Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Main Blod.v. of The Head - PDF - 73586
Hochgeladen von
ةخاشةثي0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten5 SeitenThe main arteries of the head and neck include the common carotid artery, external carotid artery, internal carotid artery, and subclavian artery. The external carotid artery divides into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery behind the neck of the mandible. Its branches supply the face and scalp. The internal carotid artery ascends through the neck and enters the cranial cavity, supplying the brain and giving rise to the ophthalmic artery which supplies the eye and surrounding structures. The main veins of the head and neck include the internal jugular vein, which drains the brain and neck into the subclavian vein, and the external jugular vein, which drains parts of the face and neck.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Main blod.v. of the head.pdf_73586
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe main arteries of the head and neck include the common carotid artery, external carotid artery, internal carotid artery, and subclavian artery. The external carotid artery divides into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery behind the neck of the mandible. Its branches supply the face and scalp. The internal carotid artery ascends through the neck and enters the cranial cavity, supplying the brain and giving rise to the ophthalmic artery which supplies the eye and surrounding structures. The main veins of the head and neck include the internal jugular vein, which drains the brain and neck into the subclavian vein, and the external jugular vein, which drains parts of the face and neck.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten5 SeitenMain Blod.v. of The Head - PDF - 73586
Hochgeladen von
ةخاشةثيThe main arteries of the head and neck include the common carotid artery, external carotid artery, internal carotid artery, and subclavian artery. The external carotid artery divides into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery behind the neck of the mandible. Its branches supply the face and scalp. The internal carotid artery ascends through the neck and enters the cranial cavity, supplying the brain and giving rise to the ophthalmic artery which supplies the eye and surrounding structures. The main veins of the head and neck include the internal jugular vein, which drains the brain and neck into the subclavian vein, and the external jugular vein, which drains parts of the face and neck.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
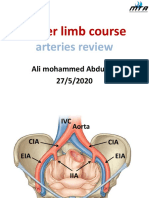
Main arteries of the head & neck
- The main arteries of the head & neck are :
1- Common carotid artery.
2- External carotid artery.
3- Internal carotid artery.
4- Subclavian artery.
Common carotid artery
- The right common carotid artery arises from the brachiocephalic trunk
( innominate artery).
- The left common carotid artery arises from the arch of the aorta in the thorax.
- They ascend on the side of the neck and at the upper border of the thyroid
cartilage , they divide into external and internal carotid arteries.
External carotid artery
- It ascends upwards & enter the parotid gland.
- It divides behind the neck of the mandible into two terminal branches :
a) Superficial temporal artery.
b) Maxillary artery.
Branches :
1- Superior thyroid artery, it supplies the thyroid gland.
2- Ascending pharyngeal artery.
3- Lingual artery supplies the tongue.
4- Facial artery supplies the face.
5- Occipital artery.
6- posterior auricular artery supplies the scalp.
7- Superficial temporal artery , it ascends upwards & supplies the scalp.
8- Maxillary artery, it runs forwards and enters the infratemporal fossa.
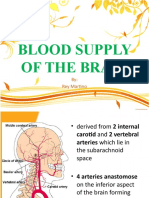
Internal carotid artery
- It ascends in the neck to the base of the skull.
- It enters the cranial cavity through the carotid canal.
- It has no branches in the neck.
- It supplies the brain in the cranial cavity, and gives ophthalmic artery which
enters the orbit to supply the eyeball, lacrimal gland, nose and gives
supratrochlear & supraorbital branches which exit from the orbit in the face
where they supply the forehead & anterior part of the scalp.
Main veins of the head & neck
1- Internal jugular vein (I.J.V.) :
- It begins just below the jugular foramen, as a continuation of the sigmoid
sinus in the cranial cavity.
- It descends in the neck and unites with the subclavian vein behind the
medial end of the clacicle to form the brachiocephalic vein (innominate
vein).
- Tributaries :
1- Common facial vein .
2- Pharyngeal veins.
3- Lingual vein.
4- Superior thyroid vein.
5- Middle thyroid vein.
2- Retromandibula vein:
- It is formed by union of superficial temporal vein and maxillary vein, and
descends in the parotid gland where it ends by dividing into anterior and
posterior divisions.
3- facial vein:
- It is formed by union of supratrochlear and supraorbital veins at the
medial angle of the eye, then it descends in the face where it unites with
the anterior division of the retromandibular vein to form the common
facial vein , which ends in the internal jugular vein.
