Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mood + Psychotic Disorders-2 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Jeremy-ann Ham0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
66 Ansichten1 SeiteMania/bipolar disorder and depression involve distinct clusters of symptoms. Mania involves elevated, irritable or nonreactive mood along with symptoms like distractibility, impulsivity, grandiosity and decreased need for sleep. Depression involves depressed, nonreactive mood and symptoms like sleep disturbance, loss of interest, guilt, fatigue, concentration problems and changes in appetite or psychomotor behavior. Psychotic disorders involve positive symptoms like delusions and hallucinations as well as negative symptoms like affective flattening and avolition. The epidemiology, diagnostic criteria and treatment of these mood and psychotic disorders are also summarized.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
MOOD + PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS-2.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMania/bipolar disorder and depression involve distinct clusters of symptoms. Mania involves elevated, irritable or nonreactive mood along with symptoms like distractibility, impulsivity, grandiosity and decreased need for sleep. Depression involves depressed, nonreactive mood and symptoms like sleep disturbance, loss of interest, guilt, fatigue, concentration problems and changes in appetite or psychomotor behavior. Psychotic disorders involve positive symptoms like delusions and hallucinations as well as negative symptoms like affective flattening and avolition. The epidemiology, diagnostic criteria and treatment of these mood and psychotic disorders are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
66 Ansichten1 SeiteMood + Psychotic Disorders-2 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Jeremy-ann HamMania/bipolar disorder and depression involve distinct clusters of symptoms. Mania involves elevated, irritable or nonreactive mood along with symptoms like distractibility, impulsivity, grandiosity and decreased need for sleep. Depression involves depressed, nonreactive mood and symptoms like sleep disturbance, loss of interest, guilt, fatigue, concentration problems and changes in appetite or psychomotor behavior. Psychotic disorders involve positive symptoms like delusions and hallucinations as well as negative symptoms like affective flattening and avolition. The epidemiology, diagnostic criteria and treatment of these mood and psychotic disorders are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
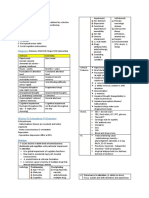
MOOD + PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS
Olivia Wu, updated 10/2018 from First Aid 2018, DGSOM lectures 2018, DSM V (https://dsm.psychiatryonline.org/doi/book/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596)
Mania/Bipolar Disorder Depression
Elevated ("feeling good") and/or irritable, nonreactive mood + DIG FAST * Depressed, nonreactive mood ("feeling down") + SIG E CAPS
1. Distractibility (response to external stimuli) 1. Sleep disturbance
2. Impulsivity/Indiscretion
2. *Interest loss (anhedonia)
3. Grandiosity
3. Guilt, feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness
4. Flight of ideas (internal) 4. Energy loss and fatigue, independent of amount of sleep
5. Activity (goal-directed) / Psychomotor Agitation 5. Concentration problems
6. Sleep (decreased need)S 6. Appetite/weight changes
7. Talkativeness/pressured speech 7. Psychomotor retardation or agitation
8. Suicidal ideation
Manic: ≥ 3 sx for > 1 wk *Always ask about depressed mood and interest loss - highly specific
If mood is only irritable (not elevated), then ≥ 4
Mood disturbance severe enough to impact social/occupational functioning or necessitate hospitalization
"1 fun week," though average episode 3-6 months MAJOR/UNIPOLAR DEPRESSIVE DYSTHYMIA DOUBLE DEPRESSION
DISORDER (MDD)
Hypomanic: ≥ 3 sx for ≥ 4 days dysthymia + acute MDD episodes
• ≥ 5 sx for ≥ 2 wks • 5 > sx ≥ 2 for ≥ 2 years
If mood is only irritable (not elevated), then ≥ 4
Mood disturbance is less severe, NOT significantly impacting social/occupational functioning • At least 1 sx is depressed mood or • No more than 2 mo. w/o sx
loss of interest/pleasure
• Other sx can include anxiety, aka PERSISTENT
BIPOLAR I BIPOLAR II CYCLOTHYMIA somatic DEPRESSIVE DISORDER
• ≥ 1 manic episode • Hypomanic + major depressive • Hypomanic + mild depressive • "2 blue weeks," though average
episode fluctuations ≥ 2 years episodes 6-12 mo.
