Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Soln 11013
Hochgeladen von
LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATAOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Soln 11013
Hochgeladen von
LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATACopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
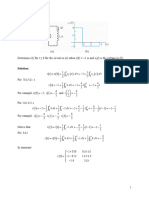
COSMOS: Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization System
Chapter 11, Solution 13.
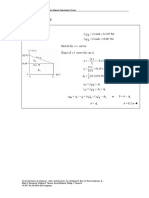
v t t
Determine velocity. ∫ − 0.15 dv = ∫ 2 a dt = ∫ 2 0.15 dt
v − ( −0.15 ) = 0.15t − ( 0.15 )( 2 )
v = 0.15t − 0.45 m/s
At t = 5 s, v5 = ( 0.15 )( 5 ) − 0.45 v5 = 0.300 m/s W
When v = 0, 0.15t − 0.45 = 0 t = 3.00 s
For 0 ≤ t ≤ 3.00 s, v ≤ 0, x is decreasing.
For 3.00 ≤ t ≤ 5 s, v ≥ 0, x is increasing.
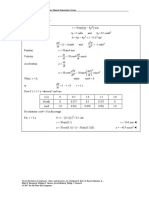
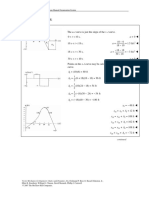
∫ −10 dx = ∫ 0 v dt = ∫ 0 ( 0.15t − 0.45) dt
x t t
Determine position.
t
(
x − ( −10 ) = 0.075t 2 − 0.45t ) 0
= 0.075t 2 − 0.45t
x = 0.075 t 2 − 0.45t − 10 m
2
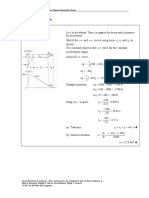
At t = 5 s, x5 = ( 0.075 )( 5 ) − ( 0.45 )( 5 ) − 10 = −10.375 m
x5 = −10.38 m W
At t = 0, x0 = −10 m (given)
At t = 3.00 s,
2
x3 = xmin = ( 0.075 )( 3.00 ) − ( 0.45 )( 3.00 ) − 10 = −10.675 mm
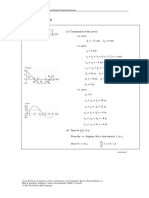
Distances traveled:
Over 0 ≤ t ≤ 3.00 s, d1 = x0 − xmin = 0.675 m
Over 3.00 s < t < 5 s, d 2 = x5 − xmin = 0.300 m
Total distance traveled: d = d1 + d 2 = 0.975 m d = 0.975 m W
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics, 8/e, Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston, Jr.,
Elliot R. Eisenberg, William E. Clausen, David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hart Solutions PDFDokument218 SeitenHart Solutions PDFJunior Alvarenga100% (7)
- Cherry QQ (S21) 2006-2013 Electrical CircuitDokument37 SeitenCherry QQ (S21) 2006-2013 Electrical CircuitPablo Sanhueza100% (2)
- Lec 1 BDokument11 SeitenLec 1 BSaad AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems: Section 7-2: Capacitors P7.2-1Dokument6 SeitenProblems: Section 7-2: Capacitors P7.2-1Heesoo YooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - Energy Storage ElementsDokument45 SeitenChapter 7 - Energy Storage ElementsGeoFurriel50% (2)
- Chapter 7 Homework SolutionDokument20 SeitenChapter 7 Homework SolutionAndy SimbañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P7.2-2, 4, 5, 7 P7.3-1, 2, 5 P7.4-1, 4 P7.5-2, 4, 13, 14, 20 P7.6-1, 3 P7.7-2, 6 P7.8-1, 3, 5, 6, 13Dokument20 SeitenP7.2-2, 4, 5, 7 P7.3-1, 2, 5 P7.4-1, 4 P7.5-2, 4, 13, 14, 20 P7.6-1, 3 P7.7-2, 6 P7.8-1, 3, 5, 6, 13Vibhuti NarayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCHOsolnDokument4 SeitenLCHOsolnDaniela F L BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 9Dokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 9Lynn Abu QaoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 9Dokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 9LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 2 Asal PhysicsDokument6 SeitenCoursebook Answers Chapter 2 Asal PhysicsIrina BodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics DynamicsDokument104 SeitenKinematics DynamicsNadiaa AdjoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 Solution Outline Q1 Ds B: T BS T DT D V V IDokument7 SeitenTutorial 2 Solution Outline Q1 Ds B: T BS T DT D V V Isamfisher1257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complemento Uchile (Semigrupos)Dokument18 SeitenComplemento Uchile (Semigrupos)robertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Solution - 6bDokument10 SeitenSolutions Solution - 6bapi-26658409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Tutorial Worksheet 1: DEN108 DynamicsDokument4 SeitenSolutions Tutorial Worksheet 1: DEN108 DynamicsgmwilliamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key For Take Home Quiz 3Dokument5 SeitenAnswer Key For Take Home Quiz 3Nexty GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inbound 8103230202756823036Dokument54 SeitenInbound 8103230202756823036zettoholenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics of Particles: Learning ContentDokument9 SeitenKinematics of Particles: Learning ContentGIYANG BATANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hibbeler D14 e CH 12 P 3Dokument1 SeiteHibbeler D14 e CH 12 P 3razonablejhunrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solucionario Capitulos 1 & 2 Ing. Mecanica - Dinamica, Robert Soutas LittleDokument211 SeitenSolucionario Capitulos 1 & 2 Ing. Mecanica - Dinamica, Robert Soutas LittleGeraldo De Los Santos100% (2)
