Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Persuasion: Starting Point
Hochgeladen von
Felipe Silva GeraldoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Persuasion: Starting Point
Hochgeladen von
Felipe Silva GeraldoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PERSUASION
Starting Point:
a. Which of your decisions (both personal and work-related) are influenced
by the following, and to what extent?
-family members/ friends/ colleagues
-media/ advertising
-politicians
-celebrities
-your boss
-sales representatives
-statistics
b. Are you easily persuaded? Give examples to explain why/ why not.
c. Can you persuade people easily? Why (not)?
1-) How does advertising manipulate what we think and the choices we
make? Read the text and compare your answers.
Just how easily are you persuaded?
How many forms of advertising do you encounter on your journey to work every
day? Can you remember any of these advertisements? Probably not, but
somehow the images you see will make an impression, whether you are aware
of it or not. Are we taken in by these messages? Of course we are, because it’s
the advertisers’ job to generate demand for the product. But how do they do it?
On a very simplistic level, advertising can be divided into three broad areas
which identify how we are influenced.
1. Need
Can you imagine a life without mobile phones? It wasn’t actually that long
ago (1992) when the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
started, and less than 1% of people globally used a mobile phone.
Clever marketing promoted the consumption of mobile phones by
highlighting their usefulness and the “necessity” of being reachable.
Advertisers targeted our busy lifestyles and sold us a tool that made
communication possible wherever we were. We didn’t actually need mobile
phones, but the need was created and the advertising was then tailored
towards it. The mobile phone industry had taken off.
2. Belonging
The images we are shown by advertisers tap into our fears of becoming an
outsider. Two of the most basic human needs are love and a sense of
belonging, so to show images of families and groups of people having fun
together subconsciouslyplays on our emotions. This powerfully persuasive
tool works especially well on young people.
Take the soft drinks industry, for example, the advertising tends to reinforce
an association between young people and the product, appealing to young
people’s desire to be “cool” and be part of the “in” group. The product itself
then becomes an icon for being “in” and young people are keen to buy into
this image.
3. Esteem
As we get older, our urge to conform becomes less important and we are
subconsciously attracted to things which gain us more respect or elevate our
social status. Advertisers put across this message by using images which
say “if you buy this you’ll be more successful, healthier, younger, a
leader…”, etc. Therefore, the person who has been holding out for
recognition of his or her earning power may buy an expensive car. Often
celebrities are selected to endorse a product because the target group
aspires to live up to this person’s image. Take the L’Oréal advertisements
for expensive hair and beauty products; the celebrities may not all be young,
but they look young and declare (in most languages), that it’s “because I’m
worth it.”
2. Discuss the following questions with a partner:
a. How many forms of advertising can you encounter on your way home
every day?
b. Can you remember any of these advertisements? How much of your
attention can they call?
c. Do you really think we are taken in by these messages?
d. Do you agree with the ideas provided by the text about the three areas
that most influence us? Why (not)?
e. Think of your own examples of advertisements which target the areas of
need, belonging or esteem and discuss how they achieve this.
f. Have you ever bought any product taking into consideration their
advertisement or the “power” the product showed? What was it?
3. Make phrases with a verb from A and a preposition/ noun phrase from
B, then match them to definitions 1-13.
A B Definition
To reinforce a demand for 1 encourage people to
buy something
To tailor into 2 to promote a
connection between two
things
To promote (sth) towards a need 3 to create the need for
something
To generate an association between 4 to adapt something to
suit a requirement
To hold across (message/idea) 5 to attract or interest
someone or something
To appeal into 6 to wait until you get
what you want
To live on (emotions) 7 to notice something
and react to it
To play up to 8 to use/ exploit
something for your own
benefit
To be taken up on 9 to be as good as
someone expected
To buy to 10 to believe in
something
To pick in by 11 to be persuaded to
believe something that
might not be true
To put out for 12 to take advantage of
someone’s feeling
To tap consumption of 13 to convey some
information
4. Think about three different advertisements. Discuss what each of them
is trying to achieve using phrases from exercise 3.
