Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
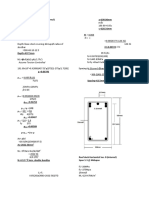
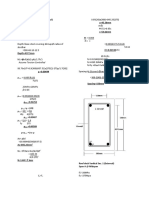
Assignment - Ii
Hochgeladen von
chritOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignment - Ii
Hochgeladen von
chritCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
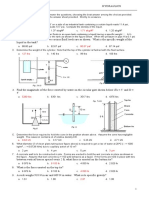
EXAMINATION
Correlation Course
EXAMINATION
8. Determine the tension acting on the lower segment of the string.
INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for each of the following
a. 9.4 kN c. 13.3 kN
questions. Mark only one answer for each item by shading the box
b. 19.7 kN d. 7.4kN
corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer sheet provided.
STRICTLY NO ERASURES ALLOWED. Use pencil no. 1 only.
Situation 4: The 250 mm x 700 mm rectangular wood panel is
formed by gluing together two boards along the 30-
ENGINEERING MECHANICS
degree seam. See figure HKAHY 3.
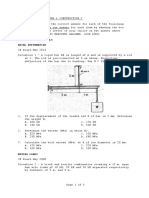
Situation 1: Given that F1 = 600 N and Ø = 30°. See figure MECH
5.1.
9. Determine the normal stress in the glued joint if P = 10 kN.
1. Which of the following most nearly gives the magnitude of the a. 28.6 kPa c. 42.9 kPa
resultant force acting on the eyebolt? b. 49.5 kPa d. 24.7 kPa
a. 750 N c. 662 N
b. 630 N d. 702 N 10. Determine the shear stress in the glued joint if P = 10 kN.
a. 24.7 kPa c. 28.6 kPa
2. Which of the following most nearly gives the direction of the b. 42.9 kPa d. 49.5 kPa
resultant force measured clockwise from the positive x axis?
a. 37.5° c. 24.4° Situation 5: The two pieces of wood are glued together along the
b. 44.6° d. 53.0° plane that is at an angle α with the longitudinal
dimension. Allowable shear stress is 1.468 MPa
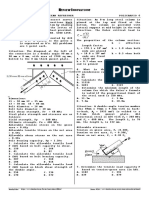
Situation 2: The cantilever truss is loaded. See figure XCBE while for the allowable normal stress it is 0.456 MPa.
99.99. Use α = 30°. See figure TDSM 67.01.
3. Which of the following gives the reaction at E?
a. 85 kN c. 70 kN
b. 60 kN d. 65 kN
4. Which of the following gives the force in member CD?
a. 57.7 kN c. 63.5kN
b. 45.9 kN d. 34.6 kN
11. What should be the dimension w so that the allowable shear
5. Which of the following gives the force in member BD? stress will not be exceeded?
a. 63.5kN c. 57.7 kN a. 130 mm c. 90 mm
b. 34.6 kN d. 45.9 KN b. 110 mm d. 150 mm
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS 12. What should be the dimension w so that the allowable normal
stress will not be exceeded?
a. 130 mm c. 90 mm
Situation 3: The bowstring has an unstretched length of 850 mm b. 110 mm d. 150 mm
and cross-sectional area of 400 mm2. It is recorded
that the stress on the upper segment of the bowstring 13. What should be the value of angle α so that the shear stress is
is 50 MPa. See figure WDRF – 02. maximum?
a. 90° c. 45°
b. 30° d. 60°
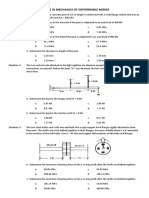
Situation 6: A cylindrical steel pressure vessel 400 mm in
diameter with a wall thickness of 20 mm is subjected
to an internal pressure of 4.5 MPa. Allowable stress
is 120 MPa
14. What is the tangential stress in the steel?
a. 40.5 MPa c. 20.3 MPa
b. 21.4 MPa d. 42.8 MPa
15. What is the longitudinal stress in the steel?
a. 40.5 MPa c. 20.3 MPa
b. 21.4 MPa d. 42.8 MPa
THEORY OF STRUCTURES
Situation 7: Given are structures. See figure GGHTI 21.2.
