Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Care Plan
Hochgeladen von
namitaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plan
Hochgeladen von
namitaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
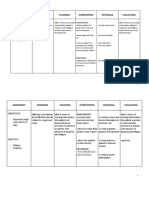
PLU School of Nursing Care Plan Form
STUDENT NAME: John Smith DATE: 10/18/19 WEEK #: 6
Patient Age/Decade: 70 Gender: M Medical/Admitting Diagnosis: Lung mass, COPD
Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Expected Interventions Evaluation Statement
(Subjective and Objective- (NANDA- includes related Outcomes/Goals (In order of priority list a (Evaluation of each goal.
Include all relevant to and as evidenced by in (Minimum of one short- minimum of 5 nursing Was the goal met,
assessment and statement) term goal and one long- interventions. One must partially met or unmet?
diagnostic data) term goal. Goal statement address teaching while Must include as evidenced
must be specific, realistic, the others should address by to support evaluation
measurable, and with a assessment and actions) of goal)
timeframe) Must include rationale
for each intervention and
site source
Subjective: Impaired gas exchange r/t Short Term- Short- Short term- Goal met
Decreased energy COPD AEB Client will maintain O2 sat Assessment- Monitor the Client maintained O2 sat
Fatigue Use of 5L O2 with between 88%-92% by the patient’s respirations and of 96% by end of shift AEB
Weakness O2 sat of 92% end of shift on 10/17/19 regularly assess breath 92% O2 sat
SOB with activity Dyspnea on sounds to be able to Use of 5L O2 by
exertion and Long Term- determine baseline and nasal Canal
Objective: resting tachypnea By the time of discharge the effectiveness of Respiratory rate
168/63; HR 84; RR Chest X ray with the client will verbalize treatment. of 18 and regular
36; SPO2 92% 5L evidence of COPD understanding of oxygen without dyspnea
NC. Expiratory administration including Rationale- Monitoring
Non-productive wheezing s/sx of hypoxia, changes in client’s Long Term- Goal met
cough demonstrate applying respiratory status are key Client demonstrated
Increased oxygen delivery devices to providing prompt understanding of oxygen
breathing effort and safety. interventions in order to administration AEB
with movement. reduce complications Verbalized how
Baseline of 3L O2 (Ignatavicius, Workman, oxygen is safely
with O2. Current Rebar, 2018, p.578). administered by
5L sat of 92%. NC at home.
Action- Administer O2 Use of effective
and titrate oxygen to cough to clear
airways
N340 Care Plan JKushner 02/03/2019
PLU School of Nursing Care Plan Form
STUDENT NAME: John Smith DATE: 10/18/19 WEEK #: 6
Patient Age/Decade: 70 Gender: M Medical/Admitting Diagnosis: Lung mass, COPD
Chest X ray with main O2 sat between 88% Knowledge and
evidence of COPD to 92% use of pursed lip
and lung mass breathing
ABG CO2 92 Rationale- All hypoxic Demonstrated use
Breath sounds: patients, even patients of portable pulse
expiratory with COPD and oximetry with
wheezing hypercarbia should verbalizing plan to
receive oxygen therapy at increase oxygen
appropriate rate in order as needed when
to decrease hypoxia and levels drop below
bring spO2 levels up to 88%.
88%-92% (Ignatavicius,
Workman, Rebar, 2018,
p.578).
Education- Demonstrate
effective coughing and
deep breathing
techniques
Rationale- Coughing
effectively can improve
gas exchange by helping
increase airflow in the
larger airways
(Ignatavicius, Workman,
Rebar, 2018, p.578).
Long-
Assessment- Auscultate
breath sounds
N340 Care Plan JKushner 02/03/2019
PLU School of Nursing Care Plan Form
STUDENT NAME: John Smith DATE: 10/18/19 WEEK #: 6
Patient Age/Decade: 70 Gender: M Medical/Admitting Diagnosis: Lung mass, COPD
Rationale- By auscultating
the clients breath sounds
the nurse can determine if
an obstruction or changes
in breath sounds have
occurred. If the nurse
notices a change it can
alert them to administer
an intervention because
airway maintenance is the
most important focus to
improve gas exchange
(Ignatavicius, Workman,
Rebar, 2018, p. 574).
Action- Administered
Steroids and
Bronchodilators as
prescribed
Rationale- Steroids and
corticosteroids are good
for long term control,
while bronchodilators are
useful for rescue therapy
(Ignatavicius, Workman,
Rebar, 2018, p.579).
