Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sistema Common Rail Definicion 1
Hochgeladen von
Leo Bressner Velasquez MoralesOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sistema Common Rail Definicion 1
Hochgeladen von
Leo Bressner Velasquez MoralesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
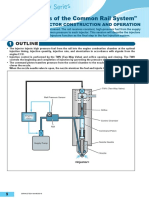
The previous series explained the fundamentals of the electronically controlled diesel fuel injection system
(ECD system). It was developed by DENSO as a countermeasure for environmental problems such as
exhaust gas and noise caused by diesel vehicles.
Next is a series introducing the fundamentals of the DENSO common rail system.
1 Common Rail System Development and Global Manufacturers
• In conventional injection pumps, injection pressure depended on the engine speed, and maximum injection pressure
was limited. There were also difficulties with other types of injection control, such as pilot injection. Addressing these
issues in a revolutionary manner, DENSO introduced the world's first commercial application of the common rail system.
Reference
Two types of common rail system are in use today.
One is a system that pressurizes the fuel and injects it
directly into the cylinders. This is called the "common rail HEUI System
system". This system has been adopted in passenger cars. Injector
Other companies, such as R. Bosch, Siemens, and Delphi
also offer their commercial versions of this system today.
High-Pressure
The other system is the Hydraulic Electric Unit Injection Engine Oil
(HEUI) system, which was developed by Caterpillar in the
United States. This system uses pressurized engine oil to Hydraulic
pressurize fuel by actuating the piston of the nozzle (injector) Pump
through which the pressurized fuel is injected. (Refer to the Fuel Tank
diagram on the right.)
Various Sensors Engine
ECU
2 What is the Common Rail System?
The common rail system uses a type of accumulation chamber called a rail to store fuel pressurized by the supply
pump, and injectors controlled by solenoid valves to spray the high-pressure fuel into the cylinders. The engine ECU
controls the injection quantity and timing of the injectors, and the pressure of fuel accumulated in the rail.
High-Pressure High-Pressure
Fuel Fuel
Rail
Supply Pump Injector
Electric Signal Electric Signal
Engine ECU
11 SERVICE TECH Vol.473 04-8
3 Features of the Common Rail System
• Because the engine ECU controls the injection system (including the injection pressure, injection rate, and injection
timing), the injection system is independent, and thus unaffected by the engine speed or load.
• Because the engine ECU controls injection quantity and timing to a high level of precision, multi-injection is possible
in a single injection stroke.
• This ensures a stable injection pressure at all times, particularly in the low engine speed range, and dramatically
decreases the amount of black smoke ordinarily emitted by a diesel engine during start-up and acceleration. As a
result, exhaust gas emissions are cleaner and reduced, and higher power output is achieved.
3-1 Injection Control Features
Injection Pressure Control
• Injection pressure is controlled to enable high-pressure injection to be performed at low engine speeds.
• Optimizes control to minimize particulate matter∗ and NOx emissions.
∗ Particulate matter is known to affect the respiratory system at high concentration levels. It consists of soluble organic matter
such as unburned oil or unburned diesel fuel in the exhaust gases, and insoluble organic matter such as soot (black smoke)
and sulfuric gas.
Injection Timing Control
Enables optimized control in accordance with driving conditions to obtain finely tuned injection timing (advance
angle).
Injection Rate Control
A small amount of fuel is sprayed before the main injection to improve engine start ability and reduce engine noise.
This small amount of fuel is controlled to optimize the injection rate (the injection quantity within a given unit of time).
Injection Quantity Control
For example, the cylinder injection quantity is corrected to ensure a uniform engine speed.
Common Rail System
Injection Pressure Control Injection Timing Control Injection Rate Control
Optimization / High Pressurization Injection
Rate
Main Injection
Injection Particulate
Pressure Matter
Electronically Controlled System
Common Rail
System
Crankshaft Angle
Injection Quantity Control
Example:
Advance
Angle Cylinder Injection Quantity Correction
Conventional
Pump
Injection Engine Injection
Quantity Speed Quantity
EngineSpeed InjectionPressure
1 3 2 4
SERVICE TECH Vol.473 04-8
12
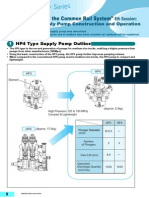
4 Common Rail System and Supply Pump Transitions
4-1 System Transitions
The first-generation common rail system for trucks was created in 1995, the first in the world. In 1999 the system
was adopted in passenger vehicles and small trucks, and became a second-generation system in the middle of 2001.
