Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Preboard 2 Geo
Hochgeladen von
LienardOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Preboard 2 Geo
Hochgeladen von
LienardCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
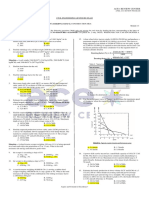
CIVIL ENGINEERS LICENSURE EXAM
(EERC Preboard - MANILA) OCTOBER 2019
HYDRAULICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING 6. Compute the coefficient of permeability of the aquifer
INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for each of the following in m/day.
questions. Mark only one answer for each item by shading the a. 51.82 c. 57.42
box corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer b. 65.09 d. 60.27
sheet provided. STRICTLY NO ERASURES ALLOWED. Use pencil
no. 1 only. 7. Compute the transmissivity of the aquifer in m2/day.
a. 1579 c. 1325
MULTIPLE CHOICE b. 1426 d. 1288
Situation 1: A wedge of wood having a specific gravity of 0.60 is 8. At which soil state can the soil be molded into any
pushed into the water by a 2 kN force. The wedge is 1 m wide. desired shape without rupture?
a. Solid c. Semi-Solid
b. Plastic d. Liquid
9. If water flows in uniformly at the rate of 45 ft 3/s in a
rectangular flume with width of 4 feet and a depth of
1.2 feet, what type of flow is it?
a. Supercritical c. Subcritical
1. Determine the submerged depth of the wedge. b. Laminar d. Turbulent
a. 1.55 m c. 1.69 m
b. 1.34 m d. 1.47 m 10. Water flows in a trapezoidal channel and running full. If
the channel has a discharge of 8 m3/s, find the base
2. Determine the speed of the wedge when it moves width for a most efficient section. n =0.012, S = 0.0008.
upward by 150 mm after the 2 kN load is released. a. 2.02 m c. 1.64 m
a. 0.48 m/s c. 0.95 m/s b. 2.59 m d. 1.77 m
b. 2.47 m/s d. 2.61 m/s
Situation 3: Water is moving in a rectangular channel to
3. What load, in addition to the 2 kN, should be added so have a Froude Number of 3.16. The channel is
that the wedge will be fully submerged? 5 m in width. The depth of flow is 1 m. If the
a. 2.6 kN c. 7.1 kN water undergoes a hydraulic jump:
b. 9.5 kN d. 4.8 kN
11. Determine the depth of flow after the jump.
4. A dam 4 m on top, 18 m at the bottom and 24 m high a. 4m c. 3m
has a water 20 m deep acting on its vertical side. What b. 5m d. 2m
is the factor of safety against overturning? Assume
weight of masonry to be 2400 kg/m3. 12. Find the Froude number after the jump.
a. 3.12 c. 1.87 a. 0.347 c. 0.395
b. 5.59 d. 3.29 b. 0.475 d. 0.565
Situation 2: A 300 mm diameter test well penetrates 27m 13. Compute the velocity after the jump
below the static water table. After 24 hours of a. 3.12 m/s c. 3.41 m/s
pumping at 69 liters/sec. the water level in an b. 2.47 m/s d. 6.45 m/s
observation well at a distance of 95m from
the test well is lowered 0.5m and the other 14. A vertical jet of water thru a nozzle supports a load of
observation well at a distance of 35m from
150 N. The velocity and diameter of the jet at the nozzle
the test well, the drawdown is 1.1m.
tip are 17.46 m/s and 3 cm respectively. Compute the
distance of load from the nozzle tip.
5. What is the rate of flow in m3/day.
a. 6m c. 4m
a. 5961.6 c. 5332.8
b. 8m d. 10 m
b. 6523.4 d. 4321.5
ENGR. ERICKNEIL D. REALUYO, MSCE, ME-1. SO, MP
CIVIL ENGINEERS LICENSURE EXAM
(EERC Preboard - MANILA) OCTOBER 2019
15. An old pipe is to be replaced by a new one with the
same diameter and length. If the friction factor of the 23. A stone weighs 460 N in air. When submerged in water,
new is 2/3 of the old, compute the ratio of flow of the it weighs 300 N. Find the specific gravity of the stone.