5. Listen to an interview with Jacob McFarlane, a marketing specialist.
a. What does he say about how advertisers approach selling s product in the
US?
b. How are Denmark, Russia and China different?
c. Do you agree with him when he says that for many people it is important to
be able to keep up with their neighbors in terms of what they have and what
they own? Why (not)?
d. How does your company market itself? Is it effective? Would you change
anything about their marketing?
e. If you had a company, how would you market that?
6. Complete comments 1-8 using the following words/ phrases from the
listening.
materialistic exploitative consumer profile USP
motivational aspirational status-anxiety market penetration
1. The way Sam is expected to take leave when he goes to trade conferences is
awful. His company just takes advantages of him- it’s so ______________.
2. We need to think again- there’s nothing at the moment to distinguish our
product from the rest on the market. Can’t you come up with an exciting
_____________.
3. Klara has a very ____________ lifestyle. She’s never satisfied with what
she’s got.- she always wants to feel that she’s moving onwards and upwards in
her career and her life.
4. Jean-Noel is totally obsessed with money and possessions- he always wants
to earn more so he can buy the latest designer products. He’s incredibly
_____________.
5. We went to an external sales-training course last week. Absolutely fantastic!
The trainer’s approach was really ____________ and I can’t wait to try out his
ideas.
6. How can we advertise this product when it’s gotsuch a high price tag? It won’t
be normal people we’re targeting- only those who hate to feel they can’t keep
up with the neighbors and who have a high level of ____________
____________.
7. I’ve just heard the competition is developing a similar product to our X1-11.
That means we have to ensure _____________ is aggressive or we’ll miss out.
8. The marketing of the new chocolate bar wasn’t very successful. Surveys
show the under 20s are buying it, but most potential customers aren’t being
reached. We’ll have to analyze our __________ _____________ again.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Messaging Made Simple Course Workbook EditableDokument71 SeitenMessaging Made Simple Course Workbook EditableMahesh Khatri100% (3)
- The Wizard of Ads (Review and Analysis of Williams' Book)Von EverandThe Wizard of Ads (Review and Analysis of Williams' Book)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Ryan Daniel Moran's 12 Months to $1 MillionVon EverandSummary of Ryan Daniel Moran's 12 Months to $1 MillionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Summary of Brian Tracy's The Psychology of SellingVon EverandSummary of Brian Tracy's The Psychology of SellingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- The Ultimate Guide To Influencing Skills by MBM 01bndnDokument15 SeitenThe Ultimate Guide To Influencing Skills by MBM 01bndnsuganya sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Guide: Building a StoryBrand: Clarify Your Message So Customers Will Listen: By Donald Miller | The Mindset Warrior Summary Guide: ( Persuasion Marketing, Copywriting, Storytelling, Branding Identity )Von EverandSummary Guide: Building a StoryBrand: Clarify Your Message So Customers Will Listen: By Donald Miller | The Mindset Warrior Summary Guide: ( Persuasion Marketing, Copywriting, Storytelling, Branding Identity )Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary, Analysis & Review of Jonah Berger's Contagious by InstareadVon EverandSummary, Analysis & Review of Jonah Berger's Contagious by InstareadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dream Buyer Avatar Worksheet: Name: Age: Education: Relationship: Occupation: Job: Income: Location: InterestsDokument7 SeitenDream Buyer Avatar Worksheet: Name: Age: Education: Relationship: Occupation: Job: Income: Location: InterestsJan Michael Lapuz100% (2)
- Unit 3-Communicating in Business Settings SSDokument26 SeitenUnit 3-Communicating in Business Settings SSUmut baran ÖzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jim Collins and Jerry Porras' Built To Last: Successful Habits of Visionary Companies SummaryVon EverandJim Collins and Jerry Porras' Built To Last: Successful Habits of Visionary Companies SummaryBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Final 374 Strategic Communication PresentationDokument34 SeitenFinal 374 Strategic Communication Presentationapi-645225205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper PlanningDokument162 SeitenPaper Planningcamila valenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Matt Mochary, Alex MacCaw & Misha Talavera's The Great CEO WithinVon EverandSummary of Matt Mochary, Alex MacCaw & Misha Talavera's The Great CEO WithinBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Drew Eric Whitman - CA$HVERTISING (Deatailed Book Notes)Dokument47 SeitenDrew Eric Whitman - CA$HVERTISING (Deatailed Book Notes)Kenneth Anderson100% (3)