This system is now compatible with a wide variety of vehicle types, from small and large trucks to passenger vehicles.
The supply pump is an integral part of the common rail system. In 1999 the HP2 supply pump was used in small
trucks and passenger vehicles. This was followed in 2001 by the HP3, a more compact and lightweight supply
pump. The HP4 pump was released in 2003, and was developed based on the HP3 for use in medium trucks.
Systems that use HP0 and HP2 pumps are called "first generation", while systems that use HP3 and HP4 pumps
are called "second generation".
1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006
Common Rail System First-Generation Common Rail System Second-Generation Common Rail System
HP0
Large Trucks
120MPa
Pre-Stroke Control
HP4
180MPa
Suction
Medium Trucks
Control
HP3
HP2 180MPa
Suction Control
135MPa ~ 145MPa
Small Trucks Suction Control
Passenger Vehicles
4-2 Higher Injection Pressure and the Supply Pump
Fuel sprayed from the nozzle turns into finer particles as the fuel injection pressure increases. This improves
combustion and reduces the amount of particulate matter in the exhaust gas. Conventionally, the maximum injection
pressure of the in-line pump (A type) and the distributor pump (VE type) was 60MPa. Due to advancement in high-
pressure applications however, recently developed fuel injection systems inject fuel at a pressure of 100MPa or
higher. The second-generation common rail system injects fuel at an extremely high pressure of 180MPa.
In-Line Pump (A Type)
Mechanical Pump Distributor Pump (VE Type)
NB Type Pump
ECD V3 Pump
1 MPa is approximately
ECD V Series
ECD V4 Pump 120 equivalent to 10.2 kgf/cm².
(First Generation) HP0 Pump 120
Common Rail Series HP2 Pump 145
(Second Generation) HP3,4 Pump 180
50 100 150 200
Injection Pressure (MPa)
13 SERVICE TECH Vol.473 04-8
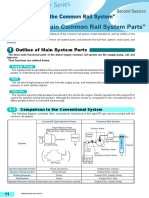
5 Common Rail System Configuration
• The common rail control system can be broadly divided into the following four areas: sensors, engine ECU, EDU,
and actuator.
• A block diagram of the overall system is shown below. Various sensors are used to detect the engine operating
conditions. These conditions include the intake air quantity, coolant temperature, intake air temperature, engine
speed and accelerator position. The engine ECU controls the actuators in accordance with the signals from these
sensors.
Block Diagram
Sensors Engine ECU Actuators
Supply Pump
Airflow Meter
Coolant Temperature Sensor
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
EDU Injector
Engine Speed Sensor
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Accelerator Position Sensor
Cylinder Recognition Sensor
Intake Restriction
Fuel Temperature Sensor Control
(Rotary Solenoid)
Rail Pressure Sensor
etc.
etc.
Sensors
The sensors detect the condition of the engine and the pump unit, convert this information into an electric signal,
and send it to the engine ECU.
Engine ECU
The engine ECU receives signals from the sensors, calculates the proper injection quantity and timing for optimal
engine operation, and sends signals to the actuators.
EDU
The EDU generates high voltage to enable high-speed injector actuation.
(The EDU is built into the engine ECU circuit in some vehicles.)
Actuators
The actuators operate to provide optimal injection quantity and timing in accordance with actuation signals
received from the engine ECU.