• +/- hypomanic or major depressive
episode, separated by any length of • NO manic episode • Criteria for other major mood • Independent of other medical
disorders not met (you don't have condition or substance use
time
"double bipolar" like you do "double
depression") SEASONAL PATTERN is a subtype
MIXED STATE is a subtype w/ manic
w/ ≥ 2 major depressive episodes in
symptoms + depressive mood AT
a seasonal pattern over ≥2 years;
THE SAME TIME. Increased suicide
often with atypical features
risk.
Other depressive subtypes
Schizophrenic spectrum • MELANCHOLIC/SEVERE: extreme neuroveg. sx
+ Positive symptoms (Psychosis) • POSPARTUM: similar to MDD
Distorted perception of reality thought to be caused by increased DA action. • PSYCHOTIC: severe depression with psychotic sx
1. Delusions - false beliefs persisting despite facts • CATATONIC
2. Hallucinations (often auditory) - perceptions in the absence of stimuli • SUBSTANCE-INDUCED
3. Disorganized speech - incoherent ("word salad"), tangential, or derailed ("loose associations" b/w sentences/phrases) • SECONDARY: assoc. w/ another medical condition
4. Disorganized/catatonic behavior • ATYPICAL: Mood reactivity, "reversed" vegetative symptoms (hypersomnia, hyperphagia leading to weight gain),
- Negative symptoms leaden paralysis, long-standing interpersonal rejection sensitivity
1. Affective flattening (less eye contact, spontaneity, emotion), avolition, anhedonia, asociality, alogia
• ADJUSTMENT DISORDER: < 5 sx, acute, normal response to life stress
BRIEF PSYCHOTIC SCHIZOPHRENIFORM SCHIZOPHRENIA SCHIZOAFFECTIVE MOOD DISORDER W/
DISORDER DISORDER DISORDER PSYCHOTIC FEATURES Epidemiology
≥ 1 sx for < 1 mo. ≥ 2 sx for 1-6 mo. • ≥ 2 sx for > 6 mo. • Schizophrenia + major • Psychotic symptoms + • Bipolar Disorders/Manic Depression: females = males
• At least 1 sx must be from # mood disorder (major major mood disorder AT • Major/Unipolar Depressive Disorder: females > males, 20s-30s
1-3 depressive or bipolar) THE SAME TIME • Schizophrenia: males > females, presents in late adolescent or early adulthood (15-25 for men, 25-35 for females)
• Psychotic sx only - NO SEPARATELY • We do not classify
mood episodes • > 2 wks. psychotic sx w/o "dysthymia/cyclothymia
major mood episode with psychotic features" Treatment
• Bipolar Disorder/Manic Depression: lifelong combo for both acute treatment and long-term maintenance
1. Mood stabilizer: Li+, valproic acid, carbamazepine, lamotrigine
§ Li+, valproic acid, carbamazepine effective for manic episodes
§ Li+, lamotrigine effective for depressive episodes
2. Atypical antipyschotic
§ Most are effective for manic episodes
§ Quetiapine, lurasidone, olanzapine effective for depressive episodes
• Major/Unipolar Depressive Disorders: CBT + SSRIs are first line, otherwise depends on side effects and tolerance.
Note that they take several weeks to take effect, so adherence is an issue. ECT for treatment-resistant patients. Light
Schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type Bipolar I w/ psychotic features box therapy for seasonal pattern.
