Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Multiple Choice Portion 1.: Unit 8: Electromagnetism
Hochgeladen von
Mr saifan and Mr shehzadOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Multiple Choice Portion 1.: Unit 8: Electromagnetism
Hochgeladen von
Mr saifan and Mr shehzadCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physics 12: Unit 8 Questions.
doc
Unit 8: Electromagnetism
Multiple Choice Portion
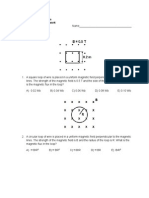
1. Four compasses are placed around a conductor carrying 6. Transformers are commonly used in which electrical
a current into the page, as shown below. Which device?
compass correctly shows the direction of the magnetic a. toaster
field due to the current? b. television set
c. electric kettle
c. d. incandescent bulb
a.
7. A dc motor is connected to a constant voltage supply.
The load on the motor decreases, allowing the motor to
rotate faster. How do the back emf and current through
the motor change?
BACK EMF CURRENT
a. decreases decreases
b. d. b. decreases increases
c. increases decreases
d. increases increases
2. What is the radius of curvature of the path of a proton
travelling at 4.7 x 105m/s in a plane perpendicular to a 8. In which of the following situations would an induced
0.52 T magnetic field? emf be produced in a rectangular loop of wire? The
a. 2.0 x 10 -8 m loop of wire is moved as indicated.
b. 5.1 x 10 -6 m
c. 9. 4 x 10 -3 m
d. 1.1 x 10 2 m
3. A motor operating at full speed draws a current of
4.0 A when connected to a 110 V source. The motor
has an armature resistance of 3.5 Ω. What is the back
emf at full speed?
a. 14 V a.
b. 96 V
c. 110 V
d. 124 V
4. In the following diagram, ammeter A shows a current
b.
a. while switch S remains closed.
b. while switch S remains opened.
c. only while switch S is being closed
d. while switch S is being opened or being closed.
c.
5. A transformer connected to a 120 V ac source has an
output of 24 V ac. If the primary coil has 330 turns,
how many turns of wire are there in the secondary coil?
a. 24 turns
b. 66 turns
c. 330 turns
d. 1 650 turns
d.
Version 2007 2 - 46 - Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 8 Questions.doc
9. The graph below shows how the magnetic flux through 12. A beam of electrons is directed into a uniform
a single loop changes with respect to time. What is the magnetic field and deflects as shown in Figure I. If a
average emf induced between t = 2.0 x 10 -3 s and beam of protons with the same speed were to enter this
t = 9.0 x 10 -3 s? same magnetic field, which of the paths shown in
Figure II would the protons take?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
a. 1.2 x10 -4 V d. 4
b. 1.8 V
c. 3.6 V 13. Which of the following graphs best shows how the
d. 25 V magnetic field B varies with the perpendicular distance
d from a long, straight current-carrying conductor?
10. Which of the following is a step-up transformer?
a. c. a.
b.
b. d.
11. A solenoid of diameter 0.018 m is 0.30 m long. A
current of 5.3 A is used to create a magnetic field of
0.25 T at the centre of the solenoid. How many turns of
wire does this solenoid have? c.
a. 6.8 x 102
b. 2.1 x 10 3
c. 1.1 x 10 4
d. 3.8 x 10 4
d.
14. For what type of input current will the output current in
a transformer be zero?
a. dc
b. ac
c. increasing dc
d. decreasing dc
15. A motor designed to operate on 120 V draws a current
of 33 A when it first starts up. At its normal operating
speed, the motor draws a current of 2.7 A. What is the
back emf at normal operating speed?
a. 9.8 V
b. 110 V
c. 120 V
d. 130 V
Version 2007 2 - 47 - Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 8 Questions.doc
16. A 35 loop square coil 0.12 m on a side is positioned in 20. A wire is in a magnetic field as shown. wire
a 0.050 T magnetic field. A 0.20 kg mass is suspended
from one side of the coil as shown in the diagram
below.
In which direction could the wire be moved to induce
an emf across the length of the wire?