Education- Encourage
abdominal or pursed lip
breathing exercises during
N340 Care Plan JKushner 02/03/2019
PLU School of Nursing Care Plan Form
STUDENT NAME: John Smith DATE: 10/18/19 WEEK #: 6
Patient Age/Decade: 70 Gender: M Medical/Admitting Diagnosis: Lung mass, COPD
episodes of increased
dyspnea.
Rationale- Diaphragmatic
or abdominal and pursed
lip breathing can be
helpful in managing
dyspneic episodes. These
techniques delay airway
compression and reduce
air trapping (Ignatavicius,
Workman, Rebar, 2018,
p.578).
Ignatavicius, D.,
Workman, M., and Rebar,
C. (2018). Medical-
surgical nursing concepts
for interprofessional
collaborative care (9th
ed.). Elsevier: St Louis,
MO.
N340 Care Plan JKushner 02/03/2019
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseVon EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument10 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle AcenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ambulatory Oxygen Therapy With Documented Self-Monitoring 2021Dokument7 SeitenAmbulatory Oxygen Therapy With Documented Self-Monitoring 2021DrasmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indicación Oxigeno Domiciliario EPOCDokument21 SeitenIndicación Oxigeno Domiciliario EPOCJULIO FLORESNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Or-Rotation 2Dokument12 SeitenNCP - Or-Rotation 2Vian RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Method For Noninvasive Measurement of Pulmonary Gas Exchange Using Expired GasDokument4 SeitenA New Method For Noninvasive Measurement of Pulmonary Gas Exchange Using Expired GasTanmay PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Learning NotesDokument260 SeitenE Learning NotesGrape JuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home-Based Long-Term Oxygen Therapy and Oxygen Conservation Devices: An Updated ReviewDokument8 SeitenHome-Based Long-Term Oxygen Therapy and Oxygen Conservation Devices: An Updated ReviewKesava Dhika VasudevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygenforend of Lifelungcancercare ManagingdyspneaandhypoxemiaDokument13 SeitenOxygenforend of Lifelungcancercare ManagingdyspneaandhypoxemiaAndrew WongkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Sepsis PDFDokument3 SeitenOxygen Sepsis PDFdimas antaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: IndependentDokument4 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: IndependentAlyssa Marie SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Halotherapy and Buteyko Breathing Technique ResearchDokument2 SeitenHalotherapy and Buteyko Breathing Technique ResearchdodikjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seteo de Oxigenoterapia en El HospitalDokument5 SeitenSeteo de Oxigenoterapia en El HospitalSofia SoharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jcopdf 4 071Dokument5 SeitenJcopdf 4 071HusnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What's New in Oxygen Therapy?: EditorialDokument3 SeitenWhat's New in Oxygen Therapy?: EditorialmilleralselmoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review ArticleDokument9 SeitenReview ArticleAyu SuwarayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 (Pilcher & Beasley) - Acute Use of Oxygen Therapy PDFDokument3 Seiten2015 (Pilcher & Beasley) - Acute Use of Oxygen Therapy PDFNicole HermosillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COPD Guideline Ver 1.8Dokument9 SeitenCOPD Guideline Ver 1.8Dina AyupnNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing: Independent: That Would Cause Breathing Respiratory Ailments in GeneralDokument2 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Independent: That Would Cause Breathing Respiratory Ailments in GeneralChristine Pialan SalimbagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 BransonDokument15 Seiten5 BransonSalsabila Munirah AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For OxygenationDokument6 SeitenNCP For OxygenationChriz LechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygenation Target in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, 2023Dokument8 SeitenOxygenation Target in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, 2023Jonathan Fierro MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen TherapyDokument59 SeitenOxygen TherapyRosi AmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- s13054 020 03409 0Dokument13 Seitens13054 020 03409 0Sidik SyafaatullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Pursed Lips Breathing For Oxygen Saturation and Peak Expiratory Flow Rate: Systematic ReviewDokument5 SeitenEffect of Pursed Lips Breathing For Oxygen Saturation and Peak Expiratory Flow Rate: Systematic ReviewRudi HariyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icu 2Dokument9 SeitenIcu 2GemilleDaphneAndradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument10 SeitenNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01.stoller - Long-Term Oxygen Treatment - 2010Dokument9 Seiten01.stoller - Long-Term Oxygen Treatment - 2010guidepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web PageDokument14 SeitenWeb Pagefenty nisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 1 N 2Dokument5 SeitenNCP 1 N 2Cuttie Anne GalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergology International: Yuji Tohda, Soichiro Hozawa, Hiroshi TanakaDokument7 SeitenAllergology International: Yuji Tohda, Soichiro Hozawa, Hiroshi TanakaMeri Fitria HandayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABC of Oxygen Therapy in Acute CareDokument4 SeitenABC of Oxygen Therapy in Acute CarefujiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rita Care PlanDokument2 SeitenRita Care Planapi-398600648100% (1)
