Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lab Equipments
Hochgeladen von
Ibne FazalOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lab Equipments
Hochgeladen von
Ibne FazalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name Mahmood-ul-hassan
Reg. No. 2019-MC-265
Date 27/2/2020
Marks
Experiment # 1
Task # 1
Introduction to Equipment
DC Power Supply:
It is a device
that is used to convert AC voltage
to DC voltage.
Construction and Working:
In basic internal
structure of power supply a
transformer is used to step down
the input voltage to required
value and a rectifier circuit is used
with capacitors to provide rectification that will give a constant voltage in output.
It has three channels. Two of them are used to get variable voltage (max
32V) and current values and one is gives fixed voltage of 5V and 3A current. There are
two rotary knobs for variable values of each channel (one for current and other for
voltage). Output can also be triggered by using output button as shown in figure. There
are two buttons between the rotary knobs. Those provide parallel and series
connection of two channels as shown in figure. When both of them are off (pushed out)
then there is no connection between both channels, when upper button is on (pushed
in) then the combined channels provided with the increase in output voltages. When
both buttons are pushed in then the output current is combined effect of both channels.
Uses:
1. It is used to provide constant voltage and current.
2. All electronic circuits needs a power source to work.
3. For electronic circuits made up of transistor and ICs, and in automation the
power supply provides a better solution for testing and calibrating the circuit.
4. In low voltage communication system power supply provides a controlled output
voltage. Applied voltage is depended how much capacitor and inductors are used.
MAHMOOD-UL-HASSAN 2019-MC-265 Page 1
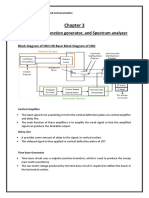
Oscilloscope:
Structure:
Internal structure:
In old oscilloscope it consists
of a cathode ray tube there for it is also
called cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO).
This tube provides the electron beam.
When this beam collides with the screen
it produces glow.
In digital oscilloscope it
consists of power supply circuit with
transistors and ICs. That not only generates
signals but also have ability to compare
signals of different types. As shown in Fig.
Parts:
1. Vertical system
2. Horizontal system
3. Display and display system
4. Trigger system
5. Front panel
Vertical System:
1. Voltage per division is shown in vertical system it is changed by scale circuit in
vertical system.
2. Increasing the voltage per division decreases the height of the graph.
3. The vertical system detects the analog voltage.
Horizontal System:
1. It consists of a sample clock.
2. It determines how much the sample input signal takes in a time.
3. Increasing the sample clock time more part or more no of waves becomes shown.
4. It is calculated in time per division.
Display System:
1. The display system is used to view the input signal.
2. The properties, values and shape of the graph is studied in display system.
3. It is controlled by display controllers from front panel.
MAHMOOD-UL-HASSAN 2019-MC-265 Page 2
Trigger System:
1. It is used to display a steady signal.
2. It starts the sample clock in such a manner that each time the signal recorded at
same point on curve.
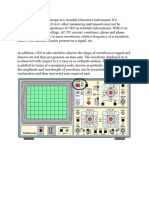
Front Panel:
In outer structure it has many controllers in form of knobs and buttons. It has
two channels. The two input signal of channels is displayed and controlled by using
rotary knobs. Each channel has two rotary knobs to set its position to Y-axis and X-axis
as shown in Fig. There is an Auto button that automatically set the scale of input signal
to display signals properly. The top bar contains controller of screen that is used to
display measured value of signals and properties of signals. The top rotary knob in
control panel is used as toggle from one place to another place in options, it works as
courser. F buttons at left side is used to select options.
Uses:
1. It is used to display and measure the input voltages or current signal.
2. It can also be used to measure the instantaneous values of signals and to compare
the values of two different signals.
3. It is used to measure the frequency, amplitude and time period of input signals.
4. It can also be used to check the quality of communication signals.
MAHMOOD-UL-HASSAN 2019-MC-265 Page 3
5. A digital oscilloscope also has the ability to examine digitized information stored
in its memory and make automatic measurements.
Function Generator:
It is a device that is used to generate wave forms of a signal of
different types such as saw-tooth, square and sinusoidal waves. Frequency and
amplitude of the graph can also be adjusted by this equipment. It is also used to
compare the quality of generated signal by circuit and by function generator. It is also
used to test and repair of electrical circuits and signals.
Structure:
The left rotary knob is used to change the frequency of signal and second row
buttons are used to change the type of waveform. Bottom right rotary knobe is used to
change the amplitude of waveform.
MAHMOOD-UL-HASSAN 2019-MC-265 Page 4
Bread Board:
It is a connection board that is
used to test a non-permanent circuit.
