Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ste05121 Spreadsheet Anchor Bolt Design
Hochgeladen von
sivaguruswamy thangarajOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ste05121 Spreadsheet Anchor Bolt Design
Hochgeladen von
sivaguruswamy thangarajCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet PIP STE05121
Revision 2, November 2003 January 2003
Company PIP
Project Project # PIP STE05121
Subject Example 1
Name Date 12/12/2002 Sheet Number 1
Checked by Check Date 7/10/2003 Total Sheets 1
LOADING CONDITIONS DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Note: Calculations are per ACI 318-02 Appendix D. Ductility required? Tension No Shear No
Nu and Vu were factored using factors from ACI 318-02? Section 9.2 Intermediate or high seismic risk? No
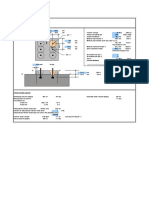
Factored tensile load (kips) = Nu = 116 Specified concrete strength (psi) = f'c = 3000
Factored shear load (kips) = Vu = perpendicular to edge 0 Cracking
Is there a built-up grout pad? Yes modification 1.4 - Located in region where there isn't cracking at service loads (ft < fr)
factor,Y7
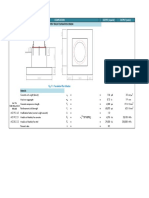
ANCHOR DATA, EMBEDMENT, AND THICKNESS OF MEMBER
Anchor material type = F1554 Gr 36 Adequate supplementary reinf. provided to resist tension loads in anchors? No
Nominal anchor diameter (in.) = 1 3/4 Adequate reinforcement provided to resist shear loads in anchors? No
Effective anchor embedment depth (in.) = hef 21.00 = hef ECCENTRICITY
Thickness of member in which anchor is anchored, (in.) = h 60.00 = h Eccentricity of tensile force on group of tensile anchors (in.)
Number of anchors in tension = n(tension) = 2 eN ' = 0 (0=single anchor)
Number of anchors in shear = n(shear) = 4 Eccentricity of shear force on group of anchors (in.)
CONCRETE FAILURE AREAS (Note ev' must be less than s perpendicular to shear) eV'= 0
Do you want to manually input the value of An? No
no EDGE DISTANCES AND SPACING
An = 200 TENSION SHEAR
Note: Units for An and Av are sq. in.
An= 3906 Edge Distance, in. Spacing, in. Edge Distance, in. Spacing, in.
Do you want to manually input the value of Av? No
no c1 = 32.00 c3 = 46.00 s1 = 0.00 c1 = 30.00 s2 = 6.00
Av = 2000 c2 = 28.00 c4 = 28.00 s2 = 6.00 c2 = 28.00
c1
NU Av = 2790 c4 = 28.00
1.5hef c1 = edge distance in direction of Vn (perp.)
1.5hef 35o
1
1.5c
VU (perpendicular) c1
c1 s1 c3
1
VU
h or 1.5c
hef
4
1
VU (parallel)
4
c 2s 2 c
1.5c
35o
VU c1
c 2 s 2c
c4 s2 c2
Breakout cone for tension Breakout cone for shear
SUMMARY OF RESULTS
DUCTILITY INTERACTION OF TENSILE AND SHEAR FORCES RESULTS
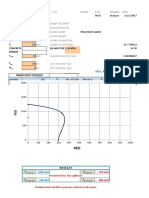
Tensile ductility not required by user input f Nn = 116.6 kips >= Nu = 116.0 kips
Shear ductility not required by user input fVn = 75.6 kips >= Vu = 0.0 kips
Nu/(fNn) + Vu/(fVn) = 0.99 + 0.00 = 0.99 <=1.2 OK
116.60
Process Industry Practices
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet PIP STE05121
Revision 2, November 2003 Output January 2003
Company PIP Sheet 1 of 1
Project Project # PIP STE05121
Subject Example 1
Name Date 12/12/2002
Checked by Check Date 7/10/2003
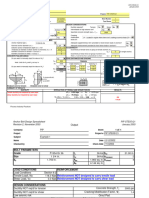
BOLT PARAMETERS
Grade F1554 Gr 36 fy 36 ksi hef 21.00 in.
Size 1 3/4 in. fut 58 ksi n(tension) 2
do 1.750 in. Ase 1.900 sq. in. n(shear) 4
Ab 4.144 sq. in.
LOAD CONDITIONS REINFORCEMENT
Load Conditions Section 9.2
Tensile Load\, Nu 116.0 kips Reinforcement NOT designed to carry tensile load
Shear Load, Vu 0.0 kips Reinforcement NOT designed to carry shear load
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Ducitlity NOT req'd for tension Concrete Strength, f'c 3000 psi
Ducitlity NOT req'd for shear Cracking Modification Factor, Y7 1.4
Low seismic risk Grout Pad
Eccentricities eN' = 0.00 in. eV' = 0.00 in.