How much current must pass through the coil in order a. to the left
for the coil to remain horizontal? b. up the page
a. 2.3 A c. into the page
b. 4.7 A d. down the page
c. 9.3 A
d. 330 A 21. An emf is induced in a coil if the magnetic flux through
the coil is
17. Which of the following diagrams shows the magnetic a. zero.
field produced by a long current-carrying wire b. changing.
c. constant and large.
d. constant and small.
22. A coil of wire contains 55 loops. The coil is rotated
such that the flux changes from 2.0 x 10-4 Wb to
8.0 x 10-4 Wb in 1.5 x 10-2 s. What is the average
induced emf?
a. 1.1 V
18. The diagram below shows an electron travelling to the b. 1.8 V
left in a magnetic field. c. 2.2 V
d. 3.7 V
23. A door bell transformer has 900 primary windings and
60 secondary windings. The secondary current is
0.30 A. What is the primary current and what is the
type of transformer?
PRIMARY CURRENT TRANSFORMER
(A) TYPE
a. 0.020 Step-Up
In which direction will the electron be deflected? b. 0.020 Step-Down
a. into the page c. 4.5 Step-Up
b. out of the page d. 4.5 Step-Down
c. towards the north pole
d. towards the south pole
24. Identify the poles of the magnets shown.
19. A doubly-ionized atom (Q = 2e) with a mass of
6.8 x 10-27 kg enters a 3.0 T magnetic field with a speed
of 5.0 x 10 7 m/s. What is the radius of the circular path
of the atom?
a. 0.35 m POLE L POLE R
b. 0.71 m a. North North
c. 1.4 m b. North South
d. 2.8 m c. South North
d. South South
Version 2007 2 - 48 - Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 8 Questions.doc
25. A 500-turn circular coil with an area of 1.54 x 10-2 m2 30. As an aircraft flies horizontally over the North Pole, a
is perpendicular to a 0.060 T field. The magnetic field 0.80 V potential difference is induced across the wings.
changes to 0.020 T in the opposite direction in 0.12 s. If the aircraft now slows to one half of the original
speed, what will the new potential difference be?
a. 0.40 V
b. 0.57 V
c. 0.80 V
d. 1.6 V
31. A coil of wire of area 1.5 x 10-3 m2 consists of 40
loops. A magnetic field is perpendicular to the face of
the coil. In a period of 0.20 s the strength of the
magnetic field decreases from 0.060 T to 0.050 T in the
same direction. What is the average emf induced in the
coil during this time?
a. 7.5 x 10 –5 V
b. 1.5 x 10 –3 V
What is the average emf induced in the coil?
c. 3.0 x 10 –3 V
a. 5.1 x 10-3 V
d. 3.3 x 10 –2 V
b. 1.0 x10-2 V
c. 2.6 V
32. The current in an electric motor running at full speed is
d. 5.1 V
2.5 A when connected to an 80 V dc source. If the
armature resistance of the motor is 4.0 Ω, what is the
26. Which of the following devices commonly uses a
back emf at this speed?
solenoid?
a. 0 V
a. kettle
b. 10 V
b. battery
c. 70 V
c. television set
d. 90 V
d. incandescent bulb
33. An ideal transformer has 150 turns in the primary coil
27. A compass placed on a table points north. In which
and 1 800 turns in the secondary coil. If the primary
direction should a conductor, placed directly above the
coil is connected to 120 V ac and draws 7.5 A of
compass, carry current in order to reverse the direction
current, what is the current in the secondary coil?
of the compass needle?
a. 0.63 A
a. east to west
b. 7.5 A
b. west to east
c. 16 A
c. north to south
d. 90 A
d. south to north
34. An electron moves in a circular orbit of radius r in a
28. In a step-up transformer, how do the primary and
magnetic field. The electron moves in a path
secondary voltages, and the primary and secondary
perpendicular to the magnetic field. If the kinetic
currents, compare to one another?
energy of the electron is doubled, what is the new
a. Vs > Vp and Is > Ip
radius of its path?
b. Vs > Vp and Is < Ip
a. ½r
c. Vs < Vp and Is > Ip
d. Vs < Vp and Is < Ip b. 2r
c. 2r
29. When a 9.0 V power supply is connected to a motor d. 4r
whose internal resistance is 0.40 Ω, a current of 1.5 A
flows through its windings. Find the back emf of the
motor.
a. 0.60 V
b. 8.4 V
c. 9.0 V
d. 9.6 V
Version 2007 2 - 49 - Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 8 Questions.doc
Written
1. A proton is travelling at 2.58 x 105 m/s towards a conductor carrying a current of 125 A. What is the magnitude of the
magnetic force acting on the proton 0.650 m from the conductor?