Explanation:
The bread board as shown in figure consists of rows and columns connected
conductively. For example one rows signed with positive or negative sign is connected
conductively and column one or any of them is connected conductively. For example
the terminal 1A and 1E is connected with each other.
Digital Multi Meter:
It is a device that is used to measure
input voltages (V), current (A) and resisters (Ω). The
voltage of current may be AC or DC. We can rotate the
Diller to get different types of measurement as shown in
figure. There are four ports on the multimeter. One is
fixed for Ground terminal and one is used for measuring
voltage and resistances and other two are used for
measuring current of two ranges. One current measuring
port measures current in mA and other measures in A.
Important Note: Do not measure high current in
milliamps switch and probe it may damage the circuit of
fuse may be burnt.
MAHMOOD-UL-HASSAN 2019-MC-265 Page 5
Task # 2
Generating a signal 5V peak voltage and 2KH frequency and
Observation on Oscilloscope
Procedure:
Connect the power line of function generator with lab power line.
Turn on the function generator by pressing the button form backside.
Toggle the screen of function generator by pressing toggle button and select the
frequency mode.
Set frequency mode to 2KH.
Toggle the screen to amplitude mode. And set Peak to Peak Voltage to 10 V.
Repeat the steps from 3 to 5 for wave forms of square wave, sinusoidal wave and
saw tooth wave.
Observation of above signals on oscilloscope:
Procedure:
Connect oscilloscope to main supply.
Start oscilloscope by pressing start button.
Turn the channel one on and channel two off.
Calibration: Calibrate the Oscilloscope by connecting probe of oscilloscope to
calibration pin. Press the auto button. Maximum voltage of probe will begin to
display. If the voltage written on the probe is same as showing the oscilloscope
the oscilloscope is calibrated.
Connect the signal to channel one.
Press the auto button for auto scaling. If we want scale by yourself we can done
by using scale knob.
Check the minimum box voltage and time division for the given scale.
MAHMOOD-UL-HASSAN 2019-MC-265 Page 6
Observations:
1. Sinusoidal wave form. 2. Saw-tooth wave form.
3. Rectangular wave form. 4. Observed Values
Calculations:
Peak Voltage = Vp = Number of Boxes x Voltage per division = 2.5 x 2V = 5V
Peak to Peak Voltage = Vp-p = 5 x 2V = 10V
Time Period = Number of Boxes x Time per division = 2.5 x 200us = 500us
Frequency = 1 / Time Period = 1/500us = 2 KHz
𝑂𝑏𝑠𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑒𝑑−𝐶𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑑
Percentage Error = x 100
𝑂𝑏𝑠𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑒𝑑
Value Observed (Oscilloscope) Calculated %error
Voltage Vp-p 10V 10V 0%
Time Period 500.4us 500us 0.0008%
Frequency 1.998 KHz 2 KHz -0.001%
MAHMOOD-UL-HASSAN 2019-MC-265 Page 7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Experiment 3Dokument16 SeitenExperiment 3Ashish patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ReportDokument12 SeitenLab ReportSarah HarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me170a - Lab 01 - Instrumentation Handout - Edited2015Dokument8 SeitenMe170a - Lab 01 - Instrumentation Handout - Edited2015andman753Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 1Dokument4 SeitenExpt 1gaurav142Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 - AC MeasurementDokument7 SeitenExperiment 1 - AC MeasurementmixchescakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1: Introduction To Electronics InstrumentationsDokument17 SeitenExperiment 1: Introduction To Electronics InstrumentationsSharifah Syed HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty ManualDokument60 SeitenFaculty ManualCookiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Session 01 Introduction To Laboratory Equipments: ObjectiveDokument10 SeitenLab Session 01 Introduction To Laboratory Equipments: ObjectiveHuma MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- تجربة 1Dokument17 Seitenتجربة 1Moaid BinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee5451 Lab3Dokument24 SeitenEee5451 Lab3sekelanilunguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Lab 1Dokument18 SeitenElectronics Lab 1Sheraz HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Learning Center University of Michigan - Dearborn: Use of The OscilloscopeDokument47 SeitenScience Learning Center University of Michigan - Dearborn: Use of The OscilloscopebingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory 2 OscilloscopeDokument9 SeitenLaboratory 2 Oscilloscopenurhafiqah100% (1)
