Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Trajectory Terms: Bullet Path - Line of Departure
Hochgeladen von
luisOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trajectory Terms: Bullet Path - Line of Departure
Hochgeladen von
luisCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
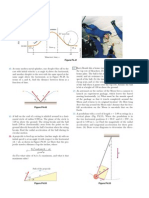
TRAJECTORY TERMS
Line of departure - The direction and path the bullet would take without gravity
Bullet path - The actual path of the bullet
Line of sight - imaginary straight line from the shooters eye to the target and beyond
Height of eye or sights above
the centerline of the bore
Maximum ordinate
The highest point the bulet achieves
in its trajectory above the line of departure.
1,5î BASELINE
100 200 300 400 500
Muzzle
Zero distance
The distance the rifle is zeroed on. Zero distance
determines the the lenght and height of the trajectory.
Factors that effect external ballistics / trajectory Terms related to external ballistics
1. Gravity - downward force pulling the projectile towards the ground Time of flight
- altitude - effect of gravity decreases when altitude increases - The amount of time it takes the bullet to reach itís destination
2. Drag - the resistance the projectile meets when travelling through air Bullet drop
(A) Air Density - The amount the bullet drops towards the ground after leaving the barrel
-Altitude - at higher altitudes air density is lower and vice versa Here the bullet travels
-Air pressure - related to humidity and temperature Muzzle velocity below the line of sight.
-Temperature - affects air density, the cooler the air the higher the air density - The speed the bullet leaves the barrel of the gun.
and vice versa
-Humidity - affects air density, the dryer the air is the higher the air density and Ballistic coefficient
vice versa - The aerodynamic efficiency of the bullet. It takes into account the
(B) Bullet Efficiency shape, weight and cross sectional area of the bullet.
- Ballistic coefficient Remaining velocity
- Muzzle velocity - Bulletís velocity after initial muzzle velocity at a specific distance.
For informational purposes only. Copyright Sniperworld.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Forensic Ballistics 2014Dokument80 SeitenForensic Ballistics 2014Rena Lyn Grace MonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On BallisticsDokument281 SeitenReview On BallisticsDariel De VeneciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of BALLISTICSDokument12 SeitenFundamentals of BALLISTICSmoury alundayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic Ballistics Ballistics Motion: Projectiles Bullets Gravity Bomb S RocketsDokument12 SeitenForensic Ballistics Ballistics Motion: Projectiles Bullets Gravity Bomb S RocketsElizabeth Veloso100% (1)
- @lesson4c ExternalDokument10 Seiten@lesson4c ExternalGesler Pilvan SainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Bore Sight CalculatorDokument5 SeitenLaser Bore Sight Calculatorbcline44325067100% (1)
- Projectile MotionDokument2 SeitenProjectile MotionHannah CenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curvilenear MotionDokument2 SeitenCurvilenear Motionsabel100% (1)
- Firearm Terminology 1Dokument80 SeitenFirearm Terminology 1api-242596953Noch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Launched at An AngleDokument2 SeitenProjectile Launched at An Anglenathaniel braceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- BALLISTICSREVIEWERDokument7 SeitenBALLISTICSREVIEWERAbigail beldanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101 Lab 10. Ballistic PendulumDokument7 Seiten101 Lab 10. Ballistic PendulumSana AshfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics in Two DimensionsDokument12 SeitenKinematics in Two DimensionsSTA. FE NHS ICTNoch keine Bewertungen
- BallisticsDokument12 SeitenBallisticsGrozny GroznyNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Powerpoint DemoDokument26 SeitenMy Powerpoint DemoJarold Kinsman AlagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Shit of Precision Shooting (Especially Advanced Ballistics) !Dokument10 SeitenBasic Shit of Precision Shooting (Especially Advanced Ballistics) !Dobredi100% (6)
- FORENSIC 106FORENSIC BALLISTICS CHAPTER 1 To Chapter5Dokument11 SeitenFORENSIC 106FORENSIC BALLISTICS CHAPTER 1 To Chapter5Edlyn PanganibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion: How Angle of Release Affects Height and RangeDokument11 SeitenProjectile Motion: How Angle of Release Affects Height and RangeTrevor James TjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion ExtraDokument6 SeitenProjectile Motion ExtraAvishek RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Externalballistics 181021165210Dokument13 SeitenExternalballistics 181021165210Petru BurduhosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion WorkbookDokument8 SeitenProjectile Motion WorkbookLorieley EugenioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yarn TensionDokument8 SeitenYarn TensionAbhinandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- External BallisticsDokument16 SeitenExternal Ballisticsblowmeasshole1911100% (1)
