Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Financial Management - Compilation of Financial Ratios
Hochgeladen von
Ice Aloja0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
399 Ansichten6 SeitenCommonly Used Financial Ratios as Tools in Making Decisions for Financial Managers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCommonly Used Financial Ratios as Tools in Making Decisions for Financial Managers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
399 Ansichten6 SeitenFinancial Management - Compilation of Financial Ratios
Hochgeladen von
Ice AlojaCommonly Used Financial Ratios as Tools in Making Decisions for Financial Managers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
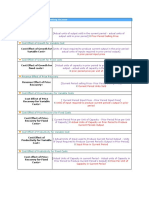
COMPILATION OF FINANCIAL RATIOS
RATIO FORMULA SIGNIFICANCE
A. Ratios used to Evaluate Short-term Financial Position (Short-term
Solvency and Liquidity)
1) Current Total Current Assets_ Test of short-term
Ratio or Total Current Liabilities debt paying ability
Working Measure of
Capital adequacy of
Ratio working capital
2) Acid Test Total Quick Assets Measures the
of Quick Total Current Liabilities firm’s ability to
Ratio pay its short-term
Quick Assets=Cash+Cash debts from its
Equivalents+ Net most liquid assets
Receivables+Marketable without having to
Securities rely on inventory
3) Working Working Capital Indicates relative
Capital to Total Assets liquidity of total
Total assets and
Assets Working Capital=Current Assets distribution of
Less Current Liabilities resources
employed
4) Cash Flow Cash + Marketable Securities + Cash Measures short-
Liquidity Flow From Operating Activities term liquidity by
Current Liabilities
Ratio considering as
cash resources
5) Defensive Quick Assets Measures length
Internal Daily Operating Cash Flow of time in days the
Ratio firm can operate
on its present
liquid resources
B. Ratios used to Evaluate Asset Liquidity and Management Efficiency
(ASSET MANAGEMENT RATIOS)
6) Receivable Net Credit Sales Measures the
Turnover Average Accounts average number
Receivable(Net) of days to collect
a receivable
Test of efficiency
collection
7) Average Age Number of Days in a Year Measure the
of Receivable Turnover average number
Receivables Or of days to collect
or Average
Collection Average Account Receivable a receivable
Period Average Daily Sales Evaluates the
Average Daily Sales= Net liquidity of
Sales/360 accounts
receivable and the
firm’s credit
policies
8) Inventory For Finished Goods or Merchandise Measures
Turnover Inventory: efficiency of the
Cost of Goods Sold firm in managing
Average Merchandise or Finished and selling
Goods Inventory inventories
For Goods in Process Inventory:
Cost of Goods Manufactured
Average Goods in Process
Inventory
For Raw Materials:
Number of times
Raw Materials Used
raw materials
Average Raw Materials Inventory
inventory was
used and
replenished during
the period
9) Average Number of Days in a Year Measures the
Age of Inventory Turnover average number
Inventories Or of days to sell or
or Number Average Inventory consume the
of Days of Average Daily Cost of Sales inventory
Inventory
10) Worki Net Sales Indicates
ng Capital Average Working Capital adequacy and
Turnover activity of working
capital
11) Paya Net Purchases Measures
ble Average Accounts Payable efficiency of the
Turnover company in
meeting trade
payable
12) Avera Average Accounts Payable Determines
ge Average Daily Purchases whether the firm
Accounts is paying its
Payable invoices on a
