Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ICT by DR.K.MALLIKARJUNA RAO PDF
Hochgeladen von
dr_mallikarjunaraoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ICT by DR.K.MALLIKARJUNA RAO PDF
Hochgeladen von
dr_mallikarjunaraoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DR K MALLIKARJU RAO, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF COMMERCE
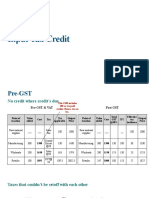
1. What is input tax credit?
Input credit means at the time of paying tax on output, you can reduce the tax you
have already paid on inputs and pay the balance amount.
Here’s how-
When you buy a product/service from a registered dealer you pay taxes on the
purchase. On selling, you collect the tax. You adjust the taxes paid at the time of
purchase with the amount of output tax (tax on sales) and balance liability of tax
(tax on sales minus tax on purchase) has to be paid to the government. This
mechanism is called utilization of input tax credit.
For example- you are a manufacturer: a. Tax payable on output (FINAL
PRODUCT) is Rs 450 b. Tax paid on input (PURCHASES) is Rs 300 c. You can
claim INPUT CREDIT of Rs 300 and you only need to deposit Rs 150 in taxes.
DR K MALLIKARJU RAO, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF COMMERCE
2. Who can claim ITC?
ITC can be claimed by a person registered under GST only if he fulfills ALL the conditions as
prescribed.
a. The dealer should be in possession of tax invoice
b. The said goods/services have been received
c. Returns have been filed.
d. The tax charged has been paid to the government by the supplier.
e. When goods are received in installments ITC can be claimed only when the last lot is received.
f. No ITC will be allowed if depreciation has been claimed on tax component of a capital good
A person registered under composition scheme in GST cannot claim ITC.
3. What can be claimed as ITC?
DR K MALLIKARJU RAO, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF COMMERCE
ITC can be claimed only for business purposes. ITC will not be available for goods or services
exclusively used for: a. Personal use b. Exempt supplies c. Supplies for which ITC is specifically
not available
4. How to claim ITC?
All regular taxpayers must report the amount of input tax credit(ITC) in their monthly GST
returns of Form GSTR-3B. The table 4 requires the summary figure of eligible ITC, Ineligible
ITC and ITC reversed during the tax period. The format of the Table 4 is given below:
A
taxpayer can claim ITC on a provisional basis in the GSTR-3B to an extent of 20% of the
eligible ITC reported by suppliers in the auto-generated GSTR-2A return. Hence, a taxpayer
should cross-check the GSTR-2A figure before proceeding to file GSTR-3B. A taxpayer could
have claimed any amount of provisional ITC until 9 October 2019. But, the CBIC has notified
that from 9 October 2019, a taxpayer can only claim not more than 20% of the eligible ITC
available in the GSTR-2A as provisional ITC. This means taht the amount of ITC reported in the
GSTR-3B from 9 October 2019 will be the total of the actual ITC in GSTR-2A and the
provisional ITC being 20% of the actual eligible ITC in the GSTR-2A. Hence, matching of the
purchase register or expense ledger with the GSTR-2A becomes crucial.
5. Reversal of Input Tax Credit
ITC can be availed only on goods and services for business purposes. If they are used for non-
business (personal) purposes, or for making exempt supplies ITC cannot be claimed . Apart from
these, there are certain other situations where ITC will be reversed.
ITC will be reversed in the following cases-
1) Non-payment of invoices in 180 days– ITC will be reversed for invoices which were not
paid within 180 days of issue.
DR K MALLIKARJU RAO, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF COMMERCE
2) Credit note issued to ISD by seller– This is for ISD. If a credit note was issued by the seller
to the HO then the ITC subsequently reduced will be reversed.
3) Inputs partly for business purpose and partly for exempted supplies or for personal
use – This is for businesses which use inputs for both business and non-business (personal)
purpose. ITC used in the portion of input goods/services used for the personal purpose must
be reversed proportionately.
4) Capital goods partly for business and partly for exempted supplies or for personal use
– This is similar to above except that it concerns capital goods.
5) ITC reversed is less than required- This is calculated after the annual return is furnished. If
total ITC on inputs of exempted/non-business purpose is more than the ITC actually reversed
during the year then the difference amount will be added to output liability. Interest will be
applicable.
The details of reversal of ITC will be furnished in GSTR-3B. To find out more about the
segregation of ITC into business and personal use and subsequent calculations, please visit
our article.
