Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Atrium
Hochgeladen von
Philip Ryken Yu0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten1 SeiteThe document summarizes key components and structures of the heart and circulatory system. It describes the heart chambers and valves, as well as layers of the heart walls. It then explains the cardiac cycle duration and normal cardiac output. Finally, it outlines the pulmonary and systemic circulations, distinguishing arteries, veins, and capillaries as well as their roles in oxygenated and deoxygenated blood transport.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document summarizes key components and structures of the heart and circulatory system. It describes the heart chambers and valves, as well as layers of the heart walls. It then explains the cardiac cycle duration and normal cardiac output. Finally, it outlines the pulmonary and systemic circulations, distinguishing arteries, veins, and capillaries as well as their roles in oxygenated and deoxygenated blood transport.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten1 SeiteAtrium
Hochgeladen von
Philip Ryken YuThe document summarizes key components and structures of the heart and circulatory system. It describes the heart chambers and valves, as well as layers of the heart walls. It then explains the cardiac cycle duration and normal cardiac output. Finally, it outlines the pulmonary and systemic circulations, distinguishing arteries, veins, and capillaries as well as their roles in oxygenated and deoxygenated blood transport.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
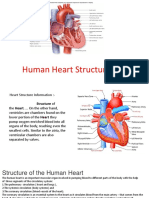
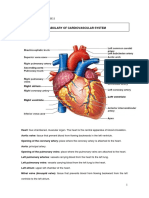
Atrium they are the receiving chambers
Ventricle they are the pumping chambers
Bicuspid valve/Mitral valve is the valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle
Tricuspid valve is the valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle
Pericardial Cavity is the cavity that surrounds the heart
Serous Fluids these are the fluids that fill body cavities
Epicardium/Visceral Pericardium the outermost layer of the heart walls
Myocardium the middle layer which is made up of thick muscle and is responsible for the heart contraction
Endocardium the innermost layer of the heart walls
Myocardial Infarction the myocardium irregularly functioning when someone has a heart attack
1.8 seconds it is how long one cardiac cycle lasts (the contraction and subsequent relaxation)
Tachycardia if heart rate is more than 100 beats per minute
Bradycardia if heart rate is less than 60 beats per minute
Cardiac Output it refers to the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute
5 liters per minute the normal cardiac output
Sphygmomanometer device used to measure blood pressure
Systolic is the measure of the force exerted when the ventricles are contracting
Diastolic is the force of blood against the blood vessel walls when the ventricles are relaxed
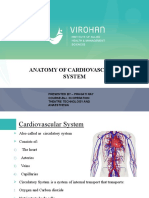
Pulmonary circulation right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs (gas exchange), pulmonary vein, left atrium,
bicuspid valve, left ventricle
Systemic circulation left ventricle, aorta, systemic arteries, capillary bed (gas exchange), systemic veins,
superior and inferior vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle
Arteries carries blood away from the heart (carries oxygenated blood)
Veins carries blood back to the heart (carries unoxygenated blood)
Capillaries are the ones that connect the arteries and veins
Pulmonary Arterythe only artery carrying unoxygenated blood
Arterioles the smallest branch of the arteries that connects into the capillaries
Aorta the largest artery in the human body
Pulmonary Vein the only vein carrying oxygenated blood
Venules the smallest branch of the veins that connects into the capillaries
Great Saphenous Vein the longest vein in the human body
Tunica Adventitia/Tunica Externa it is the outermost layer and is made up of connective tissue
Tunica Media it is made up of muscular tissue and is thicker in arteries than in veins
Tunica Intima/Tunica Interna it is the innermost layer and is made up of a single layer of endothelial cells
Antecubital Fossais the area where you can find the veins to do phlebotomy and is located anterior to your elbow
Whole blood 55% plasma, 45% formed elements
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Anatomy WordDokument4 SeitenAnatomy Wordarezoo bahramiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syok Hipovolemik EnglishDokument25 SeitenSyok Hipovolemik Englishatmarida 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- HeartDokument8 SeitenHeartCitra Idtu ChiperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDokument2 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of HeartSimran JosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System DR Aarti Abhishek Shah NmimsDokument33 SeitenCardiovascular System DR Aarti Abhishek Shah NmimsnoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Sys Part 1Dokument10 SeitenCardiovascular Sys Part 1LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 8. Cardiovascular SystemDokument35 SeitenLect 8. Cardiovascular Systemrukhsanatariq299Noch keine Bewertungen