- EE100supplementary Notes 14Dokument11 SeitenEE100supplementary Notes 14foof faafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.27: Given: Find: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.27: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bontet Gaming FisikaDokument4 SeitenBontet Gaming FisikaXyzer SkippingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bontet Gaming FisikaDokument4 SeitenBontet Gaming FisikaXyzer SkippingNoch keine Bewertungen
- D T T D T T D T D: D Represent The Distance Between A and B. LetDokument7 SeitenD T T D T T D T D: D Represent The Distance Between A and B. LetDiego Escobar MoncadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics Unit 5Dokument68 SeitenEngineering Mechanics Unit 5SundraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 01 Sec 5Dokument5 SeitenCH 01 Sec 5김성준Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 3 - SolutionDokument8 SeitenExercise 3 - SolutionFatimah Azzahra ArhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 1-CircuitsDokument8 SeitenHomework 1-CircuitsDanielle AwonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.16 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 1.16 PDFGabriel CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6-02-Interpolasi LagrangeDokument16 Seiten6-02-Interpolasi LagrangenaufalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Paper AnswersDokument4 SeitenPractice Paper AnswersshineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soln 11006Dokument1 SeiteSoln 11006LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT Presentation (Physics-Mecahanics)Dokument22 SeitenMIT Presentation (Physics-Mecahanics)mevlana3992Noch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS Problem Set 1Dokument10 SeitenPHYS Problem Set 1khaizanjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Numerical Methods: Prof. P. K. JhaDokument82 SeitenTo Numerical Methods: Prof. P. K. JharbansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probset 2Dokument5 SeitenProbset 2Princess Niña B. PedrosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Assessment Answers 2 Asal Physics CBDokument4 SeitenSelf Assessment Answers 2 Asal Physics CBarnavpro23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engmec2 LQ1Dokument6 SeitenEngmec2 LQ1Martin Nicolas ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 2Dokument3 SeitenHW 2Puji dyukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 15.: DV A KT DT DV V DV KT DTDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 15.: DV A KT DT DV V DV KT DTLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE GATE 2021 February 7 3 PM Converted 1Dokument5 SeitenECE GATE 2021 February 7 3 PM Converted 12512bindumadhaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF - 2024-02-17T152551.510Dokument10 SeitenPDF - 2024-02-17T152551.510zuimaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics 2Dokument14 SeitenDynamics 2mirapazcookeNoch keine Bewertungen
- P 6 Week 2Dokument8 SeitenP 6 Week 2Danica RafolsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manual PDFDokument36 SeitenDwnload Full Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manual PDFbaddishimmanetltp100% (10)
- HW& Midterm SolutionsDokument44 SeitenHW& Midterm SolutionsSamuel HollisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions ManualDokument31 SeitenFull Download Engineering Mechanics Dynamics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manualthumbapofhyiu100% (36)
- 209 Position vs. Time Graphs WorksheetDokument4 Seiten209 Position vs. Time Graphs WorksheetAnna KopsickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11. Kinematics of Particles: Rectilinear MotionDokument73 SeitenChapter 11. Kinematics of Particles: Rectilinear MotionChristopher Traifalgar CainglesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering DynamicsDokument23 SeitenEngineering DynamicssadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 2004: Electric Circuit Analysis: T T T T QDokument3 SeitenECE 2004: Electric Circuit Analysis: T T T T QPao JJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter2 PDFDokument13 SeitenChapter2 PDFnur antashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Invariant Set TheoremDokument11 SeitenLocal Invariant Set TheoremAhmad RahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Von EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYVon EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99Von EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Von EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Noch keine Bewertungen