6. Determine the average normal strain in the string.
a. 0.06604 c. 0.06064
b. 0.05717 d. 0.05771
7. Determine the applied pull of the archer on the arrow.
a. 9.4 kN c. 13.3 kN
b. 19.7 kN d. 7.4 kN
Engr. Erickneil D. Realuyo, CE, ME-1, SO
EXAMINATION
Correlation Course
16. Determine whether the structure is unstable, statically
determinate or statically indeterminate. If it is statically
indeterminate, state the degree of indeterminacy. Refer to
structure a. Situation 9: See figure QPGE 0.01.
a. Statically Determinate
b. Unstable
c. Statically Indeterminate to the 2°
d. Statically Indeterminate to the 3°
17. Determine whether the structure is unstable, statically
determinate or statically indeterminate. If it is statically
indeterminate, state the degree of indeterminacy. Refer to
structure b.
a. Statically Determinate
b. Unstable
c. Statically Indeterminate to the 1°
d. Statically Indeterminate to the 2°
18. Determine whether the structure is unstable, statically
determinate or statically indeterminate. If it is statically
indeterminate, state the degree of indeterminacy. Refer to
structure c.
a. Statically Determinate
b. Unstable
c. Statically Indeterminate to the 2°
d. Statically Indeterminate to the 3°
19. Determine whether the structure is unstable, statically
determinate or statically indeterminate. If it is statically 25. Determine whether truss a is unstable, statically determinate or
indeterminate, state the degree of indeterminacy. Refer to statically indeterminate. If it is statically indeterminate, state the
structure d. degree of indeterminacy.
a. Statically Determinate a. Statically Determinate
b. Unstable b. Unstable
c. Statically Indeterminate to the 3° c. Statically Indeterminate to the 1°
d. Statically Indeterminate to the 4° d. Statically Indeterminate to the 2°
Situation 8: See figure KDST 45.0. 26. Determine whether truss b is unstable, statically determinate or
statically indeterminate. If it is statically indeterminate, state the
20. What is the degree of indeterminacy of frame a? degree of indeterminacy.
a. 5° c. 6° a. Statically Determinate
b. 7° d. 8° b. Unstable
c. Statically Indeterminate to the 4°
21. What is the degree of indeterminacy of frame b? d. Statically Indeterminate to the 5°
a. 7° c. 8°
b. 6° d. 5° 27. Determine whether truss c is unstable, statically determinate or
statically indeterminate. If it is statically indeterminate, state the
22. What is the degree of indeterminacy of frame c? degree of indeterminacy.
a. 7° c. 8° a. Statically Determinate
b. 6° d. 5° b. Unstable
c. Statically Indeterminate to the 1°
23. What is the degree of indeterminacy of frame d? d. Statically Indeterminate to the 2°
a. 7° c. 8°
b. 6° d. 5° Situation 10: Each member of the truss has a cross-sectional area
2
of 400 mm . Use E = 200 GPa. See figure AAB 1.11.
24. What is the degree of indeterminacy of frame e?
a. 17° c. 18°
b. 16° d. 15°
28. Which of the following most nearly gives the horizontal
displacement of B?
a. 0.423 mm c. 0.667 mm
Engr. Erickneil D. Realuyo, CE, ME-1, SO
EXAMINATION
Correlation Course
b. 0.507 mm d. 0.367 mm Situation 14: A triangular beam has a length of 10 meters. It has
an effective depth of 400 mm and a base of 350 mm.
2
29. Which of the following most nearly gives the vertical The steel reinforcement is 3,300 mm . A uniformly
displacement of C? distributed load of 15 kN/m is acting on the beam.
a. 0.461 mm c. 0.0511 mm Use n = 8 and a steel cover of 50 mm.
b. 0.0375 mm d. 0.203 mm
38. Determine the maximum stress that the concrete experiences.
30. Determine the vertical deflection of point E. Each member has a a. 59.00 MPa c. 68.94 MPa
cross-sectional area of 4.5 in.2. E = 29(103) ksi. See figure DKSY b. 55.12 MPa d. 62.50 MPa
2.1.