new to the old pipe. a. 3.214 c. 1.645
a. 0.85 c. 1.41 b. 2.141 d. 2.875
b. 1.22 d. 0.91
24. A block of wood 0.20 m thick is floating in seawater (s
Situation 4: An open cylindrical tank 30 cm in diameter and = 1.03). The specific gravity of the wood is 0.65. Find the
80 cm high partially filled with water is rotated minimum area of the wooden block to support a man
about its vertical axis at a speed of 240 rpm. weighing 80 kg.
a. 0.215 m2 c. 1.053 m2
16. What would be the depth of water if the tank is brought b. 2.150 m 2
d. 2.310 m2
to rest so that no water will be spilled out?
a. 0.36 m c. 0.44 m 25. An iceberg having a specific gravity of 0.92 is floating
b. 0.32 m d. 0.72 m on salt water of specific gravity of 1.03. If the volume of
ice above the water surface is 1000 m3, what is the total
17. At what speed would it be rotated so that 1.40 liters of volume of ice?
water will be spilled out? a. 9364 m3 c. 10422 m3
a. 242.75 rpm c. 256.30 rpm b. 8402 m 3
d. 11789 m3
b. 245.80 rpm d. 249.65 rpm
26. A tank with vertical sides, 3 m deep, 1.2 m square is
18. At what speed should it be rotated so that the pressure filled to a depth of 2.7 m with water. A cube of wood (s
at the center of the bottom of the tank is zero? = 0.50) measuring 60 cm on an edge is placed inside
a. 256.73 rpm c. 248.97 rpm the container and floats. Find the weight of the volume
b. 258.32 rpm d. 252.22 rpm of water displaced.
a. 2.64 kN c. 5.48 kN
19. A container 10 m wide and 10 m long contains water 2 b. 3.14 kN d. 1.06 kN
m high and is accelerating to the right at a rate of 2.45
m/s2. Find the minimum pressure at the base.
a. 5.65 kPa c. 8.45 kPa
b. 7.37 kPa d. 9.14 kPa Situation 5: The actual velocity in the contracted section of a jet
of liquid flowing from a 2 inches diameter orifice is 28 ft/s under
20. A 1.25 cm diameter orifice in a vertical wall of a tank a head of 15 ft.
under a constant head of 5.50 m discharges 0.45 m3 in
9.50 minutes. Find the coefficient of discharge. 27. Determine the value of the coefficient of velocity.
a. 0.48 c. 0.56 a. 0.805 c. 0.409
b. 0.62 d. 0.68 b. 0.901 d. 0.706
21. A wooden block having a specific gravity of 0.60, 40 mm 28. If the measured discharge is 0.403 ft3/sec, determine the
x 60 mm x 3.5 m long is made to float in water. How coefficient of contraction.
many kilograms of stone having specific gravity of 3.25
a. 0.66 c. 0.56
should be attached at the bottom to make the wooden
b. 0.60 d. 0.54
block float 300 mm exposed to atmosphere?
a. 4.7 kg c. 3.8 kg
29. Determine the coefficient of discharge.
b. 2.9 kg d. 3.2 kg
a. 0.485 c. 0.231
b. 0.387 d. 0.594
22. A body having a specific gravity of 0.70 floats on a liquid
with specific gravity of 0.80. The volume of the body
30. A liquid having a specific gravity of 0.788 flows at 3.2
above the liquid surface is what percent of its total
m/s through a 100 – mm diameter pipe line. Assume f
volume?
= 0.0158. Find the head loss per kilometer of the pipe.
a. 87.5% c. 12.5%
a. 82.46 m c. 65.87 m
b. 90.0% d. 10.0%
b. 78.98 m d. 99.99 m
ENGR. ERICKNEIL D. REALUYO, MSCE, ME-1. SO, MP
CIVIL ENGINEERS LICENSURE EXAM
(EERC Preboard - MANILA) OCTOBER 2019
39. A block of wood floats in water with 20 cm projecting
31. A turbine is rated at 600 hp when the flow of water above the water surface. The same block when placed
through it is 0.61 m3/s. Assuming efficiency of 87%, what in oil (s = 0.80) floats with 15 cm projecting above the
is the head acting on the turbine? oil surface. Find the specific gravity of the block.
a. 98.76 m c. 76.95 m a. 0.45 c. 0.50
b. 85.97 m d. 100.23 m b. 0.64 d. 0.72
32. Neglecting air resistance, determine to what height a Situation 7: A retaining wall 6 m. high is supporting a
vertical jet of water could rise if projected with a velocity horizontal backfill having a dry unit weight of
of 20 m/sec? 1600 kg/m3. The cohesionless soil has an angle
a. 10.34 m c. 20.39 m of friction of 32° and a void ratio of 0.68.