DESIGN FOR TENSION DESIGN FOR SHEAR
Steel Strength Ns 220.4 kips Steel Strength Vs 211.6 kips
Concrete breakout strength of
Concrete breakout anchor(s), Perpendicular to
strength of anchor(s) Ncb or Ncbg 166.6 kips edge Vcb or Vcbg 108.0 kips
Pullout strength of Concrete pryout strength of
anchors (s) nNpn 278.5 kips anchor(s) Vcp 333.2 kips
Concrete sideface
blowout strenght of Nsb or Nsbg
headed anchor(s) (governing) NA
EDGE DISTANCES, SPACINGS, SUMMARY OF RESULTS
FAILURE AREAS TENSION
Steel Capacity 165.3 kips
Tension Shear Concrete Capacity 116.6 kips
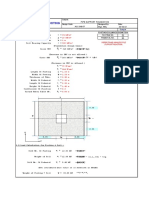
c1 s1 c3 c1 32.00 in. 30.00 in. Tensile ductility not required by user input
c2 28.00 in. 28.00 in. SHEAR
4
c 2 s 2c
c3 46.00 in. Steel Capacity 137.5 kips
c4 28.00 in. 28.00 in. Concrete Capacity 75.6 kips
s1 0.00 in. Shear ductility not required by user input
s2 6.00 in. 6.00 in. INTERACTION OF TENSILE AND SHEAR FORCES
An or Av 3906.0 sq. in. 2790.0 sq. in. 116.6 kips = fNn* >= Nu = 116.0 kips
Calculated Calculated 75.6 kips = fV n
*
>= Vu = 0.0 kips
Nu/(fNn*) + Vu/(fVn*) = 0.99 + 0.00 <= 1.2
OK
*Multiplied by 0.75 if intermediate or high seismic area
Process Industry Practices
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet PIP STE05121
Revision 2, November 2003 January 2003
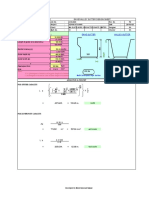
c1 s1 c3
4
Direction of load
c
2
s
c2
Notes:
1. Determinations concerning fitness for purpose and particular matters or application of the Practice
to particular project or engineering situations should not be made solely on information contained
in these materials. All Practices or guidelines are intended to be consistent with applicable laws
and regulations including OSHA requirements. To the extent these Practices or guidelines should
conflict with OSHA or other applicable laws or regulations, such laws or regulations must be
followed. Consult an appropriate professional before applying or acting on any material contained
in or suggested by the Practice.
2. This spreadsheet has been developed utilizing ACI 318-02 Appendix D and PIP STE05121. It will
give shear and tensile capacities of an anchor or anchor group and the concrete around the
anchor or anchor group. It will also let the user know if the anchor configuration is ductile (refer to
PIP STE05121, section 6). The user needs to use this spreadsheet in combination with ACI 318-
02 Appendix D and PIP STE05121. This spreadsheet merely saves the user time in laborious
calculations but is no substitute for the engineer’s expertise.
3. The spreadsheet works for any number of bolts in tension and/or shear.
4. For 1, 2, or 4 bolts in a rectangular pattern, this spreadsheet will calculate A n and Av. For other
numbers of bolts and bolt patterns, the user needs to calculate and input A n and Av.
5. For tensile loads, if the user has 1, 2, or 4 bolts in a rectangular pattern, the user should provide c 1
through c4 and s1 and s2. For 1 bolt, s1 and s2 should be input as 0 (zero). For 2 bolts, either s1 or
s2 should be input as 0. Note: Only the bolts in tension shall be considered. If there are bolts in
shear only, ignore them.
6. For shear loads c1, c2, c4 and s2 are required inputs. c1 could be different for shear than for
tension. Note: Only the bolts in shear shall be considered. If there are bolts in tension only ignore
them. If there is only one bolt (or 2 bolts in line of load), s2 = 0.
7. If the user is using rebar to resist either tensile or shear loads applied to the anchor, this needs to
be indicated in the spreadsheet. The rebar needs to develop the required strength in accordance
with ACI 318. See Section 7 of PIP STE05121.
8. If reinforcement is provided to resist tension, then the concrete breakout strength of the anchor in
tension will not be used in checking the anchor size. Furthermore, if a ductile material is specified
for the anchor, the anchor is automatically ductile in tension.
9. If reinforcement is provided to resist shear, then the concrete breakout strength of the anchor in
shear and the concrete pryout strength of the anchor in shear will not be used in checking the
anchor size. Furthermore, if a ductile material is specified for the anchor, the anchor is
automatically ductile in shear.
Process Industry Practices
PIP STE05121
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet
Revision 2, November 2003
Calculations January 2003
Selected Bolt: 1 3/4 in. F1554 Gr 36 No. of Bolts
do = 1.750 in. Ase = 1.900 sq. in. fy = 36 ksi nt(tension) = 2
hef = 21.0 in. Abrg = 4.144 sq. in. fut = 58 ksi nv(shear) = 4
Note: Figures in parenthesis and in red refer to equations or paragraphs in ACI 318-02, Appendix D.