• Atypical depression: MAOIs are most effective
• Schizophrenia: atypical antipsychotics
○ Clozapine is best bet for unresponsive patients
○ "Responsivity" = at least 20% reduction in symptoms
○ Negative symptoms often persist
Schizoaffective disorder, MDD type MDD w/ psychotic features
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Simply Psych Cheat Sheets Dsm5 Part 1 LissaurDokument2 SeitenSimply Psych Cheat Sheets Dsm5 Part 1 LissaurChhitiz Kiran ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSM 5 Made EasyDokument6 SeitenDSM 5 Made EasyTesita100% (3)
- The Quick Survival Guide for Mood Disorders: A Process Made SimpleVon EverandThe Quick Survival Guide for Mood Disorders: A Process Made SimpleNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSM 5 CriteriaDokument6 SeitenDSM 5 CriteriaCarmela ArcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Status Exam Template 03Dokument1 SeiteMental Status Exam Template 03رجمه ديوان100% (1)
- Clinical Guide to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Mental DisordersVon EverandClinical Guide to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Mental DisordersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatry EoY History SampleDokument11 SeitenPsychiatry EoY History SampleNicholasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSM-5 Self Examination QandA 11Dokument1 SeiteDSM-5 Self Examination QandA 11leksey24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology - (5) Psychotic DrugsDokument8 SeitenPharmacology - (5) Psychotic DrugsSamantha DiegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varun Kumar, 2017 - Getting Started in PsychiatryDokument148 SeitenVarun Kumar, 2017 - Getting Started in PsychiatryBernard FZ100% (1)
- Racism and Psychiatry: Contemporary Issues and InterventionsVon EverandRacism and Psychiatry: Contemporary Issues and InterventionsMorgan M. MedlockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Work-Up Template For StudentsDokument2 SeitenPsychiatric Work-Up Template For StudentsTommy FuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatry Made Simple: Dr. Pete’S Guide to Your Mental HealthVon EverandPsychiatry Made Simple: Dr. Pete’S Guide to Your Mental HealthNoch keine Bewertungen
- SchizophreniaDokument2 SeitenSchizophreniaIT’S ME HAYLA100% (1)
- AnxietyDokument4 SeitenAnxietyIT’S ME HAYLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale PDFDokument2 SeitenColumbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale PDFAlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMHNP Case Study - EditedDokument7 SeitenPMHNP Case Study - EditedSoumyadeep BoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Mind That Found Itself An AutobiographyVon EverandA Mind That Found Itself An AutobiographyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in PsychiatryVon EverandThe Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in PsychiatryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- DSM-5 Essentials: The Savvy Clinician's Guide to the Changes in CriteriaVon EverandDSM-5 Essentials: The Savvy Clinician's Guide to the Changes in CriteriaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Week 2 (OSCE CASC Book II 2018-19) 03.09.2018Dokument48 SeitenWeek 2 (OSCE CASC Book II 2018-19) 03.09.2018Andrew WdsmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prescribing Psychotropics: From Drug Interactions to PharmacogeneticsVon EverandPrescribing Psychotropics: From Drug Interactions to PharmacogeneticsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Assessment and Evaluation: 2008 Edition Rhoda K Hahn, MD Lawrence J. Albers, MDDokument85 SeitenAssessment and Evaluation: 2008 Edition Rhoda K Hahn, MD Lawrence J. Albers, MDAlbghdadi CristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurocognitive DisorderDokument3 SeitenNeurocognitive DisorderIT’S ME HAYLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatry Grand NotesDokument10 SeitenPsychiatry Grand NotesNathan T. CheungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia: Depression, Hallucinations, Symptoms, and SolutionsVon EverandSchizophrenia: Depression, Hallucinations, Symptoms, and SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- LMSW Exam Prep Pocket Study Guide: Professional Values, Ethics, and RelationshipsVon EverandLMSW Exam Prep Pocket Study Guide: Professional Values, Ethics, and RelationshipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teenage Health Concerns: How Parents Can Manage Eating Disorders In Teenage ChildrenVon EverandTeenage Health Concerns: How Parents Can Manage Eating Disorders In Teenage ChildrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Status ExamDokument7 SeitenMental Status ExamDanielle BanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psych TemplateDokument1 SeitePsych TemplateWilliam Yang100% (1)