b. 15.76 m d. 18.79 m
40. Determine the Rankine active force on the wall.
Situation 6: An orifice 80 mm in diameter was placed 0.96 m a. 133.67 kN c. 282.60 kN
above the ground at the vertical side of an b. 86.76 kN d. 74.09 kN
upright cylindrical tank 3 m in diameter. When
opened, it hits the ground initially 2 m away 41. Determine the Rankine active force on the wall if water
from the orifice. The initial flow rate was 0.0161 logging occurs at a depth of 3.5 m. from the ground.
m /sec when water surface was 1.4 m above
3
a. 81.1 kN c. 116.3 kN
the orifice. b. 94.8 kN d. 111.8 kN
33. How long will the jet reach the ground? 42. Determine the location of the resultant active force from
a. 0.442 sec c. 0.446 sec the bottom.
b. 0.431 sec d. 0.416 sec a. 1.89 c. 1.74 m
b. 2.08 m d. 2.19 m
34. Find the coefficient of velocity.
a. 0.927 c. 0.735 Situation 8: The laboratory compaction test of a certain type of
b. 0.912 d. 0.863 soil gives a maximum dry density of 1.486
Mg/m3 with an optimum moisture content of
35. Determine the coefficient of discharge. 12.5%. The following are the results of a field
a. 0.736 c. 0.612 unit weight determination test using sand cone
b. 0.546 d. 0.805 method.
Volume of soil excavated from the hole = 0.001337 m3
36. A rectangular channel 6.2 m by 1.2 m deep is lined with Weight of soil from the hole when wet = 2220 g
a smooth stone, well laid and has a hydraulic slope of Weight of dry soil = 1890 g
0.001. Use n = 0.013. What is the capacity of the
channel? 43. Determine the field unit weight of soil.
a. 14.32 m /s3
c. 15.46 m /s3
a. 1.66 g/cc c. 1.78 g/cc
b. 16.43 m3/s d. 11.29 m3/s b. 1.43 g/cc d. 1.27 g/cc
37. What size of new cast iron pipe shall be used to carry 44. Determine the in situ moisture content of soil.
0.284 cubic meters per second with a head loss of 10.56 a. 20.10 % c. 17.46 %
m per kilometer? n =0.019. b. 14.56% d. 11.26 %
a. 649 mm c. 498 mm
b. 304 mm d. 513 mm 45. Determine the relative compaction.
a. 93.90 % c. 98.20 %
38. 1.8 m wide rectangular canal carries a flow of 2.4 m3/s. b. 95.15 % d. 97.33 %
What is the critical depth? b. 0.00321 d. 0.00506
a. 0.433 m c. 0.566 m
b. 0.667 m d. 0.812 m
ENGR. ERICKNEIL D. REALUYO, MSCE, ME-1. SO, MP
CIVIL ENGINEERS LICENSURE EXAM
(EERC Preboard - MANILA) OCTOBER 2019
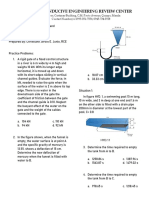
Situation 9: A wooden storage vat full of oil sp. gr. = 0.80
is in the form of a frustum of a cone, 2 m.
diameter at the top , 4 m. diameter at the
bottom and 3 m high. It is provided with 2 steel
hoops, one at the top and one at the bottom.
46. Compute the hydrostatic force on the side of the
container.
a. 171.74 kN c. 177.47 kN
b. 111.47 kN d. 117.74 kN
47. Compute the location of the hydrostatic force measured
from the bottom of the tank.
a. 0.90 m c. 0.85 m
b. 1.17 m d. 1.33 m
48. Compute the force in the bottom hoop.
a. 41.21 kN c. 58.87 kN
b. 85.87 kN d. 42.11 kN
Situation 10: A soil has an unconfined compressive strength of
120 kpa. In a triaxial compression test, a
specimen of the same soil when subjected to
a chamber pressure of 40 kpa failed at an
additional stress of 160 kpa.