Steel Strength in Tension: Ns = nAsefut (fut < 1.9fy and fut < 125 ksi) = 220.4 kips (D-3)
1. Concrete breakout strength of anchor in tension:
hef(max) = 21.0 in. Use hef = 21.0 in. (D.5.2.3)
AN(calc) = 3906.0 sq. in. Use AN = 3906.0 sq. in. ANo = 9hef2 = 3969.0 sq. in. (D-6)
Y1 = [1/(1 + 2eN'/3hef) <= 1] = 1.00 (D-9)
cmin = 28.0 in. Y2 = 0.967 (D-10 or D-11)
Y3 = 1.25 (D.5.2.6) Nb
= 140.1 kips (D-7 or D-8)
Ncb or Ncbg = (AN/ANo)Y1Y2Y3Nb = 166.6 kips (D-4 or D-5)
2. Pullout strength of anchor in tension:
Y4 = 1.4 (D.5.3.6) Np = Abrg8f'c = 99.5 kips (D-13)
For n bolts, nNpn = nY4Np = 278.5 kips (D-12)
3. Concrete side-face blowout strength of headed anchor in tension:
c = 32.0 in. c2 = 28.0 in. c2/c = 1.14
Side-face blowout strength does not apply.
Nsb = 160c(Abrg)0.5(f'c)0.5 = NA (D-15) Nsb (modified) = NA (D.5.4.1)
Side blowout group effects do not apply.
Nsbg = (1+so/6c)Nsb = NA (D-16) so = 0
Nsb or Nsbg (governing) = NA
Steel Strength of Fastener in Shear:
Vs = nAse(0.6 fut)*(0.8 if there is a grout pad) = 211.6 kips (D-18 & D.6.1.3)
1. Concrete breakout strength of anchor in shear:
Av(calc) = 2790.0 sq. in. Use Av = 2790.0 sq. in. Avo = 4.5c12 = 4050.0 sq. in. (D-22)
AV (max) = nAVo = 16200.0 sq. in. (D.6.2.1) Use min Av = 2790.0 sq. in.
l = min (8do and hef) = 14.0 in. (D.0 - Notation for l)
Process Industry Practices Sheet 4 of 10
PIP STE05121
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet
Revision 2, November 2003
Calculations January 2003
c1 (max) = 30.0 in. (D.6.2.4) Use c1 = 30.00 in.
Vb = 7(l/do)0.2(do)0.5(f'c)0.5(c1)1.5 = 126.3 kips (D-23)
Y5 = 1/(1 + 2eV'/3c1) <= 1 = 1 (D-25)
Y6 = [0.7+0.3(c2/(1.5c1) if c2 < 1.5c1, 1.0 if c2 >= 1.5c1] = 0.887 (D-26 [Errata] or D-27)
Y7 = 1.4 (D.6.2.7)
Vcb or Vcbg = (AV/AVo)Y5Y6Y7Vb = 108.0 kips (D-20 or D-21) Shear perpendicular to edge <------- Applies
243.7 kips (D-20 or D-21) Shear parallel to edge <-------- NA
2. Concrete pryout strength of anchor in shear:
kcp = 2 (D.6.3.1) Ncb = 166.6 kips (D-4)
Vcp = kcpNcb = 333.2 kips (D-28)
Summary of Results:
Tension: f for steel = 0.75 f for concrete = 0.70 (D.4.4)
Steel capacity = fNn[*0.75 if inter. or high seismic risk] = 165.3 kips (D.3.3)
Concrete capacity = fNn[*0.75 if inter. or high seismic risk] = 116.6 kips (D.3.3) Ductility Req'd?
Governing mode of concrete failure: Concrete breakout strength of anchor in tension Tension 0
Shear: f for steel = 0.65 f for concrete = 0.70 (D.4.4)
Steel capacity = fVn[*0.75 if inter. or high seismic risk] = 137.5 kips (D.3.3)
Conc. capacity = fVn[*0.75 if inter. or high seismic risk] = 75.6 kips (D.3.3) Shear 0
Governing mode of concrete failure: Concrete breakout strength of anchor in shear
Interaction of tensile and shear forces: (D.7)
fNn = 116.6 kips fVn = 75.6 kips
0.2fNn = 23.3 kips 0.2fVn = 15.1 kips
Nu = 116.0 kips Vu = 0.0 kips
Nu/(fNn) = 0.99 Vu/(fVn) = 0.00
Applicable equation = (D-1) 116.60 OK
Process Industry Practices Sheet 5 of 10
PIP STE05121
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet
Revision 2, November 2003
Calculations January 2003
Supplementary Calculations
Calculation for An and cmax
input If < 1.5 hef, 1, else 0 Find cmax
Edge distance (c1) = 32 0 0
Edge distance (c2) = 28 1 28
Edge distance (c3) = 46 0 0
Edge distance (c4) = 28 1 28
Total sides < 1.5 hef = 2
cmax* = 28
Anchor spacing (s1) = 0
Anchor spacing (s2) = 6
* For pedestals with edge distances on 3 sides less than 1.5h ef, cmax is the largest edge distance of those 3 sides. For pedestals with
4 sides less than 1.5hef, cmax is the second largest edge distance less than 1.5hef. It has been determined that the calculated capacity
of the concrete will decrease by as much as 40% even though AN is being increased if all 4 edge distances are being used. ACI has
been contacted about this problem and is working toward revising this portion of the code. The PIP CSA Function Teaam has agreed
that this meets the intent of the code and is conservative.