SERVICE TECH Vol.473 04-8 (Bi-monthly publication)
Date of publication : August 20, 2004 C 2004
Editorial department : Service Department, DENSO
100% recycled papers are used in this magazine. SERVICE TECH Vol.473 04-8
14
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- VP44 Service ManualDokument39 SeitenVP44 Service Manualhelder100% (5)
- Peter Szekeres-Solutions To Problems of A Course in Modern Mathematical Physics - Groups, Hilbert Space and Differential Geometry PDFDokument382 SeitenPeter Szekeres-Solutions To Problems of A Course in Modern Mathematical Physics - Groups, Hilbert Space and Differential Geometry PDFMed Chouaybi0% (1)
- HINO J08C J05C Type Engine PDFDokument29 SeitenHINO J08C J05C Type Engine PDFDiego Cadena100% (3)
- Service Manual: Pub. No. EE14E-11130Dokument39 SeitenService Manual: Pub. No. EE14E-11130Marcelo Diesel81% (16)
- VP44 Service Manualpdf PDF FreeDokument39 SeitenVP44 Service Manualpdf PDF FreeTin Doan dinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bosch cp4 PumpDokument4 SeitenBosch cp4 PumpIonut-alexandru Iordache100% (5)
- Hino Common Rail j05d J08eDokument50 SeitenHino Common Rail j05d J08eAnonymous yjK3peI793% (15)
- 273243957-DENSO-Common-Rail-Isuzu-6HK1-6SD1-Service-Manual-Pages Backup PDFDokument9 Seiten273243957-DENSO-Common-Rail-Isuzu-6HK1-6SD1-Service-Manual-Pages Backup PDFjwd100% (1)
- Common Rail Direct Injection-UbrizgavanjeDokument60 SeitenCommon Rail Direct Injection-UbrizgavanjeMarijan100% (1)
- Common Rail SystemDokument30 SeitenCommon Rail SystemJunaidi Juna Westborneo100% (3)
- Common Rail High Pressure Fuel Injection 9-2010Dokument33 SeitenCommon Rail High Pressure Fuel Injection 9-2010gmmarinov100% (5)
- Presentasi Common RailDokument71 SeitenPresentasi Common RailArif Suharto100% (3)
- Diesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedVon EverandDiesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (7)
- P3 Past Papers Model AnswersDokument211 SeitenP3 Past Papers Model AnswersEyad UsamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Kuliah Aseptik Dan Antiseptik CompressDokument60 SeitenPDF Kuliah Aseptik Dan Antiseptik CompressRasyid avicenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isuzu Common RailDokument40 SeitenIsuzu Common RailManos Stavrou100% (25)
- Fuel Injection Pump PDFDokument11 SeitenFuel Injection Pump PDFRico SitumorangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doosan Engine DX Serie NON DPF TrainingDokument136 SeitenDoosan Engine DX Serie NON DPF TrainingEslam Mansour100% (5)
- Service Manual: Common Rail System For OPEL 4EE2 Type EngineDokument32 SeitenService Manual: Common Rail System For OPEL 4EE2 Type EngineTarık gündoğdu100% (2)
- Service Manual: Common Rail System For ISUZU 4HK1 / 6HK1 Type EngineDokument49 SeitenService Manual: Common Rail System For ISUZU 4HK1 / 6HK1 Type EngineLeonardo Medina100% (1)
- Mechanics of A Diesel Fuel Injection SystemDokument8 SeitenMechanics of A Diesel Fuel Injection Systemekitriandi0% (1)
- R1600G M03 Engine enDokument10 SeitenR1600G M03 Engine enMayer PrucilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Injection System M274Dokument53 SeitenFuel Injection System M274Abu SAUD100% (2)
- 4 D 56Dokument52 Seiten4 D 56cartronix2010100% (6)
- SISTEMA DE CONTROL Y CONTROL DE INYECCION DE COMBUSTIBLE en Common Rail. 11Dokument4 SeitenSISTEMA DE CONTROL Y CONTROL DE INYECCION DE COMBUSTIBLE en Common Rail. 11Leo Bressner Velasquez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Rail Diesel InjectionDokument13 SeitenCommon Rail Diesel InjectionDejan Matic67% (3)
- 4M4 Gr13ADokument34 Seiten4M4 Gr13AGPRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combution Optimization of Diesel EngineDokument4 SeitenCombution Optimization of Diesel EngineRitesh ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TC02MMC03 - CRSDokument49 SeitenTC02MMC03 - CRSMohd FairusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Rail Diesel InjectionDokument13 SeitenCommon Rail Diesel InjectionDejan Matic100% (1)
- CRDIDokument31 SeitenCRDIJawahar Raj100% (3)
- C Rail Bosch Textbook HMCDokument41 SeitenC Rail Bosch Textbook HMCThuyết Rau Má100% (3)
- Fundamental of Diesel EngineDokument23 SeitenFundamental of Diesel EngineRita MandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSP 020 Common - RailDokument30 SeitenSSP 020 Common - Railvenkateshyadav2116Noch keine Bewertungen