49. Determine the cohesion of the soil.
a. 37.50 kpa c. 45.62 kpa
b. 42.42 kpa d. 48.01
kpa
50. Determine the angle of internal friction.
a. 14.90° c. 17.88°
b. 15.22° d. 19.47°
ENGR. ERICKNEIL D. REALUYO, MSCE, ME-1. SO, MP
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fluid Mech May 2021Dokument5 SeitenFluid Mech May 2021Naigell SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyDokument2 SeitenHydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyAngelica RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydau GeoDokument9 SeitenHydau GeoAngelica TecsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evals Fluids Answersheet Nov2021Dokument10 SeitenEvals Fluids Answersheet Nov2021Yedda M IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Dokument9 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Hyd MayDokument13 Seiten2019 Hyd MayChantal Faye GacusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irrigation Problems: Properties of Fluids, Pressures & DamsDokument6 SeitenIrrigation Problems: Properties of Fluids, Pressures & DamsJeiel ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEOTECHNICAL AND HYDRAULICS ENGINEERING EVALUATION EXAMDokument2 SeitenGEOTECHNICAL AND HYDRAULICS ENGINEERING EVALUATION EXAMArianna Denyse Gasgonia100% (1)
- Hydrau 1Dokument3 SeitenHydrau 1Mayya BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil-Engineering-Reviewer-NOV 2011Dokument83 SeitenCivil-Engineering-Reviewer-NOV 2011aomine100% (1)
- Cebu University CE Review 3 quiz on structural steel designDokument3 SeitenCebu University CE Review 3 quiz on structural steel designNikki Marie G OclaritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Open TanksDokument10 SeitenTwo Open TanksMaverick TimbolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeDokument3 SeitenApr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeChrisjohn Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC 3Dokument4 SeitenRC 3Mayya BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Media3116916508017834053 2Dokument7 SeitenLocal Media3116916508017834053 2Ben BenbenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1 Problem 8:: Dy DX y 3e - 5 2 e + 8 LN 5xDokument6 SeitenProblem 1 Problem 8:: Dy DX y 3e - 5 2 e + 8 LN 5xPrince Winderic G. Aclan100% (1)
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam: Eview NnovationsDokument3 SeitenMay 2022 Ce Board Exam: Eview NnovationsKian Inductivo100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDokument5 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hge Mid PreboardDokument7 SeitenHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDokument13 SeitenStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 601Dokument8 Seiten601Allan Añavisa Ostique Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics Coaching 3Dokument21 SeitenHydraulics Coaching 3lenard dongsal100% (1)
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Dokument3 SeitenHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Registered Civil Engineer Licensure ExamDokument8 SeitenRegistered Civil Engineer Licensure ExamMecy Ann RectraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keyanalytic ExamDokument5 SeitenKeyanalytic ExamIvy Vanessa OlapNoch keine Bewertungen
- XVI To XVII PDFDokument28 SeitenXVI To XVII PDFAmira Ramlee0% (1)
- Refresher HYD Part2Dokument2 SeitenRefresher HYD Part2Lionel LapuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringDokument1 SeiteRefresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringMadelyn Oronos100% (1)
- STEEL DESIGN EVALUATIONDokument3 SeitenSTEEL DESIGN EVALUATIONMichael James ll BanawisNoch keine Bewertungen
- HGE Refresher QuestionsDokument8 SeitenHGE Refresher QuestionsCj SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Dokument2 SeitenCE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Lemuel TeopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel 3Dokument3 SeitenSteel 3Mayya Bona100% (1)
- Hyd Ref 7Dokument2 SeitenHyd Ref 7emielyn lafortezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Module 13 - Materials For Construction (Answer Key)Dokument2 SeitenCE Module 13 - Materials For Construction (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH Final PreboardDokument8 SeitenMATH Final PreboardKristelle V. TorrealbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel PDFDokument3 SeitenSteel PDFCj Delos Reyes Macanas100% (1)