- Q4 M2 Activity No 2Dokument2 SeitenQ4 M2 Activity No 2David UtahNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORENSIC BALLISTICS ANALYSISDokument37 SeitenFORENSIC BALLISTICS ANALYSISRosemarie Manang HagnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EO Using Small Satellites CapabilitiesDokument36 SeitenEO Using Small Satellites CapabilitiesМРязанскийNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Ballistics - Hornady Manufacturing, IncDokument15 SeitenExternal Ballistics - Hornady Manufacturing, IncThiago NeryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Criminalistic CRIM BOOSTER28129466vxdswwxchhDokument6 SeitenCriminalistic CRIM BOOSTER28129466vxdswwxchhLioliza Mae G. ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Branches of BallisticsDokument9 Seiten4 Branches of BallisticsLeo Restian OlaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic BallisticsDokument3 SeitenForensic BallisticsDenver TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic BallisticsDokument3 SeitenForensic BallisticsDenver TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air-Jet Weft Insertion System Part 2Dokument11 SeitenAir-Jet Weft Insertion System Part 2Neeraj BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.3 Effects of Shooting Uphill or DownhillDokument5 Seiten3.3 Effects of Shooting Uphill or Downhillblowmeasshole19110% (1)
- Registration of Government-Owned FirearmsDokument235 SeitenRegistration of Government-Owned Firearmsjanharold valdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim Lesson 1.4 The Three Main Branches of BallisticsDokument6 SeitenPrelim Lesson 1.4 The Three Main Branches of BallisticsTIPAY, EMELIE L.100% (1)
- Understand external ballistics with this concise guideDokument18 SeitenUnderstand external ballistics with this concise guideblowmeasshole1911100% (1)
- Projectile Lab SimulationDokument2 SeitenProjectile Lab SimulationJoshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 D SVGR KKi 5 D3 XPM TZ9 T LIs W7 YLn JCJ I00Dokument6 Seiten1 D SVGR KKi 5 D3 XPM TZ9 T LIs W7 YLn JCJ I00Omar MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThePhysic of SoccerDokument15 SeitenThePhysic of SoccersumitchakravarthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic 6Dokument42 SeitenForensic 6Rafael Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Las No. 2Dokument8 SeitenLas No. 2santos.johnandrei719Noch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile MotionDokument55 SeitenProjectile MotionBhryan Hans TulaylayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cone 2223Dokument11 SeitenCone 2223HiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow over an American Football Simulation ResultsDokument8 SeitenFlow over an American Football Simulation ResultsRizqi RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Message 3Dokument6 SeitenMessage 3k a b b a l a h d y i n g d e f e a t d e a t hNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision - DPP 01 (Motion in A Plane)Dokument5 SeitenRevision - DPP 01 (Motion in A Plane)Demon SlayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branches of BallisticsDokument6 SeitenBranches of BallisticsJefferson AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios Serway - Movimientos.Dokument2 SeitenEjercicios Serway - Movimientos.jddiazmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bane Bless Command: Enchantment Enchantment EnchantmentDokument4 SeitenBane Bless Command: Enchantment Enchantment EnchantmentasdasdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science SonDokument26 SeitenScience SonBlue SkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 Projectile Motion Launched Horizontally and at An AngleDokument16 SeitenScience 9 Projectile Motion Launched Horizontally and at An AngleAlvin OliverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Projectile Motion ExplainedDokument5 SeitenPrinciples of Projectile Motion ExplainedChen Peck Lian100% (1)
- 2-5 New Error Codes PDFDokument13 Seiten2-5 New Error Codes PDFdacem torres cruz100% (1)