- CRS Parts OutlineDokument4 SeitenCRS Parts OutlineVôĐốiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental of Diesel EngineDokument23 SeitenFundamental of Diesel EngineAyah Nofa PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common RailDokument30 SeitenCommon RailRowan CorneliusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common RailDokument30 SeitenCommon RailrowanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Engine Fuel Injection SystemDokument17 SeitenDiesel Engine Fuel Injection SystemKen ColeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oly 1300edi HeuiDokument39 SeitenOly 1300edi HeuiTengri89 TengriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Simulation of The Common RailDokument7 SeitenModeling and Simulation of The Common RailMozãoFragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 13E Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemDokument57 SeitenGroup 13E Electronically Controlled Fuel Systemandleralfonso7308Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sistem Bahan Bakar Common Rail - Pengenalan Sistem, Komponen, Dan SensorDokument19 SeitenSistem Bahan Bakar Common Rail - Pengenalan Sistem, Komponen, Dan SensorAfrijal FakhriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fi PomDokument34 SeitenFi PomDixit ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isuzu 6hk1 6sd1 Type EngineDokument23 SeitenIsuzu 6hk1 6sd1 Type Engineابن حمزة الخدري الخدريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denso CR - Hp2 NissanDokument31 SeitenDenso CR - Hp2 NissanMarcelo Diesel86% (7)
- Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection SystemsDokument35 SeitenGasoline Electronic Fuel Injection SystemsatulsemiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4M4 Gr13E PDFDokument36 Seiten4M4 Gr13E PDFcristian garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 96 Manifold InjectionDokument9 Seiten96 Manifold InjectionNandepu Sravan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel (WP12)Dokument24 SeitenFuel (WP12)Baligh TrabelsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint Fuel Injection SystemsDokument17 SeitenPowerpoint Fuel Injection Systemsanitadas19Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Session Injector Construction and OperationDokument4 Seiten8th Session Injector Construction and OperationВячеслав ГлушакNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Rail Diesel Injection (Done)Dokument14 SeitenCommon Rail Diesel Injection (Done)Dejan MaticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bosch CRI Book PDFDokument61 SeitenBosch CRI Book PDFEko Sunaryo100% (1)
- Unit Injector: Nozzle Types, Electronic Fuel Injection System (EFI), GDI, MPFI, DTSIDokument65 SeitenUnit Injector: Nozzle Types, Electronic Fuel Injection System (EFI), GDI, MPFI, DTSIMUDIT DWIVEDINoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel 2Dokument24 SeitenDiesel 2Musa TandiarrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint Fuel Injection SystemsDokument17 SeitenPowerpoint Fuel Injection SystemsShivanandNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 (Common Rail Diesel)Dokument48 SeitenCHAPTER 2 (Common Rail Diesel)Muhd Nasri100% (3)
- 2. Forsthoffer's Rotating Equipment Handbooks: PumpsVon Everand2. Forsthoffer's Rotating Equipment Handbooks: PumpsBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesVon EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Sensores Del Sistema de Control CR 10 PDFDokument4 SeitenSensores Del Sistema de Control CR 10 PDFLeo Bressner Velasquez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Operacion - InglesDokument194 SeitenManual de Operacion - InglesGustavo Alonso Cappa Salas100% (1)
- SISTEMA DE CONTROL Y CONTROL DE INYECCION DE COMBUSTIBLE en Common Rail. 11Dokument4 SeitenSISTEMA DE CONTROL Y CONTROL DE INYECCION DE COMBUSTIBLE en Common Rail. 11Leo Bressner Velasquez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Sistema Egr en Common Rail PDFDokument4 SeitenEl Sistema Egr en Common Rail PDFJuan Carlos Neyra BlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bomba de Alta Predion Denso Hp4Dokument4 SeitenBomba de Alta Predion Denso Hp4pepeladazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SISTEMA DE CONTROL Y CONTROL DE INYECCION DE COMBUSTIBLE en Common Rail. 11Dokument4 SeitenSISTEMA DE CONTROL Y CONTROL DE INYECCION DE COMBUSTIBLE en Common Rail. 11Leo Bressner Velasquez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine 4g61, 4663, 4664Dokument108 SeitenEngine 4g61, 4663, 4664asmar_me100% (4)
