Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Organic Tests
Hochgeladen von
Olivia WithersOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Organic Tests
Hochgeladen von
Olivia WithersCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
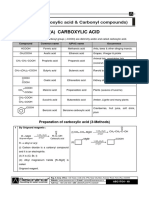
Organic Tests
Test Observation Deduction
1. Solubility Layers/cloudy Insoluble: non-polar e.g. alkanes, alkenes, halogenoalkanes
Miscible/colourless solution forms Soluble: polar/forms H-bonds/low molecular mass e.g. carboxylic acid
2. Odour Characteristic Odour: Vinegar Ethanoic acid
Nail varnish remover Propanone
3. Combustion Ease of ignition?
Burns with sooty/smoky/yellow flame Unsaturated (alkene) or high molecular mass, possible functional group with C=C
Burns with non-luminous/clean/blue flame with no smoke/soot Could be saturated low molecular mass with possibly oxygen
No residue Could be saturated low molecular mass with possibly oxygen
Black residue Carbon residue from a unsaturated or high molecular mass compound with possible functional C=C
4. pH of Solution Indicator turns red/orange/yellow pH < 7 Acidic carboxylic acid
Indicator turns dark blue/green pH > 7 Acidic group 1 salts of carboxylic acid
5. Bromine Water Liquids do not mix. Two layers are formed. Orange bromine layer Immiscible in water. Confirms unknown is unsaturated alkene. (Electrophilic addition takes place)
Measure 1cm3 of unknown into test tube. turns colourless.
Add equal amount of Bromine water,
stopper the test tube and carefully shake.
If organic is gas, bubble through bromine Two colourless layers formed, organic layer orange, aqueous Bromine is more soluble in organic solvent than water, but does not react so no alkene is in it.
water. layer orange to pale yellow
Liquids mix to form an even layer. Mixture turns orange to Two liquids are miscible, confirms is an unknown unsaturated compound with a C=C present.
colourless immediately R = H or alkly group (Electrophilic addition takes place)
6. Acidified Potassium Liquids do not mix together. Two layers form. Potassium Immiscible in water. Confirms is a unsaturated compound such as an alkene. C=C is present.
Manganate manganate turns purple to colourless
Add 2cm3 of unknown with 2cm3 of Electrophilic addition may take place
sulphuric acid and 1cm3 of PM. Stopper
and shake carefully.
7. PCl5 Vigourous fizzing. Misty steamy fumes which turn damp litmus Gas evolved is acidic – HCl. Unknown compound contains hydroxy group.
Add half a spatula to dry test tube to paper blue to red. Alcohol can be identified R-CH2-OH
1cm3 of unknown. Test with damp blue
R = H or an alkyl group and halogenation of alcohol is occurred.
litmus paper.
8. Bubble Through Silver White precipitate is formed when fumes bubbled through solution HCl dissolves in water, alcohol is identified from this. Halogenation of alcohol has occured
Nitrate
9. Acidified Potassium Orange solution turns green when warming. Odour may be Alcohol has been oxidised. Primary alcohols can be further oxidised from aldehyde to carboxylic
Dichromate detected acid
Add 1cm3 of unknown organic substance Secondary alcohols are oxidised to ketones. Two R groups attatched to C-OH
to a test tube followed by 1cm3 of dilute
sulphuric acid and 6 drops of PD, warm in
water bath. No colour change. Remains orange No redox reaction has taken place, tertiary alcohol is present. 3 R groups attached to C-OH
10.Silver Nitrate On addition of silver nitrate Halide ion produced during hydrolysis of halogen atom (alkaline hydrolysis)
1cm3 of unknown, add 1cm3 of ethanol Pale Yellow (Iodine)
with 2cm3 of dilute sodium hydroxide.
Cream (Bromine)
Warm mixture in water bath for 3
minutes. Add 2cm3 of nitric acid, then 6 White (Chlorine)
drops of silver nitrate.
11. Addition of Ammonia Precipitate dissolves in dilute ammonia to leave colourless solution Chlorine is found
Precipitate dissolves in conc ammonia to leave colourless solution Bromine is found
Precipitate doesn’t dissolve in any ammonia Iodine is found
12. Brady’s Reagent Yellow/ orange crystals are formed Either an aldehyde or ketone present. Can be distinguished with melting point test.
13. Fehling/ Benedict Turns solution from blue to brown/red Aldehyde present.
Ketone the test does not work. (Elimination)
14. Tollen’s Reagent Creates a silver mirror on the test tube Aldehyde present.
Careful not to let dry and set alight. Can be explosive.