4- External jugular vein:
- It is formed by union of the posterior auricular vein and posterior division
of the retromandibular vein, then descends obliquily on the sternomastoid
muscle where it ends in the subclavian vein.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- UlangkajiDokument15 SeitenUlangkajiYusnizan Mohamad YusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of BrainDokument38 SeitenBlood Supply of BrainKaif Khan100% (2)
- Blood Suppply of Head and NeckDokument19 SeitenBlood Suppply of Head and NeckGanapathyGaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The Neck and HeadDokument56 SeitenBlood Supply of The Neck and HeadAdrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of BrainDokument12 SeitenBlood Supply of BrainSharon Rose Genita Medez100% (1)
- Blood Supply To The BrainDokument5 SeitenBlood Supply To The Brainadaumed0% (1)
- Blood Supply of Head and NeckDokument44 SeitenBlood Supply of Head and NeckPatrick DycocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Arteries of The Head and NeckDokument29 SeitenMajor Arteries of The Head and NeckghanimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Scalp: It Is The Soft Tissuess That Covers The Vault of Skull. ItDokument20 SeitenThe Scalp: It Is The Soft Tissuess That Covers The Vault of Skull. ItEshwar ThiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The Head, Neck and BrainDokument34 SeitenBlood Supply of The Head, Neck and BrainChong Xue FengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokument55 SeitenBlood Supply of The BrainueumanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intracranial Circulation: Presented BY Dr. Shambhu Shah 1 Yr P.G N.M.C THDokument14 SeitenIntracranial Circulation: Presented BY Dr. Shambhu Shah 1 Yr P.G N.M.C THsheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 13 - Arteries of H & NDokument29 SeitenLec 13 - Arteries of H & Nbf28215Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply Head and NeckDokument6 SeitenBlood Supply Head and Necksahana2791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokument63 SeitenBlood Supply of The BrainMartha MulusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of Head Neck16-2-20192nd YearDokument10 SeitenBlood Supply of Head Neck16-2-20192nd Yearmikaelfelix627Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokument32 SeitenBlood Supply of The BrainShimmering MoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arteries of Head and Neck/dental Implants Course by Indian Dental AcademyDokument28 SeitenArteries of Head and Neck/dental Implants Course by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course and Distribution of External and Internal CarotidDokument34 SeitenCourse and Distribution of External and Internal CarotidMarvel NnaemekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Cerebrovascular Anatomy and Nerves of Lower LimbDokument48 SeitenL1 Cerebrovascular Anatomy and Nerves of Lower LimbAshraf NabilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokument37 SeitenBlood Supply of The BrainueumanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmic ArteryDokument23 SeitenOphthalmic ArterySARAVANANNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Blood Supply of The Brain and Spinal CordDokument41 SeitenThe Blood Supply of The Brain and Spinal CordRtvc RoldanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Vessels of Head and NeckDokument19 SeitenBlood Vessels of Head and Neckdemonleolucifer3467Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokument11 SeitenBlood Supply of The Brainneleh grayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bloodsupplyof Head and NeckDokument29 SeitenBloodsupplyof Head and NeckFaisal BalochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokument66 SeitenBlood Supply of The BrainMustafa IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Carotid Artery.: Enter The Skull Through The Foramen Magnum, Then Join To Form The Basilar ArteryDokument17 SeitenInternal Carotid Artery.: Enter The Skull Through The Foramen Magnum, Then Join To Form The Basilar ArteryGeorgie StephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of Head and NeckDokument42 SeitenBlood Supply of Head and NeckhoneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head Lect 2 FaceDokument25 SeitenHead Lect 2 Facebasil145.syrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood SupplyDokument10 SeitenBlood Supplysyed ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokument21 SeitenBlood Supply of The Brainrey martinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arteries of The Head and NeckDokument23 SeitenArteries of The Head and NeckFatima Kh SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The Central Nervus SystemDokument37 SeitenBlood Supply of The Central Nervus Systemaditya febriansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The Brain and Dural Venous SinusesDokument68 SeitenBlood Supply of The Brain and Dural Venous Sinusesأمال داودNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of Head and NeckDokument29 SeitenBlood Supply of Head and NeckBM mugalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscles of The FaceDokument18 SeitenMuscles of The FaceEshwar ThiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Four Cranial Nerves and Cervical PlexusDokument41 SeitenLower Four Cranial Nerves and Cervical PlexusDrAshraf M ElgamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of Cerebral CortexDokument3 SeitenBlood Supply of Cerebral CortexashrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The Brain - ModifiedDokument24 SeitenBlood Supply of The Brain - ModifiedSamo BeainoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Blood Supply of The BrainDokument83 SeitenChapter 3 Blood Supply of The BrainMustafe Nouh Ma�alin QasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of CVS: 4. Blood Vessels of The Head & NeckDokument37 