Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
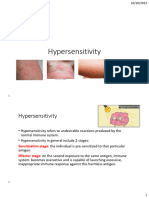
Hypersensitivity Reactions PDF
Hochgeladen von
Ronald BeasleyOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hypersensitivity Reactions PDF
Hochgeladen von
Ronald BeasleyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Goku Notes
Hypersensitivity Reactions LATE PHASE REACTION
Lecturer: Dra. Leila Ferrer
Can happen 2-8 hours later without additional exposure to
antigen
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS More intense infiltration of tissues with eosinophils,
neutrophils, basophils, monocytes and CD4 T cells
Exaggerated or misdirected immune response With mucosal epithelial damage
May be immediate or delayed
Occurs when an already sensitizied individual is re- SYSTEMIC ANAPHYLAXIS
exposed to the same foreign substance
Results in tissue injury or other pathophysiological Occur after administration of heterologous proteins (e.g.
changes Antisera, hormones, enzymes, polysaccharides and
drugs)
Ensuing tissue injury may be caused by: Exposure - itching, hives and skin erythema - contraction
of the respiratory bronchioles + respiratory distress
Release of vasoactive substances (+) laryngeal edema
Phagocytosis or lysis of cells Basis for skin test
Activation of inflammatory and cytolytic
components of complement system CLINICAL EXAMPLES
Release of cytokines (e.g. TNF), proteolytic enzymes
and other mediators of tissue injury or inflammation 1. Atopic disorders:
Allergic rhinitis
TYPE 1 HYPERSENSITIVITY Hay fever
Asthma
Immediate or anaphylactic type Atopic dermatitis
IgE mediated Urticaria
Occurs within minutes
Provoked by re exposure to the same antigen (by contact, 2. Anaphylaxis
inhalation, ingestion or injection)
Local or systemic
PRIMARY MEDIATORS
Local anaphylaxis
A. Biogenic amines
Atopy - genetically determined predisposition to develop
localized anaphylactic reactions to inhaled or ingested 1. Histamine
allergens 2. Adenosine - enhance mast cell mediator release
Positive family history - chr.5q31
With higher serum IgE levels compared to the general B. Chemotactic mediators
population
1. Enzymes - proteases, acid hydrolases (primary mediators)
2 phases:
2. Proteoglycans - heparin, chondroitin sulfate - package and
Initial Response store other mediators in the granules
Late Phase Reaction
SECONDARY MEDIATORS
INITIAL RESPONSE
1. Leukotrienes - LTC4, LTD4 - most potent vasoactive and
Vasodilation, vascular leakage, smooth muscle spasms or spasmogenic agents known; LTB4 (chemotaxis)
glandular secretions 2. Prostaglandin D2 - most abundant in mast cells
5-30 mins after exposure 3. PAF - release of histamine, bronchospasm, increased
Subside in 60 mins vascular permeability, vasodilation
4. Cytokines - e.g. TNF alpha, IL-1, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6
Goku Notes Page 1
Goku Notes
DIAGNOSIS CLINICAL EXAMPLES
History Myasthenia gravis - acetylcholine
Skin prick test - positive wheal and flare receptors
Blood eosinophilia Goodpasture’s syndrome - type IV
RAST (radioallergosorbent assay) collagen
Pernicious anemia - intrinsic factor
TREATMENT Acute rheumatic fever - antibodies vs
Streptococcal antigens cross react with
Anti-histamine - acts on first phase only the heart
Corticosteroids- late phase reaction
Desensitization - induce tolerance; no IgE production - TYPE III HYPERSENSITIVITY
deplete already bound IgE
Immune complex mediated
TYPE II HYPERSENSITIVITY Formation of immune complexes in circulation - deposit in
various tissues - trigger classical pathway of complement
Mediated by antibodies directed toward antigens present activation
on the surface of cells and other tissue components Produce damage as they localize within blood vessel walls
IgG and IgM or when trapped in filtering structures ( renal glomeruli)
Antigenic determinants - intrinsic or exogenous
CLINICAL EXAMPLES
MECHANISMS:
A. EXOGENOUS
1. Complement dependent reactions
INFECTIOUS AGENTS
Antibody-complement- mediated lysis
1. BACTERIA
Antibody (IgG and IgM) + antigen on cell surface -
activation of complement system - (+) MAC
Y. enterocolitica - arthritis
Results to MAC activation and later on tissue injury
Streptococci - GN, infective endocarditis
T. pallidum - glomerulonephritis
CLINICAL EXAMPLES
2. VIRUSES
Transfusion reactions
Erythroblastosis fetalis
Hep B, CMV - polyarteritis nodosa
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia,
agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia - (+)
3. PARASITES
antibodies vs own blood cells
Pemphigus vulgaris - antibodies vs
Plasmodium, schistosoma -
desmosomes
glomerulonephritis
Drug reactions
4. FUNGI
2. Antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity
Actinomycetes - farmer’s lung
Due to NK activity - non sensitized cells with Fc receptors
Ab + Ag - activation of NK cells - bind to Fc fragment of
IgG - cell lysis without phagocytosis B. ENDOGENOUS
Destruction of targets too large to be phagocytosed
(parasites, tumor cells) + graft rejection Nuclear antigens - SLE
Immunoglobulins - rheumatoid arthritis
ANTIBODY MEDIATED CELLULAR DYSFUNCTION Tumor antigens - glomerulonephritis
Antibodies directed against cell surface receptors - impair
or dysregulate function
Goku Notes Page 2
Goku Notes
SERUM SICKNESS 2 MECHANISMS OF T CELL MEDIATED CYTOTOXICITY
Patient forms antibodies to xenogeneic Ig administered 1. Perforin granzyme dependent killing
during passive immune therapy regimens
Positive immunity cause perforation of plasma membrane
ARTHUS REACTION 2. Fas- FasL dependent killing
Higher levels of antibody with booster activation of apoptosis
Localized area of tissue necrosis due to acute immune
complex vasculitis
Complexes precipitate in the vessel wall - fibrinoid
necrosis
TYPE IV HYPERSENSITIVITY
Cell mediated hypersensitivity
Initiated by sensitized T lymphocytes
Principal pattern of immunologic response to intracellular
microbiologic agents particularly Mycobacterium
tuberculosis as well as viruses, fungi, protozoa and
parasites
2 forms:
1. Delayed type hypersensitivity
Mediated by CD4 T cells
1st exposure to Ag - CD4 T cells + class II MHC -
differentiation of naive CD4 T cells to TH1 cells - release
of IL-12, IFN- gamma, IL-2, TNF alpha and lymphotoxins
CLINICAL EXAMPLES
Tuberculin skin test
Contact dermatitis
Granulomatous
inflammation
2. T cell mediated cytotoxicity
Mediated by CD8 + T cells
Sensitized CD8 + t cells kill antigen bearing target cells
CLINICAL EXAMPLES
Graft rejection
Virus infection
Tumor immunity
Goku Notes Page 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Topic 11 - Hypersensitivity and Autoimmuninty ProblemsDokument7 SeitenTopic 11 - Hypersensitivity and Autoimmuninty ProblemsMatt Andrei P. SongcuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument9 SeitenHypersensitivityJirah RuedasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity-1 Very ImportantDokument114 SeitenHypersensitivity-1 Very ImportantNusrat JahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 21 - HypersensitivityDokument25 SeitenLecture 21 - Hypersensitivityapi-3703352100% (2)
- Hypersensitivity: Dr. Sudheer KherDokument37 SeitenHypersensitivity: Dr. Sudheer KherAbdiladif Ahmed Mohamed100% (1)
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDokument12 SeitenHypersensitivity Reactionsella Sy100% (1)
- Hypersensitivity 150525050534 Lva1 App6892 PDFDokument117 SeitenHypersensitivity 150525050534 Lva1 App6892 PDFPriya Dharshini PalanimuthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Undisarable and Alterd ImmunotyDokument81 SeitenChapter 11 Undisarable and Alterd ImmunotyTofikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument46 SeitenUnit 3tanmai nooluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imunologi Dasar Penyakit Alergi: OlehDokument38 SeitenImunologi Dasar Penyakit Alergi: OlehtalithanrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On Immunology-HypersensitivityDokument45 SeitenSeminar On Immunology-HypersensitivitySalman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of A Child With Immune DisordersDokument4 SeitenNursing Care of A Child With Immune DisordersChin T. OndongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Veterinary Programe UB: Dr. Sri Murwani, DRH, MPDokument46 SeitenMedical Veterinary Programe UB: Dr. Sri Murwani, DRH, MPrifqi rahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 5 Hypersesitivity Fall 2023Dokument13 SeitenLec 5 Hypersesitivity Fall 2023lara.kharroubi33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment and Management of Pt's W/ Allergic Disorders: Physiologic OverviewDokument11 SeitenAssessment and Management of Pt's W/ Allergic Disorders: Physiologic OverviewChristina RichardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity Word Document-1Dokument23 SeitenHypersensitivity Word Document-1Dan 04Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMMUNOPATHOLOGYDokument78 SeitenIMMUNOPATHOLOGYсветлый попов100% (2)