39. Determine the location of the neutral axis measured from the
apex so that balance condition is achieved. Use f’c = 21 MPa
and fs = 138 MPa.
a. 187.23 mm c. 123.08 mm
b. 134.67 mm d. 141.57 mm
40. Determine the balanced moment capacity.
a. 122.14 KN.m c. 111.05 KN.m
b. 128.55 KN.m d. 119.43 KN.m
Situation 15: A reinforced concrete beam has a width of 300 mm
and a total depth of 450 mm. The longitudinal bars at
the top are 2 – 28 mm Ø and 4 – 32 mm Ø at the
bottom. Concrete strength is f’c = 21 MPa and steel
a. 0.0079 in. c. 0.0121 in. yield strength fy= 275 MPa. Steel cover is 70 mm.
b. 0.0097 in. d. 0.0135 in. 41. What is the transformed moment of inertia?
a. 1874.95 x 106 mm4
Situation 11: Given is a truss. See figure XBDT 3.1. b.
6
1768.19 x 10 mm
4
c. 1916.26 x 106 mm4
d. 2024.58 x 106 mm4
42. What is the moment capacity?
a. 190.16 kN.m c. 153.28 kN.m
b. 114.02 kN.m d. 141.27 kN.m
43. What is the safest uniformly distributed load that the beam can
carry if the length of the beam is 8 meters?
a. 23.77 kN/m c. 19.16 kN/m
b. 14.25 kN/m d. 17.66 kN/m
Situation 16: A rectangular concrete beam has a width of 400 mm
and an effective depth of 700 mm. It is reinforced
with five 28-mm diameter bars for tension only.
Concrete strength is f’c = 21 MPa and steel yield
31. Calculate the vertical displacement of joint A if members AB and strength fy= 275 MPa.
2
BC experience a temperature increase of 200°F. Take A = 2 in. ,
-6 3
α = 6.60(10 )/°F and E = 29(10 ) ksi. 44. Which of the following most nearly gives the depth of the
a. 0.507 in. c. 0.633 in. rectangular compression stress block?
b. 0.487 in. d. 0.583 in. a. 122.95 mm c. 118.58 mm
b. 126.74 mm d. 111.39 mm
32. Calculate the vertical displacement of joint A if member AE is
fabricated 0.5 in. too short. 45. Which of the following most nearly gives the distance of the
a. 1.25 in. c. 1.12 in. neutral axis from the extreme compression concrete?
b. 1.40 in. d. 1.33 in. a. 139.51 mm c. 131.05 mm
b. 149.11 mm d. 144.65 mm
Situation 12: The truss given has diagonals which cannot support
a compressive force. See figure ECKT 2.0. 46. Which of the following most nearly gives the ultimate moment
capacity of the beam?
a. 488.22 kN-m c. 520.57 kN-m
b. 468.51 kN-m d. 542.46 kN-m
Situation 17: A rectangular reinforced concrete beam has a width
of 350 mm and an effective depth of 650 mm. The
beam is reinforced with 8-28 mm diameter tension
bars. Concrete strength is f’c = 20.70 MPa and steel
yield strength is fy = 275 MPa.
47. Which of the following most nearly gives the steel ratio?
a. 2.17% c. 2.35%
b. 2.71% d. 2.53%
33. Determine approximately the force in member ED.
a. 4.0 kN c. 0 48. Which of the following most nearly gives the depth of the
b. 2.4 kN d. 8.0 kN rectangular compression stress block?
a. 274.08 mm c. 219.97 mm
34. Determine approximately the force in member EB. b. 258.79 mm d. 232.97 mm
a. 0 c. 8.0 kN
b. 4.0 kN d. 2.4kN 49. Which of the following most nearly gives the ultimate moment
capacity of the beam?