timely basis
13) Oper Average Age of Inventories + Measures the
ating Cycle Average Age of Receivables average number
or of days to convert
Conversion inventories to
Period cash
14) Fixed Net Sales Test roughly the
Assets Average Net Fixed Assets efficiency of
Turnover management in
keeping property,
plant, and
equipment (PPE)
Measures the level
of use of PPE
15) Asset Net Sales Measure efficiency
Turnover Total Assets of the firm in
managing all
assets
16) Capit Total Assets Measures
al Intensity Net Sales efficiency of the
Ratio firm to generate
sales through
employment of its
resources
Ratios used to Measure Long-Term Financial Position or
Stability/Leverage
17) Debt Total Liabilities Shows proportion
Ratio Total Assets of all assets that
are financed with
debt
Measures
percentage of
funds provided by
creditors
18) Equit Total Equity Indicates
y Ratio Total Assets proportion of
assets provided by
owners. Reflects
financial strength
and caution to
creditors
19) Debt Total Liabilities Measures debt
to Equity Total Equity relative to
Ratio amounts of
resources
provided by
owners
Compares
resources
provided by
creditors with
resources
provided by
shareholders
20) Fixed Fixed Assets (net) Reflects extent of
Assets to Total Long-term Liabilities investment in
Long-term long-term assets
Liabilities financed from
long-term debt
21) Fixed Fixed Assets (net) Measures the
Assets to Total Equity proportion of
Total owner’s capital
Equity invested in fixed
assets
22) Fixed Fixed Assets (net) Measures
Assets to Total Assets investment in
Total long-term capital
Assets assets
23) Book Ordinary shareholder’s equity Measures
value per No. of outstanding ordinary recoverable
share of shares amount in the
ordinary event of
shares liquidation if
assets are realized
at their book
values
24) Times Net Income Before Interest and Measures how
Interest Taxes many times
Earned Annual Interest Charges interest expense
Ratio is covered by
operating profit
25) Times Net Income After Taxes Indicates ability to
Preferred Preferred Dividends Requirement provide dividends
Dividend for preference
Requiremen
t Earned
Ratios used to Measure Profitability and Returns to Investors
26) Gross Gross Profit Measures profit
Profit Net Sales generated after
Margin Gross profit refers to Net Sales consideration of
minus Cost of Sales cost of products
sold
27) Oper Operating Profit Measures profit
ating Profit Net Sales generated after
Margin Operating profit refer to EBIT consideration of
operating costs
28) Net Net Profit Measures profit
Profit Net Sales generated after
Margin consideration of
all expenses and
revenues
Measures the
percentage of net
income or net
profit to sales
29) Cash Cash Flow from Operating Measures ability of
Flow Activities the firm to
Margin Net Sales translate sales to
cash
30) Rate Net Profit Measures overall
of Return Average Total Assets efficiency of the
on Assets Or firm in managing
Asset Turnover x Net Profit assets and
Margin generating profits
If there is interest-bearing debt, ROA
is equal to: A measure of the
Net Income + [Interest Expense (1- productivity of
Tax Rate)] assets regardless
Average Total Assets
how the assets
are financed
31) Rate Net income Measures rate of
of return Average Ordinary Equity return on
on equity Or resources
Return on Assets x Equity provided by
Multiplier owners
Equity Multiplier=1/Equity Ratio
32) Earni Net Income less preferred Peso return on
ngs per dividends requirement each ordinary
share Average Ordinary Shares share.