- Chapter 2 HydrateDokument38 SeitenChapter 2 HydrateTaha Azab MouridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 9Dokument1 SeiteHomework 9Nat Dabuét0% (1)
- Man Bni PNT XXX 105 Z015 I17 Dok 886160 03 000Dokument36 SeitenMan Bni PNT XXX 105 Z015 I17 Dok 886160 03 000Eozz JaorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source:: APJMR-Socio-Economic-Impact-of-Business-Establishments - PDF (Lpubatangas - Edu.ph)Dokument2 SeitenSource:: APJMR-Socio-Economic-Impact-of-Business-Establishments - PDF (Lpubatangas - Edu.ph)Ian EncarnacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- LC For Akij Biax Films Limited: CO2012102 0 December 22, 2020Dokument2 SeitenLC For Akij Biax Films Limited: CO2012102 0 December 22, 2020Mahadi Hassan ShemulNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper: 1 Definitive Guide To Data QualityDokument18 SeitenWhite Paper: 1 Definitive Guide To Data QualityGonçalo MartinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabian Aspect OrbsDokument8 SeitenSabian Aspect Orbsellaella13100% (2)
- 7 - Monte-Carlo-Simulation With XL STAT - English GuidelineDokument8 Seiten7 - Monte-Carlo-Simulation With XL STAT - English GuidelineGauravShelkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diverging Lenses - Object-Image Relations: Previously in Lesson 5 Double Concave LensesDokument2 SeitenDiverging Lenses - Object-Image Relations: Previously in Lesson 5 Double Concave LensesleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polysep... Sized For Every Application: Psg-7 Psg-15 Psg-30 Psg-60 Psg-90Dokument1 SeitePolysep... Sized For Every Application: Psg-7 Psg-15 Psg-30 Psg-60 Psg-90Carlos JiménezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aditya Academy Syllabus-II 2020Dokument7 SeitenAditya Academy Syllabus-II 2020Tarun MajumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard DiskDokument9 SeitenHard DiskAmarnath SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dec 2-7 Week 4 Physics DLLDokument3 SeitenDec 2-7 Week 4 Physics DLLRicardo Acosta Subad100% (1)
- Dog & Kitten: XshaperDokument17 SeitenDog & Kitten: XshaperAll PrintNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Install Metal LathDokument2 SeitenHow To Install Metal LathKfir BenishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nominal GroupDokument3 SeitenNominal GroupSrourNoch keine Bewertungen
- KRAS QC12K-4X2500 Hydraulic Shearing Machine With E21S ControllerDokument3 SeitenKRAS QC12K-4X2500 Hydraulic Shearing Machine With E21S ControllerJohan Sneider100% (1)
- Spanish Greeting Card Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenSpanish Greeting Card Lesson Planrobert_gentil4528Noch keine Bewertungen
- RH-A Catalog PDFDokument1 SeiteRH-A Catalog PDFAchmad KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plan Lectie Clasa 5 D HaineDokument5 SeitenPlan Lectie Clasa 5 D HaineCristina GrapinoiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPW, Vol.58, Issue No.44, 04 Nov 2023Dokument66 SeitenEPW, Vol.58, Issue No.44, 04 Nov 2023akashupscmadeeaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation 59TP6A 08SIDokument92 SeitenInstallation 59TP6A 08SIHenry SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Transformers WorkDokument15 SeitenHow Transformers Worktim schroderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approvals Management Responsibilities and Setups in AME.B PDFDokument20 SeitenApprovals Management Responsibilities and Setups in AME.B PDFAli LoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- D E S C R I P T I O N: Acknowledgement Receipt For EquipmentDokument2 SeitenD E S C R I P T I O N: Acknowledgement Receipt For EquipmentTindusNiobetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of The Internet in EducationDokument23 SeitenUse of The Internet in EducationAlbert BelirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap1 - Engineering in TimeDokument12 SeitenCap1 - Engineering in TimeHair Lopez100% (1)
- Board of Technical Education (Student Marksheet)Dokument2 SeitenBoard of Technical Education (Student Marksheet)Manoj SainiNoch keine Bewertungen