- Parts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsDokument47 SeitenParts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsJasmin GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular NotesDokument16 SeitenCardiovascular NotesPRAGATI RAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument26 SeitenCardiovascular SystemdumbledoreaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter I - Cardiovascular System: HeartDokument2 SeitenChapter I - Cardiovascular System: HeartIndranil SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVS Heart Complete PDFDokument364 SeitenCVS Heart Complete PDFNabeel HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDokument2 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartPTV SportsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The HeartDokument5 SeitenAnatomy of The HeartxXjhmXxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Dokument60 SeitenAcfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Bala GanapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy5.heart and Large VesselesDokument73 SeitenAnatomy5.heart and Large VesselesAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The HeartDokument18 SeitenAnatomy of The Heartvanessaresullar100% (1)
- Human Heart ScienceDokument7 SeitenHuman Heart ScienceJewel Kathryn MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th Week Practical LessonsDokument11 Seiten10th Week Practical LessonstheodorastanerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Austin Journal of Clinical CardiologyDokument15 SeitenAustin Journal of Clinical CardiologyAustin Publishing GroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDokument14 SeitenCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Heart StructureDokument9 SeitenHuman Heart StructureSayali Patil100% (2)
- Is The Innermost Layer of Tissue That Lines The Chambers of The Heart. Its CellsDokument2 SeitenIs The Innermost Layer of Tissue That Lines The Chambers of The Heart. Its Cellsmichelle marquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charter College: T.Miller - 7/2017Dokument28 SeitenCharter College: T.Miller - 7/2017Waqar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Physiology NotesDokument56 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology NotesChristina Gonez100% (2)
- Vocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Dokument7 SeitenVocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Agustín Bravo Arreyes100% (2)
- Anatomy of The HeartDokument8 SeitenAnatomy of The HeartAbigail BrillantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Lec.6Dokument5 SeitenAnatomy Lec.6aminqasm111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heart AnatomyDokument19 SeitenHeart Anatomydeepika kushwahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts Science and Health VI The HeartDokument3 SeitenHandouts Science and Health VI The HeartjairaestrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 024-Premedical Circulatory SystemDokument31 Seiten024-Premedical Circulatory Systemchealzea asuncsionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of A Human HeartDokument3 SeitenAnatomy of A Human HeartKina KinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeartDokument27 SeitenHeartJeevitha VanithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVS 2Dokument153 SeitenCVS 2khalidtalal8000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, LudhianaDokument56 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, Ludhianapreet kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- The HeartDokument24 SeitenThe HeartAnubhav MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TheHumanCirculatorySystem (Renu)Dokument20 SeitenTheHumanCirculatorySystem (Renu)onlinebaijnathNoch keine Bewertungen
- القلبDokument11 SeitenالقلبNajwa AbdualgaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cardiovascular SystemDokument15 SeitenThe Cardiovascular SystemVim Flores QuirosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System Semis ReviewerDokument18 SeitenCardiovascular System Semis ReviewerReggie PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 - HeartDokument5 SeitenChapter 13 - Heartbussniesm05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument20 SeitenCardiovascular SystemYna MacatangayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 (Heart)Dokument10 SeitenLecture 5 (Heart)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm With Stanford A DissectionDokument5 SeitenThoracic Aortic Aneurysm With Stanford A Dissectionallyx_mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument34 SeitenCardiovascular SystemHira KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System - Lecture IDokument4 SeitenCardiovascular System - Lecture IpragantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartMuri CajucomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Austin CardiologyDokument15 SeitenAustin CardiologyAustin Publishing GroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument4 SeitenCardiovascular Systembuhia.quennieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Circulatory SystemDokument4 SeitenBiology - Circulatory SystemAstrynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDokument69 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of HeartRitu Arun Kaushik100% (1)
- Anaphysio of The HeartDokument6 SeitenAnaphysio of The HeartChamCham AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument6 SeitenCardiovascular Systemapi-297526590Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System - Transportation 1Dokument28 SeitenCardiovascular System - Transportation 1Louise Mica Lee100% (1)
