Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pathophysio PDF
Hochgeladen von
Donna BellaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pathophysio PDF
Hochgeladen von
Donna BellaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
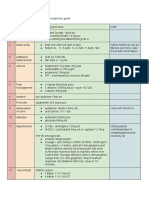
Pathophysiology of AKI
Predisposing Precipitating
factor Etiologies factor
Anti infective
Underlying therapy usage,
Nephrotoxic
renal herbal
substances
insufficiency supplement
usage
Respiratory
Pt. hx. of URTI Acute Kidney Injury Sepsis
failure
Shock/trauma Heart Failure
Causes Causes
Pt. with
Old age (over High blood
hypertension
60 y.o.) Ischemic Toxic acute pressure
stage II
acute tubular tubular
necrosis necrosis
Race / Ethnicity Leads to
Inadequate
Leads to
kidney tissue
perfusion
Nephrotoxic Imbalanced
Ischemic nutrition: less
damage to
necrosis
tubules than body
requirements
Activity
intolerance
Impaired Excess fluid
Easy fatigability, tubular
Weakness of
volume R/T
endothelial Weight loss,
extremities Loss of appetite renal
function
dysfunction
Blood tinged Bilateral pitting
urine pedal edema
+4,
Risk for Increased RBC Swelling on
infection and WBC in both ankles Decreased
urine Onset phase cardiac
Decreased output R/T
CBC-decreased
urinary output alterations in
levels of RBC
and preload
hemoglobin Elevated serum
creatinine
Elevated blood Oliguric
pressure phase Shortness of Etiology
breath
Strong
Ineffective
bounding Pruritic skin Patient
pulses breathing Pathophysiology
symptoms
Oliguric/ lesions present
pattern
Pallor palm and anuric phase on bilateral
palpebral forearms Nursing
Pt. history
conjunctive Diagnosis
Factors
Recovery
phase
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- PUD A Case StudyDokument1 SeitePUD A Case StudyDonna BellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDNQI® - Pressure Injury Training v. 6.0 - Module 1Dokument1 SeiteNDNQI® - Pressure Injury Training v. 6.0 - Module 1Donna BellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDNQI® - Pressure Injury Training v. 6.0 - Module IIDokument1 SeiteNDNQI® - Pressure Injury Training v. 6.0 - Module IIDonna Bella0% (1)
- NDNQI® - Pressure Injury Training v. 6.0 - Module 1Dokument1 SeiteNDNQI® - Pressure Injury Training v. 6.0 - Module 1Donna BellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 10th Monthly Compliance Report On Parkland Memorial HospitalDokument92 Seiten10th Monthly Compliance Report On Parkland Memorial HospitalmilesmoffeitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferraris M La HermeneuticaDokument310 SeitenFerraris M La HermeneuticaantoniomarkusNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABCDEFGHI Systematic Approach To Wound Assessment and ManagementDokument36 SeitenABCDEFGHI Systematic Approach To Wound Assessment and ManagementsaerodinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral Diarrheal Diseases CorrectDokument39 SeitenViral Diarrheal Diseases Correctmehrshad Farahpour Gp5Noch keine Bewertungen
- ST George's Outpatient Services Directory & Referral Guide 2010/2011Dokument116 SeitenST George's Outpatient Services Directory & Referral Guide 2010/2011St George's Healthcare NHS TrustNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PediaDokument2 SeitenNCP PediaAdrian John DecolongonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ey e Commerce PharmacyDokument12 SeitenEy e Commerce PharmacyAdi SudewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methodology and Project Design 4Dokument4 SeitenMethodology and Project Design 4api-706947027Noch keine Bewertungen
- 27Dokument2 Seiten27Helen UgochukwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Psychopathology: The Study of Abnormal Psychology Is TheDokument34 SeitenUnderstanding Psychopathology: The Study of Abnormal Psychology Is TheJudyangaangan03Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ April 2015Dokument15 SeitenMCQ April 2015Sylphana Astharica LawalataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study RopivacaineDokument2 SeitenDrug Study Ropivacainerica sebabillonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Physiotherapy in Antenatal and Post-Natal Care: Dr. Venus Pagare (PT)Dokument74 SeitenRole of Physiotherapy in Antenatal and Post-Natal Care: Dr. Venus Pagare (PT)Haneen Jehad Um Malek100% (1)
- Covid Vaccine Statistics PDFDokument12 SeitenCovid Vaccine Statistics PDFNICOLAENoch keine Bewertungen
- Flare-Ups After Endodontic Treatment: A Meta-Analysis of LiteratureDokument5 SeitenFlare-Ups After Endodontic Treatment: A Meta-Analysis of LiteratureDr.O.R.GANESAMURTHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Design For Trainings - TB - HIVDokument7 SeitenActivity Design For Trainings - TB - HIVSample BakeshopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Drug ChartDokument22 SeitenMaster Drug ChartMahadhir AkmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 69Dokument47 SeitenChapter 69Benjamin SchauerteNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAB I SomatoformDokument3 SeitenBAB I SomatoformDewiRekmawatiPradaswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoid Leukemia in DogsDokument15 SeitenLymphoid Leukemia in Dogstaner_soysurenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daniela GarciaDokument8 SeitenDaniela GarciaSagar ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- NICE Guidelines 2009 - Borderline Personality Disorder Treatment and ManagementDokument41 SeitenNICE Guidelines 2009 - Borderline Personality Disorder Treatment and ManagementbechurinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymyalgia Rheumatic Symptoms Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument2 SeitenPolymyalgia Rheumatic Symptoms Diagnosis and TreatmentHas SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge Deficit and Risk For DiarrheaDokument3 SeitenKnowledge Deficit and Risk For DiarrheaRico Mae ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health Case StudyDokument15 SeitenMental Health Case Studyapi-653708698Noch keine Bewertungen
- Great Critical Care ReliefDokument9 SeitenGreat Critical Care ReliefBenedict FongNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAMPHLETDokument2 SeitenPAMPHLETMarshin Thea CelociaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maxicare List of PhysiciansDokument3.952 SeitenMaxicare List of PhysiciansEdrian Boado75% (4)
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDokument12 SeitenCommon Medical AbbreviationsShania Kate Ledesma ManabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2UDokument47 Seiten2Uucnursingcesdev2008100% (3)