6. Reconciliation of ITC
ITC claimed by the person has to match with the details specified by his supplier in his GST
return. In case of any mismatch, the supplier and recipient would be communicated regarding
discrepancies after the filling of GSTR-3B. Learn how to go about reconciliation through our
article on GSTR-2A Reconciliation. Please read our article on the detailed explanation of the
reasons for mismatch of ITC and procedure to be followed to apply for re-claim of ITC.
7. Documents Required for Claiming ITC
The following documents are required for claiming ITC: 1. Invoice issued by the supplier of
goods/services 2. The debit note issued by the supplier to the recipient (if any) 3. Bill of entry 4.
An invoice issued under certain circumstances like the bill of supply issued instead of tax invoice
if the amount is less than Rs 200 or in situations where the reverse charge is applicable as per
GST law. 5. An invoice or credit note issued by the Input Service Distributor(ISD) as per the
invoice rules under GST. 6. A bill of supply issued by the supplier of goods and services or both.
8. Special cases of ITC
a. ITC for Capital Goods
ITC is available for capital goods under GST.
However, ITC is not available for- i. Capital Goods used exclusively for making exempted goods
ii. Capital Goods used exclusively for non-business (personal) purposes Note: No ITC will be
allowed if depreciation has been claimed on tax component of capital goods.
DR K MALLIKARJU RAO, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF COMMERCE
b. ITC on Job Work
A principal manufacturer may send goods for further processing to a job worker. For example, a
shoe manufacturing company sends half-made shoes (upper part) to job workers who will fit the
soles. In such a situation the principal manufacturer will be allowed to take credit of tax paid on
the purchase of such goods sent on job work.
ITC will be allowed when goods are sent to job worker in both the cases:
1. From principal’s place of business
2. Directly from the place of supply of the supplier of such goods
However, to enjoy ITC, the goods sent must be received back by the principal within 1
year (3 years for capital goods).
c. ITC Provided by Input Service Distributor (ISD)
An input service distributor (ISD) can be the head office (mostly) or a branch office or registered
office of the registered person under GST. ISD collects the input tax credit on all the purchases
made and distribute it to all the recipients (branches) under different heads like CGST,
SGST/UTGST, IGST or cess.
d. ITC on Transfer of Business
This applies in cases of amalgamations/mergers/transfer of business. The transferor will have
available ITC which will be passed to the transferee at the time of transfer of business.
Please visit our other articles discussing ITC under GST in detail.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Industrial Enterprises Act 2020 (2076): A brief Overview and Comparative AnalysisVon EverandIndustrial Enterprises Act 2020 (2076): A brief Overview and Comparative AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Input Tax Credit - GST IndiaDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Input Tax Credit - GST Indiaaslam_bechemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Tax CreditDokument8 SeitenInput Tax CreditPranjal AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 - GST Liability & Input Tax CreditDokument13 SeitenUnit 4 - GST Liability & Input Tax CreditPrathik PsNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST-603 Unit-3Dokument23 SeitenGST-603 Unit-3GauharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer of Input Tax Credit and Its Related Issues: Who Can Claim ITC?Dokument11 SeitenTransfer of Input Tax Credit and Its Related Issues: Who Can Claim ITC?Vishal DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Tax Credit (GST)Dokument16 SeitenInput Tax Credit (GST)ravi.pansuriya07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Input Tax CreditDokument5 SeitenInput Tax CreditSowmya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- H4 - GST at GVC: Spark For The Day "Dokument6 SeitenH4 - GST at GVC: Spark For The Day "Kenny PhilipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Tax CreditDokument16 SeitenInput Tax CreditPreeti SapkalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itc FormsDokument5 SeitenItc FormssaranistudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDT Saar CA Final CH 8 Input Tax Credit by CA Mahesh Gour Handwritten NotesDokument27 SeitenIDT Saar CA Final CH 8 Input Tax Credit by CA Mahesh Gour Handwritten NotesRonita DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCM ChargesDokument9 SeitenRCM Chargesnallarahul86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reverse Charge MechanismDokument10 SeitenReverse Charge Mechanismnallarahul86Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To File GST ITC-01 and FAQsDokument15 SeitenHow To File GST ITC-01 and FAQsYours YoursNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Audit Points GSTDokument14 SeitenInternal Audit Points GSTAJAY K & ASSOCIATESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Practice