Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Economic Impact On China
Hochgeladen von
Jorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Economic Impact On China
Hochgeladen von
Jorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DOI: 10.1002/jmv.
25706
COMMENTARY
Economic impacts of Wuhan 2019‐nCoV on China
and the world
Foster K. Ayittey1 | Matthew K. Ayittey2 | Nyasha B. Chiwero1 |
3 4
Japhet S. Kamasah | Christian Dzuvor
1
Department of Chemical Engineering, Curtin University Malaysia, Miri, Sarawak, Malaysia
2
Agricultural Extension Office, Ministry of Food and Agriculture, Adidome, Ghana
3
Medical Research Assistant, Kumasi Centre for Collaborative Research in Tropical Medicine, Kumasi, Ghana
4
Department of Chemical Engineering, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia
Correspondence
Foster Kofi Ayittey, Department of Chemical Engineering, Curtin University Malaysia, CDT 250, 98009 Miri, Sarawak, Malaysia.
Email: Ayittey.FosterKofi@postgrad.curtin.edu.my
Uncertainties over the Wuhan 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019‐ the US, with the rest of the world. During the SARS‐CoV outbreak in
nCoV), which has killed at least 1,775 people and sickened more than China from 2002 to 2003, the global economy was estimated to
70,000 as of February 17,1 has interrupted global trade and supply have lost roughly $40 billion.9 Currently, as China has an economy
chains, depressing asset prices, and forced multinational businesses 8 to 9 times larger than it had during the SARS epidemic, and is
to make hard decisions with limited information. even more connected to the rest of the world, experts believe that
Wuhan has been identified as a principal financial hub for central the total impact of the 2019‐nCoV on global economy could be quite
China. It is a significant transportation and trade center, hosting the huge.4 As China now contributes approximately 16.3% of the world's
headquarters of the nation's major local steel and vehicle makers. GDP, the country has been the main growth driver worldwide, with
The city also serves as home to more than 300 factories of the the IMF estimating that China alone accounted for 39% of global
world's best 500 companies, including Microsoft, German software economic growth in 2019.10 This implies that any slowdown in
2
company SAP, and French car maker Groupe PSA. In recent years, the nation's economy could likely send waves across the global
its monetary development has been recorded to have surpassed economy.11 Figure 1 presents the growth of China's GDP and its share
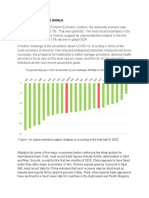
China's national growth, with a GDP growth of 7.8% in 20192 as of the global GDP from 2003 to 2018.
against the national average of 6.1%.3 After the spreading of the When China reopened its essential businesses on Monday,
recent viral disease, numerous firms have now evacuated their expat February 3, 2020, the markets dropped sharply in value due to the
workers from the city and temporarily halted business activities. The extended Lunar New Year holidays. The benchmark Shanghai Com-
strict travel restrictions that have been enforced in Wuhan and dif- posite Index fell 7.7%, shedding about $375 billion in market value in
ferent urban communities in Hubei are expected to have ripple its steepest 1‐day decline since August 2015. The Shenzhen Com-
effects throughout China and beyond, as far as trade is concerned. posite also experienced an 8.4% decline in value. Other business
Among the industries that would be negatively impacted, retail, sectors, retail, consumer services, and transportation stocks too led
tourism, and hospitality sectors are likely to be most affected.4 the declines.12
With over 70 000 movie theatres closed down in mainland According to IHS Markit Automotive, 11 of the Chinese pro-
China,5 and several airlines canceling flights to and from China – dis- vinces which are on strict lockdown account for more than two‐thirds
rupting tourism and other business activities – the economic impact of vehicle production in the country. These provinces equally supply
of the novel coronavirus is already extending beyond the borders of auto‐parts to carmakers in the US, Europe, and South Korea. If the
6–8
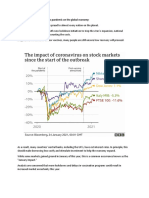
Hubei. This impact is quite obvious in the rattled stock market. It manufacturing companies remain idle until February 10, 2020, the
is quite interesting how the lockdown of a province with a population experts believe that there could be production loss of about 350 000
just a bit less than that of France or the UK has threatened to be a units. This figure could skyrocket to over 1.7 million units if the
blow to the global economy. This could be said to be amplified by the outbreak situation continues until mid‐March, equating to about
thorough integration of China, the second‐largest economy behind 32.3% decline from precrisis expectations.13 Similarly, S&P believes
J Med Virol. 2020;92:473–475. wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jmv © 2020 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. | 473
474 | AYITTEY ET AL.
