Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Case 2
Hochgeladen von
Davis KallanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Case 2
Hochgeladen von
Davis KallanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Case 4.
25
HISTORY: A 22-year-old female presented with severe right lower quadrant pain, nausea, and vomiting
FIGURE 4.25.1 FIGURE 4.25.2
FIGURE 4.25.3
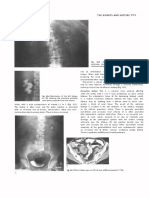
FINDINGS: Transvaginal scan, sagittal image DISCUSSION: The incidence of ectopic pregnancy
through the uterus (Fig. 4.25.1) shows normal endo- has increased in recent years and is seen in 1%
metrial stripe without any intrauterine gestational to 2% of all pregnancies in United States (44–46). It
sac. There is significant amount of free fluid noted most commonly occurs in fallopian tubes (97%) but
posterior to the uterus. Figure 4.25.2 through the can occur in cervix, ovary, cornua of the uterus or
right adnexa shows a large anechoic cystic mass even intra-abdominally. Among the tubal pregnan-
(O), which represents right ovary with corpus luteal cies, ampulla is the most common site of implanta-
cyst. Anterior to that, there is an echogenic ring-like tion. If the patient’s beta-hCG is more than 1,500
structure (short arrows) that represents an extrauter- to 2,000 mIU/mL and an intrauterine pregnancy is
ine gestational sac. A small yolk sac (long arrow) is not seen on a transvaginal scan, an ectopic preg-
also present within the gestation sac. Figure 4.25.3 nancy should be suspected (New9). Patients usually
is a color Doppler US image through the right ad- present with lower abdominal pain. The risk fac-
nexal region showing increased vascularity around tors include previous tubal surgery, previous ectopic
the gestational sac. pregnancy, infertility treatment, and intrauterine
contraceptive device. On ultrasound, tubal preg-
DIAGNOSIS: Right ectopic pregnancy nancy usually presents as a complex adnexal mass,
4 / ULTRASOUND 217
(c) 2015 Wolters Kluwer. All Rights Reserved.
Case 4.25 (Continued)
which may show increased peripheral vascularity Aunt Minnie’s Pearls
frequently termed as ring of fire appearance. Pres-
ence of complex free fluid and a complex adnexal Inability to demonstrate an intrauterine gestational sac
mass suggests ruptured ectopic pregnancy in the ap- with transvaginal scan in a patient with beta-hCG lev-
propriate setting. Uterine endometrium may show els of >2,000 mIU/mL should always raise suspicion for
thickening owing to decidual reaction but without an ectopic pregnancy.
a gestational sac. Occurrence of concomitant in-
trauterine and ectopic pregnancy is extremely rare Endometrial (decidual) cysts may be seen even with
(1:30,000). Ovaries may show cystic changes from ectopic pregnancy (pseudosac) and should not be
corpus luteum formation and increased peripheral mistaken for a true sac. Demonstration of a yolk sac
vascularity, which in many cases may be mistaken within an intrauterine gestational sac more accurately
for an ectopic pregnancy. confirms an intrauterine pregnancy.
218 AUNT MINNIE’S ATLAS AND IMAGING-SPECIFIC DIAGNOSIS
(c) 2015 Wolters Kluwer. All Rights Reserved.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Case 1Dokument2 SeitenCase 1Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney 1Dokument2 SeitenKidney 1Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1Dokument2 SeitenCase 1Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoodDokument2 SeitenGoodDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney 2Dokument2 SeitenKidney 2Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney 3Dokument2 SeitenKidney 3Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney 4Dokument2 SeitenKidney 4Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KidneyDokument2 SeitenKidneyAnandraojs JsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiology Is The Science That UsesDokument1 SeiteRadiology Is The Science That UsesDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Imaging: Small-Bowel Obstruction: State-of-the-Art Imaging and Its Role in Clinical ManagementDokument1 SeiteClinical Imaging: Small-Bowel Obstruction: State-of-the-Art Imaging and Its Role in Clinical ManagementDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Imaging 2Dokument1 SeiteClinical Imaging 2Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AzygouDokument1 SeiteAzygouDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AADokument1 SeiteAADavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CatholicDokument2 SeitenCatholicDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindi Cinema (Bollywood)Dokument3 SeitenHindi Cinema (Bollywood)Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marana Simhasanam Vanaprastham: Malayalam Cinema Is TheDokument1 SeiteMarana Simhasanam Vanaprastham: Malayalam Cinema Is TheDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Indian CinemaDokument1 SeiteHistory of Indian CinemaDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV RamanDokument1 SeiteCV RamanDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- About NSD: On 28 February 1928, DR C.V Raman Had Announced The Discovery of TheDokument1 SeiteAbout NSD: On 28 February 1928, DR C.V Raman Had Announced The Discovery of TheDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TamilDokument2 SeitenTamilDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Studies, Now