- Student ManualDokument61 SeitenStudent ManualCookiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The OscilloscopeDokument5 SeitenThe OscilloscopeSadiq IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 33 ProjectDokument20 SeitenEe 33 ProjectJozar TumabiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ManualDokument65 SeitenLab ManualHuma MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation Lab Lab Manual: Vi SemesterDokument41 SeitenElectronic Measurement & Instrumentation Lab Lab Manual: Vi SemesterMy JaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 NotesDokument9 SeitenUnit 4 NotesPrathamesh BhavsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Labmanual 1Dokument78 SeitenElectronic Labmanual 1bipul ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Sweep Generator Is Called Time Base Generator?Dokument4 SeitenWhy Sweep Generator Is Called Time Base Generator?prabodhmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical ElectronicsDokument107 SeitenPractical ElectronicsSaeed Ali Shahani100% (2)
- Basra Engineering Technical Collage UUUUUDokument16 SeitenBasra Engineering Technical Collage UUUUUزينب عبد الناصر عاتي عبدالله الموحيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation Lab ManualDokument14 SeitenInstrumentation Lab ManualAmulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 3 Oscilloscope and Voltage MeasurementDokument7 SeitenExp 3 Oscilloscope and Voltage MeasurementusmpowerlabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4: Measuring Instruments and Power/Signal Sources: 1-Digital MultimeterDokument8 SeitenLecture 4: Measuring Instruments and Power/Signal Sources: 1-Digital MultimeterHuzaifa RehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syed Ali Abbas-Bmef19M012: Lab Session 01 Introduction To Laboratory EquipmentsDokument10 SeitenSyed Ali Abbas-Bmef19M012: Lab Session 01 Introduction To Laboratory Equipmentsdani chNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument7 SeitenLab 1Rasha HashimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fa19-Bee-180 Lab Rep 1 EtcsDokument13 SeitenFa19-Bee-180 Lab Rep 1 EtcsRANA AHMADNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscilloscope FamiliarizationDokument5 SeitenOscilloscope FamiliarizationJaycee50% (2)
- Introduction To The OscilloscopeDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To The OscilloscopeStudentsHeartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 9Dokument13 SeitenLab 9Abu BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- OscilloscopeDokument9 SeitenOscilloscopeQadeer Khan100% (1)
- Be Lab ManualDokument96 SeitenBe Lab ManualBhargav garlapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Oscilloscope and Function Generator Lab 1Dokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Oscilloscope and Function Generator Lab 1Suleman MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practicas de OsciloscopioDokument9 SeitenPracticas de OsciloscopiokarolcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 11 Single Phase Inverter Part IDokument7 SeitenExp 11 Single Phase Inverter Part Iusmpowerlab0% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Chap 3 Notes.Dokument13 SeitenChap 3 Notes.Mohit kaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 03Dokument6 SeitenLab 03Hanzala NoumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emi Lab Manual PDFDokument39 SeitenEmi Lab Manual PDFMadhusudhanan RamaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 5 Oscilloscope X-Y Mode, Function Generator and Lissajous Polar (2012)Dokument13 SeitenExp 5 Oscilloscope X-Y Mode, Function Generator and Lissajous Polar (2012)usmpowerlabNoch keine Bewertungen
- CroDokument4 SeitenCroRajan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2 MSDokument43 SeitenUnit2 MSchandramohan murugan100% (1)
- Lab 1 Introduction To The Use of The Digilent'S Analog DiscoveryDokument6 SeitenLab 1 Introduction To The Use of The Digilent'S Analog DiscoveryFredy Alzate100% (1)
- Science Learning Center University of Michigan - Dearborn: Use of The OscilloscopeDokument49 SeitenScience Learning Center University of Michigan - Dearborn: Use of The OscilloscopeAlex ZadicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term Project Topic: Function of Cro (Cathod Ray Osciiloscope) & Application of Function GeneratorDokument5 SeitenTerm Project Topic: Function of Cro (Cathod Ray Osciiloscope) & Application of Function Generatorshailesh singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE - 111 Basic Electronics: Experiment # 1Dokument8 SeitenEE - 111 Basic Electronics: Experiment # 1khazima UmairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1Dokument3 SeitenExperiment 1chetan_bhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDokument6 SeitenCathode Ray Oscilloscopeindrav32Noch keine Bewertungen