35. Determine approximately the force in member AB. a. 625.40 kN-m c. 650.46 kN-m
a. 21.3 kN c. 20.0 kN b. 658.38 kN-m d. 634.72 kN-m
b. 18.5 kN d. 0
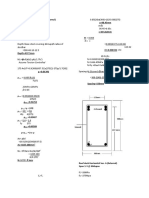
Situation 18: A reinforced concrete beam has a cross section as
REINFORCED CONCRETE DESIGN shown. Use f’c = 30 MPa, fy = 345 MPa and As =
2
2033 mm . The diameter of the rebar is 20 mm and
Situation 13: A reinforced concrete beam has a width of 280 mm the concrete cover is 60 mm.
and an effective depth of 520 mm. It is reinforced for
tension only with 5-28 mm diameter bars. Material
strengths are f’c = 21 MPa and fs = 128 MPa.
Assume n = 9. Use Working Stress Design.
36. Which of the following most nearly gives the location of the
neutral axis from the extreme compression concrete?
a. 276.52 mm c. 236.77 mm
b. 302.85 mm d. 193.07 mm
37. Which of the following most nearly gives the moment capacity of
the beam?
a. 173.82 kN-m c. 138.16 kN-m
b. 111.03 kN-m d. 157.89 kN-m
Engr. Erickneil D. Realuyo, CE, ME-1, SO
EXAMINATION
Correlation Course
a. 547.4 kN c. 273.7 kN
b. 226.2 kN d. 452.4 KN
60. Compute the value of P based on block shear.
a. 1248.0 kN c. 771.2 kN
b. 896.0 kN d. 1208.0 kN
Situation 21: A double-row butt joint is used as a connection. It is
made up of two 210 mm by 12 mm cover plates and
210 mm by 20 mm main plate. The plates are to be
connected by 22 mm diameter rivets. The allowable
stresses are 65 MPa for shear, 83 MPa for tension,
and 135 MPa for bearing. Assume that each hole is 3
mm larger than the rivet diameter.
50. Which of the following most nearly gives the depth of
compression block?
a. 200 mm c. 250 mm
b. 100 mm d. 150 mm
51. Which of the following most nearly gives the compressive
strength of concrete? 61. Calculate the largest value of P that can be applied without
a. 701.39 kN c. 882.45 kN exceeding the allowable stress for shear.
b. 660.78 kN d. 600.56 kN a. 225.3 kN c. 127.6 kN
b. 98.8 kN d. 197.7 kN
52. Which of the following most nearly gives the nominal moment
capacity? 62. Calculate the largest value of P that can be applied without
a. 329 kN.m c. 343 kN.m exceeding the allowable stress for bearing.
b. 313 kN.m d. 365 kN.m a. 285.1 kN c. 237.6 kN
b. 270.0 kN d. 324.0 kN
Situation 19: For the beam below;
f’c = 27 MPa Steel cover = 100 mm 63. Calculate the largest value of P that can be applied without
fy = 270 MPa As = 4 – 32 mm Ø exceeding the allowable stress for tension.
a. 330.8 kN c. 348.6 kN
b. 418.3 kN d. 265.6 kN
Situation 22: A staggered bolted connection is shown in the figure.
The plates are 12 mm thick and 350 mm wide. The
bolts are 25 mm in diameter. Effective bolt hole is 2
mm larger than the bolt diameter. For this problem, a
= 80 mm, b = 40 mm, c = 55 mm, and d = 90 mm.
Refer to figure STDS 89.
53. Which of the following most nearly gives the depth of
compression block?
a. 224.64 mm c. 276.49 mm
b. 308.56 mm d. 336.96 mm
54. Which of the following most nearly gives the compressive
strength of concrete?
a. 728.36 mm c. 868.59 mm
b. 693.14 mm d. 625.04 mm
55. Which of the following most nearly gives the nominal moment 64. Which of the following most nearly gives the effective net width
capacity? for the chain 1-2-3?
a. 297.10 kN.m c. 304.21 kN.m a. 291.22 mm c. 296.30 mm
b. 239.17 kN.m d. 214.35 kN.m b. 279.05 mm d. 288.46 mm
STEEL DESIGN 65. Which of the following most nearly gives the effective net width
for the chain 1-2-3-4?