Provides Its Mite in The Field of Higher Education Imparting The MostDokument1 SeiteManagement Studies, Now Provides Its Mite in The Field of Higher Education Imparting The MostDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cinema of IndiaDokument4 SeitenCinema of IndiaDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GQ (Indian Edition) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument2 SeitenGQ (Indian Edition) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 42 Diabetic Retinopathy Classification and Typical LesionsDokument1 Seite42 Diabetic Retinopathy Classification and Typical LesionsDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonometry PDFDokument1 SeiteTonometry PDFDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivitisDokument1 SeiteConjunctivitisDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retinal DetachDokument1 SeiteRetinal DetachDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Concept MapDokument8 SeitenRenal Concept MapDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnaesthesiaDokument1 SeiteAnaesthesiaDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 2002 CT Saturation and Polarity TestDokument11 Seiten2002 CT Saturation and Polarity Testhashmishahbaz672100% (1)
- Turbine Flowmeters-Commonly Asked Questions and Answers: For Chemical Composition Information.)Dokument8 SeitenTurbine Flowmeters-Commonly Asked Questions and Answers: For Chemical Composition Information.)Alexander KlmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0n9) O6..,w48j-GDokument14 Seiten0n9) O6..,w48j-GMocha FurrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultural AnthropologyDokument12 SeitenCultural AnthropologyTRISH BOCANoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded System Lab ManualDokument67 SeitenEmbedded System Lab Manualsaim100% (1)
- Reflection - Reading and Writing 3Dokument3 SeitenReflection - Reading and Writing 3Quỳnh HồNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duties and Responsibilities - Filipino DepartmentDokument2 SeitenDuties and Responsibilities - Filipino DepartmentEder Aguirre Capangpangan100% (2)
- MBA 2nd Sem SyllabusDokument6 SeitenMBA 2nd Sem SyllabusMohammad Ameen Ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence Based Practice in Nursing Healthcare A Guide To Best Practice 3rd Edition Ebook PDFDokument62 SeitenEvidence Based Practice in Nursing Healthcare A Guide To Best Practice 3rd Edition Ebook PDFwilliam.tavares69198% (50)
- Uxc01387a PDFDokument16 SeitenUxc01387a PDFmahesh123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kpolovie and Obilor PDFDokument26 SeitenKpolovie and Obilor PDFMandalikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOMESDokument23 SeitenDOMESMukthesh ErukullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boeing SWOT AnalysisDokument3 SeitenBoeing SWOT AnalysisAlexandra ApostolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sip Poblacion 2019 2021 Revised Latest UpdatedDokument17 SeitenSip Poblacion 2019 2021 Revised Latest UpdatedANNALLENE MARIELLE FARISCALNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSS 2 (7th&8th) May2018Dokument2 SeitenDSS 2 (7th&8th) May2018Piara SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCP-027 VectraLCPDesignGuideTG AM 0613Dokument80 SeitenLCP-027 VectraLCPDesignGuideTG AM 0613Evert100% (1)
- Fabric DefectsDokument30 SeitenFabric Defectsaparna_ftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of DC-DC Boost Converter: September 2016Dokument5 SeitenDesign and Analysis of DC-DC Boost Converter: September 2016Anonymous Vfp0ztNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - Adaptation AssignmentDokument3 SeitenLesson 3 - Adaptation AssignmentEmmy RoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance Plan-75FDokument3 SeitenQuality Assurance Plan-75Fmohamad chaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 17 Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum BADARANDokument10 SeitenModule 17 Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum BADARANLance AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIVE2304 C1-1 Hydrological CycleDokument54 SeitenCIVE2304 C1-1 Hydrological CyclenaserNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument14 Seiten1Cecille GuillermoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Should We Allocate Scarce Resources Over Our Business Portfolio?Dokument20 SeitenHow Should We Allocate Scarce Resources Over Our Business Portfolio?Vivek AryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pinterest or Thinterest Social Comparison and Body Image On Social MediaDokument9 SeitenPinterest or Thinterest Social Comparison and Body Image On Social MediaAgung IkhssaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Success - Stakeholders 1 PDFDokument7 SeitenProject Success - Stakeholders 1 PDFMoataz SadaqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Temperature PDFDokument56 SeitenBody Temperature PDFBanupriya-Noch keine Bewertungen
- NHD Process PaperDokument2 SeitenNHD Process Paperapi-122116050Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cryptocurrency Research PDFDokument59 SeitenCryptocurrency Research PDFAnupriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3-CP For Armed Conflict SituationDokument23 SeitenChapter 3-CP For Armed Conflict Situationisidro.ganadenNoch keine Bewertungen