- InstrumentationDokument5 SeitenInstrumentationchnxyeyed14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oscilloscope and Rc-Circuits Physics 230, Lab 5 Objective: Name PartnerDokument5 SeitenOscilloscope and Rc-Circuits Physics 230, Lab 5 Objective: Name PartnerSanira LasanthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual Electronics EngineeringDokument67 SeitenLab Manual Electronics EngineeringMuhammad Anas ToheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Lab Oscilloscope Rev03Dokument8 SeitenAC Lab Oscilloscope Rev03Abdelaziz AbdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2 - Half Wave RectifierDokument8 SeitenExperiment 2 - Half Wave RectifierRandred GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC 307 Power Electronics and Instrumentation Lecture Notes, Module 6Dokument21 SeitenEC 307 Power Electronics and Instrumentation Lecture Notes, Module 6vpzfaris100% (1)
- Regulator - ESTAmat MH Mounting Instructions MV1151 (Sept 2000)Dokument11 SeitenRegulator - ESTAmat MH Mounting Instructions MV1151 (Sept 2000)Ieremeiov Vladimir100% (1)
- Time Varying SignalsDokument17 SeitenTime Varying SignalsDiego Cancino SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Inggris Text - Kelas 9Dokument27 SeitenTugas Inggris Text - Kelas 9salviane.theandra.jNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Terrorism NotesDokument3 SeitenWhat Is Terrorism NotesSyed Ali HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bloomsbury Fashion Central - Designing Children's WearDokument16 SeitenBloomsbury Fashion Central - Designing Children's WearANURAG JOSEPHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydropneumatic Booster Set MFDokument5 SeitenHydropneumatic Booster Set MFdonchakdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement AnalysisDokument18 SeitenFinancial Statement AnalysisAbdul MajeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet Housekeeping Week - 8 - Grades 9-10Dokument5 SeitenActivity Sheet Housekeeping Week - 8 - Grades 9-10Anne AlejandrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Constructor and DistructorDokument15 Seiten12 Constructor and DistructorJatin BhasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Structure and Leverage: Multiple Choice: ConceptualDokument53 SeitenCapital Structure and Leverage: Multiple Choice: ConceptualArya StarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS Charcoal Powder PDFDokument3 SeitenMSDS Charcoal Powder PDFSelina VdexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctions in SentencesDokument8 SeitenConjunctions in SentencesPunitha PoppyNoch keine Bewertungen
- License Fee PaidDokument1 SeiteLicense Fee Paidmy nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datalogic tl46 A Manual - 230104 - 140343Dokument2 SeitenDatalogic tl46 A Manual - 230104 - 140343Emmanuel Baldenegro PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Army Watercraft SafetyDokument251 SeitenArmy Watercraft SafetyPlainNormalGuy2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 07 EPANET Tutorial-SlidesDokument26 Seiten07 EPANET Tutorial-SlidesTarhata Kalim100% (1)
- Bai Tap Av 12 Thi Diem Unit TwoDokument7 SeitenBai Tap Av 12 Thi Diem Unit TwonguyenngocquynhchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1ST Term J1 Fine Art-1Dokument22 Seiten1ST Term J1 Fine Art-1Peter Omovigho Dugbo100% (1)
- Ajsl DecisionMakingModel4RoRoDokument11 SeitenAjsl DecisionMakingModel4RoRolesta putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straw Bale ConstructionDokument37 SeitenStraw Bale ConstructionelissiumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Safety ChecklistDokument3 SeitenChemical Safety ChecklistPillai Sreejith100% (10)
- Multi Core Architectures and ProgrammingDokument10 SeitenMulti Core Architectures and ProgrammingRIYA GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Travelstart Ticket (ZA10477979) PDFDokument2 SeitenTravelstart Ticket (ZA10477979) PDFMatthew PretoriusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and The Other Terrestrial WorldsDokument27 SeitenChapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and The Other Terrestrial WorldsEdwin ChuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adigrat University: College of Engineering and Technology Department of Chemical EnginneringDokument39 SeitenAdigrat University: College of Engineering and Technology Department of Chemical EnginneringSeid Aragaw100% (1)
- Hansen Aise Im Ch12Dokument66 SeitenHansen Aise Im Ch12Rizki19maretNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elerick Ron Cynthia 1983 SouthAfricaDokument4 SeitenElerick Ron Cynthia 1983 SouthAfricathe missions networkNoch keine Bewertungen
- @InglizEnglish-4000 Essential English Words 6 UzbDokument193 Seiten@InglizEnglish-4000 Essential English Words 6 UzbMaster SmartNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBPO008E FrontmatterDokument13 SeitenPBPO008E FrontmatterParameswararao Billa67% (3)
- One Foot in The Grave - Copy For PlayersDokument76 SeitenOne Foot in The Grave - Copy For Playerssveni meierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amsterdam Pipe Museum - Snuff WorldwideDokument1 SeiteAmsterdam Pipe Museum - Snuff Worldwideevon1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gummy Bear Story RubricDokument1 SeiteGummy Bear Story Rubricapi-365008921Noch keine Bewertungen