ReviewDokument9 SeitenExam Practice ReviewSafi NurulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation IiDokument60 SeitenTaxation IiAnkush GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Business Administration, DDU Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur-273009Dokument7 SeitenDepartment of Business Administration, DDU Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur-273009Amit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Payment Under GSTDokument7 SeitenTax Payment Under GSTAbhay GroverNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST - GOODS & Service Tax What Is GSTDokument4 SeitenGST - GOODS & Service Tax What Is GSTsubbiah kailasamNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is GSTDokument31 SeitenWhat Is GSTBIKRAM KUMAR BEHERANoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Notes GSTDokument8 SeitenUnit 3 Notes GSTayusha dasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Tax Credit Under GSTDokument7 SeitenInput Tax Credit Under GSTskumarcwacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Training Report 127411Dokument7 SeitenField Training Report 127411deepak mauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fails To Make Payment To The Supplier Within 180 Days From The Date of Issue of InvoiceDokument58 SeitenFails To Make Payment To The Supplier Within 180 Days From The Date of Issue of InvoiceGiri SukumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) GuidelinesDokument1 SeiteInput Tax Credit (ITC) GuidelinesRahul PurswaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Introduction To GST 1.1 Basics of GST 1.1.1 What Is GST?Dokument13 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction To GST 1.1 Basics of GST 1.1.1 What Is GST?Ashutosh papelNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST Understanding Form GSTR 3BDokument10 SeitenGST Understanding Form GSTR 3BAkhil SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- @GSTMCQ Chapter 5 Input Tax CreditDokument15 Seiten@GSTMCQ Chapter 5 Input Tax CreditIndhuja MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Issues of Compliance in GSTDokument8 SeitenIssues of Compliance in GSTMahiya Ahmad100% (1)
- Cma Inter GR 1 Financial Accounting Ebook June 2021 OnwardsDokument358 SeitenCma Inter GR 1 Financial Accounting Ebook June 2021 OnwardsSarath KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProjectDokument37 SeitenProjectcontactnilkanth123Noch keine Bewertungen
- TaxationDokument7 SeitenTaxationstk2796Noch keine Bewertungen
- BBA 6th Semester Study Material For GST (Unit III)Dokument6 SeitenBBA 6th Semester Study Material For GST (Unit III)Priya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST and It Ppt. GRP.6Dokument32 SeitenGST and It Ppt. GRP.6BANANI DASNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Overview of Maharashtra Value Added Tax: IndexDokument10 SeitenA Overview of Maharashtra Value Added Tax: IndexAdnan ParkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST NotesDokument39 SeitenGST NotesCrick CompactNoch keine Bewertungen
- Registration, Taxation & Accounting Compliance of Construction IndustryDokument52 SeitenRegistration, Taxation & Accounting Compliance of Construction IndustryJohn Erick FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I.4 - Levy and Collection of GSTDokument38 SeitenUnit I.4 - Levy and Collection of GSTFake MailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Input Tax CreditDokument21 SeitenChapter 8 - Input Tax Creditmadaanakansha91Noch keine Bewertungen
- CA Ashish Chaudhary 1Dokument30 SeitenCA Ashish Chaudhary 1sonapakhi nandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST TradersDokument11 SeitenGST TradersSHAIK AHMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE DOCTRINES - 2020 Jurisprudence Updates (SC and CTA Cases)Dokument12 SeitenCASE DOCTRINES - 2020 Jurisprudence Updates (SC and CTA Cases)Carlota VillaromanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Registration Under: (Goods & Services Tax)Dokument4 SeitenRegistration Under: (Goods & Services Tax)Arjun LeninNoch keine Bewertungen
- RefundDokument34 SeitenRefunddhruv MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Tax Credit or ITCDokument14 SeitenInput Tax Credit or ITCgriefernjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument9 SeitenUntitledsuyash dugarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA ProjectDokument47 SeitenCA Projectitaxsan198Noch keine Bewertungen
- GST Unit 3 (2021)Dokument43 SeitenGST Unit 3 (2021)Anwesha HotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST Filing and ComplianceDokument1 SeiteGST Filing and ComplianceRahul PurswaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- (H) VISem BCH6.2 GST Week3 AnkitaTomarDokument23 Seiten(H) VISem BCH6.2 GST Week3 AnkitaTomarRAJBIR SINGH TADANoch keine Bewertungen