- Maximum Stresses On A Pole Subjected To Combined LoadingsDokument2 SeitenMaximum Stresses On A Pole Subjected To Combined LoadingsShiela GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro May. 2017 Prob PDFDokument8 SeitenHydro May. 2017 Prob PDFDroffilc Nav Cm MulihamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics review module on relative equilibrium of fluidsDokument1 SeiteHydraulics review module on relative equilibrium of fluidsYeddaMIlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eval Exam 3 Review Nov 2021Dokument5 SeitenEval Exam 3 Review Nov 2021Iris FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher Module 03 (M2) - Integral CalculusDokument1 SeiteRefresher Module 03 (M2) - Integral CalculusJessa Mae CabusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design 9 Nov 2020 PDFDokument1 SeiteSteel Design 9 Nov 2020 PDFJustine Ejay MoscosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review innovations mechanical engineering exam problemsDokument3 SeitenReview innovations mechanical engineering exam problemsKian InductivoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher GEO Part1Dokument2 SeitenRefresher GEO Part1Lionel LapuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution:: Problem 22 - HydraulicsDokument14 SeitenSolution:: Problem 22 - HydraulicsJan Vindhya Jopson PradesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Properties Practice ProblemsDokument4 SeitenFluid Properties Practice ProblemsRitsu TainakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus Problem SetDokument1 SeiteCalculus Problem SetJoyce DueroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Preboard Exam - MsteDokument8 SeitenSecond Preboard Exam - MsteCzatrina QuintasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDokument36 SeitenFluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingFrancis Philippe CariñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Refresher Module 1Dokument4 SeitenMath Refresher Module 1Nicole RodilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos1 MidtermDokument2 SeitenTos1 MidtermMa.Zyra M. DascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conc 1 - Nov 2020Dokument2 SeitenConc 1 - Nov 2020Glenn CalingasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel column design and analysis problemsDokument12 SeitenSteel column design and analysis problemsDan Casurao100% (1)
- Structural Soln Nov 2018 PDFDokument19 SeitenStructural Soln Nov 2018 PDFrey martiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Preboard Design 2021Dokument2 SeitenFinal Preboard Design 2021Vic NairaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsDokument18 SeitenSoil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsBemzar SamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDokument1 SeiteRefresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsMadelyn OronosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sw3 Answer KeyDokument1 SeiteSw3 Answer KeyPati DukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problem 11 Fluid Mechanics & HydraulicsDokument1 SeitePractice Problem 11 Fluid Mechanics & HydraulicsAbilay FroilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Refresher Course ProblemsDokument4 SeitenHydraulics and Geotechnical Refresher Course ProblemsELMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serra Food CorporationDokument2 SeitenSerra Food CorporationLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphing Unit AssignmentDokument6 SeitenGraphing Unit AssignmentLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Beam Schedule PDFDokument1 Seite06 Beam Schedule PDFLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utilizing Classified Concrete Waste for Subbase in PavementsDokument7 SeitenUtilizing Classified Concrete Waste for Subbase in PavementsLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lienard Data Sheet 01 05 21Dokument1 SeiteLienard Data Sheet 01 05 21LienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Draft (Revised For Pub)Dokument72 SeitenFinal Draft (Revised For Pub)LienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Master FileDokument1 SeiteSite Master FileLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Quiz 1 (Lesson 1) Formulas & ProblemsDokument2 SeitenTrigonometry Quiz 1 (Lesson 1) Formulas & ProblemsLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- LigayaDokument8 SeitenLigayaLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 - Report 3 (REV091219)Dokument16 Seiten22 - Report 3 (REV091219)LienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Koro AgsikapanDokument1 SeiteWhat Is Koro AgsikapanLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7 RA 9184Dokument20 SeitenLecture 7 RA 9184Lienard100% (1)
- APPLEDokument2 SeitenAPPLELienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choral Fest RequirementsDokument2 SeitenChoral Fest RequirementsLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Thesis PDFDokument68 SeitenBest Thesis PDFLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Thesis PDFDokument68 SeitenBest Thesis PDFLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gray 2018 Yp 12 Final DesignDokument1 SeiteGray 2018 Yp 12 Final DesignLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdditionalDokument2 SeitenAdditionalLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cradle of Excellence Online InvitationDokument2 SeitenCradle of Excellence Online InvitationLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authorization LetterDokument1 SeiteAuthorization LetterLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Planning and Transpo LectureDokument60 SeitenUrban Planning and Transpo LectureLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- AppleDokument2 SeitenAppleLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines Water Code SummaryDokument4 SeitenPhilippines Water Code SummaryLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of speech overviewDokument5 SeitenParts of speech overviewLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban - Final ProjectDokument41 SeitenUrban - Final ProjectLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group NameDokument1 SeiteGroup NameLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- PICE-PUPSC30 Champion CertificateDokument3 SeitenPICE-PUPSC30 Champion CertificateLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Thesis PagesDokument19 SeitenSample Thesis Pagesdavy_lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computation StudioDokument2 SeitenComputation StudioLienardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical: ManualDokument24 SeitenTechnical: ManualRytis AmbrasasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obo Commissioning 9Dokument75 SeitenObo Commissioning 998257002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Building 1 Building 2Dokument1 SeiteBuilding 1 Building 2Frederick TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sohail Khan's Construction Experience CVDokument6 SeitenSohail Khan's Construction Experience CVAdnan MunirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 14 MasonryDokument10 SeitenLec 14 Masonryamjad aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akpark: Cover Sheet - ElectricalDokument10 SeitenAkpark: Cover Sheet - ElectricalEngr M.Arshad KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mounting On Concrete DSBDokument4 SeitenMounting On Concrete DSBRolando AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innvo8 Squash Court Panel System: Specification InformationDokument5 SeitenInnvo8 Squash Court Panel System: Specification InformationDaniil TriznoNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Performance Louvers For Curtain Wall SystemsDokument8 SeitenHigh Performance Louvers For Curtain Wall Systemszeynepuzunoglu6Noch keine Bewertungen
- NEC 316.10 Ampacity Table For Cable Conductor SizingDokument1 SeiteNEC 316.10 Ampacity Table For Cable Conductor SizingHumayun RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRCS Cover - To Author PDFDokument1 SeiteDRCS Cover - To Author PDFAJAY SHINDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Staad Training Day 1Dokument116 SeitenStaad Training Day 1Bee AnquilianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 4550-0 1978 - General IntroductionDokument8 SeitenBS 4550-0 1978 - General IntroductionAhmed BabikirNoch keine Bewertungen
- I7529078919 - Pinch Valve For High Viscous FluidsDokument6 SeitenI7529078919 - Pinch Valve For High Viscous Fluidsticaram rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input EchoDokument62 SeitenInput EchoAkhil JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material 2 2021Dokument94 SeitenMaterial 2 2021Buildings Sub Division No. 1 MultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kursus Rekabentuk Sistem Pintu Air Untuk Pengairan Dan SaliranDokument174 SeitenKursus Rekabentuk Sistem Pintu Air Untuk Pengairan Dan SaliranHarith FadhilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hashi Complete WD 30.05.2023Dokument2 SeitenHashi Complete WD 30.05.2023tocheckpapershadow01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Fit-Up Verification: Employee TrainingDokument10 SeitenWeld Fit-Up Verification: Employee TrainingMohammad RizwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid Filling NozzlesDokument16 SeitenLiquid Filling NozzlesFlavioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzhou Tianyu Electric Co., LTD.: KYN31-24 Armored Metal-Enclosed SwitchgearDokument22 SeitenFuzhou Tianyu Electric Co., LTD.: KYN31-24 Armored Metal-Enclosed SwitchgearRusman LumbantoruanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPV135 - 2650002536 - Control Piston Valves and Add-On Pieces Equipamento CATERPILLAR 938KDokument4 SeitenHPV135 - 2650002536 - Control Piston Valves and Add-On Pieces Equipamento CATERPILLAR 938KRodrigues de OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule Q (Quality Requirements)Dokument86 SeitenSchedule Q (Quality Requirements)jeswinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Thermal Expansion Coefficient ConcreteDokument4 SeitenSteel Thermal Expansion Coefficient Concretejohny BavitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOYOTA Yaris 1.33 VVT-i 1NR-FE: Timing Chain: Removal/installationDokument17 SeitenTOYOTA Yaris 1.33 VVT-i 1NR-FE: Timing Chain: Removal/installationMapaqui Mapaqui100% (1)
- Fort Jadhavgadh Urban Design Case StudyDokument8 SeitenFort Jadhavgadh Urban Design Case StudyAishwarya KambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lts-Cvg-P01-16-0005-A4 Daar PDFDokument32 SeitenLts-Cvg-P01-16-0005-A4 Daar PDFSanjoy SanyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapping India DEFDokument74 SeitenMapping India DEFAlaina LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF MC NorskDokument56 SeitenPDF MC NorskIsaac EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fencing, Compound Wall and Gate: by Ar. Pranoti LadDokument49 SeitenFencing, Compound Wall and Gate: by Ar. Pranoti Ladbishal dasNoch keine Bewertungen