F I G U R E 1 Growtaaah of China's GDP
and its shares in global GDP11
Source: World Bank, OECD
the nation's auto‐parts production could suffer up to a 50% decline. Vietnam's tourist industry is expected to lose up to $7.7 billion in
Some carmakers have already expressed concerns over the shortage the first 3 months of this year.15 As Chinese arrivals in Thailand
of car parts. Hyundai has reported the shutdown of its domestic are expected to decline by 80% in the first 4 months of 2020, the
factories after running out of parts from China. The managers of governor of the Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT) estimates
various carmakers in the US and Europe have also expressed con- that the nation could loss $3.1 billion in revenue.18 Aside Vietnam
cerns over the likely disruptions in business if China does not resume and Thailand, the tourism industries of Indonesia, Singapore, South
a full supply of parts to them within a week.14 According to industry Korea, Malaysia, Cambodia, Hong Kong, Japan, Australia, and
consultant LMC Automotive, China's auto market will shrink 3% to many more countries across the world are expected to be hit by
5% in 2020 if the coronavirus outbreak continues into the second the outbreak.19
15
quarter. When the loss of commerce, trade, tourism, and major impacts
Aside the automotive industry, tourism across the world has on global supply chains are taken into consideration, the economic
been affected gravely due to the outbreak, as China is recognized impacts of the outbreak will be vast both within China and globally. A
by the United Nation Tourism Organization (UNWTO) as a true market diagnosis completed by Bloomberg economists, concludes
leader in global tourism, both as a source market and as a leading that China's first‐quarter GDP growth may slip to 4.5% year‐on‐year.
destination.16 The China Outbound Tourism Research Institute According to an estimated modelling by the same experts, to analyze
observed that 6.3 million Chinese tourists traveled abroad during the expected losses to different countries across the world, the
the 2019 Lunar New Year holiday, generating travel revenue of global GDP is likely to decline by roughly 0.42% in first quarter of
around $73 billion, but the figures have reduced drastically in the year due to the outbreak. This is illustrated in Figure 2. That
2020.17 The impact on tourism beyond China is also significant, notwithstanding, the Bloomberg economists believe that it is too
according to reliable sources. Due to Chinese tours being canceled early to tell the full impact of the fatal disease since the infection has
and a general recession in domestic and international travelers, not attained its peak yet.20
F I G U R E 2 Percentage point deviation in
year‐on‐year growth from Q1 202020
Source: Bloomberg Economics
AYITTEY ET AL. | 475
Some capital economists, however, estimate that, without urgent 10. International Monetary Fund. https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/
global actions to curtail the Wuhan 2019‐nCoV within the shortest 2019/10/18/na102319‐prolonged‐uncertainty‐weighs‐on‐asias‐
economy. Accessed February 9, 2020.
possible time, China is expected to lose up to $62 billion21 in the first
11. CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2020/02/06/coronavirus‐the‐hit‐to‐the‐
quarter of the year, while the world is likely to lose over $280 billion global‐economy‐will‐be‐worse‐than‐sars.html. Accessed February
within the same period.15 This conclusion compares closely to the 9, 2020
World Banks estimation that even a weaker flu pandemic, such as the 12. The Wall Street Journal. https://www.wsj.com/articles/chinese‐markets‐
tumble‐on‐mounting‐coronavirus‐fears‐11580695672?mod=article_inline.
2009 H1N1 viruses, could still wipe 0.5% off global GDP, which
Accessed February 8, 2020.
amounts to approximately $300 billion.22 13. IHS Markit. http://news.ihsmarkit.com/prviewer/release_only/slug/
impacts‐of‐coronavirus‐containment‐effort‐ripple‐through‐global‐
OR CID economy. Accessed February 9, 2020.