16. Alkane PROCESS OF ELIMINATION
17. Addition of Magnsium Bubbling/fizzing/metal dissolving Carboxylic acid is present, hydrogen gas is given off
18. Addition of Sodium Steady bubbling/fizzing/metal dissolves Hydrogen gas is given off. Ionic compound that is a white solid. Probably an alcohol (primary,
secondary or tertiary)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Polane T, Polyurethane Enamel ADokument2 SeitenPolane T, Polyurethane Enamel A김도균Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Minor Constituents On Cold Flow Properties and PerformanceDokument9 SeitenEffects of Minor Constituents On Cold Flow Properties and PerformanceNestor Armando Marin SolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aoac983 16Dokument1 SeiteAoac983 16Alejandra Duque GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 09Dokument34 SeitenChapter 09Shirota Kurtnavalu Rnd LptNoch keine Bewertungen
- DFDVDVVCVCX XC VXC VX VXCVVCXDokument14 SeitenDFDVDVVCVCX XC VXC VX VXCVVCXaadadadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Aspect of Caustic Soda in BangladeshDokument4 SeitenMarket Aspect of Caustic Soda in BangladeshFarida Akhter RunuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABC 4 (Theory Exercise)Dokument16 SeitenABC 4 (Theory Exercise)Mayank GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6BI01 01 Que 20110516Dokument28 Seiten6BI01 01 Que 20110516shshovon2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 2Dokument6 SeitenLab Report 2api-257035141Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report - Impact TestingDokument13 SeitenLab Report - Impact Testingapi-404653452100% (1)
- Biogeochemical Cycle 1Dokument35 SeitenBiogeochemical Cycle 1Chaos HadesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ras Abu Aboud Stadium & Precinct Project: Chemical Name Coshh MsdsDokument1 SeiteRas Abu Aboud Stadium & Precinct Project: Chemical Name Coshh Msdssharon Aisha malroy100% (1)
- Unsaturated Polyester CuringDokument4 SeitenUnsaturated Polyester Curingbehzadl98100% (1)
- Treatment of Waste Generated From Cement Industry and Their Treatment-A ReviewDokument12 SeitenTreatment of Waste Generated From Cement Industry and Their Treatment-A ReviewCharles RichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem1011 Exam Practice Test 2Dokument27 SeitenChem1011 Exam Practice Test 2Chirisuu PantsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fish Protein FingerprintingDokument23 SeitenFish Protein Fingerprintingrahmi93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tri Pure Isolation ReagentDokument8 SeitenTri Pure Isolation ReagentMiftahuddin MadjidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msds HCLDokument7 SeitenMsds HCLKhalfina MaharaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 3 - Reacting Masses, Solutions & ConcentrationsDokument4 SeitenEx 3 - Reacting Masses, Solutions & ConcentrationsLeon Lim Teck ShernNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Microorganism in Municipal Solid Waste AssigntDokument6 SeitenImportance of Microorganism in Municipal Solid Waste AssigntGabriel TambweNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Oleaginous Bases:: (I) Glycero - GelatinDokument2 SeitenA. Oleaginous Bases:: (I) Glycero - GelatinSwerika KotteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparation of Fruit FlavorsDokument12 SeitenPreparation of Fruit FlavorsPatricia HariramaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Microbes in Sustainable DevelopmentDokument14 SeitenRole of Microbes in Sustainable DevelopmentRaj K.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination Chem 1 PDFDokument10 SeitenCoordination Chem 1 PDFSundar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yingyang (China) Aroma Chemical Group: Certificate of AnalysisDokument5 SeitenYingyang (China) Aroma Chemical Group: Certificate of AnalysisFrancisco Riascos GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Chemistry Olympiad 2014 (Problems)Dokument80 SeitenInternational Chemistry Olympiad 2014 (Problems)Science Olympiad Blog100% (7)
- GondorukemDokument6 SeitenGondorukemriskyhendra1817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Success Achiever Chmeistry Organic Chemistry PDFDokument44 SeitenSuccess Achiever Chmeistry Organic Chemistry PDFmadheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDokument16 SeitenPolymerase Chain ReactionGENESIS sHINENoch keine Bewertungen
- FR2-Isolation of Proteins and Color ReactionDokument4 SeitenFR2-Isolation of Proteins and Color ReactionKriziaoumo P. OrpiaNoch keine Bewertungen