- 07.02.04 Oxygen ProtocolDokument3 Seiten07.02.04 Oxygen Protocolnila choirun nailiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Delivery NHSDokument26 SeitenOxygen Delivery NHSdr satnam kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effectiveness of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy For Acute Respiratory Failure With HypercapniaDokument7 SeitenEffectiveness of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy For Acute Respiratory Failure With Hypercapniarahma_husna_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Insights Into The Measurement of Carbon DioDokument20 SeitenRecent Insights Into The Measurement of Carbon DiostellacharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Therapy: Skills and ProceduresDokument87 SeitenOxygen Therapy: Skills and ProceduresVIA GABRIELLE OCENARNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Capnographic Sensor Using Acoustic Virial Equation For Diagnostic ApplicationsDokument4 SeitenA Capnographic Sensor Using Acoustic Virial Equation For Diagnostic ApplicationsHari PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyDokument3 SeitenPre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arm Am M Ent Arium Trading and Serv IcesDokument3 SeitenArm Am M Ent Arium Trading and Serv IcesMaverick SarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icu 2Dokument9 SeitenIcu 2GemilleDaphneAndradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan On Community-Acquired PneumoniaDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan On Community-Acquired Pneumoniabeatrice angelineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimizing Preoxygenation in AdultsDokument18 SeitenOptimizing Preoxygenation in AdultsBruna Gonçalves FerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inhaler MedicationsDokument11 SeitenInhaler MedicationsNayzstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abr10742 FMDokument4 SeitenAbr10742 FMeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygenation For Rle BSN 2Dokument17 SeitenOxygenation For Rle BSN 2Dakayu Amin LugitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument2 SeitenImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manajemen Dan Terapi Oksigenasi - DFADokument36 SeitenManajemen Dan Terapi Oksigenasi - DFAAhyar MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDokument3 SeitenImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 674 FullDokument7 Seiten674 FullKhai DastaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fisiologia Respiratoria para Anestesiologos 2019 PDFDokument14 SeitenFisiologia Respiratoria para Anestesiologos 2019 PDFAlvarez Flores GilmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Editorials: Assessing The Dose of Supplemental Oxygen: Let Us Compare MethodologiesDokument2 SeitenEditorials: Assessing The Dose of Supplemental Oxygen: Let Us Compare MethodologiesJafar JilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nasal High Ow Oxygen in Acute Respiratory Failure: Thematic Series: HOW I DO IT. Serie Editor: Stefano NavaDokument8 SeitenNasal High Ow Oxygen in Acute Respiratory Failure: Thematic Series: HOW I DO IT. Serie Editor: Stefano NavaHector VillamarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapeutic AssignmentDokument4 SeitenTherapeutic AssignmentSylvester WasongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMJ 33300034Dokument3 SeitenBMJ 33300034kamillaCruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inoue Et Al. - 2017 - Prevalence and Characteristics of Asthma-COPD OverDokument8 SeitenInoue Et Al. - 2017 - Prevalence and Characteristics of Asthma-COPD OverĐức Tài NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 031.bridge To NCLEX Review Question AnswersDokument7 SeitenChapter - 031.bridge To NCLEX Review Question AnswersJackie JuddNoch keine Bewertungen
- OXYGEN and Devices Imp 2020Dokument6 SeitenOXYGEN and Devices Imp 2020rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child Immunization Coverage - A Critical Review: ArticleDokument7 SeitenChild Immunization Coverage - A Critical Review: ArticlenamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The MMR Vaccine and Autism: Sensation, Refutation, Retraction, and FraudDokument3 SeitenThe MMR Vaccine and Autism: Sensation, Refutation, Retraction, and FraudnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Joint Poisoning 2018Dokument34 SeitenBone Joint Poisoning 2018namitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WK 1 Intro CNCPTN Infl F19Dokument42 SeitenWK 1 Intro CNCPTN Infl F19namitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Maintenance and Promotion