- Fundamentlsof Rotor and Power Train Maintenance Techniques and ProceduresDokument68 SeitenFundamentlsof Rotor and Power Train Maintenance Techniques and ProceduresrfriosEPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Forensic 104Dokument7 SeitenChapter 1 Forensic 104joseph maulionNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Physics NotesDokument18 SeitenSPM Physics NotesJerry LowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic Ballistics Intro 1Dokument32 SeitenForensic Ballistics Intro 1Angie SangagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Reflection and Refraction GuideDokument29 SeitenLight Reflection and Refraction Guideanwar9602020Noch keine Bewertungen
- USMC Technical Data Sheet For Less Than Lethal Munitions Demolition Associated Items USA 2007Dokument103 SeitenUSMC Technical Data Sheet For Less Than Lethal Munitions Demolition Associated Items USA 2007jobseekeramatx100% (1)
- Weapons Santiago PathfinderDokument6 SeitenWeapons Santiago PathfinderTerrence SteeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ammunition Performance DataDokument9 SeitenAmmunition Performance DataRicardo RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rifle - AR15 - CORE15 M4 Scout Manual - Purchased 15-0824 Rural KingDokument16 SeitenRifle - AR15 - CORE15 M4 Scout Manual - Purchased 15-0824 Rural KingMike HendersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blaser Lrs 2Dokument4 SeitenBlaser Lrs 2tototoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ammunition Types and Characteristics for 5.56mm WeaponsDokument2 SeitenAmmunition Types and Characteristics for 5.56mm Weaponsdonnyvid100% (1)
- BRNO Stopper Manual - enDokument10 SeitenBRNO Stopper Manual - enjeffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Auto Colt 1911 HlebooksDokument19 SeitenFull Auto Colt 1911 Hlebookstor100% (11)
- Aaron Dean Supplemental Report #2 RedactedDokument4 SeitenAaron Dean Supplemental Report #2 Redactedredrum media100% (1)
- Reloading Guide: For Centerfire CartridgesDokument47 SeitenReloading Guide: For Centerfire Cartridgesremi GALEA100% (1)
- Ruger American Rimfire Target Rifle Spec SheetDokument3 SeitenRuger American Rimfire Target Rifle Spec SheetAmmoLand Shooting Sports NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FBI Defensive Systems Unit Ballistic Research Facility FBIAcademyDokument21 SeitenFBI Defensive Systems Unit Ballistic Research Facility FBIAcademyWalmor Silva de Souza100% (1)
- Colt-Browning Model 1895 Machine Gun (Potato Digger)Dokument7 SeitenColt-Browning Model 1895 Machine Gun (Potato Digger)blowmeasshole1911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common Sub .... CHPT 4... Weapon TrainingDokument13 SeitenCommon Sub .... CHPT 4... Weapon TrainingĒ Vì LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horizons Below: Moderate 197 Intro "Leave... " Verse I "Never... "Dokument10 SeitenHorizons Below: Moderate 197 Intro "Leave... " Verse I "Never... "neowzeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ballistics Ppt.08Dokument46 SeitenBallistics Ppt.08Kevin Abendan100% (1)
- Basic Identification of Ammunition in Ukraine v3.0 - English - Bomb Techs Without Borders - 3, 2023 - Bomb Techs Without Borders - Anna's ArchiveDokument692 SeitenBasic Identification of Ammunition in Ukraine v3.0 - English - Bomb Techs Without Borders - 3, 2023 - Bomb Techs Without Borders - Anna's ArchiveArthur SoaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAS Research Note 43 СтрелковоеDokument4 SeitenSAS Research Note 43 СтрелковоеvoenpromNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diana Stormrider PY-4449-8647 ManualDokument12 SeitenDiana Stormrider PY-4449-8647 ManualMr HamakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTAI BrochureDokument10 SeitenCTAI BrochureThinkDefence100% (5)
- BARRETT 2021 Firearm Catalog REV1Dokument23 SeitenBARRETT 2021 Firearm Catalog REV1СергейNoch keine Bewertungen
- IWI Negev - WikipediaDokument52 SeitenIWI Negev - WikipediaYuvaraj BhaduryNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCRP 3-01A Rifle MarksmanshipDokument116 SeitenMCRP 3-01A Rifle MarksmanshipJustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMR Trailboss Handgun Reloading Data March 2010Dokument6 SeitenIMR Trailboss Handgun Reloading Data March 2010Heywood JablowmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Halo RPGDokument10 SeitenHalo RPGTimothy Klott100% (3)
- Buildingbolt Action Rifles Engl.Dokument52 SeitenBuildingbolt Action Rifles Engl.Ai MaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ragnar Skanaker - Master Competitive Pistol Shooting (2016)Dokument174 SeitenRagnar Skanaker - Master Competitive Pistol Shooting (2016)lt castroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ra 10591Dokument25 SeitenRa 10591Anthea Louise Rosino100% (1)
- Bren LMG ManualDokument7 SeitenBren LMG ManualGasMaskBobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combat Tactics & Injury RisksDokument2 SeitenCombat Tactics & Injury RisksSturm Novahl0% (1)