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 76.: A Is 24 Ft/s. Using A T T TDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 76.: A Is 24 Ft/s. Using A T T TLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Soln11069 PDFDokument1 SeiteSoln11069 PDFLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 77.: DX V DT DV A DTDokument2 SeitenChapter 11, Solution 77.: DX V DT DV A DTLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Soln11073 PDFDokument1 SeiteSoln11073 PDFLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 75.: Sketch The Curves. Slope of Curve For Car ADokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 75.: Sketch The Curves. Slope of Curve For Car ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 65.: T A T ADokument2 SeitenChapter 11, Solution 65.: T A T ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 74.: Sketch The CurvesDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 74.: Sketch The CurvesLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 63.: at A ADokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 63.: at A ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 67.: T AA ADokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 67.: T AA ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 68Dokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 68LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Sketch Curve For First 660 FT.: Chapter 11, Solution 72Dokument2 SeitenSketch Curve For First 660 FT.: Chapter 11, Solution 72LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 64Dokument2 SeitenChapter 11, Solution 64LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Soln 11049Dokument1 SeiteSoln 11049LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 50Dokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 50LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 57.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Anchor, Positive To The RightDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 57.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Anchor, Positive To The RightLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Soln 11060Dokument1 SeiteSoln 11060LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 58.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Anchor, Positive To The RightDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 58.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Anchor, Positive To The RightLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 54.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Right Supports, Increasing To The LeftDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 54.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Right Supports, Increasing To The LeftLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 62Dokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 62LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Soln 11162Dokument2 SeitenSoln 11162LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 56.: Let X Be Position Relative To Left Anchor. at Right AnchorDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 56.: Let X Be Position Relative To Left Anchor. at Right AnchorLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 51.: Let XDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 51.: Let XLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 55.: Let X Be Position Relative To Left Anchor. at The Right AnchorDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 55.: Let X Be Position Relative To Left Anchor. at The Right AnchorLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 40.: T y A G y TDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 40.: T y A G y TLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 53.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Right Supports, Increasing To The LeftDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 53.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Right Supports, Increasing To The LeftLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Place The Origin at A When T 0. Motion Of: Chapter 11, Solution 42Dokument1 SeitePlace The Origin at A When T 0. Motion Of: Chapter 11, Solution 42LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 48.: X X V VDokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 48.: X X V VLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 35Dokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 35LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 43Dokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 43LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11, Solution 45.: V V at V T V V V A T ADokument1 SeiteChapter 11, Solution 45.: V V at V T V V V A T ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Application Library ManualDokument918 SeitenHeat Transfer Application Library Manualmeysam NaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP - Technical Seminar For Cathodic Protection To GOGC DesignDokument21 SeitenCP - Technical Seminar For Cathodic Protection To GOGC DesignLjiljana MiskovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cartesian Coordinate SystemDokument12 SeitenThe Cartesian Coordinate SystemSarah SuccariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asad - Utilization of FAC As Lightweight Filler in Cement-Based CompositesDokument12 SeitenAsad - Utilization of FAC As Lightweight Filler in Cement-Based CompositesShan RatnayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation Engineering Lecture-4Dokument16 SeitenTransportation Engineering Lecture-4Avishya JaswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9791 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesDokument6 Seiten9791 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesBebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-11 Light PPT-2Dokument33 SeitenCH-11 Light PPT-2SUHANEERIYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Projection Radiography, Also Called ConventionalDokument11 SeitenProjection Radiography, Also Called ConventionalRaziv Maulana UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water InfluxDokument13 SeitenWater InfluxTaha SartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications and Characteristics of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51)Dokument6 SeitenApplications and Characteristics of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51)catalinccNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psib 20130524aDokument1 SeitePsib 20130524aLéandre Ettekri NdriNoch keine Bewertungen
- tp2 Vom-1Dokument4 Seitentp2 Vom-1HoussamdineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Assessment of Ship StructuresDokument25 SeitenFatigue Assessment of Ship StructuresAlex TheodoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archives of Oral Biology: ReviewDokument10 SeitenArchives of Oral Biology: ReviewEDER YAHIR MONROY MENDOZANoch keine Bewertungen
- Built-Up Battened Columns Under Lateral Cyclic Loading: Dipti R. Sahoo, Durgesh C. RaiDokument11 SeitenBuilt-Up Battened Columns Under Lateral Cyclic Loading: Dipti R. Sahoo, Durgesh C. RaiKhaled Abdel SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEC 60076-3 ED 3.0 2013-07 Clause 5Dokument2 SeitenIEC 60076-3 ED 3.0 2013-07 Clause 5Erhan KarabasNoch keine Bewertungen
- For NA EU WB37 Intelligent Battery Safety Guidelines v1.0Dokument27 SeitenFor NA EU WB37 Intelligent Battery Safety Guidelines v1.0ramon romahnNoch keine Bewertungen
- KRMF706ESS00 Tech Sheet - W10738568 - Kitchen AidDokument2 SeitenKRMF706ESS00 Tech Sheet - W10738568 - Kitchen AidEdison EspinalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Grading in Electrical MachinesDokument4 SeitenField Grading in Electrical MachinesPaawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of UV SpectrosDokument10 SeitenPrinciple of UV SpectrosHesham AlsoghierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electrochemistry: CHEM 7234 CHEM 720Dokument56 SeitenFundamentals of Electrochemistry: CHEM 7234 CHEM 720Marcelo CalegaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction - Concept of StressDokument24 SeitenIntroduction - Concept of StressShantanu PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation of SuperstructureDokument247 SeitenDesign Calculation of SuperstructureMrinal KayalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS7-IR Test Report For Electrical DrumsDokument1 SeiteCS7-IR Test Report For Electrical DrumsAbdullah Al-ObaidyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demonstration of Microscope and Its PartsDokument5 SeitenDemonstration of Microscope and Its PartsSujoy Tontubay100% (1)
- EPM - 07 - 07S - Manual - ENTESDokument4 SeitenEPM - 07 - 07S - Manual - ENTESAhmed Mohamed Kamal El-DeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Https:downloads Hindawi Com:archive:2016:7249743Dokument14 SeitenHttps:downloads Hindawi Com:archive:2016:7249743Rashmita BaruahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Efficient 5-HP BLDC Motor For Solar Water Pump and Performance Comparison With Induction Motor CounterpartDokument4 SeitenDevelopment of Efficient 5-HP BLDC Motor For Solar Water Pump and Performance Comparison With Induction Motor CounterpartDhinu LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Pack and Formulae of Chapter 4Dokument15 SeitenStudy Pack and Formulae of Chapter 4RatanakNoch keine Bewertungen