Calculate for Av and c1(max)
input If < 1.5 c1, 1, else 0
Edge distance (c1) = 30 1
Edge distance (c2) = 28 1
Edge distance (c4) = 28 1
Total sides < 1.5 c1 = 3
Anchor spacing (s2) = 6
Process Industry Practices Sheet 6 of 10
PIP STE05121
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet
Revision 2, November 2003
Tables January 2003
Minimum Maximum Fy Fut
Anchor Material Type Ductile?
Size Size ksi ksi
1 A307-Type A 4 0 60 Yes
2 A307-Type C 4 36 58 Yes
3 A36 8 36 58 Yes
4 F1554 Gr 36 2 36 58 Yes
5 F1554 Gr 55 2 55 75 Yes
6 F1554 Gr 105 2 105 125 Yes
7 A 193 Gr B7 2.5 105 125 Yes
8 A 193 Gr B7 2.51 4 95 115 Yes
9 A 193 Gr B7 4.01 7 75 100 Yes
10 A354 Gr BC 4 109 125 Yes
11 A354 Gr BD 4 130 150 Yes
12 A449 1 92 120 Yes
13 A449 1.01 1.5 81 105 Yes
14 A449 1.51 3 58 90 Yes
1 A307, Type A, Fu = 60 1
2 A307-Type C, Fu = 58 2
3 A36, Fu = 58 3 Row = 4 Adequate Reinforcement Provided to Resist Tension Loads in Anchors?
4 F1554 Gr 36 4 User's answer = 2 = no
5 F1554 Gr 55 5 fy = 36
MUST CHECK CONCRETE for ....
6 F1554 Gr 105 6 1. Concrete breakout strength of anchor (concrete cone)
7 A193 Gr B7 7 fut = 58 2. Pullout strength of anchor
8 A354 Gr BC 9 3. Concrete side-face blowout strength of headed anchor
9 A354 Gr BD 10 Ductile anchor bolt mat'l The anchor is NOT automatically DUCTILE for tension and
Yes phi factor (D.4.4) = 0.70.
10 A449 14
Bolt Type Used: 4 do = 1.75 inch
Adequate Reinforcement Provided to Resist Shear Loads in Anchors?
Bolt Diameter: 10 do Ase Abrg* hef,min User's answer = 2 = no
1 1/2 0.500 0.142 0.467 6.0 MUST CHECK ....
2 5/8 0.625 0.226 0.671 7.5 1. Concrete breakout strength of anchor (concrete cone)
3 3/4 0.750 0.334 0.911 9.0 2. Concrete pryout strength of anchor (backside of anchor)
4 7/8 0.875 0.462 1.188 10.5 The anchor is NOT automatically DUCTILE for shear and
phi factor (D.4.4) = 0.70.
5 1 1.000 0.606 1.501 12.0
Process Industry Practices Sheet 7 of 10
PIP STE05121
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet
Revision 2, November 2003
Tables January 2003
6 1 1/8 1.125 0.763 1.851 13.5
7 1 1/4 1.250 0.969 2.237 15.0
8 1 3/8 1.375 1.160 2.659 16.5
9 1 1/2 1.500 1.410 3.118 18.0 Load Combinations per
10 1 3/4 1.750 1.900 4.144 21.0 ACI ……....….(D 4.4) 1 Section 9.2
11 2 2.000 2.500 5.316 24.0 (D 4.5) 2 Appendix C
12 2 1/4 2.250 3.250 6.633 27.0 1
13 2 1/2 2.500 4.000 8.095 30.0
14 2 3/4 2.750 4.930 9.703 33.0 Perpendicular or 1
15 3 3.000 5.970 11.456 36.0 parallel to edge? perpendicular to edge
16 4 4.000 11.080 19.923 48.0 (D.6.2.1 (a), (b), or (c)) parallel to edge
* Heavy Hex
Ductility Required for Intermediate or High Ductility Required for
Tension?
2 Seismic Risk?
2 2
Shear?
1 Yes 1 Yes 1 Yes
2 No 2 No 2 No
Built-up Grout Pad? 1 Y7: 4
1 Yes 1 1.0 1.0 - No edge reinf or edge reinf rebar < #4
2 No 2 1.2 1.2 - Edge reinf rebar >= #4
3 1.4 1.4 - Edge reinf rebar >=#4 + stirrups @ <= 4 in.