- Management of Clients With Problems of The Cardiovascular SystemDokument7 SeitenManagement of Clients With Problems of The Cardiovascular Systemjerry smatt dumtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- P.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2ADokument29 SeitenP.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2AAlea Jane AranjuezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Wall of The Heart Consists of Three Layers of TissueDokument4 SeitenThe Wall of The Heart Consists of Three Layers of TissuehahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument34 SeitenCardiovascular Systemurooj100% (1)
- Heart: StructureDokument11 SeitenHeart: StructureKert trocioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashok Leyland Project ReportDokument40 SeitenAshok Leyland Project ReportGovind kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rockwell Allen BradleyDokument73 SeitenRockwell Allen BradleymaygomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSMTT-27 E1 PDFDokument8 SeitenSSMTT-27 E1 PDFblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSBDokument3 SeitenTSBnoe dela vegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLAC DynamicDokument294 SeitenFLAC DynamicMaximillian KrisnadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS-Interface Devices: (Slave Modules)Dokument48 SeitenAS-Interface Devices: (Slave Modules)Muhamad PriyatnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IJETR022563Dokument5 SeitenIJETR022563erpublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreDokument10 SeitenInstitute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreMUmairQrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planetary Characteristics: © Sarajit Poddar, SJC AsiaDokument11 SeitenPlanetary Characteristics: © Sarajit Poddar, SJC AsiaVaraha Mihira100% (11)
- Local AnesthesiaDokument55 SeitenLocal AnesthesiaAhmed MagdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Versana Premier Transducer GuideDokument4 SeitenVersana Premier Transducer GuideDigo OtávioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam 3 KEY (Solutions)Dokument13 SeitenPractice Exam 3 KEY (Solutions)joseNoch keine Bewertungen
- NavaDokument2 SeitenNavasaikiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical BOQ 07.12.2021 New Boq R4 05-01-2022 Final 16.02.2022Dokument92 SeitenElectrical BOQ 07.12.2021 New Boq R4 05-01-2022 Final 16.02.2022Upendra ChariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All TimeDokument4 SeitenThe 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All Timeungku1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elements or Appurtenances of The Stilling BasinsDokument21 SeitenElements or Appurtenances of The Stilling BasinsAhmad PshtiwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of Phodi Process With Mutation in Bhoomi (Simultaneous Approval of Phodi and The Mutation)Dokument19 SeitenIntegration of Phodi Process With Mutation in Bhoomi (Simultaneous Approval of Phodi and The Mutation)seshadrimn seshadrimnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assembly Manual, Operation and Maintenance Round Vibrating Screen Model: Tav-Pvrd-120Dokument15 SeitenAssembly Manual, Operation and Maintenance Round Vibrating Screen Model: Tav-Pvrd-120Sandro Garcia Olimpio100% (1)
- IbnTaymiyyah Theological EthicsDokument361 SeitenIbnTaymiyyah Theological EthicsDado Daki100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodDokument6 SeitenChapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodMbali MagagulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Park Design Submission PDFDokument20 SeitenIt Park Design Submission PDFSAKET TYAGI100% (1)
- Baldor Motor TestDokument14 SeitenBaldor Motor TestChecho BuenaventuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 510 1453 1 PB Tiang ReklameDokument6 Seiten510 1453 1 PB Tiang ReklameGunaedy UtomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TotSK 3.0Dokument22 SeitenTotSK 3.0PedroNoch keine Bewertungen
- DHL Product Solutions Portfolio 2017Dokument1 SeiteDHL Product Solutions Portfolio 2017Hanzla TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Human Geography Review Unit 2Dokument18 SeitenAP Human Geography Review Unit 2BaselOsman50% (2)
- Multilicative ABC IndexDokument6 SeitenMultilicative ABC IndexBalachandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and MagnetismDokument29 SeitenElectricity and MagnetismNashrul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Six Types of Simple MachinesDokument4 SeitenThe Six Types of Simple MachinesmarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Training Report (Kapar Power Plant)Dokument40 SeitenIndustrial Training Report (Kapar Power Plant)Hakeemi Baseri100% (2)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (82)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (32)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesVon EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1412)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (254)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceVon EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (51)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsVon EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (39)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlVon EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (60)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingVon EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1138)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)