2. When an electric drill turns at normal operating speeds, there is little heat produced in the motor windings. When drilling
harder material, the drill motor turns much slower than normal and overheats. Using principles of physics, give an
explanation for the increased heat in the windings.
3. A 0.400 m long solenoid has 6 720 turns of wire. A current of 14.5 A flows in the solenoid. An electron inside the solenoid
travels perpendicular to the axis of the solenoid with a speed of 6.50 x 10 5 m/s . What is the magnitude of the magnetic force
acting on the electron?
4. A 16.0 V power supply is used to run a dc motor. When the motor is jammed so that it cannot turn, it draws a current of
12.0 A.
a. What is the back or counter emf when the motor runs freely, drawing a current of 2.50 A?
b. Using principles of physics, explain why the motor draws a much higher current when jammed than when running
freely.
5. A solenoid of length 0.85 m has a radius of 0.10 m . A current of 25 A flows through its 7 600 turns. Within this solenoid, a
0.12 m wire moves as shown and develops an emf of 0.055 V across its ends.
With what speed does the wire move perpendicular to the solenoid’s magnetic field?
6. A proton enters a magnetic field of magnitude 2.4 x 10-2 T at a speed of 5.0 x 105 m/s perpendicular to the field.
a. What magnetic force acts on the proton?
b. What is the radius of the proton’s circular path?
7. Electrons accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 300 V enter a 4.1 x 10-2 T magnetic field at right angles.
What is the radius of curvature of the path taken by the electrons?
Version 2007 2 - 50 - Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 8 Questions.doc
8. An ideal transformer is connected to a 12 V ac power supply. The light bulb connected to the secondary of the transformer is
lit (Figure A). The transformer is then connected to a 12 V dc battery (Figure B).
a. The bulb will (check one response)
o not be lit.
o be dimmer.
o have the same brightness.
o be brighter.
b. Using principles of physics, explain your answer to a).
Answers
Multiple Choice
1. A 6. B 11. C 16. B 21. B 26. C 31. C
2. C 7. C 12. B 17. D 22. C 27. A 32. C
3. B 8. D 13. A 18. A 23. B 28. B 33. A
4. D 9. C 14. A 19. A 24 A 29. B 34. B
5. B 10. D 15. B 20. A 25. D 30. A
Written
1. F = Bqv =(µoI÷2πd) x q v = 1.6 x 10-18 N
2. When the motor turns at normal operating speeds, the rotating coils act as a generator and produce a back emf. This back emf
reduces the effective voltage across the coil so only a small current flows, producing a small amount of heat (I 2 R) . When the
motor slows, the generator effect, and thus the back emf, is reduced. This means more of the line voltage is applied to the small
resistance of the armature resulting in more current and in turn the motor produces more heat.
3. F = Bqv =(µo N ÷ l I) x q v = 3.18 x 10 -14 N
4. a) R = V ÷ I = 1.3 Ω Vb = V app – IR = 16 V – (1.3Ω x 2.5 A) = 12.7 V
b) When running freely, the motor acts as a generator producing an emf that opposes the applied
voltage (1 mark). When the motor is jammed (1 mark), there is no back emf (1 mark) and thus
no opposition to the current (1 mark), which is therefore larger.
5. ε = Blwv = µo (N ÷ ls )I lwv v = 1.6 m/s
6. a) F = qv B = 1.9 x 10-15 N
b) Fc = Fb mv2÷r = qvB r = 0.22 m
7. Step one PE = KE qV = ½ mv2 v = 1.0 x 107 m/s
Step two: FB = Fc Bqv = mv2÷r r = 1.4 x 10-3 m
8. a) not be lit
b) Faraday’s law states that an induced current is produced by a changing flux. Since a battery provides a dc current
there is no flux change in the transformer. Therefore, there is no induced current.