Situation 20: Two plates each with thickness 20 mm are bolted a. 272.62 mm c. 260.71 mm
together with six 20-mm diameter bolts forming a lap b. 269.45 mm d. 265.38 mm
connection. The hole diameters are 2 mm larger than
the bolt diameters. Allowable shear stress on bolts 66. Which of the following most nearly gives the critical effective net
Fv = 120 MPa. The plates used are A36 steel with Fy area?
2 2
= 248 MPa and Fu = 400 MPa. Use S1 = 50 mm, S2 a. 3,184.50 mm c. 3,271.50 mm
= 100 mm and S3 = 90 mm. See figure STDKO 3. b. 3,233.44 mm2 d. 3,128.50 mm2
Situation 23: Two steel plates, each 400 mm wide and 13 mm
thick, are to be joined together by welded lap splice.
The weld used is E80. See figure STMN 10.
56. Compute the value of P based on yielding of gross area. 67. What is the maximum size of the fillet weld that can be used
a. 455.7 kN c. 565.4 kN according to the NSCP?
b. 760.0 kN d. 891.0 KN a. 11.5 mm c. 10.0 mm
b. 12.0 mm d. 10.5 mm
57. Compute the value of P based on tearing of net area.
a. 584.0 kN c. 864.0 kN 68. What is the effective area of the fillet weld using the maximum
b. 711.6 kN d. 434.5 kN size allowed by the NSCP?
2 2
a. 5938.8 mm c. 6504.4 mm
58. Compute the value of P based on bearing on plates. b. 6787.2 mm
2
d. 5656.0 mm
2
a. 1267.2 kN c. 1444.0 kN
b. 1376.5 kN d. 1152.0 kN 69. What is the maximum load that can be resisted by the weld using
the maximum size allowed by the NSCP?
59. Compute the value of P based on shearing of bolts. a. 1076.31 kN c. 935.92 kN
Engr. Erickneil D. Realuyo, CE, ME-1, SO
EXAMINATION
Correlation Course
b. 982.71 kN d. 1123.10 KN
Situation 24: A 160x100x12 angular section is welded to a
column’s flange. The angle is A36 steel with Fy = 248
MPa. The weld is E80 electrode with Fu = 550 MPa.
The centroid of the angle measured along its long leg
is y = 55 mm. See figure STMMJ 56.
70. Which of the following most nearly gives the design force P?
a. 464.26 kN c. 421.40 kN
b. 442.83 kN d. 453.54 kN
71. Which of the following most nearly gives the total length of the
weld using 11 mm fillet weld?
a. 345.10 mm c. 353.45 mm
b. 361.79 mm d. 328.40 mm
72. Which of the following most nearly gives the value of a?
a. 124.37 mm c. 118.63 mm
b. 112.89 mm d. 121.50 mm
Situation 25: An 80 mm x 80 mm x 9 mm angular section is
welded to an 11-mm thick gusset plate. The angular
member is A36 steel with Fy = 248 MPa and Fu =
400 MPa. The electrode used is E60 with Fu = 414
MPa. The cross sectional area of the angle is 1360
mm2. Dimensions a and b are 70 mm and 140 mm,
respectively. See figure STVXS 09.
73. Determine the value of P based on the gross area.
a. 202.37 kN c. 238.24 kN
b. 217.50 kN d. 195.60 kN
74. Determine the value of P based on the net area if the strength
reduction coefficient is 0.85.
a. 228.00 kN c. 231.20 kN
b. 239.29 kN d. 257.25 kN
75. Determine the value of P based on block shear in the gusset
plate along the weld.