SeitenAnatomy of CVS: 4. Blood Vessels of The Head & Necksultan khabeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head and NeckDokument11 SeitenHead and NeckHisham ChomanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMFS Clinics Exam Notes V Course 2020Dokument330 SeitenOMFS Clinics Exam Notes V Course 2020Vagelis RaftopoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRAINDokument8 SeitenBRAINaravind kishanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Facial Artery: Course and RelationsDokument9 SeitenThe Facial Artery: Course and Relationsvipul51190Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The Brain & Spinal Cord by DR SarwarDokument52 SeitenBlood Supply of The Brain & Spinal Cord by DR SarwarashrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiology: (LECTURE-3)Dokument6 SeitenAngiology: (LECTURE-3)আহানাফ তাহমিদ শব্দNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Scalp & FaceDokument39 SeitenL1 Scalp & FaceMohammad HilmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro 10 Cerebrovascular Supply StudentDokument36 SeitenNeuro 10 Cerebrovascular Supply StudentLeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arterial Blood Supply of The BrainDokument27 SeitenArterial Blood Supply of The BrainFirdaus SeptiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Presentation ScriptDokument2 SeitenAnatomy Presentation ScriptMikey ZhitnitskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Scalp and FaceDokument33 SeitenAnatomy of The Scalp and FaceSaidu TanimuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Suppy of BrainDokument54 SeitenBlood Suppy of BrainZoya MoraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of BrainDokument48 SeitenBlood Supply of BrainAravind VPNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRP 6 - Vascular Supply of The Head and Neck Compres - 240109 - 091500Dokument51 SeitenGRP 6 - Vascular Supply of The Head and Neck Compres - 240109 - 091500kyleaustincalibo8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Facial NerveDokument20 SeitenFacial Nervealmazmulu76Noch keine Bewertungen
- FaceDokument31 SeitenFaceikawaraztutyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scalp: Dr. ManuniDokument18 SeitenScalp: Dr. ManuniVinus VaghelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 ScalpDokument28 Seiten4 ScalpPiniel MatewosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The Head NeckDokument21 SeitenBlood Supply of The Head NeckShadowStormNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arteries ReviewDokument75 SeitenArteries ReviewfakhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument5 SeitenCirculatory SystemMissDyYournurse100% (1)
- Anatomy Heart CadaverDokument6 SeitenAnatomy Heart CadaverDeanne Kathleen VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cavum ThoraxDokument26 SeitenCavum ThoraxMelsya H UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Router7031 NS-01-002 CNV AllAccessGuideDokument20 SeitenRouter7031 NS-01-002 CNV AllAccessGuideAHMAD FUADNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiography AtlasDokument10 SeitenAngiography AtlasNavojit ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Vessels Study GuideDokument2 SeitenBlood Vessels Study GuideAce J. Gonzales100% (2)
- Death Case Presentation StrokeDokument66 SeitenDeath Case Presentation StrokeGrace SihotangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre - Lab # 4 - Circulatory System: Label The Diagrams of Anterior, Posterior and Coronal View of The HeartDokument23 SeitenPre - Lab # 4 - Circulatory System: Label The Diagrams of Anterior, Posterior and Coronal View of The Heartmpetrov_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Extremities Blood SupplyDokument35 SeitenUpper Extremities Blood Supplylovelots1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of HeartDokument51 SeitenBlood Supply of HeartHema Malani MurthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of HeartDokument20 SeitenBlood Supply of HeartPraneethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomi Vaskularisasi MandibulaDokument9 SeitenAnatomi Vaskularisasi MandibulaLouis HutahaeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human CirculationDokument1 SeiteHuman Circulationkanikabhowmick237Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intracranial ArteriesDokument98 SeitenIntracranial ArteriesAgnesthesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9693610Dokument64 Seiten9693610Ljubica NikolicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapa 1: Gusto Neformirano VezivoDokument3 SeitenMapa 1: Gusto Neformirano VezivoazraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 Lecture PresentationDokument88 Seiten22 Lecture PresentationLeilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Arteries of The Head and NeckDokument7 SeitenMajor Arteries of The Head and NeckJack MarlowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of Cerebral CortexDokument3 SeitenBlood Supply of Cerebral CortexashrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle of WillisDokument12 SeitenCircle of Willisveegeer100% (1)
- Blood Supply Head and NeckDokument6 SeitenBlood Supply Head and Necksahana2791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Suppply of Lower LimbDokument8 SeitenBlood Suppply of Lower LimbCamille Magdirila100% (1)
- Heart Labels CardiovascularDokument2 SeitenHeart Labels CardiovascularThurkhesan MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formular EcocardiografieDokument2 SeitenFormular EcocardiografieAlexandra IonesiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arkus Aorta 1Dokument21 SeitenArkus Aorta 1Indah YoulpiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of Upper LimbDokument36 SeitenBlood Supply of Upper Limbteklay100% (2)
- BMS 2 Topik 2 Worksheet 2022Dokument40 SeitenBMS 2 Topik 2 Worksheet 2022Elma Soraya Kania Terapi GigiNoch keine Bewertungen