14. Financial Times. https://www.ft.com/content/166b69ec‐47eb‐3c96‐
Foster K. Ayittey http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3129-2053
a7ba‐343d57aec637. Accessed February 7, 2020.
Nyasha B. Chiwero http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2341-3548 15. Nikkei Asian Review. https://asia.nikkei.com/Spotlight/Coronavirus‐
Japhet S. Kamasah http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0369-555X outbreak/Coronavirus‐latest‐US‐citizen‐dies‐in‐Wuhan‐after‐infection.
Christian Dzuvor http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9109-051X Accessed February 8, 2020.
16. UNWTO. https://unwto.org/unwto‐statement‐on‐the‐novel‐coronavirus‐
outbreak. Accessed February 9, 2020.
REFERENC ES
17. Channel News Asia. https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/
1. Caixin Global. https://www.caixinglobal.com/2020/wuhan‐virus‐live‐ commentary/wuhan‐virus‐coronavirus‐tourism‐worst‐hit‐countries‐
update/. Accessed February 17, 2020. cities‐china‐12377622. Accessed February 9, 2020.
2. South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/economy/china‐ 18. The ASEAN Post. https://theaseanpost.com/article/coronavirus‐what‐
economy/article/3047426/explained‐why‐wuhan‐so‐important‐ about‐thailands‐tourism. Accessed February 9, 2020.
chinas‐economy‐and‐potential. Accessed February 8, 2020. 19. HIS Markit. https://ihsmarkit.com/research‐analysis/chinas‐stock‐
3. South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/economy/china‐ markets‐slump‐on‐wuhan‐virus.html. Accessed February 11, 2020.
economy/article/3046476/china‐gdp‐growth‐last‐year‐was‐61‐cent‐ 20. Bloomberg. “Charting the Global Economic Impact of the Coronavirus”.
slowest‐rate‐29‐years. Accessed February 8, 2020. https://www.bloomberg.com/graphics/2020‐global‐economic‐impact‐of‐
4. Health Affairs. https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/hblog2020 wuhan‐novel‐coronavirus/. Accessed February 11, 2020.
0203.393483/full/. Accessed February 8, 2020. 21. CNN Business. https://edition.cnn.com/2020/01/31/economy/china‐
5. Quartz. https://qz.com/1791867/the‐coronavirus‐outbreak‐is‐crippling‐ economy‐coronavirus/index.html. Accessed February 9, 2020.
chinas‐film‐industry/. Accessed February 8, 2020. 22. CNN Business. https://edition.cnn.com/2020/02/08/business/coronavirus‐
6. Global News. https://globalnews.ca/news/6440822/china‐virus‐stock‐ global‐economy/index.html. Accessed February 11, 2020.
market/. Accessed February 8, 2020.
7. Business Standard. https://www.business‐standard.com/article/pti‐
stories/china‐virus‐outbreak‐may‐wallop‐economy‐financial‐markets‐
120012200837_1.html. Accessed February 8, 2020.
8. Richmond News. https://www.richmond‐news.com/news/asia‐pacific‐ How to cite this article: Ayittey FK, Ayittey MK, Chiwero NB,
business/stocks‐oil‐fall‐as‐china‐virus‐rattles‐markets‐1.24061887. Kamasah JS, Dzuvor C. Economic impacts of Wuhan
Accessed February 8, 2020. 2019‐nCoV on China and the world. J Med Virol. 2020;92:
9. NBC News. https://www.nbcnews.com/business/markets/sars‐wiped‐
473–475. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25706
40‐billion‐world‐markets‐what‐will‐coronavirus‐do‐n1122151. Accessed
February 8, 2020.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Survival Kit EssentialsDokument12 SeitenSurvival Kit EssentialsDarious Kater100% (2)
- A Treasure of Treasures PDFDokument9 SeitenA Treasure of Treasures PDFJacobo CisnerosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yeast ProductionDokument35 SeitenYeast ProductionVu Hong ThangNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDL2009 - Poisoned Pages - Brood of The Mother Spore (v1) (2020)Dokument6 SeitenSDL2009 - Poisoned Pages - Brood of The Mother Spore (v1) (2020)Aqua YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Impact of CovidDokument7 SeitenEconomic Impact of Covidrishi pereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Corona Virus On Global EconomyDokument10 SeitenImpact of Corona Virus On Global EconomyAsif Sadat 1815274060Noch keine Bewertungen
- Welcoming and Greeting The GuestDokument3 SeitenWelcoming and Greeting The GuestrenatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Food ContaminationDokument29 SeitenChapter 7 Food ContaminationMylene NapalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Q2 Health LASDokument46 SeitenGrade 7 Q2 Health LASjanet otana100% (1)
- Board Exam March2019 Let QuestionsDokument19 SeitenBoard Exam March2019 Let QuestionsLeleth Trasporte Enojardo - Valdez100% (1)