Outstanding Indicate ability to
pay dividends
33) Price/ Market Value per Share of Measures
Earnings Ordinary Shares relationship price
Ratio Earnings per Share of Ordinary of ordinary shares
Shares in the open
market and profit
earned on a per
share basis
34) Divid Dividends per share Shows percentage
end Payout Earnings per share of earnings paid to
shareholders
35) Divid Annual Dividends per Share Shows the rate
end Yield Market Value per Share of earned by
Ordinary Shares shareholders from
dividends relative
to current price of
stock
36) Divid Dividends Paid/Declared Shows portion of
ends Per Ordinary Shares Outstanding income distributed
Share to shareholders on
a per share basis
37) Rate Net Income Measures the
of return Average Current Assets profitability of
on average current assets
current invested
assets
References:
Financial Management by Ma. Elenita Cabrera
Management Advisory Services Reviewer by Rodelio Roque
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- California Complaint for Wrongful Foreclosure, Fraud, 17200 Violations, Violation of California Civil Code Section 2924j and 2924k, Violation of Rosenthal Fair Debt Collection Act, Negligence and Conversiont FormDokument31 SeitenCalifornia Complaint for Wrongful Foreclosure, Fraud, 17200 Violations, Violation of California Civil Code Section 2924j and 2924k, Violation of Rosenthal Fair Debt Collection Act, Negligence and Conversiont FormCameron Totten88% (16)
- Tutorial 7 (Week 9) - Managerial Accounting Concepts and Principles - Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDokument7 SeitenTutorial 7 (Week 9) - Managerial Accounting Concepts and Principles - Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisVincent TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Income Tax OUTLINEDokument22 SeitenFederal Income Tax OUTLINErufus.kingslee3327100% (7)
- PAS 1 With Notes - Pres of FS PDFDokument75 SeitenPAS 1 With Notes - Pres of FS PDFFatima Ann GuevarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management Solution Manual CabreraDokument3 SeitenFinancial Management Solution Manual CabreraJuda Mae Gieg33% (3)
- Working Capital Management PoliciesDokument5 SeitenWorking Capital Management Policieslerryroyce100% (1)
- BSA181A Interim Assessment Bapaud3X: PointsDokument8 SeitenBSA181A Interim Assessment Bapaud3X: PointsMary DenizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management by CabreraDokument8 SeitenFinancial Management by Cabrerachahunay0% (1)
- PLDT Vs - Estranero, GR No.192518, Oct 15, 2014 FactsDokument2 SeitenPLDT Vs - Estranero, GR No.192518, Oct 15, 2014 FactsHoreb FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic AccountingDokument28 SeitenForensic AccountingADITYA MAHAJAN63% (8)
- Chapter 2: Management Accounting and The Business EnvironmentDokument2 SeitenChapter 2: Management Accounting and The Business EnvironmentEmma Mariz Garcia100% (1)
- Level Up - Conceptual Framework ReviewerDokument15 SeitenLevel Up - Conceptual Framework Reviewerazithethird100% (1)
- 1 - Cash ManagementDokument8 Seiten1 - Cash ManagementAngela Shaine Castro GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactive Model of An EconomyDokument142 SeitenInteractive Model of An Economyrajraj999Noch keine Bewertungen
- With Diclosure On Transition To The Pfrs For Ses, See Below Example in No.18Dokument2 SeitenWith Diclosure On Transition To The Pfrs For Ses, See Below Example in No.18Allyssa Camille Arcangel100% (2)
- Basic Consideration in MAS Management Accounting EnvironmentDokument25 SeitenBasic Consideration in MAS Management Accounting EnvironmentLeslie Beltran Chiang100% (1)
- Taxation Review: General Principles and Key ConceptsDokument175 SeitenTaxation Review: General Principles and Key Conceptssha marananNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA Cabrera 2010 - SolManDokument4 SeitenMA Cabrera 2010 - SolManCarla Francisco Domingo40% (5)
- Projected Sales Cash Receipts Accounts Receivables Budgets Cash Budget AnalysisDokument3 SeitenProjected Sales Cash Receipts Accounts Receivables Budgets Cash Budget AnalysisJamaica Marjadas100% (1)
- Notes in Preferential TaxationDokument57 SeitenNotes in Preferential TaxationJeremae Ann Ceriaco100% (1)