- Composition Scheme Sec. 10: Ques-1 What Is Composition Levy Under GST?Dokument12 SeitenComposition Scheme Sec. 10: Ques-1 What Is Composition Levy Under GST?Tapan BarikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fails To Make Payment To The Supplier Within 180 Days From The Date of Issue of InvoiceDokument54 SeitenFails To Make Payment To The Supplier Within 180 Days From The Date of Issue of InvoiceKrishna Chaitanya DammalapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India: Input Tax Credit (ITC)Dokument24 SeitenGoods and Services Tax (GST) in India: Input Tax Credit (ITC)Noman AreebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itc FinalDokument47 SeitenItc FinalarshiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST EcommerceDokument2 SeitenGST EcommerceSonal JoganiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Law - Penal ProvisionsDokument23 SeitenTax Law - Penal ProvisionsArsalan Ahmad100% (1)
- Suraj Sir 1Dokument8 SeitenSuraj Sir 1Avinash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxguru - In-Section 10 CGST Act 2017 Composition Levy Under GSTDokument5 SeitenTaxguru - In-Section 10 CGST Act 2017 Composition Levy Under GSTTheEnigmatic AccountantNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Business Ideas PDFDokument53 Seiten50 Business Ideas PDFSuman Adak33% (3)
- The 9 Building BlocksDokument72 SeitenThe 9 Building BlocksDakuro A EthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binaries 101 PDFDokument9 SeitenBinaries 101 PDFGeña GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Competitive StrategyDokument17 SeitenLecture 5 - Competitive StrategySachin kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature, Scope and Challenges of Industrial MarketingDokument33 SeitenNature, Scope and Challenges of Industrial MarketingJohn SeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist of Key Figures: Kieso Intermediate Accounting, Twelfth EditionDokument4 SeitenChecklist of Key Figures: Kieso Intermediate Accounting, Twelfth EditionEdi F SyahadatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Activities and Its Objectives Power PointDokument15 SeitenMarketing Activities and Its Objectives Power PointTimothy Manyungwa IsraelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To: ErvicesDokument152 SeitenIntroduction To: ErvicesBhawna SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kashato Shirts: General JournalDokument34 SeitenKashato Shirts: General JournalJade Cruz100% (1)
- ZEESHAN ProjectReport On Advertising ManagementDokument79 SeitenZEESHAN ProjectReport On Advertising ManagementRohit PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case UpdatedDokument16 SeitenCase UpdatedFaisi GikianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1 Review ProblemsDokument2 SeitenExam 1 Review ProblemsAdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earnest Money Receipt AgreementDokument3 SeitenEarnest Money Receipt AgreementwilliesyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing PlanDokument11 SeitenMarketing PlanleopiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmaceutical Sales Director Manager in USA Resume Dan McCoyDokument2 SeitenPharmaceutical Sales Director Manager in USA Resume Dan McCoyDanMcCoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Dokument2 SeitenTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Anutosh Bhaskar100% (1)
- Introduction To Business TaxesDokument60 SeitenIntroduction To Business TaxesRobilyn BollosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deductions From Gross IncomeDokument8 SeitenDeductions From Gross IncomeChe Poblete CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mkt501 - 3 - Midterm Paper Solved by Silentlips.... NewDokument6 SeitenMkt501 - 3 - Midterm Paper Solved by Silentlips.... Newzahidwahla1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sofa Invoice Amazon PDFDokument2 SeitenSofa Invoice Amazon PDFSyed Aqueel Haider100% (1)
- Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2016 Value PropositionDokument14 SeitenMicrosoft Dynamics CRM 2016 Value PropositionAdhi FirmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 11Dokument73 SeitenPaper 11Nagamahesh JogyalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation Law Review Final ExaminationsDokument4 SeitenTaxation Law Review Final ExaminationsRufino Gerard MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SATAPHULDokument7 SeitenSATAPHULsataphulsahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English For Logistics: Essential Vocabulary To Get The Job Done Right - FluentU Business English Blo PDFDokument18 SeitenEnglish For Logistics: Essential Vocabulary To Get The Job Done Right - FluentU Business English Blo PDFAndrew PerishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract For Artist and Gallery AgreementDokument7 SeitenContract For Artist and Gallery AgreementMirelaStefanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Promotion - BFSIDokument10 SeitenSales Promotion - BFSIAdnan patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ans Mini Case 2 - A171 - LecturerDokument14 SeitenAns Mini Case 2 - A171 - LecturerXue Yin Lew100% (1)
- Grind Export Files (C621957)Dokument34 SeitenGrind Export Files (C621957)JovyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lawn Master Manufactures Riding Lawn Mowers That It Sells ToDokument1 SeiteLawn Master Manufactures Riding Lawn Mowers That It Sells ToAmit PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen