShiela Mae ArguellesNoch keine Bewertungen
- On-Demand Warehousing: Edgistfy Innovation Challenge Case Study 2020Dokument11 SeitenOn-Demand Warehousing: Edgistfy Innovation Challenge Case Study 2020vivek singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1Dokument5 SeitenPaper 1saiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matching Strategy To Industry and Company SituationsDokument22 SeitenMatching Strategy To Industry and Company SituationsShah Maqsumul Masrur TanviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Point Method - Compensable Factors: ST ND RD TH THDokument2 SeitenPoint Method - Compensable Factors: ST ND RD TH THChelsea Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Model WorksheetDokument2 SeitenJob Model WorksheetChelsea Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bibliography: Performance Appraisal/Management QuestionsDokument3 SeitenBibliography: Performance Appraisal/Management QuestionsChelsea Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Car Rental Driver: Job DescriptionDokument3 SeitenCar Rental Driver: Job DescriptionChelsea Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Decision AnalysisDokument3 SeitenHRM Decision AnalysisChelsea Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation Problem HWDokument5 SeitenTransportation Problem HWChelsea Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- EFE Matrix Strategic ManagementDokument3 SeitenEFE Matrix Strategic ManagementChelsea Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Freedom ReportDokument20 SeitenEconomic Freedom ReportChelsea Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Spec For Adding Access To View Spool Output For Batch Jobs VSO - 5484501Dokument8 SeitenSecurity Spec For Adding Access To View Spool Output For Batch Jobs VSO - 5484501Rumpa MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- API Advisory 10 Invoicing and Payment Terms English Translation 20191220Dokument2 SeitenAPI Advisory 10 Invoicing and Payment Terms English Translation 20191220Yusri WyeuserieyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presenting Furnito - The Next Generation Odoo Ecommerce Theme For Furniture Industry PDFDokument4 SeitenPresenting Furnito - The Next Generation Odoo Ecommerce Theme For Furniture Industry PDFjuanatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harish Kumar R S (A Study On Brand Loyalty Towards Baby)Dokument6 SeitenHarish Kumar R S (A Study On Brand Loyalty Towards Baby)danny kanniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Controlling Simplified: Mohammed RashidDokument13 SeitenSAP Controlling Simplified: Mohammed RashidSUNNY LUNKERNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUTORIAL CHAPTER ELASTICITY StudentDokument7 SeitenTUTORIAL CHAPTER ELASTICITY StudentfiqahkemetotNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMW Integrative Case StudyDokument2 SeitenBMW Integrative Case StudyMairene Castro100% (1)
- Cibil - Report (P - JAYSINGH YADAV - 26 - 05 - 2023 12 - 23 - 04)Dokument5 SeitenCibil - Report (P - JAYSINGH YADAV - 26 - 05 - 2023 12 - 23 - 04)Geeta MallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCDA Press Release Insurance FraudDokument6 SeitenOCDA Press Release Insurance Fraudapi-3808536Noch keine Bewertungen
- Birhan Final Research PaperDokument109 SeitenBirhan Final Research PaperyibeltalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B2B The Element Value PDFDokument4 SeitenB2B The Element Value PDFIfkar NaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- PQ 0047220Dokument3 SeitenPQ 0047220Divino Edgar LacambraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fashion Channel: Harvard Business Publishing Case Study by Wendy StahlDokument9 SeitenThe Fashion Channel: Harvard Business Publishing Case Study by Wendy Stahlyukio1989100% (4)
- Instructions:: Candor Cash Flow SolutionDokument1 SeiteInstructions:: Candor Cash Flow SolutionPirvuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saraswati 1Dokument65 SeitenSaraswati 1Naira Puneet BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapa Conceptual Valentina AlarcónDokument4 SeitenMapa Conceptual Valentina AlarcónRosa mariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyundai D4a d4d Engine Service ManualDokument13 SeitenHyundai D4a d4d Engine Service Manualjoemeadows110401kib100% (137)
- Full Download Test Bank For Mcgraw Hill Connect Resources For Whittington Principles of Auditing and Other Assurance Services 20e PDF Full ChapterDokument36 SeitenFull Download Test Bank For Mcgraw Hill Connect Resources For Whittington Principles of Auditing and Other Assurance Services 20e PDF Full Chaptersaturantbruniontvg0100% (24)
- Startegic Managemnt Assignment 1Dokument16 SeitenStartegic Managemnt Assignment 1Syeda ZehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goal Assure BrochureDokument20 SeitenGoal Assure BrochureBharat19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Andre Gunder Frank - The Organization of Economic Activity in The Soviet Union - Weltwirtschaftliches Archiv, Bd. 78 (1957) PDFDokument54 SeitenAndre Gunder Frank - The Organization of Economic Activity in The Soviet Union - Weltwirtschaftliches Archiv, Bd. 78 (1957) PDFLarissa BastosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conventions of A TV ADDokument8 SeitenConventions of A TV ADDamiano88Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1460-2820-1-PB (1) (1), ClareteDokument27 Seiten1460-2820-1-PB (1) (1), ClaretefdizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Text Book PDFDokument4 SeitenA Text Book PDFAqib MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ILM Super Series) Institute of Leadership & Mana - Caring For The Customer Super Series, Fourth Edition - Pergamon Flexible Learning (2002)Dokument117 Seiten(ILM Super Series) Institute of Leadership & Mana - Caring For The Customer Super Series, Fourth Edition - Pergamon Flexible Learning (2002)bankadhi100% (1)
- Problems and Prospects of Street Vendors:: A Study With Reference To Visakhapatnam CityDokument20 SeitenProblems and Prospects of Street Vendors:: A Study With Reference To Visakhapatnam Cityarbaz kaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOS PPT Env ScanDokument11 SeitenMOS PPT Env ScanKrishna kishor tiwariNoch keine Bewertungen