- Vanilla Donuts KICADokument8 SeitenVanilla Donuts KICARia50% (2)
- The Impact of COVID-19 in The Philippines: An Economic StudyDokument8 SeitenThe Impact of COVID-19 in The Philippines: An Economic StudyMary Grace CuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doodh Ka RishtaDokument237 SeitenDoodh Ka RishtaImran Muslim0% (1)
- Work Immersion Portfolio 1Dokument21 SeitenWork Immersion Portfolio 1Karen morboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Impacts of Wuhan 2019-Ncov On China and The WorldDokument7 SeitenEconomic Impacts of Wuhan 2019-Ncov On China and The WorldElias Rodriguez HendersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of COVID19 On Global EconomyDokument9 SeitenThe Impact of COVID19 On Global Economyمحمود عليمىNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics StatsDokument25 SeitenEconomics StatsYashasvi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coronavirus (Covid-19) and Its Effects On The World and Indian EconomyDokument11 SeitenCoronavirus (Covid-19) and Its Effects On The World and Indian EconomyDarpanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Training Program (OTP) 2020 Subject: Current Affairs Assignment #1Dokument4 SeitenOnline Training Program (OTP) 2020 Subject: Current Affairs Assignment #1vishal sinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Institutions: Covid 19 - Global and PakistanDokument14 SeitenFinancial Institutions: Covid 19 - Global and PakistanmuhammadvaqasNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does Coronavirus Spread?Dokument38 SeitenHow Does Coronavirus Spread?Abhay SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijrbm - Unexpected Ramifications of Corona Pandemic (Rizwan)Dokument7 SeitenIjrbm - Unexpected Ramifications of Corona Pandemic (Rizwan)Impact JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Corona Virus On Indian EconomyDokument6 SeitenImpact of Corona Virus On Indian EconomyMayank Kumar50% (2)
- Assignment II Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic On Global Economy and International BusinessDokument7 SeitenAssignment II Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic On Global Economy and International BusinessVance UrsulumNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEDA - Addressing The Social and Economic Impact of The COVID 19 Pandemic PDFDokument21 SeitenNEDA - Addressing The Social and Economic Impact of The COVID 19 Pandemic PDFnoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Corona Virus On The Global Economy: February 2020Dokument3 SeitenImpact of Corona Virus On The Global Economy: February 2020Ihsaan Gulzar AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Corona On World EconomyDokument6 SeitenEffects of Corona On World EconomyManish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Corona Virus On The Global Economy: February 2020Dokument3 SeitenImpact of Corona Virus On The Global Economy: February 2020Uzzal AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Interesting Data About Corona Patients Compiled by TV-9Dokument7 SeitenSome Interesting Data About Corona Patients Compiled by TV-9NISHANT395Noch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 and Its Impact On The International EconomyDokument17 SeitenCOVID-19 and Its Impact On The International EconomyGeetika Khandelwal100% (7)
- Impactof Corona Virusonthe Global Economy SAKIBMAHMUDDokument3 SeitenImpactof Corona Virusonthe Global Economy SAKIBMAHMUDBorhan NidamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taiwan: Group No.: 21Dokument5 SeitenTaiwan: Group No.: 21Aditya AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment #3: Impact of COVID-19 Submitted By: SHIWANI 17990Dokument2 SeitenAssignment #3: Impact of COVID-19 Submitted By: SHIWANI 17990shiwani khetpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business-Case - Group-DiscussionDokument24 SeitenBusiness-Case - Group-DiscussionMy Nguyen Thi Tra VOCFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uae Social Studies Paper FinalDokument11 SeitenUae Social Studies Paper FinalJana TaboadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global and Local Market Outlook v5Dokument11 SeitenGlobal and Local Market Outlook v5ShinThant LinnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Social Media On Preferences of Women For Fashion Apparel Brands in East Godavari District of AndhrapradeshDokument11 SeitenImpact of Social Media On Preferences of Women For Fashion Apparel Brands in East Godavari District of AndhrapradeshAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of The Coronavirus Pandemic On The Global EconomyDokument8 SeitenThe Impact of The Coronavirus Pandemic On The Global Economymd tarequl islamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid-19 Economy Paragraph & Sources For NINOVADokument5 SeitenCovid-19 Economy Paragraph & Sources For NINOVAokyayisil0735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Editorial: Covid-19 Pandemic and International Tourism DemandDokument5 SeitenEditorial: Covid-19 Pandemic and International Tourism DemandCaterpillar MinithesisNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID 19 Financial Markets by FS CoachingDokument16 SeitenCOVID 19 Financial Markets by FS CoachingLCT Gaming717Noch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of The Whole WorldDokument4 SeitenImpact of The Whole Worldوسيم أكرمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact On Indian Economy For COVID 19Dokument15 SeitenImpact On Indian Economy For COVID 19The Second Life GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of Economics Assignment: RecessionDokument9 SeitenPrinciple of Economics Assignment: RecessionSrikanth RevellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kushal Jesrani 26 Research MethodologyDokument70 SeitenKushal Jesrani 26 Research MethodologyKushal JesraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coronavirus (Covid-19) and Its Effects On The World and Indian EconomyDokument11 SeitenCoronavirus (Covid-19) and Its Effects On The World and Indian EconomyDarpanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Global Recovery Q3Dokument26 Seiten2020 Global Recovery Q3studyhotelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Covid 19 On Indian EconomyDokument4 SeitenImpact of Covid 19 On Indian EconomyHaripriya VNoch keine Bewertungen
- ContempworldDokument4 SeitenContempworldTrisha FontanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serial No.2Dokument16 SeitenSerial No.2Srikanth RevellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Covid-19 Has Affected The Global EconomyDokument4 SeitenHow Covid-19 Has Affected The Global Economyমো. জসীমউদ্দীনNoch keine Bewertungen
- Articles Send By: What Is The Impact of Coronavirus On Indian Economy? - A ReviewDokument12 SeitenArticles Send By: What Is The Impact of Coronavirus On Indian Economy? - A ReviewMayank TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AyushiPatel - A044 - Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic On Indian Economy - .Dokument9 SeitenAyushiPatel - A044 - Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic On Indian Economy - .Ayushi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid 19 PrashanthDokument11 SeitenCovid 19 Prashanthkochanparambil abdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroductionDokument6 SeitenIntroductionArnab SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature ReviewDokument2 SeitenLiterature ReviewAnkita MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid-19 Effects On IBT - LINSODokument2 SeitenCovid-19 Effects On IBT - LINSOHazraphine LinsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic On Vietnam's EconomyDokument5 SeitenImpact of COVID-19 Pandemic On Vietnam's EconomyTuyết Nhi PhạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of COVID 19 On China S Trade and Outward FDI and Related CountermeasuresDokument11 SeitenThe Impact of COVID 19 On China S Trade and Outward FDI and Related CountermeasuresMatheus F. FröhlichNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMPACT OF COVID'19 On India's GDP: - Ashutosh Kabra, I BBADokument8 SeitenIMPACT OF COVID'19 On India's GDP: - Ashutosh Kabra, I BBAdprabha99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Himanshi Popli (Synopsis)Dokument12 SeitenHimanshi Popli (Synopsis)AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid-19 Impact On Indian Economy and Supply ChainDokument11 SeitenCovid-19 Impact On Indian Economy and Supply ChainShubham JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economy and Covid-19Dokument8 SeitenEconomy and Covid-19drishti guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Valuation Airplane Investments As An Asset Class 1St Edition David Yu Full ChapterDokument51 SeitenAircraft Valuation Airplane Investments As An Asset Class 1St Edition David Yu Full Chapterwilliam.rameriz209100% (7)
- Secdocument 259Dokument47 SeitenSecdocument 259donna.groves662Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Coronavirus On The EconomyDokument22 SeitenThe Impact of Coronavirus On The EconomyRizwan Sherani100% (1)