Version 2007 2 - 51 - Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Test - Unit 3 - Energy and MomentumDokument4 SeitenTest - Unit 3 - Energy and Momentumascd_msvuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Assessment PDFDokument76 SeitenAlgebra Assessment PDFmath magicNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPH 3u1 Practice ExamDokument4 SeitenSPH 3u1 Practice ExamasjiodjwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honors Physics Midterm Review: Exam DayDokument8 SeitenHonors Physics Midterm Review: Exam DayEarl averzosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For College Physics 1st Edition by EtkinaDokument55 SeitenTest Bank For College Physics 1st Edition by EtkinaaosdjaskdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Physics Questions AnswersDokument2 SeitenAtomic Physics Questions AnswersPradeep ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 12 Worksheet CircuitryDokument2 SeitenPhysics 12 Worksheet CircuitryDezta Fandity' VantycaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Potential and EnergyDokument6 SeitenElectric Potential and Energykw2533Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Calculus 11 WorkbookDokument44 SeitenPre-Calculus 11 Workbooklogicalbase3498Noch keine Bewertungen
- 20-21 Electromagnetism and Induced EMFDokument19 Seiten20-21 Electromagnetism and Induced EMFkw2533Noch keine Bewertungen
- Faraday Lab2Dokument2 SeitenFaraday Lab2Joe SchlekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Work Energy and PowerDokument7 SeitenUnit 4 Work Energy and PowerSabia IdrisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics Quiz + KeyDokument3 SeitenElectrostatics Quiz + KeyClaire CastillanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Physics Multiple Choice Questions - MCQs - With Answer On Circular Motion TopicDokument12 SeitenClass 11 Physics Multiple Choice Questions - MCQs - With Answer On Circular Motion TopicRakesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy FSC 2 Mcqs Ch12 TestDokument3 SeitenPhy FSC 2 Mcqs Ch12 TestSyed Waqas Ahmed100% (1)
- Investigatory ProjectDokument16 SeitenInvestigatory ProjectsuhaybNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction: University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman)Dokument16 SeitenChapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction: University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman)Rachelle Saavedra100% (2)
- Electromagnetic InductionDokument26 SeitenElectromagnetic Inductionqpncsoriano100% (1)
- Elastic Collision With C++Dokument12 SeitenElastic Collision With C++qud86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21 Electromagnetic Induction and Farady's Law: Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli)Dokument73 SeitenChapter 21 Electromagnetic Induction and Farady's Law: Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli)KarissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresDokument17 SeitenTest Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresaimeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Chapter36Dokument14 SeitenTB Chapter36qvrlenarasegtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 - Temperature, Heat, and The First Law of ThermodynamicsDokument18 SeitenChapter 18 - Temperature, Heat, and The First Law of ThermodynamicsVV Cephei100% (1)
- Science 10 - Provicial Study GuideDokument282 SeitenScience 10 - Provicial Study GuideJP Navarro100% (1)
- AP Physics C Magnetism MCDokument21 SeitenAP Physics C Magnetism MCShameem AkhterNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Chapter33Dokument18 SeitenTB Chapter33qvrlenarasegtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Chapter02Dokument21 SeitenPhysics Chapter02Basharat AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetism Session 2 QuestionsDokument80 SeitenElectromagnetism Session 2 QuestionsJohn English100% (1)
- AP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 4 EnergyDokument7 SeitenAP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 4 EnergyNikhita Rajesh100% (1)
- TEST-09 (Uniform Circular Motion)Dokument2 SeitenTEST-09 (Uniform Circular Motion)abdullah naseerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charging & Discharging of Capacitor PDFDokument4 SeitenCharging & Discharging of Capacitor PDFHemanth GedelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 - MCQDokument12 SeitenUnit 4 - MCQrohitsalave29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Static Equilibrium Elasticity and Fracture: Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli)Dokument24 SeitenChapter 9 Static Equilibrium Elasticity and Fracture: Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli)KarissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction Practice Problems-2009!05!13Dokument15 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction Practice Problems-2009!05!13anon020202Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter # 11 HeatDokument6 SeitenChapter # 11 HeatSIR USMAN KHAN50% (2)