- Love Is The Killer App PDFDokument5 SeitenLove Is The Killer App PDFTeguh RahardjoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emotional Appeal For Brand BuildingDokument33 SeitenEmotional Appeal For Brand Buildingnirojroutray1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Art of Persuasive StorytellingDokument7 SeitenThe Art of Persuasive StorytellingGabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Graham Cochrane's How to Get Paid for What You KnowVon EverandSummary of Graham Cochrane's How to Get Paid for What You KnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Little Red Book of Selling-WDokument8 SeitenLittle Red Book of Selling-WShashank Nigam100% (1)
- Viral Marketing: Crafting Shareable Content: Exercise HandoutDokument10 SeitenViral Marketing: Crafting Shareable Content: Exercise HandoutFilip-Bogdan Serban-DraganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 11 Sold OutDokument29 SeitenUnit 11 Sold OutMartinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business English Conversation by EFE Putri PeronDokument14 SeitenBusiness English Conversation by EFE Putri PeronBaso IvviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Simone Seol's The Fearless Marketing Bible for Life CoachesVon EverandSummary of Simone Seol's The Fearless Marketing Bible for Life CoachesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gary Vaynerchuk’s #AskGaryVee: One Entrepreneur’s Take on Leadership, Social Media, and Self-Awareness | SummaryVon EverandGary Vaynerchuk’s #AskGaryVee: One Entrepreneur’s Take on Leadership, Social Media, and Self-Awareness | SummaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Will the Real You Please Stand Up: Show Up, Be Authentic, and Prosper in Social MediaVon EverandWill the Real You Please Stand Up: Show Up, Be Authentic, and Prosper in Social MediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral Marketing: Crafting Shareable Content: Exercise HandoutDokument10 SeitenViral Marketing: Crafting Shareable Content: Exercise Handout齊藤 裕之Noch keine Bewertungen
- Attributes of A Good Salesperson - Knowledge, Skills and Attitude - Overall Personality-The Psychology of PersuasionDokument7 SeitenAttributes of A Good Salesperson - Knowledge, Skills and Attitude - Overall Personality-The Psychology of PersuasionSRIDEVI BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inglés Reading PDFDokument1 SeiteInglés Reading PDFAlmudena Ros GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 10 - Unit 6Dokument49 SeitenEnglish 10 - Unit 6Mary Ann Igoy0% (1)
- A Joosr Guide to… Start with Why by Simon Sinek: How Great Leaders Inspire Everyone to Take ActionVon EverandA Joosr Guide to… Start with Why by Simon Sinek: How Great Leaders Inspire Everyone to Take ActionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Intuition For SuccessDokument10 SeitenPractical Intuition For SuccessTarun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advertising Manipulation Video Advanced 082023Dokument5 SeitenAdvertising Manipulation Video Advanced 082023LénaetMarco LenyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Content Marketing for PR: How to build brand visibility, influence and trust in today’s social ageVon EverandContent Marketing for PR: How to build brand visibility, influence and trust in today’s social ageBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Summary of Patrick Bet-David's Your Next Five MovesVon EverandSummary of Patrick Bet-David's Your Next Five MovesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Click Here For The Full BookDokument43 SeitenClick Here For The Full Bookrakesh4233Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing StrategiesDokument6 SeitenMarketing StrategiesEster Benicio BenicioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Andrew Macarthy's 500 Social Media Marketing TipsVon EverandSummary of Andrew Macarthy's 500 Social Media Marketing TipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Conscious Self Marketing To Convince OthersDokument18 SeitenUsing Conscious Self Marketing To Convince OthersMeereya100% (1)