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards NotesDokument2 SeitenConceptual Framework and Accounting Standards NotesKing Nufayl SendadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxn 3100 Instructional Module 1 PDFDokument5 SeitenTaxn 3100 Instructional Module 1 PDFSandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management by Cabrera Solution ManualDokument3 SeitenFinancial Management by Cabrera Solution Manualmhar lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Cost Analysis PDFDokument4 SeitenDifferential Cost Analysis PDFVivienne Lei BolosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Analysis of Operating Income and Final VarianceDokument2 SeitenStrategic Analysis of Operating Income and Final VarianceZen OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpAudCh10-CBET-01-501E-Toralde, Ma - Kristine E.Dokument6 SeitenOpAudCh10-CBET-01-501E-Toralde, Ma - Kristine E.Kristine Esplana ToraldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts (Cost Accounting)Dokument9 SeitenBasic Concepts (Cost Accounting)alexandro_novora6396Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acctg 15 - Midterm ExamDokument6 SeitenAcctg 15 - Midterm ExamAngelo LabiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Practice Set ReviewerDokument9 SeitenTax Practice Set Reviewerjjay_santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four-Variance Method Explained for Overhead Cost AnalysisDokument3 SeitenFour-Variance Method Explained for Overhead Cost AnalysisMeghan Kaye LiwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFRS 15 New FridayDokument73 SeitenIFRS 15 New Fridaynati67% (3)
- Preparation of Financial StatementsDokument3 SeitenPreparation of Financial StatementsMarc Eric Redondo0% (1)
- Strategic Tax Management ReviewerDokument47 SeitenStrategic Tax Management ReviewerJoyce Macatangay100% (1)
- Lyceum-Northwestern University: L-NU AA-23-02-01-18Dokument8 SeitenLyceum-Northwestern University: L-NU AA-23-02-01-18Amie Jane MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAR 0-ValixDokument5 SeitenFAR 0-ValixKetty De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting Concept and Application by Cabrera PDFDokument29 SeitenManagement Accounting Concept and Application by Cabrera PDFChristine Joy BoliverNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFRS 10 13Dokument2 SeitenPFRS 10 13Patrick RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyze financial statements with this SEO-optimized multiple choice quizDokument15 SeitenAnalyze financial statements with this SEO-optimized multiple choice quizPrincess Corine BurgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISA 265 Summary: Communicating Deficiencies in Internal Control To Those Charged With Governance and ManagementDokument2 SeitenISA 265 Summary: Communicating Deficiencies in Internal Control To Those Charged With Governance and ManagementtruthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Cost ManagementDokument4 SeitenStrategic Cost ManagementRanie MonteclaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Audit ReportsDokument7 SeitenUnderstanding Audit ReportsDanielle VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 1 Introduction To Strategic Business Analysis and Overview To Management ConsultancyDokument4 SeitenMODULE 1 Introduction To Strategic Business Analysis and Overview To Management ConsultancyPrinces S. RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- FNC6030 - Case 2Dokument5 SeitenFNC6030 - Case 2Louredaine MalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acc202 - Auditing Theory and PracticeDokument9 SeitenAcc202 - Auditing Theory and PracticeEsha Jain100% (1)
- MAS Theory AnswerDokument7 SeitenMAS Theory Answerhanna jeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- May 28, 2015-CH 10-Basic Income Tax Patterns-Valencia & RoxasDokument18 SeitenMay 28, 2015-CH 10-Basic Income Tax Patterns-Valencia & RoxasgoerginamarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDokument22 SeitenFundamentals of Assurance ServicesMargie Abad Santos100% (1)
- IFRS 9 Financial Instruments - F7Dokument39 SeitenIFRS 9 Financial Instruments - F7TD2 from Henry HarvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decentralization and Segment Reporting: Key Aspects ExplainedDokument3 SeitenDecentralization and Segment Reporting: Key Aspects ExplainedYousuf SoortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 004Dokument30 SeitenChap 004Tariq Kanhar100% (1)
- Additional InformationDokument6 SeitenAdditional InformationBabylyn NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ais MidtermDokument5 SeitenAis MidtermMosabAbuKhaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Next-X Inc - FinalDokument9 SeitenNext-X Inc - FinalJam Xabryl AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratios Used To Evaluate Short Term Financial Position (Short Term Solvency and Liquidity)Dokument3 SeitenRatios Used To Evaluate Short Term Financial Position (Short Term Solvency and Liquidity)MJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commonly Used RatiosDokument12 SeitenCommonly Used Ratiosg.canoneo.59990.dcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statements Analysis PDFDokument6 SeitenFinancial Statements Analysis PDFEstrada, Jemuel