4 1.4 1.4 - Located in region where there isn't cracking at service loads (ft < fr)
Concrete Failure Modes Capacity (kips)
1 Concrete breakout strength of anchor in tension 166.6 1 Applicable Interaction Equation
2 Pullout strength of fastener in tension 278.5 2 1 (D-1) fNn >= Nu
3 Concrete side-face blowout strength of anchor in tension NA 3 2 (D-2) fVn >= Vu
4 Concrete breakout strength of anchor in shear 108.0 4 3 (D-29) Nu/(fNn) + Vu/(fVn) <= 1.2
5 Concrete pryout strength of anchor in shear 333.2 5
Use Equation 1
Governing Tension Concrete Capacity = 166.6 kips Manual
Concrete Failure Mode for Tension = 1 An 2 Manual Av 2
1 Yes 1 Yes
Governing Shear Concrete Capacity = 108.0 kips 2 No 2 No
Concrete Failure Mode for Shear = 4
Process Industry Practices Sheet 8 of 10
PIP STE05121
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet
Revision 2, November 2003
Glossary January 2003
Abrg bearing area of the head of stud or anchor bolt, in.2
ANo projected concrete failure area of one anchor, for calculation of strength in tension, when not
limited by edge distance
AN projected concrete failure area of an anchor or group of anchors, for calculation of strength in
tension
Ase effective cross-sectional area of anchor, in.2
AVo projected concrete failure area of one anchor, for calculation of strength in shear, when not limited
by corner influences, spacing, or member thickness
AV Projected concrete failure area of an anchor or group of anchors, for calculation of strength in
shear
c distance from center of an anchor shaft to the edge of concrete, in.
c1 distance from center of an anchor shaft to the edge of concrete in one direction, in. Where shear
force is applied to anchor, c1 is in the direction of the shear force. For tension, c1 is the minimum
edge distance.
c2
distance from center of an anchor shaft to the edge of concrete in the direction orthogonal to c 1, in.
cmax the largest of the edge distances that are less than or equal to 1.5h ef, in. (used only for the case of
3 or 4 edges).
cmin the smallest of the edge distances that are less than or equal to 1.5h ef, in.
do shaft diameter of anchor bolt, in.
du diameter of head of stud or anchor bolt or equivalent diameter of effective perimeter of an added
plate or washer at the head of the anchor, in.
eN' eccentricity of normal force on a group of anchors; the distance between the resultant tension load
on a group of anchors and the centroid of the group of anchors loaded in tension, in.
eV' eccentricity of shear force on a group of anchors; the distance between the point of shear force
application and the centroid of the group of anchors resisting shear in the direction of the applied
shear, in.
f'c specified compressive strength of concrete, psi
fct specified tensile strength of concrete, psi
fr modulus of rupture of concrete, psi
ft calculated tensile stress in a region of a member, psi
fy specified yield strength of anchor steel, psi
fut specified tensile strength of anchor steel, psi
h thickness of member in which an anchor is anchored measured parallel to anchor axis, in.
hef effective anchor embedment depth, in.
k coefficient for basic concrete breakout strength in tension
kcp coefficient for pryout strength
l load bearing length of anchor for shear, not to exceed 8d o, in.; hef for anchors with a constant
stiffness over the full length of the embedded section, such as headed studs.
n number of anchors in a group
Nb basic concrete breakout strength in tension of a single anchor in cracked concrete, lb.
Ncb nominal concrete breakout strength in tension of a single anchor, lb.
Ncbg nominal concrete breakout strength in tension of a group of anchors, lb.
Nn nominal strength in tension, lb.
Np pullout strength in tension of a single anchor in cracked concrete, lb.
Process Industry Practices Page 9 of 10
PIP STE05121
Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet
Revision 2, November 2003
Glossary January 2003
Npn nominal pullout strength in tension of a single anchor, lb.
Nsb side-face blowout strength of a single anchor, lb.
Nsbg side-face blowout strength of a group of anchors, lb.
Ns nominal strength of a single anchor in tension as governed by the steel strength, lb.
Nu factored tensile load, lb.
s anchor center-to-center spacing, in.
so spacing of the outer anchors along the edge in a group, in.
t thickness of washer or plate, in.
Vb basic concrete breakout strength in shear of a single anchor in cracked concrete, lb.
Vcb nominal concrete breakout strength in shear of a single anchor, lb.
Vcbg nominal concrete breakout strength in shear of a group of anchors, lb.
Vn nominal strength in shear, lb.
Vp pullout strength in shear of a single anchor in cracked concrete, lb.
Vpn nominal pullout strength in shear of a single anchor, lb.
Vsb side-face blowout strength of a single anchor, lb.
Vsbg side-face blowout strength of a group of anchors, lb.
Vs nominal strength of a single anchor in shear as governed by the steel strength, lb.
Vu factored tensile load, lb.