- Spillovercovid 19 Coronavirusglobaleconomypetersonoziliarunthankom FINAL1Dokument28 SeitenSpillovercovid 19 Coronavirusglobaleconomypetersonoziliarunthankom FINAL1Nandini KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Coronavirus On The Economy of Bangladesh, India and ChinaDokument22 SeitenThe Impact of Coronavirus On The Economy of Bangladesh, India and ChinaRizwan Sherani100% (2)
- Overcoming COVID-19 in Bhutan: Lessons from Coping with the Pandemic in a Tourism-Dependent EconomyVon EverandOvercoming COVID-19 in Bhutan: Lessons from Coping with the Pandemic in a Tourism-Dependent EconomyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is The Short Version of The Big Five Inventory (BFI-S) Applicable For Use in Telephone Surveys?Dokument18 SeitenIs The Short Version of The Big Five Inventory (BFI-S) Applicable For Use in Telephone Surveys?Jorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Model of Emotional Intelligence and Con Ict Management Strategies: A Study in Seven CountriesDokument26 SeitenA Model of Emotional Intelligence and Con Ict Management Strategies: A Study in Seven CountriesJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elijah, Examination of Personality TraitsDokument23 SeitenElijah, Examination of Personality TraitsJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 67 KobraFarahi 4 PDFDokument13 Seiten67 KobraFarahi 4 PDFJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lang2011 Article ShortAssessmentOfTheBigFiveRob PDFDokument20 SeitenLang2011 Article ShortAssessmentOfTheBigFiveRob PDFJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is The Short Version of The Big Five Inventory (BFI-S) Applicable For Use in Telephone Surveys?Dokument18 SeitenIs The Short Version of The Big Five Inventory (BFI-S) Applicable For Use in Telephone Surveys?Jorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 - People Management Skills, Employee Attrition, and Manager Rewards - An Empirical AnalysisDokument136 Seiten2020 - People Management Skills, Employee Attrition, and Manager Rewards - An Empirical AnalysisJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principal Component Clustered Factors For Determining Study Performance in Computer Programming ClassDokument20 SeitenPrincipal Component Clustered Factors For Determining Study Performance in Computer Programming ClassJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jocs 14596Dokument8 SeitenJocs 14596Jorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Pone 0197485Dokument16 SeitenJournal Pone 0197485Jorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schmitt JCCP 2007 PDFDokument40 SeitenSchmitt JCCP 2007 PDFJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat Sheet R - Graficos Con Ggplot2Dokument2 SeitenCheat Sheet R - Graficos Con Ggplot2rbenignijNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fleseriu@ohsu - Edu: Via Free AccessDokument13 SeitenFleseriu@ohsu - Edu: Via Free AccessJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring The Costs and Economic Consequences of Unsafe Abortion in Mexico City Before LegalisationDokument14 SeitenExploring The Costs and Economic Consequences of Unsafe Abortion in Mexico City Before LegalisationJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farewell Seguro PopularDokument2 SeitenFarewell Seguro PopularJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Costs and Cost Effectiveness of Providing First-Trimester, Medical and Surgical Safe Abortion Services in Kwazulu-Natal Province, South AfricaDokument16 SeitenThe Costs and Cost Effectiveness of Providing First-Trimester, Medical and Surgical Safe Abortion Services in Kwazulu-Natal Province, South AfricaJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomic EpidemicsDokument30 SeitenMacroeconomic EpidemicsJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomic Implications of COVID-19:: Can Negative Supply Shocks Cause Demand Shortages?Dokument37 SeitenMacroeconomic Implications of COVID-19:: Can Negative Supply Shocks Cause Demand Shortages?Jorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPI Interventions Markel 2007Dokument12 SeitenNPI Interventions Markel 2007Jorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Alternative First-Trimester Pregnancy Termination Strategies in Mexico CityDokument12 SeitenCost-Effectiveness Analysis of Alternative First-Trimester Pregnancy Termination Strategies in Mexico CityJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imperial College COVID19 NPI Modelling 16-03-2020Dokument20 SeitenImperial College COVID19 NPI Modelling 16-03-2020Zerohedge100% (11)