- Allergic DisordersDokument20 SeitenAllergic DisorderskiyoorexenNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument49 SeitenHypersensitivityAkanksha MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 HypersensitivityDokument21 SeitenChapter 12 HypersensitivityJalil HaddadinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity Part 1Dokument43 SeitenHypersensitivity Part 1Ravi KoppoluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Prakash Nagarkatti, Ph.D. E-Mail: Pnagark@uscmed - Sc.edu)Dokument7 SeitenHypersensitivity Reactions: Prakash Nagarkatti, Ph.D. E-Mail: Pnagark@uscmed - Sc.edu)anon_60614972Noch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Tjok. Istri Anom Saturti, Sppd. MarsDokument16 SeitenDR - Tjok. Istri Anom Saturti, Sppd. MarsYogiswara KarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergen Sensitization: Primary MediatorsDokument14 SeitenAllergen Sensitization: Primary Mediatorsjelly bean100% (1)
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Kpalcantara@fatima - Edu.phDokument3 SeitenAdverse Drug Reactions: Kpalcantara@fatima - Edu.phakita dimaaalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altered ImmunityDokument35 SeitenAltered ImmunityNur SetsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACFrOgD Ivh1HlFBmRKx99Bik4FAJUheevf3fgdW VZ94rucueiVi3Y98hoan3mvajX 3kDv0mL w0eCee4ZIpStyL1qH3aSR59hBO11CwxZsX0 Bm19VOgy4 297R5uJlAzjkztaCIlg9B3uHH7Dokument3 SeitenACFrOgD Ivh1HlFBmRKx99Bik4FAJUheevf3fgdW VZ94rucueiVi3Y98hoan3mvajX 3kDv0mL w0eCee4ZIpStyL1qH3aSR59hBO11CwxZsX0 Bm19VOgy4 297R5uJlAzjkztaCIlg9B3uHH7jomel rondinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clin Immunology Lecture 3 For DentistsDokument97 SeitenClin Immunology Lecture 3 For Dentistsnaveenyadav7857Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology in Health and DiseasesDokument7 SeitenImmunology in Health and DiseasesLianneRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACFrOgD Ivh1HlFBmRKx99Bik4FAJUheevf3fgdW VZ94rucueiVi3Y98hoan3mvajX 3kDv0mL w0eCee4ZIpStyL1qH3aSR59hBO11CwxZsX0 Bm19VOgy4 297R5uJlAzjkztaCIlg9B3uHH7Dokument3 SeitenACFrOgD Ivh1HlFBmRKx99Bik4FAJUheevf3fgdW VZ94rucueiVi3Y98hoan3mvajX 3kDv0mL w0eCee4ZIpStyL1qH3aSR59hBO11CwxZsX0 Bm19VOgy4 297R5uJlAzjkztaCIlg9B3uHH7jomel rondinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type I Hypersensitivity: Anaphylactic Urticaria RhinorrheaDokument14 SeitenType I Hypersensitivity: Anaphylactic Urticaria RhinorrheaEleenaAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.11 Hypersensitivity (Dr. Dacula)Dokument5 Seiten1.11 Hypersensitivity (Dr. Dacula)John Benedict BondocNoch keine Bewertungen
- RX HIPERSENSITIVITYDokument34 SeitenRX HIPERSENSITIVITYEvie WulansariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Kpalcantara@fatima - Edu.phDokument3 SeitenAdverse Drug Reactions: Kpalcantara@fatima - Edu.phCamille WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment and Management of Patient's With Allergic ReactionsDokument13 SeitenAssessment and Management of Patient's With Allergic ReactionsLau ColastreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity Innate Immunity: When The Going Gets Tough, The Tough Gets Going...Dokument7 SeitenImmunity Innate Immunity: When The Going Gets Tough, The Tough Gets Going...dtimtimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergy and HypersensitivityDokument49 SeitenAllergy and HypersensitivityMoshe Cohen'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13-Hypersensitivities Type I With Audio 2021Dokument24 Seiten13-Hypersensitivities Type I With Audio 2021Rami AlhilliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of The Immune Response and Inflammation 3Dokument47 SeitenDisorders of The Immune Response and Inflammation 3Cres Padua QuinzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Pharmacy Government Colllege University FaisalabadDokument85 SeitenCollege of Pharmacy Government Colllege University FaisalabadzaheerbdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immuno Sero - 1st Week NotesDokument2 SeitenImmuno Sero - 1st Week NotesTreyton Sekani LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- H-Y Yang: National Yang-Ming UniversityDokument72 SeitenH-Y Yang: National Yang-Ming UniversityShing