a. 370.80 kN c. 383.78 kN
b. 469.06 kN d. 453.20 kN
Engr. Erickneil D. Realuyo, CE, ME-1, SO
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Design Preboard 3 ADokument8 SeitenDesign Preboard 3 ALester Sarmiento100% (1)
- Practice Problems - Strema Part 3Dokument3 SeitenPractice Problems - Strema Part 3Meverlyn RoqueroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Department: P R E - B O A R D E X A M I N A T I O NDokument8 SeitenCivil Engineering Department: P R E - B O A R D E X A M I N A T I O NBrian Unciano100% (1)
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam: Eview NnovationsDokument3 SeitenMay 2022 Ce Board Exam: Eview NnovationsKian Inductivo100% (1)
- Engineering Achievement Exam ReviewDokument12 SeitenEngineering Achievement Exam ReviewJade Paul D. BesanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapua Institute of Technology Department of CegeDokument15 SeitenMapua Institute of Technology Department of CegeNicole RodilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Preboard Design 2021Dokument2 SeitenFinal Preboard Design 2021Vic NairaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER STATICS EXAMDokument3 SeitenF.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER STATICS EXAMAve de GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Dokument6 SeitenSeac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Joshua John Julio100% (1)
- Tos 2Dokument3 SeitenTos 2Allyanna Elise DiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Module 40 Steel4 Part2 Nov2021Dokument1 SeiteReview Module 40 Steel4 Part2 Nov2021Dream CatcherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringDokument1 SeiteRefresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringMadelyn Oronos100% (1)
- Hge Mid PreboardDokument7 SeitenHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Wala LangDokument3 SeitenWala LangEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolveDokument2 SeitenSolveJea Clarie Mendioro Espinas67% (3)
- UT25Dokument2 SeitenUT25mike reyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topics Problem Set 9 - Structural Theory (Final) 1ST Term 2020-2021Dokument1 SeiteTopics Problem Set 9 - Structural Theory (Final) 1ST Term 2020-2021Levi John Corpin AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Dokument9 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 16Dokument1 SeiteCE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 16Dale MalazzabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsDokument3 SeitenExcellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsGlaiza Marie100% (1)
- Design PreboardDokument9 SeitenDesign PreboardReinyl Angelo Cruz100% (1)
- PREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set ADokument2 SeitenPREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set AEngr. HLDCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural ExDokument14 SeitenStructural ExSheryll de Guzman0% (1)
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADokument2 SeitenQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- Steel 3Dokument3 SeitenSteel 3Mayya Bona100% (1)
- (XPERTZ) Preboard Exam 1ST HGE Nov 2022Dokument9 Seiten(XPERTZ) Preboard Exam 1ST HGE Nov 2022Fely Joy RelatoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Innovations Manila - Cebu - Davao First Evaluation ExamDokument2 SeitenReview Innovations Manila - Cebu - Davao First Evaluation Examaja øNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEEL DESIGN EVALUATIONDokument3 SeitenSTEEL DESIGN EVALUATIONMichael James ll BanawisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review - Hydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Soil MechanicsDokument4 SeitenReview - Hydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Soil MechanicsPaulyne TuganoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kippap Diagnostic Exam May 2022Dokument9 SeitenKippap Diagnostic Exam May 2022Maryrose Aguirre SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrau Geo 1Dokument8 SeitenHydrau Geo 1Marichu Davillo GarbilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil-Engineering-Reviewer-NOV 2011Dokument83 SeitenCivil-Engineering-Reviewer-NOV 2011aomine100% (1)