NursingDokument29 SeitenHealth Maintenance and Promotion NursingnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.intro To Pediatric NursingDokument23 Seiten1.intro To Pediatric NursingnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapeutic CommunicationDokument15 SeitenTherapeutic CommunicationnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment: Mental Health Care PlanDokument3 SeitenAssessment: Mental Health Care PlannamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Basis For Mental HealthDokument25 SeitenBiological Basis For Mental HealthnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pic NursingDokument6 SeitenPic NursingnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upload Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsDokument2 SeitenUpload Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurs Mental HealthDokument28 SeitenNurs Mental HealthnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Skill Books PDFDokument384 SeitenClinical Skill Books PDFnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDokument33 SeitenPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGL101 Chapter 1Dokument3 SeitenENGL101 Chapter 1namitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE Pneumonia EnglishDokument35 SeitenCASE Pneumonia EnglishDhiya Ul AzkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Physiology: Ventilation Perfusion DiffusionDokument6 SeitenRespiratory Physiology: Ventilation Perfusion DiffusionShiara Ruth EdrosoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcome Criteria Actual EvaluationDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcome Criteria Actual EvaluationPabhat Kumar50% (2)
- 4 5814470955174463831Dokument45 Seiten4 5814470955174463831random personsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- History Taking of Respiratory SystemDokument24 SeitenHistory Taking of Respiratory SystemNadiya Elfira BilqisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kerosene ToxicityDokument12 SeitenKerosene ToxicityMohamed Abo SeifNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIA Health Declaration FormDokument4 SeitenAIA Health Declaration FormkotisanampudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Recovering CovidDokument7 SeitenPulmonary Rehabilitation in Recovering CovidsukiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cairo: Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation, 6th EditionDokument6 SeitenCairo: Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation, 6th Editionفاتن المطيريNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Claim Form 4) Series # August 2018: Month Day Year Hour MinDokument2 Seiten(Claim Form 4) Series # August 2018: Month Day Year Hour MinDondy Viñas SenosinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Case TakingDokument6 SeitenPulmonary Case TakingDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Ventilation ManagementDokument3 SeitenAdvanced Ventilation ManagementAnka EremiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroidectomy Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenThyroidectomy Nursing Care PlanRnspeakcom100% (1)
- 60 Second EMTDokument29 Seiten60 Second EMTstripec30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Staff Nurse - Set CDokument16 SeitenQuestion Paper Staff Nurse - Set CJasmine Praveen100% (1)
- Pediatric Concept MapDokument7 SeitenPediatric Concept Mapapi-508020518Noch keine Bewertungen
- PAROS (Case 2)Dokument2 SeitenPAROS (Case 2)Carl Michael RazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine History Taking-Final-06062015Dokument112 SeitenMedicine History Taking-Final-06062015Dr. Karan AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDokument2 SeitenBreast Cancer Concept MapMaria Cristina100% (1)
- TNCC Study GuideDokument6 SeitenTNCC Study Guidekristinekat96% (24)
- Gero Study GuideDokument42 SeitenGero Study GuideAbby Schmidt100% (1)
- Webquest Respiratory DistressDokument12 SeitenWebquest Respiratory Distressapi-361357754Noch keine Bewertungen
- 757Dokument46 Seiten757David DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Articular RheumatismDokument3 SeitenAcute Articular RheumatismcristinamihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pericardial EffusionDokument41 SeitenPericardial Effusionanon_516278156Noch keine Bewertungen
- AsthmaDokument16 SeitenAsthmaSivaramakrishna Markandeya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Case Files Family Medicine 5E Nov 6 2020 - 1260468593 - Mcgraw Hill PDF Full Chapter PDFDokument67 SeitenEbook Case Files Family Medicine 5E Nov 6 2020 - 1260468593 - Mcgraw Hill PDF Full Chapter PDFannie.holland975100% (23)
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Hiv)Dokument8 SeitenRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Hiv)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Assessment Rle Case ScenarioDokument5 SeitenHealth Assessment Rle Case ScenarioSuzete PagaduanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrehospitalCTASParamedicGuide December312016 Version2.0 PDFDokument98 SeitenPrehospitalCTASParamedicGuide December312016 Version2.0 PDFSaifullah RachmanNoch keine Bewertungen