Ming TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune SystemDokument36 SeitenImmune SystemAyessa Yvonne PanganibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnaphylaxisDokument4 SeitenAnaphylaxisyaminduhairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar WordDokument32 SeitenSeminar Wordslmnkhn1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Allergic Reactions: Ahmad Asraf Bin AmirullahDokument28 SeitenAllergic Reactions: Ahmad Asraf Bin Amirullahasraf amirullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity Reactions IBDDokument5 SeitenHypersensitivity Reactions IBDferdudz schneiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kelainan Imunologi Dan Sist HematopoietikDokument93 SeitenKelainan Imunologi Dan Sist Hematopoietikhendra sandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument20 SeitenHypersensitivityJAIRA RIEYELLE LIPANANoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity: Mark Christian D. Duatin, RMTDokument43 SeitenHypersensitivity: Mark Christian D. Duatin, RMTJoyce Anne Faith Estrella100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Clients With Allergic DisordersDokument12 SeitenNursing Care of Clients With Allergic Disordersbwee bweeNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Pharmacy - Department of Medical TechnologyDokument7 SeitenUniversity of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Pharmacy - Department of Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDokument12 SeitenHypersensitivity Reactionsanime listNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphylaxis and Anaphylactoid ReactionsDokument19 SeitenAnaphylaxis and Anaphylactoid Reactionsgpengg1425Noch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument27 SeitenHypersensitivitysucram2889Noch keine Bewertungen
- Allergy: B Cells (B Lymphocytes)Dokument4 SeitenAllergy: B Cells (B Lymphocytes)Xarius FidelNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Finals HypersensitivityDokument16 SeitenMS Finals HypersensitivityMutya XDNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypersensitivityDokument85 SeitenHypersensitivityAlina LubnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Allergic/Hypersensitivity Disorders 2014 PHYSIOLOGIC OVERVIEW: ANTIBODIES React With Allergens byDokument9 SeitenAdult Allergic/Hypersensitivity Disorders 2014 PHYSIOLOGIC OVERVIEW: ANTIBODIES React With Allergens byRye AnchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunointervention in Autoimmune Diseases: Papers Based on an International Meeting in Paris, France, in June 1988Von EverandImmunointervention in Autoimmune Diseases: Papers Based on an International Meeting in Paris, France, in June 1988J. F. BachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goku Notes: Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (Bunyaviruses, Arenaviruses, Filoviruses) - Dra. Ma. Ellery MendezDokument5 SeitenGoku Notes: Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (Bunyaviruses, Arenaviruses, Filoviruses) - Dra. Ma. Ellery MendezRonald BeasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Influenza PDFDokument5 SeitenInfluenza PDFRonald BeasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology PDFDokument6 SeitenImmunology PDFRonald BeasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flavivirus Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos: Goku NotesDokument9 SeitenFlavivirus Lecturer: Dr. Jaime Santos: Goku NotesRonald BeasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Borrelia and Leptospira Lecturer: Dra. Ferrer: Goku NotesDokument3 SeitenBorrelia and Leptospira Lecturer: Dra. Ferrer: Goku NotesRonald BeasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goku Notes: Anaerobes Lecturer: Dr. LimDokument3 SeitenGoku Notes: Anaerobes Lecturer: Dr. LimRonald BeasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatotrophic Viruses PDFDokument9 SeitenHepatotrophic Viruses PDFRonald BeasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opportunistic Mycoses - DR SantosDokument20 SeitenOpportunistic Mycoses - DR SantosRonald BeasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 3 1 First Line of DefenseDokument33 SeitenChapter 3 3 1 First Line of Defenseapi-237856591Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vidas - Minividas Light PresentationDokument26 SeitenVidas - Minividas Light PresentationYaser AlaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology Micro LabDokument56 SeitenImmunology Micro LabMarielle Anne TuazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Selected Autoimmune Diseases: Lecture From Pathological Physiology November 11, 2004Dokument50 SeitenPathophysiology of Selected Autoimmune Diseases: Lecture From Pathological Physiology November 11, 2004Meity ElvinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Dokument16 SeitenCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Not meNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Draft Study Material Ranchi Region-1Dokument89 SeitenFinal Draft Study Material Ranchi Region-1Chitransh AwasthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIP Report - Priyanka Saha - MR1 - 2019-2005-0001-0040Dokument53 SeitenSIP Report - Priyanka Saha - MR1 - 2019-2005-0001-0040radhikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Pharmacology - ImmunopharmacologyDokument17 Seiten10 Pharmacology - ImmunopharmacologyArnoldBorromeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are T Cells and B Cells - Google SearchDokument8 SeitenWhat Are T Cells and B Cells - Google Searchraj kishan srinivasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductiontothe Immune SystemDokument25 SeitenIntroductiontothe Immune SystemUyên HuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On: Therapeutic Value of AdjuvantsDokument13 SeitenPresentation On: Therapeutic Value of AdjuvantsShamim MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Live All Questions Final2020Dokument47 SeitenLive All Questions Final2020Hab AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Questions and Answers On Pathogens and ImmunityDokument3 Seiten15 Questions and Answers On Pathogens and Immunitymfenn1997100% (1)
- Immunology Exam Q's With AnswersDokument26 SeitenImmunology Exam Q's With AnswersHavardKrovel87% (55)
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2021Dokument25 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2021Milka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro - para FINALDokument53 SeitenMicro - para FINALfilchibuff94% (18)
- 24 Lecture PresentationDokument85 Seiten24 Lecture PresentationWide PutinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A23605 ImmunologyDokument4 Seiten9A23605 ImmunologysivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytokines and Prostaglandins in Immune Homeostasis and Tissue Destruction in Periodontal DiseaseDokument32 SeitenCytokines and Prostaglandins in Immune Homeostasis and Tissue Destruction in Periodontal DiseaseDiana GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosepartaion Engineering: Ch.1: Bioseparation & Biological MaterialsDokument89 SeitenBiosepartaion Engineering: Ch.1: Bioseparation & Biological MaterialsAlex MaximusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune System As Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexcelDokument3 SeitenImmune System As Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexcelShela HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- NATS 1670 Recorded Lecture NotesDokument29 SeitenNATS 1670 Recorded Lecture NotescanaliphilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Position Document: Ige-Mediated Cow'S Milk Allergy: Allergologia Et ImmunopathologiaDokument20 SeitenPosition Document: Ige-Mediated Cow'S Milk Allergy: Allergologia Et ImmunopathologiaJair EduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy of Infections (Amb 710)Dokument33 SeitenImmunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy of Infections (Amb 710)CHINEDU CHUKWUBIKE0% (1)
- The Benefits of VaccineDokument2 SeitenThe Benefits of VaccineNav AriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Vaccines, Vaccine Development and ProductionDokument5 SeitenUnderstanding Vaccines, Vaccine Development and ProductionAni IoanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igcse Biology Revision Finale!!Dokument143 SeitenIgcse Biology Revision Finale!!sohaila ibrahim100% (1)
- Lymphocyte Proliferation AssayDokument5 SeitenLymphocyte Proliferation AssayMuhammad Fattah FazelNoch keine Bewertungen
- OuchterlonyDokument4 SeitenOuchterlonyd_caasi100% (1)
- Cancer Immunotherapy: An Update: Abul K. Abbas Ucsf Abul - Abbas@ucsf - EduDokument26 SeitenCancer Immunotherapy: An Update: Abul K. Abbas Ucsf Abul - Abbas@ucsf - EduHarits AmrullohNoch keine Bewertungen