- Circulat Motion ProblemsDokument15 SeitenCirculat Motion ProblemsSadiki WallaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF Preparation For EngineeringDokument20 SeitenElectrostatics Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF Preparation For EngineeringPatel DipenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro MagsDokument4 SeitenElectro MagsVan Daryl C MonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics XII Chapter# 12 Practice SheetDokument4 SeitenPhysics XII Chapter# 12 Practice SheetGhulam NabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23Dokument26 SeitenChapter 23Carlos Arturo AlanizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam 2Dokument9 SeitenPractice Exam 2i5piritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Review - CH 3 Motion in Two Dimensions Practice TestDokument6 SeitenWeb Review - CH 3 Motion in Two Dimensions Practice TestAref DahabrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasteringPhysics - Assignments10 - 9 - 11Dokument12 SeitenMasteringPhysics - Assignments10 - 9 - 11Dylan StefanskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Physics FormulaeDokument99 Seiten1 Physics FormulaeAbrar FaqeehNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP FR Quiz #5 2D MotionDokument7 SeitenAP FR Quiz #5 2D MotionRobbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scholars College of Sciences Muridke Physics Chapter #14Dokument1 SeiteScholars College of Sciences Muridke Physics Chapter #14Muhammad Hassan MaqsoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliability, Validity, AccuracyDokument5 SeitenReliability, Validity, AccuracySilvia100% (6)
- Chapter No 2 Scalars and VectorsDokument14 SeitenChapter No 2 Scalars and VectorsRizwan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Gravitation Practice QuizDokument4 SeitenUniversal Gravitation Practice QuizSrnt YyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics Notes - MagnetismDokument8 SeitenAP Physics Notes - MagnetismAndy HeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHET Magnetism - Lab Grade: NameDokument4 SeitenPHET Magnetism - Lab Grade: NameAyhan AbdulAzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.multiple Choice QuestionsDokument8 Seiten4.multiple Choice QuestionsJatin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10a-Electrostatics MC Practice ProblemsDokument38 Seiten10a-Electrostatics MC Practice ProblemsJanel EdwardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significant Figures: Mr. Chong Kwai KunDokument23 SeitenSignificant Figures: Mr. Chong Kwai KunkwaikunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Theory QuestionsDokument5 SeitenQuantum Theory Questionsdevender singh50% (2)
- First Year Physics Chapter Wise Mcqs PDFDokument49 SeitenFirst Year Physics Chapter Wise Mcqs PDFabuzar khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Career Development Practice in Canada: Perspectives, Principles, and ProfessionalismVon EverandCareer Development Practice in Canada: Perspectives, Principles, and ProfessionalismNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ordinary Differential Equations: 1971 NRL—MRC ConferenceVon EverandOrdinary Differential Equations: 1971 NRL—MRC ConferenceLeonard WeissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Pack 3 - Class 2 - 19 23 April ChkedDokument7 SeitenStudy Pack 3 - Class 2 - 19 23 April ChkedMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mother Teresa - The Angel of MercyDokument2 SeitenMother Teresa - The Angel of MercyMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 2 Study Pack 1 and Answer SheetDokument7 SeitenClass 2 Study Pack 1 and Answer SheetMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: Vector Dynamics: Multiple Choice PortionDokument7 SeitenUnit 2: Vector Dynamics: Multiple Choice PortionMr saifan and Mr shehzad100% (1)
- Assignment-1 Microwave Transmission Lines: Microwaves and Radar 10EC54Dokument2 SeitenAssignment-1 Microwave Transmission Lines: Microwaves and Radar 10EC54Mr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsDokument7 SeitenMultiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave Engineering Assignment - 1 Issue: 28/08/2017 Submission: 02/09/2017 Set1Dokument4 SeitenMicrowave Engineering Assignment - 1 Issue: 28/08/2017 Submission: 02/09/2017 Set1Mr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Portion: Unit 7: Electric CircuitsDokument6 SeitenMultiple Choice Portion: Unit 7: Electric CircuitsMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.microwave TheorySampleDokument23 Seiten15.microwave TheorySampleMr saifan and Mr shehzad0% (1)
- Electro - Pneumatic I: Woksyop Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Ii BDA 18301Dokument24 SeitenElectro - Pneumatic I: Woksyop Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Ii BDA 18301Praven KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airtec KN05 Solenoid Valve PDFDokument4 SeitenAirtec KN05 Solenoid Valve PDFJessicalba LouNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 01728 1 - 44 R006 Device Summary of STGDokument45 SeitenEE 01728 1 - 44 R006 Device Summary of STGVinoth Kumar100% (1)
- Genesis 3.8L Section 9Dokument52 SeitenGenesis 3.8L Section 9Nacho MowjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eagle Quantum Premier 8 Channel Discrete Input/Output Module (DCIO) EQ3700DCIODokument8 SeitenEagle Quantum Premier 8 Channel Discrete Input/Output Module (DCIO) EQ3700DCIOEl Che CheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physicy Test XDokument12 SeitenPhysicy Test XMerimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UW Solenoid ValveDokument3 SeitenUW Solenoid ValvehuttoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GovernorDokument43 SeitenGovernorVIJIOCL100% (2)
- Section11 Proportional ValvesDokument48 SeitenSection11 Proportional ValvesHENRY LLOFREL CORREA LOPEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- 720G 08182003Dokument66 Seiten720G 08182003Rodolfo YanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newport Serv Man E150Dokument69 SeitenNewport Serv Man E150quezon100% (1)
- E380b PDFDokument12 SeitenE380b PDFanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0625 w14 QP 33Dokument20 Seiten0625 w14 QP 33Haider Ali100% (2)
- Living Science Electric Current and Its Effects: AnswerDokument11 SeitenLiving Science Electric Current and Its Effects: AnswerNaitik SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transducer: TypesDokument39 SeitenTransducer: Typestujuh belasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac/Dc Distribution Panel: Electrical System 3500B Generator Set With EMCP 3Dokument4 SeitenAc/Dc Distribution Panel: Electrical System 3500B Generator Set With EMCP 3hector gutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 4 PDFDokument66 SeitenLec 4 PDFTharakaKaushalyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix B: Diagnostic Codes, 3000/4000 Product FamiliesDokument3 SeitenAppendix B: Diagnostic Codes, 3000/4000 Product FamiliesĐại Anh HùngNoch keine Bewertungen
- SV97Dokument2 SeitenSV97nclogesh_1981Noch keine Bewertungen
- DL650 S5Dokument34 SeitenDL650 S5Ferdi EsmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Codigo P076aDokument6 SeitenCodigo P076aOscar VillaseñorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrovalvula Atos Dhi 610 23Dokument4 SeitenElectrovalvula Atos Dhi 610 23daniloaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Komatsu FB10 20М 12Dokument529 SeitenKomatsu FB10 20М 12thành trung phạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14M Motor Grader Electrical System: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsDokument6 Seiten14M Motor Grader Electrical System: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic Symbolsmanu luvungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMF University Question BankDokument10 SeitenEMF University Question Banknavin222Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mitsubish Rv1a Rv2aj Standard Specifications ManualDokument106 SeitenMitsubish Rv1a Rv2aj Standard Specifications ManualRoby NicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ) Design and Fabrication of Automatic Pneumatic Braking System Using Object Detecting For Four WheelersDokument5 Seiten) Design and Fabrication of Automatic Pneumatic Braking System Using Object Detecting For Four WheelersretechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link-Belt LS-108 Hylab 5 Hydraulic Diagram PDFDokument14 SeitenLink-Belt LS-108 Hylab 5 Hydraulic Diagram PDFKOK100% (3)
- DS-1201 - W60 - W80 - W90 Series LR 10 2014 - tcm11-10502Dokument28 SeitenDS-1201 - W60 - W80 - W90 Series LR 10 2014 - tcm11-10502ChemicalProgrammerNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMETEK SAZ SBC Plastic Case SolenoidsDokument4 SeitenAMETEK SAZ SBC Plastic Case Solenoidsgabriel anunnakiNoch keine Bewertungen