- How Advertising Manipulates Your Choices and Spend Reading Comprehension Exercises - 68683Dokument1 SeiteHow Advertising Manipulates Your Choices and Spend Reading Comprehension Exercises - 68683makaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Tom Kelley & David Kelley's Creative ConfidenceVon EverandSummary of Tom Kelley & David Kelley's Creative ConfidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Donald Miller & Dr. J.J. Peterson's Marketing Made SimpleVon EverandSummary of Donald Miller & Dr. J.J. Peterson's Marketing Made SimpleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brand Purpose - The Definitive GuideDokument175 SeitenBrand Purpose - The Definitive GuideGabriel SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 2023Dokument14 SeitenModule 2 2023ubpi eswlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dewi Handariatul Mahmudah 20231125 122603 0000Dokument2 SeitenDewi Handariatul Mahmudah 20231125 122603 0000Dewi Handariatul MahmudahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service ExcellenceDokument19 SeitenService ExcellenceAdipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment MS-28 Course Code: MS - 28 Course Title: Labour Laws Assignment Code: MS-28/TMA/SEM - II /2012 Coverage: All BlocksDokument27 SeitenAssignment MS-28 Course Code: MS - 28 Course Title: Labour Laws Assignment Code: MS-28/TMA/SEM - II /2012 Coverage: All BlocksAnjnaKandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marking SchemeDokument8 SeitenMarking Schememohamed sajithNoch keine Bewertungen
- People vs. PinlacDokument7 SeitenPeople vs. PinlacGeenea VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Pricing of Deposit ServicesDokument37 SeitenDesign and Pricing of Deposit ServicesThe Cultural CommitteeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romeo and Juliet: Unit Test Study GuideDokument8 SeitenRomeo and Juliet: Unit Test Study GuideKate Ramey100% (7)
- Ethical Dilemma Notes KiitDokument4 SeitenEthical Dilemma Notes KiitAritra MahatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merger and Acquisition Review 2012Dokument2 SeitenMerger and Acquisition Review 2012Putri Rizky DwisumartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Study GuideDokument3 SeitenChapter 6 Study GuidejoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- S0260210512000459a - CamilieriDokument22 SeitenS0260210512000459a - CamilieriDanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flipkart Labels 23 Apr 2024 10 18Dokument4 SeitenFlipkart Labels 23 Apr 2024 10 18Giri KanyakumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConsignmentDokument2 SeitenConsignmentKanniha SuryavanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test 01 - Part ADokument9 SeitenPractice Test 01 - Part AJose David Pascacio GrandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment LA 2 M6Dokument9 SeitenAssignment LA 2 M6Desi ReskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample of Notarial WillDokument3 SeitenSample of Notarial WillJF Dan100% (1)
- WHO in The Philippines-Brochure-EngDokument12 SeitenWHO in The Philippines-Brochure-EnghNoch keine Bewertungen
- NegotiationDokument29 SeitenNegotiationNina LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ,وثيقة تعارفDokument3 Seiten,وثيقة تعارفAyman DarwishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profil AVANCER FM SERVICES SDN BHDDokument23 SeitenProfil AVANCER FM SERVICES SDN BHDmazhar74Noch keine Bewertungen
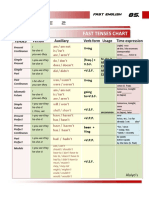
- Table 2: Fast Tenses ChartDokument5 SeitenTable 2: Fast Tenses ChartAngel Julian HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Behaviour Monitoring (ABM)Dokument2 SeitenAutomated Behaviour Monitoring (ABM)prabumnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReinsuranceDokument142 SeitenReinsuranceabhishek pathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gogo ProjectDokument39 SeitenGogo ProjectLoyd J RexxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Louis I Kahn Trophy 2021-22 BriefDokument7 SeitenLouis I Kahn Trophy 2021-22 BriefMadhav D NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authors & Abstract Guideline V-ASMIUA 2020Dokument8 SeitenAuthors & Abstract Guideline V-ASMIUA 2020tiopanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DESIGNATIONDokument16 SeitenDESIGNATIONSan Roque ES (R IV-A - Quezon)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Account Number:: Rate: Date Prepared: RS-Residential ServiceDokument4 SeitenAccount Number:: Rate: Date Prepared: RS-Residential ServiceAhsan ShabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocampo - v. - Arcaya-ChuaDokument42 SeitenOcampo - v. - Arcaya-ChuaChristie Joy BuctonNoch keine Bewertungen