- Developing Images: Mind Development, Hallucinations and All Mind Disorders Including AutismVon EverandDeveloping Images: Mind Development, Hallucinations and All Mind Disorders Including AutismNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs For NeurolepticsDokument1 SeiteDrugs For Neurolepticssyamil_daudNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSYCH 011 Clinical Diagnosis of Neurocognitive DisorderDokument7 SeitenPSYCH 011 Clinical Diagnosis of Neurocognitive DisorderKaye NeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuroanatomy For The Psychiatrist: Textbook of PsychiatryDokument37 SeitenNeuroanatomy For The Psychiatrist: Textbook of Psychiatrykrysdana22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 7 Psychiatric AssessmentDokument54 SeitenSession 7 Psychiatric AssessmentPetroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Status ExaminationDokument72 SeitenMental Status Examinationsherief marouf100% (1)
- Neuropsychitric Assessment PDFDokument1 SeiteNeuropsychitric Assessment PDFKaye CorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template For History in PsychiatryDokument3 SeitenTemplate For History in PsychiatryDeedz01100% (1)
- Suicide Risk Assessment Guide NSWDokument1 SeiteSuicide Risk Assessment Guide NSWapi-254209971Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychopharmacology in Medically Ill PatientsDokument21 SeitenPsychopharmacology in Medically Ill PatientsAklile TsegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomarkers and Mental Illness: It’s Not All in the MindVon EverandBiomarkers and Mental Illness: It’s Not All in the MindNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLINICAL SPECIALIST IN CHILD AND ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRIC AND MENTAL HEALTH NURSING: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandCLINICAL SPECIALIST IN CHILD AND ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRIC AND MENTAL HEALTH NURSING: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Massachusetts General Hospital Textbook on Diversity and Cultural Sensitivity in Mental HealthVon EverandThe Massachusetts General Hospital Textbook on Diversity and Cultural Sensitivity in Mental HealthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Clinical Psychiatry Fourth EditionVon EverandFoundations of Clinical Psychiatry Fourth EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 2 - Diagnosis & Classification in PsychiatryDokument22 Seiten2 - Diagnosis & Classification in PsychiatryKholoud KholoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSM-IV Criteria MnemonicsDokument4 SeitenDSM-IV Criteria Mnemonicsleonyap100% (1)
- Fig psychiatricAssessmentFormDokument4 SeitenFig psychiatricAssessmentFormabbey jane mallillin100% (1)
- Intermittent Explosive Disorder: Etiology, Assessment, and TreatmentVon EverandIntermittent Explosive Disorder: Etiology, Assessment, and TreatmentEmil F. CoccaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation PBL 12 Bipolar DisorderDokument65 SeitenCase Presentation PBL 12 Bipolar DisorderKim S GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Checklist For Incorporation of Video Visits (Telemedicine)Dokument2 SeitenA Checklist For Incorporation of Video Visits (Telemedicine)Jeremy-ann HamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clerkship Primer Online VersionDokument24 SeitenClerkship Primer Online Versionpaul_stefenson10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mood + Psychotic Disorders-2 PDFDokument1 SeiteMood + Psychotic Disorders-2 PDFJeremy-ann HamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floor SheetDokument2 SeitenFloor SheetJeremy-ann HamNoch keine Bewertungen
- USMLE Reference Lab ValuesDokument2 SeitenUSMLE Reference Lab ValuesquezacotlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final - 2018 CA-1 Tutorial Textbook - Smartphone or Tablet-3Dokument342 SeitenFinal - 2018 CA-1 Tutorial Textbook - Smartphone or Tablet-3Nick-Hugh Wisdom100% (1)
- Physical Exam: Anesthetic Plan: Asa #Dokument1 SeitePhysical Exam: Anesthetic Plan: Asa #Jeremy-ann HamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child Abuse & Neglect: SciencedirectDokument19 SeitenChild Abuse & Neglect: Sciencedirectana raquelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ian KerrDokument91 SeitenIan Kerrnini345Noch keine Bewertungen