- Design 1qsy1718 QuestionsDokument9 SeitenDesign 1qsy1718 QuestionsRachel Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Xpertz) Mockboard Exam HGE Nov 2022Dokument8 Seiten(Xpertz) Mockboard Exam HGE Nov 2022Fely Joy RelatoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Board Exam Review QuestionsDokument4 SeitenCE Board Exam Review QuestionsMayya BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 11 of 11Dokument39 SeitenPage 11 of 11John Paulo GregorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAM MAY 2022 ALVAREZ 1Dokument3 SeitenREVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAM MAY 2022 ALVAREZ 1Mayya BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos1 MidtermDokument2 SeitenTos1 MidtermMa.Zyra M. DascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE199 2L 1Q1819 HGE 1st Take PDFDokument8 SeitenCE199 2L 1Q1819 HGE 1st Take PDFCristal Haze VictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Policarpio 6 - Refresher SECDokument2 SeitenPolicarpio 6 - Refresher SECJohn RoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Cebu Forces and Equilibrium ReviewDokument6 SeitenUniversity of Cebu Forces and Equilibrium Reviewjovar jumao-asNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feu Hydraulics PreboardDokument2 SeitenFeu Hydraulics PreboardEla Macabante100% (1)
- Ce 602 Set CDokument9 SeitenCe 602 Set CJade Paul D. BesanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 42 - USD Beams RiDokument2 SeitenModule 42 - USD Beams RiClark SibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument19 SeitenUntitledRojane FloraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Design and Construction ProblemsDokument12 SeitenStructural Design and Construction ProblemsCath100% (1)
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAMDokument3 SeitenREVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAMKian Inductivo100% (1)
- Refresher HYD Part2Dokument2 SeitenRefresher HYD Part2Lionel LapuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esplana RCDDokument4 SeitenEsplana RCDNaigell Solomon100% (1)
- Review Module: - Strength of Materials 1 Part 1Dokument2 SeitenReview Module: - Strength of Materials 1 Part 1John andre MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preboard Examination 1 - Structural Engineering (Set A) : Situation 6Dokument4 SeitenPreboard Examination 1 - Structural Engineering (Set A) : Situation 6Jaycee UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Review - Steel Design Problems SolvedDokument3 SeitenCE Review - Steel Design Problems SolvedLemuel TeopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Beam Design ProblemsDokument14 SeitenConcrete Beam Design ProblemsPrincess Gupo Tañas100% (1)
- Hge Pre-Board QuestionnaireDokument3 SeitenHge Pre-Board QuestionnairegregNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esplana SteelDesign3Dokument1 SeiteEsplana SteelDesign3Naigell SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 3: Eview NnovationsDokument3 SeitenMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 3: Eview NnovationsKian InductivoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Design ReviewDokument4 SeitenTimber Design ReviewalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
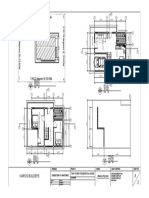
- Civil Engineering Assignment ProblemsDokument3 SeitenCivil Engineering Assignment ProblemschritNoch keine Bewertungen
- 94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetDokument4 Seiten94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetJ O M A RNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuizDokument2 SeitenQuizTheod VilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roofdeck. Hor - Sec.A.Ex Final Na ToDokument9 SeitenRoofdeck. Hor - Sec.A.Ex Final Na TochritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roofdeck. Ver - Sec.3.In Final Na ToDokument7 SeitenRoofdeck. Ver - Sec.3.In Final Na TochritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roofdeck. Hor - Sec.B.In Final Na ToDokument9 SeitenRoofdeck. Hor - Sec.B.In Final Na TochritNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument1 Seite1chritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roofdeck. Ver - Sec.1.Ex Final Na ToDokument7 SeitenRoofdeck. Ver - Sec.1.Ex Final Na TochritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Assignment ProblemsDokument3 SeitenCivil Engineering Assignment ProblemschritNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Way SlabDokument1 SeiteOne Way SlabchritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - IDokument4 SeitenAssignment - IchritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 1Dokument3 SeitenAssignment - 1chritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zhao 2018Dokument16 SeitenZhao 2018chritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Born For YouDokument3 SeitenBorn For YouchritNoch keine Bewertungen