f strength reduction factor
Y1 modification factor, for strength in tension, to account for anchor groups loaded eccentrically
Y2 modification factor, for strength in tension, to account for edge distances smaller than 1.5h ef
Y3 modification factor, for strength in tension, to account for cracking
Y4 modification factor, for pullout strength, to account for cracking
Y5 modification factor, for strength in shear, to account for anchor groups loaded eccentrically
Y6 modification factor, for strength in shear, to account for edge distances smaller than 1.5h ef
Y7 modification factor, for strength in shear, to account for cracking
Process Industry Practices Page 10 of 10
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Anchor BoltDokument7 SeitenAnchor BoltChris OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zamil Sample CalculationsDokument108 SeitenZamil Sample CalculationsAshraf KhalifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Design Parameters:: Loads: 1Dokument5 SeitenBasic Design Parameters:: Loads: 1Timo SchenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Z-Purlin Design SummaryDokument49 SeitenMetal Z-Purlin Design SummaryKanchan Raja SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4119-Sa-00315523 - A - 01 - Piping Design PremiseDokument20 Seiten4119-Sa-00315523 - A - 01 - Piping Design Premisesivaguruswamy thangaraj100% (1)
- 4119-Sa-00315523 - A - 01 - Piping Design PremiseDokument20 Seiten4119-Sa-00315523 - A - 01 - Piping Design Premisesivaguruswamy thangaraj100% (1)
- 2017.09.12 - Load CombinationDokument22 Seiten2017.09.12 - Load CombinationMos Lugtu100% (1)
- ASCE ASD Load CombinationsDokument2 SeitenASCE ASD Load Combinationsrodriguez.gaytanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4251-FD-00379827 - C - 02 - Piping Layout & DesignDokument22 Seiten4251-FD-00379827 - C - 02 - Piping Layout & Designsivaguruswamy thangaraj100% (1)
- Cold Vent Stack Foundation DesignDokument13 SeitenCold Vent Stack Foundation Designdoverman0% (1)
- Evo Design - Structural Design: Calculation SheetDokument4 SeitenEvo Design - Structural Design: Calculation SheetVij Vaibhav VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor BoltDokument8 SeitenAnchor Boltazwan50% (2)
- Flust-Extended End Plate ConnectionDokument8 SeitenFlust-Extended End Plate ConnectionamachmouchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Girder - Tutorial Midas CivilDokument59 SeitenComposite Girder - Tutorial Midas CivilAndiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Footing DesignDokument1 SeiteCombined Footing Designbalaji gmscNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap MM Master DataDokument19 SeitenSap MM Master DataImran PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolt Shear CapacityDokument12 SeitenBolt Shear Capacityrajedmaglinte0% (1)
- Anchors Reinforcement DesignDokument1 SeiteAnchors Reinforcement DesignManoj JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Design ValuesDokument4 SeitenBasic Design Valuesnenpatel-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Column Base Plate Analysis: Blue Cells Are Input DataDokument1 SeiteSteel Column Base Plate Analysis: Blue Cells Are Input DataHansal Soni0% (1)
- Base Plate Design Excel DesignDokument120 SeitenBase Plate Design Excel DesignOmPrakash33% (3)
- Bolt End Plate Moment ConnectionDokument50 SeitenBolt End Plate Moment ConnectionMarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Bolt Moment Connection DesignDokument12 SeitenFour Bolt Moment Connection DesignDarshan Panchal0% (1)
- Eave Valley Gutter Design Sheet For KspanDokument1 SeiteEave Valley Gutter Design Sheet For KspanBipin AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bracing - DetDokument48 SeitenBracing - DetAUNGPSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alstom Stress 3Dokument36 SeitenAlstom Stress 3sivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Larsen & Toubro Limited - Ecc Division: Engineering Design and Research CentreDokument1 SeiteLarsen & Toubro Limited - Ecc Division: Engineering Design and Research CentreOuseppachan AmbookenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural analysis and design of shedDokument24 SeitenStructural analysis and design of shedvtalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor Bolt - StrengthDokument2 SeitenAnchor Bolt - StrengthSana UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet Revision 0a, April 2003Dokument12 SeitenAnchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet Revision 0a, April 2003Vietanh PhungNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASCE 7-10 - Table 13.6.1Dokument2 SeitenASCE 7-10 - Table 13.6.1Angelique Sutanto100% (1)
- Topographic Wind Factor KZT - ASCE 7-10Dokument2 SeitenTopographic Wind Factor KZT - ASCE 7-10zubairmeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- M24 DIA Anchor Bolt ReinforcementDokument2 SeitenM24 DIA Anchor Bolt ReinforcementYash SutharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 8686 1 2012Dokument54 SeitenIso 8686 1 2012Shahroze Mustafa50% (2)
- ANCHOR BOLT DESIGN DETAILSDokument2 SeitenANCHOR BOLT DESIGN DETAILSkumsbamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post-Installed Rebar Connection BasicsDokument69 SeitenPost-Installed Rebar Connection BasicsJeevan ShendreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Model For Non-Bearing Column SplicesDokument15 SeitenDesign Model For Non-Bearing Column SplicesBobaru MariusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor Bolt and Base PlateDokument4 SeitenAnchor Bolt and Base Platevijaystructural100% (1)