- Perspective: New England Journal MedicineDokument3 SeitenPerspective: New England Journal MedicineJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid 2Dokument7 SeitenCovid 2TBP_Think_Tank100% (2)
- Corona Virus and The Great Influenza PandemicDokument26 SeitenCorona Virus and The Great Influenza PandemicHafeez ullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farewell Seguro PopularDokument2 SeitenFarewell Seguro PopularJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect Public Health Measures UsaDokument6 SeitenEffect Public Health Measures UsaJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swine FluDokument16 SeitenSwine FluJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pandemics Depress The Economy, Public Health Interventions Do Not: Evidence From The 1918 FluDokument45 SeitenPandemics Depress The Economy, Public Health Interventions Do Not: Evidence From The 1918 FluJorge Eduardo Sánchez MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVIDEconomicCrisis PDFDokument227 SeitenCOVIDEconomicCrisis PDFFreddy KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Use Efficiency Of: TomatoesDokument8 SeitenWater Use Efficiency Of: TomatoesbagororoNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Be Print All PDFDokument13 SeitenTo Be Print All PDFyaritzas santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 99/100, 10 Level Prestige Towers, Residency Road, Bangalore 560025 +91 9742211488, +91 9742211446Dokument2 Seiten99/100, 10 Level Prestige Towers, Residency Road, Bangalore 560025 +91 9742211488, +91 9742211446Vignesh EkambaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hotel Promotion Report Start UpDokument20 SeitenHotel Promotion Report Start UpniloyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal PAT Bhsa Inggris Kelas XI 2022Dokument23 SeitenSoal PAT Bhsa Inggris Kelas XI 2022Syamsul RidwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dabbawala TransformationDokument5 SeitenDabbawala TransformationROHIT CHOUDHARYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 4 YemochiDokument22 SeitenGroup 4 YemochiJane GawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respons Pertumbuhan Dan Produksi Tanaman Okra (Abelmoschus Esculantus L. Moench) Terhadap Waktu Pemangkasan Pucuk Dan Pemberian Pupuk NPKDokument9 SeitenRespons Pertumbuhan Dan Produksi Tanaman Okra (Abelmoschus Esculantus L. Moench) Terhadap Waktu Pemangkasan Pucuk Dan Pemberian Pupuk NPKStepeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tle Cookery Grade 10 Module 3Dokument22 SeitenTle Cookery Grade 10 Module 3Lilac QtNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Personal Consumption Audit: Product/FoodDokument2 SeitenMy Personal Consumption Audit: Product/FoodRica DumalaogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1: Grammar and Vocabulary Test A Unit 1: Grammar and Vocabulary Test BDokument12 SeitenUnit 1: Grammar and Vocabulary Test A Unit 1: Grammar and Vocabulary Test BNatalia VivonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction of Caffeine From Tea LeavesDokument8 SeitenExtraction of Caffeine From Tea LeavesCesarah CabungcalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prueba de Diagnóstico 6th REVISADODokument3 SeitenPrueba de Diagnóstico 6th REVISADODenisse RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tribes Nomads and Settled CommunitiesDokument6 SeitenTribes Nomads and Settled CommunitiesPriya Chaurasia 7BNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Animal Organ SystemsDokument2 Seiten07 Animal Organ SystemsJohn Carlo MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Pts Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 - 115225Dokument5 SeitenSoal Pts Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 - 115225Halmut AlfadellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-2 Sales Concepts: Monetary TermDokument14 SeitenUnit-2 Sales Concepts: Monetary TermHimanshu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation End-Of-1St-Term Test English - Grade 8: Archimedes SchoolDokument23 SeitenConsolidation End-Of-1St-Term Test English - Grade 8: Archimedes SchoolNguyên Khôi BùiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floor Plan Set 2 1 Is To 200Dokument1 SeiteFloor Plan Set 2 1 Is To 200Hanzel Shaun PahayupanNoch keine Bewertungen