- CariosDokument5 SeitenCarioschritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultimaker PC Technical Data SheetDokument3 SeitenUltimaker PC Technical Data SheetFelipe TeixeiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapt 7Dokument8 SeitenRapt 7tailieuxaydung2019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Creep and High Temperature Failure: OutlineDokument6 SeitenCreep and High Temperature Failure: OutlineAravind PhoenixNoch keine Bewertungen
- NanotecnologiaDokument25 SeitenNanotecnologiaLuiz VendraminiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Casting ProcessesDokument33 SeitenFundamentals of Casting ProcessesIhsan Naufal RidhwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Methods of Al Recyc PDFDokument6 SeitenNew Methods of Al Recyc PDFSrinivasa Rao PulivartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Rise Shear Wall Strength and DuctilityDokument6 SeitenHigh-Rise Shear Wall Strength and Ductilitymr.xinbombayNoch keine Bewertungen
- UltraTech Powergrout NS2Dokument2 SeitenUltraTech Powergrout NS2Savalia HardikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aws HardnessDokument4 SeitenAws HardnessAlanka PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Notes On Underground Excavations in Rock (2006)Dokument134 SeitenClass Notes On Underground Excavations in Rock (2006)Alma Ramić100% (1)
- Advanced - Materials - S-2 Glass - AgyDokument20 SeitenAdvanced - Materials - S-2 Glass - AgyHalcon_PeregrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static FailureDokument40 SeitenStatic FailureFatimah Nik MazlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- H, I, WF Hot Rolled Shape: Sectional Dimension Informative ReferencesDokument2 SeitenH, I, WF Hot Rolled Shape: Sectional Dimension Informative ReferencesSiap Siap100% (2)
- EMT 3253-Solid and Structural Mechanics IDokument1 SeiteEMT 3253-Solid and Structural Mechanics IezraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Acquisition in Mechanical Testing of Materials and It's ComponentsDokument19 SeitenData Acquisition in Mechanical Testing of Materials and It's ComponentsMuhammad FahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005 - How To Make Auxetic Fibre Reinforced CompositesDokument10 Seiten2005 - How To Make Auxetic Fibre Reinforced CompositesSubramani PichandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modified BitumenDokument26 SeitenModified BitumenVizag Roads100% (2)
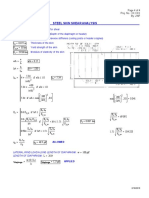
- Steel Skin Shear Analysis: Page 4 of 4 Proj. No.: XX - XXX By: JWFDokument1 SeiteSteel Skin Shear Analysis: Page 4 of 4 Proj. No.: XX - XXX By: JWFHassan Ali SadiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity: Engineering Physics Materials by Praveen N. Vaidya, SDMCET, DharwadDokument9 SeitenElasticity: Engineering Physics Materials by Praveen N. Vaidya, SDMCET, DharwadpraveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories of Failure Under Static LoadDokument44 SeitenTheories of Failure Under Static LoadSnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundación Universidad Del Norte Departamento de Ingenieria Mecanica Materials Science Laboratory Page 1 of 6 Microhardness GuideDokument6 SeitenFundación Universidad Del Norte Departamento de Ingenieria Mecanica Materials Science Laboratory Page 1 of 6 Microhardness GuidetavoberrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shelf Life & GV - PET GuideDokument4 SeitenShelf Life & GV - PET GuideSomasundaram Yamaraja100% (2)
- Photoluminescence and Optical Absorption in Cds Se NanocrystalsDokument3 SeitenPhotoluminescence and Optical Absorption in Cds Se NanocrystalsSIMETNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voided Slab Design Tutorial ENG v1fDokument46 SeitenVoided Slab Design Tutorial ENG v1fhungryghoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- BET Sample Data PDFDokument6 SeitenBET Sample Data PDFAniruddha PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 Module 1 STM & Problems DR - Ajitha PHY1701Dokument15 SeitenClass 9 Module 1 STM & Problems DR - Ajitha PHY1701Abhijit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Properties Uses GuideDokument16 SeitenMaterials Properties Uses GuideMallesh KaruparthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRP Strengthening of Concrete Structures - DesignDokument15 SeitenFRP Strengthening of Concrete Structures - Designshafiullah100% (1)
- Statics and Mechnics of StructuresDokument511 SeitenStatics and Mechnics of StructuresPrabu RengarajanNoch keine Bewertungen