- Steel Stair Case ModelDokument33 SeitenSteel Stair Case ModelOmer HayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roark's FormulasDokument14 SeitenRoark's FormulasDavide FerrareseNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHS Base Plate DesignDokument1 SeiteCHS Base Plate DesignOlusegun S. AjibolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CivilBay Structural Engineering Spreadsheet Tutorial on Anchorage DesignDokument153 SeitenCivilBay Structural Engineering Spreadsheet Tutorial on Anchorage Designhatot100% (1)
- Design of Base PlateDokument258 SeitenDesign of Base PlateDushyantha Jayawardena100% (2)
- 4251-RA-00379913 - D - 01 - Regulatory Compliance PlanDokument42 Seiten4251-RA-00379913 - D - 01 - Regulatory Compliance Plansivaguruswamy thangaraj100% (1)
- M16 Anchor Bolt Design CalculationDokument4 SeitenM16 Anchor Bolt Design CalculationYash SutharNoch keine Bewertungen
- NORSOK L-002 Edition 3, July 2009 PDFDokument36 SeitenNORSOK L-002 Edition 3, July 2009 PDFKarthick VenkatswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANALYSIS OF PRECAST SEGMENTAL CONCRETE BRIDGESDokument32 SeitenANALYSIS OF PRECAST SEGMENTAL CONCRETE BRIDGESMathew Sebastian100% (6)
- Pump Head CalculationDokument6 SeitenPump Head CalculationSHANTANU PATHAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Corbel Design SummaryDokument14 SeitenConcrete Corbel Design Summarynavneet3bawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 - Design of Rigid PavementsDokument32 Seiten8 - Design of Rigid PavementsBAMS100% (1)
- Anchor Bolt Design For Tension and ShearDokument7 SeitenAnchor Bolt Design For Tension and ShearJohn BuntalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 18 3D Tunnel Simulation Using Core ReplacementDokument27 SeitenTutorial 18 3D Tunnel Simulation Using Core ReplacementAleksandar Milidrag100% (1)
- RCC Lab ReportDokument18 SeitenRCC Lab ReportShuvanjan Dahal50% (4)
- STE05121 Spreadsheet REV1 JUL03Dokument11 SeitenSTE05121 Spreadsheet REV1 JUL03arcelitasNoch keine Bewertungen
- VME BrochureDokument20 SeitenVME Brochuresivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miter B1 ADokument55 SeitenMiter B1 AFarid TataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor BoltsDokument10 SeitenAnchor BoltsLex LiwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hollo Bolt Technical Information File029418Dokument8 SeitenHollo Bolt Technical Information File029418Chris FindlayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACPA City Street Pavement DesignDokument8 SeitenACPA City Street Pavement DesignFelipe Fernández100% (1)
- Pressure Equipment Directive - SMOEDokument95 SeitenPressure Equipment Directive - SMOEsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOTAL CAPABILITIES IN THE PIPELINE INDUSTRYDokument34 SeitenTOTAL CAPABILITIES IN THE PIPELINE INDUSTRYseeralan balakrishnan100% (1)
- Appendix 1 - Scope of WorkDokument13 SeitenAppendix 1 - Scope of WorkNimra NaveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Base Plate by EurocodeDokument13 SeitenDesign of Base Plate by EurocodeBharati MajlekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BasePlate 1 Check 46.8TDokument63 SeitenBasePlate 1 Check 46.8TrustamriyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Load Calculation As Per Russia Code PDFDokument7 SeitenWind Load Calculation As Per Russia Code PDFDušan ŠebekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insert Plate CheckDokument6 SeitenInsert Plate CheckSatish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GratingDokument8 SeitenGratingGhanshyam PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Steel Design CalculationsDokument21 SeitenStructural Steel Design CalculationsthiệnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Chequered Plate DesignDokument2 SeitenDesign of Chequered Plate DesignadihindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design FootingsDokument9 SeitenDesign FootingsRupesh KhandekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Girt design calculations for major and minor axis loadsDokument4 SeitenGirt design calculations for major and minor axis loadsvijaystructuralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressor Shelter: Velocity of PressureDokument3 SeitenCompressor Shelter: Velocity of PressurerohitnrgNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASCE 7-05 Seismic Loads - Puerto RicoDokument5 SeitenASCE 7-05 Seismic Loads - Puerto Ricojrjdengineers100% (1)
- Shear Lug Verification Example 12Dokument1 SeiteShear Lug Verification Example 12Nasrul AdliNoch keine Bewertungen
- RHS & SHS Welding DesignDokument1 SeiteRHS & SHS Welding DesignMyat Thu Zar KhineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind On Pipes and TraysDokument4 SeitenWind On Pipes and TraysAnonymous h87K4sTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule of anchor bolts and typical detailsDokument1 SeiteSchedule of anchor bolts and typical detailsShuvam SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eccentric Footing Design Based On ACI 318-14: Input Data Design SummaryDokument3 SeitenEccentric Footing Design Based On ACI 318-14: Input Data Design SummaryFatima tuz ZohraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AISC 13ed - LRFD Bolted Moment Connections Post r4Dokument614 SeitenAISC 13ed - LRFD Bolted Moment Connections Post r4kfischer13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ste05121spreadsheet Anchor Bolt Design PDF FreeDokument10 SeitenSte05121spreadsheet Anchor Bolt Design PDF Freeveeran08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ci33 1112 Pernos de AnclajeDokument10 SeitenCi33 1112 Pernos de AnclajeShadin Asari ArabaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet Revision 0a, April 2003Dokument11 SeitenAnchor Bolt Design Spreadsheet Revision 0a, April 2003Hammad Ahmed KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnchlationDokument5 SeitenAnchlationSurianshah shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor Bolt CalculationsDokument5 SeitenAnchor Bolt Calculationssivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verified Mariner Master Pipe Support Frame Rev 1Dokument36 SeitenVerified Mariner Master Pipe Support Frame Rev 1sivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- AG Base Plate With Moment Axial CompressionDokument4 SeitenAG Base Plate With Moment Axial Compressionsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updating layout per subcon and client feedbackDokument2 SeitenUpdating layout per subcon and client feedbacksivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- DN02 SM L SP 0007 - 01iDokument6 SeitenDN02 SM L SP 0007 - 01isivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updating layout per subcon and client feedbackDokument2 SeitenUpdating layout per subcon and client feedbacksivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1litres/s 3.6m3/h 1bar 14.5psi 1cfm 1.70m3/h 1kg/cm2 0.980665 BarDokument1 Seite1litres/s 3.6m3/h 1bar 14.5psi 1cfm 1.70m3/h 1kg/cm2 0.980665 Barsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivar Aasen Field Development Project - PDQ: G Eneral Arrangement DrawingDokument15 SeitenIvar Aasen Field Development Project - PDQ: G Eneral Arrangement Drawingsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivar Aasen Field Development Project - PDQ: G Eneral Arrangement DrawingDokument15 SeitenIvar Aasen Field Development Project - PDQ: G Eneral Arrangement Drawingsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PipingDokument30 SeitenPipingsivaguruswamy thangaraj100% (1)
- NoBo Singapore Visit MoMDokument6 SeitenNoBo Singapore Visit MoMsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFD CatDokument1 SeitePFD Catsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- SivaDokument1 SeiteSivavickyc1593Noch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Ih 2001Dokument3 Seiten21 Ih 2001sivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- m61 Export Gas Lift GasDokument4 Seitenm61 Export Gas Lift Gassivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- !NA1 '/PS-002' Q All Atta For Ce Var !myq Own of $!na1 HANDLE (2,109) !myq 'Element Not Found' Endhandle $P $!MYQDokument1 Seite!NA1 '/PS-002' Q All Atta For Ce Var !myq Own of $!na1 HANDLE (2,109) !myq 'Element Not Found' Endhandle $P $!MYQsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efaafsdfasdferaeeqer EreerweDokument1 SeiteEfaafsdfasdferaeeqer Ereerwesivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master data upload processDokument1 SeiteMaster data upload processsivaguruswamy thangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarboDur Shear StrengthDokument16 SeitenCarboDur Shear StrengthrogirosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Use of Superabsorbent Polymers To Reduce Cracki - 2014 - Cement and ConcreteDokument8 SeitenThe Use of Superabsorbent Polymers To Reduce Cracki - 2014 - Cement and ConcreteKatarzyna OsowskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETL 1110-2-321 Reliability of Navigation Structures PDFDokument23 SeitenETL 1110-2-321 Reliability of Navigation Structures PDFAnonymous huM1Y0DlLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edoc - Pub - Steam Turbine Inspection Bhel PDFDokument26 SeitenEdoc - Pub - Steam Turbine Inspection Bhel PDFKarthikeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typical Waterstop Properties: Hardness - ASTM D2240Dokument4 SeitenTypical Waterstop Properties: Hardness - ASTM D2240Dicky PramonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomaterials, Artificial Organs and Tissue EngineeringDokument21 SeitenBiomaterials, Artificial Organs and Tissue Engineeringanılcan korkmazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectangualar Plate With Hole - 1Dokument3 SeitenRectangualar Plate With Hole - 1siddesha K MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filler Effect of Pozzolanic Materials On The Strength andDokument11 SeitenFiller Effect of Pozzolanic Materials On The Strength andДанило ГадайчукNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design, Analysis, Fabrication and Testing of A Formula Car ChassisDokument10 SeitenDesign, Analysis, Fabrication and Testing of A Formula Car ChassisSavalia HardikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pba 5 Polyurethane Bonded Revetments Design Manual WWW Arcadis NL IMPORTANTDokument102 SeitenPba 5 Polyurethane Bonded Revetments Design Manual WWW Arcadis NL IMPORTANTvoch007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isoplast Industrial ResinsDokument1 SeiteIsoplast Industrial ResinsJou0411Noch keine Bewertungen
- Policarbonato Macizo Polygal Plazit PDFDokument4 SeitenPolicarbonato Macizo Polygal Plazit PDFnicolas peraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Design Guide For The Refractory Linings Vesselpnd Transfer LinesDokument17 SeitenA Design Guide For The Refractory Linings Vesselpnd Transfer LinesPooria1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nopola 2018Dokument6 SeitenNopola 2018sean.hoffmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Exhaust Valve of An IC Engine by Using Finite Element AnalysisDokument10 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Exhaust Valve of An IC Engine by Using Finite Element AnalysisIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.10.1 - LRFD Pile Design - 2Dokument15 Seiten3.10.1 - LRFD Pile Design - 2Minahil SherazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Materials 9th Edition Hibbeler Solutions ManualDokument57 SeitenMechanics of Materials 9th Edition Hibbeler Solutions Manualjizyfoxyv50% (2)