- APA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Separation Anxiety Disorder Adult PDFDokument3 SeitenAPA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Separation Anxiety Disorder Adult PDFMelissandreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methamphetamine PsychosisDokument138 SeitenMethamphetamine Psychosisamalda06100% (1)
- Red Cross Psychological First Aid Book PDFDokument23 SeitenRed Cross Psychological First Aid Book PDFJankov1105100% (1)
- Beck-Institute-Eating Disorder PresentationDokument28 SeitenBeck-Institute-Eating Disorder PresentationninaanjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pendekatan Dan Teknik Terapi PsikososialDokument64 SeitenPendekatan Dan Teknik Terapi PsikososialGurfak LatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Detection of Postnatal Depression. Development of The 10-ItemDokument6 SeitenEdinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Detection of Postnatal Depression. Development of The 10-ItemKyze LQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal Psychology Practice ExamDokument10 SeitenAbnormal Psychology Practice ExamAlistair GordonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse Class IX English Communicative Sample Paper - 1 SAIDokument8 SeitenCbse Class IX English Communicative Sample Paper - 1 SAIYousuf SaitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1000 Psychiatry MCQ QuestionsDokument141 Seiten1000 Psychiatry MCQ QuestionsDana Ahmed90% (10)
- Joseph Zubin, Howard F. Hunt - Comparative Psychopathology - Animal and Human-Grune & Stratton (1967)Dokument370 SeitenJoseph Zubin, Howard F. Hunt - Comparative Psychopathology - Animal and Human-Grune & Stratton (1967)Víctor FuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolutano and Evangelista Final PaperDokument59 SeitenBolutano and Evangelista Final PaperAria IsipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gardner + Moore 2004 - The Multi-Level Classification System For Sport PsychologyDokument21 SeitenGardner + Moore 2004 - The Multi-Level Classification System For Sport Psychologyshima dalirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topics For Social Work Research PapersDokument7 SeitenTopics For Social Work Research Papersgvzph2vh100% (1)
- Fetishism or Fetishistic Disorder at The Adolescence - Revised - 5Dokument40 SeitenFetishism or Fetishistic Disorder at The Adolescence - Revised - 5Anton B Lond ElNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evil or Ill PDFDokument335 SeitenEvil or Ill PDFrahuldevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic ScienceDokument10 SeitenForensic ScienceNehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 6 2014Dokument48 SeitenJune 6 2014fijitimescanadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Research FinalDokument15 SeitenNursing Research Finalapi-3746713100% (1)
- Myths of Psychology: A Widely Held But False Belief or IdeaDokument3 SeitenMyths of Psychology: A Widely Held But False Belief or IdeaMuhammad Naseem KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- T W O A: HE Omen F LeitheiaDokument23 SeitenT W O A: HE Omen F LeitheiaFCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postpartum Depression TheoryDokument9 SeitenPostpartum Depression TheoryJan Oneille Y. Valles100% (1)
- Eating Disorders About More Than FoodDokument8 SeitenEating Disorders About More Than Foodandrea diazgranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief History of Advocacy in Mental Health, The Roots of The Recovery MovementDokument19 SeitenBrief History of Advocacy in Mental Health, The Roots of The Recovery MovementAndre BarkilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Proposal PosterDokument1 SeiteResearch Proposal Posterapi-310193189Noch keine Bewertungen
- District Mental Health Program - Need To Look Into Strategies in The Era of Mental Health Care Act, 2017 and Moving Beyond Bellary ModelDokument2 SeitenDistrict Mental Health Program - Need To Look Into Strategies in The Era of Mental Health Care Act, 2017 and Moving Beyond Bellary ModelHarish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Larsson Et Al. (2013) - High Prevalence of Childhood Trauma in Patients With Schizophrenia Spectrum and Affective DisorderDokument5 SeitenLarsson Et Al. (2013) - High Prevalence of Childhood Trauma in Patients With Schizophrenia Spectrum and Affective Disorderlixal5910Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review On Factors Affecting Students Academic PerformanceDokument10 SeitenLiterature Review On Factors Affecting Students Academic PerformanceafmzuiqllaaabjNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMT - Expressive Arts AssignmentDokument12 SeitenDMT - Expressive Arts AssignmentShireen ChaturvediNoch keine Bewertungen