A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Commonly Used RatiosDokument12 SeitenCommonly Used RatioscyrilljoypNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name Formula Significance: 1. Current RatioDokument7 SeitenName Formula Significance: 1. Current RatioChaeminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turnover Average Average Rate: Efficiency Ratios)Dokument2 SeitenTurnover Average Average Rate: Efficiency Ratios)Yuri MinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAS 08 - FS Analysis PDFDokument20 SeitenMAS 08 - FS Analysis PDFAaron tamboongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 MAS - FS AnalysisDokument8 Seiten06 MAS - FS AnalysisRimuru TempestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement Analysis Antonio Jaramillo DayagDokument11 SeitenFinancial Statement Analysis Antonio Jaramillo DayagAldrin RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Financial Statement Analysis - P1Dokument5 SeitenModule 1 - Financial Statement Analysis - P1Jose Eduardo GumafelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payment Rate Dispute in Engineering Services CaseDokument4 SeitenPayment Rate Dispute in Engineering Services CaseCeline GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use The Following Information To Answer The Question BelowDokument3 SeitenUse The Following Information To Answer The Question BelowmarychanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRR Vs WACCDokument4 SeitenIRR Vs WACC04071990100% (1)
- Four Sector ModelDokument2 SeitenFour Sector ModelVishal Patel100% (1)
- Pigmy DepositDokument2 SeitenPigmy DepositVirendra PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globalisation's Impact on Income Inequality (39Dokument3 SeitenGlobalisation's Impact on Income Inequality (39Arqam WaqarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObliCon - Quiz Part 1 of 4Dokument2 SeitenObliCon - Quiz Part 1 of 4Mi MingkaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investing in Stocks and Shares GuideDokument7 SeitenInvesting in Stocks and Shares GuideRifqi Novriyandana100% (1)
- Loan Repayment Amortization Schedule For Jeremy KarpelDokument2 SeitenLoan Repayment Amortization Schedule For Jeremy KarpelMichael AndersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NESTLE' PAKISTAN Final PresentationDokument15 SeitenNESTLE' PAKISTAN Final PresentationUmme Laila JatoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Prime Rate: How It WorksDokument7 SeitenWhat Is The Prime Rate: How It WorksJason CarterNoch keine Bewertungen
- International financial forces impacting businessDokument29 SeitenInternational financial forces impacting businessY.h. TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mahesh, Project ProposalDokument7 SeitenMahesh, Project ProposalPrateek PasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020.04.16 Update To Bondholders PDFDokument17 Seiten2020.04.16 Update To Bondholders PDFhyenadogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Security Protection in NepalDokument27 SeitenSocial Security Protection in NepalBindu Gaire SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Conjugal Partnership of Gains: Exclusive Property of Each SpouseDokument8 SeitenChapter 4 Conjugal Partnership of Gains: Exclusive Property of Each SpousequasideliksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neha Singh Project TybafDokument31 SeitenNeha Singh Project Tybafneha 779100% (1)
- Folio Add Math )Dokument6 SeitenFolio Add Math )Farah Umaira JamalludinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 5 - Time Value of Money - Annuity 8. Jones Corporation Borrowed P9, 000 From Brown Corporation On Jan 1. 1,978 and P12,000Dokument10 SeitenProblem Set 5 - Time Value of Money - Annuity 8. Jones Corporation Borrowed P9, 000 From Brown Corporation On Jan 1. 1,978 and P12,000Kenneth Peña Javier100% (2)
- Timothy - Chap 12Dokument43 SeitenTimothy - Chap 12Chaeyeon JungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recommended Budget 2011Dokument375 SeitenRecommended Budget 2011clilly8037Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Sandeep Malu Associate Professor SVIM, IndoreDokument14 SeitenDr. Sandeep Malu Associate Professor SVIM, Indorechaterji_aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobilization of Saving Deposit of EveresDokument55 SeitenMobilization of Saving Deposit of EveresBadri maurya100% (1)
- Car Loan: Application FormDokument6 SeitenCar Loan: Application FormVijay BhemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Financial LiteracyDokument21 SeitenMeasuring Financial LiteracySaumya Jain Nigam100% (1)
- MBA Project Listing on Printing ServicesDokument51 SeitenMBA Project Listing on Printing ServicesDevrajNoch keine Bewertungen