Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit 2: Vector Dynamics: Multiple Choice Portion
Hochgeladen von
Mr saifan and Mr shehzadOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 2: Vector Dynamics: Multiple Choice Portion
Hochgeladen von
Mr saifan and Mr shehzadCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physics 12: Unit 2 Questions.
doc
Unit 2: Vector Dynamics
Multiple Choice Portion
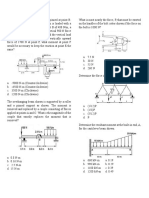
1. Which one of the following best describes the motion 5. A ball is rolled off a horizontal roof at 16 m/s. After
of a projectile close to the surface of the Earth? leaving the roof, how long will the ball take to reach a
(Assume no friction) speed of 18 m/s?
Vertical Acceleration Horizontal Acceleration a. 0.20 s
a. constant constant b. 0.84 s
b. constant changing c. 1.8 s
c. changing constant d. 2.5 s
d. changing changing
6. Which one of the following is a vector quantity?
2. A 3.00 kg object is being accelerated vertically a. time
upwards at 2.80 m/s2 , as shown. b. speed
c. energy
cord d. displacement
2.80 m/s2
7. Unless acted on by an external net force, an object
3.00 kg will stay at rest or
a. come to rest.
ground b. decelerate at a constant rate
What is the tension in the cord? c. slow down from a given speed.
a. 8.40 N d. continue to move in a straight line at a constant
b. 21.0 N speed
c. 29.4 N
d. 37.8 N 8. A car is travelling at a constant speed of 26.0 m/s
down a slope, which is 12. 0° to the horizontal.
3. Three forces act at point P at the same time, as shown What is the vertical component of the car’s velocity?
on the force vector diagram below. a. 5.41 m/s
b. 9.80 m/s
2.0 N
c. 25.4 m/s
d. 26.0 m/s
P
12.0 N
9. A 65.0 kg block is being accelerated along a level
surface. The applied force is 500 N and the friction
10.0 N force is 300 N. What is the coefficient of friction
between the block and the surface?
What is the magnitude of the resultant force vector? a. 0.31
a. 14.4 N b. 0.47
b. 17.0 N c. 0.78
c. 20.0 N d. 1.30
d. 24.0 N
10. A 2.00 kg object, initially at rest on the ground, is
4. A 4.00 kg block is accelerated along a level surface at accelerated vertically by a rope, as shown. The object
3.00 m/s2 . The applied force is 20.0 N. reaches a height of 3.00 m in 1.50 s.
3.00 m/s2 rope
4.00 kg 20.0 N 2.00 kg
What is the coefficient of friction between the block
and the surface? 3.0 m
a. 0.20
b. 0.31
c. 0.51
d. 0.67 What is the tension in the rope during the acceleration?
a. 5.33 N
b. 14.3 N
c. 23.6 N
d. 24.9 N
Version 2007 2-8- ©Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 2 Questions.doc
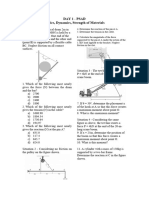
11. A constant force is applied to an object on a 17. Which of the following is not a vector?
frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram below. a. mass
b. impulse
Force c. velocity
d. momentum
The resulting motion has
a. constant velocity. 18. A passenger jet needs to reach a speed of 100 m/s on
b. constant momentum the runway for takeoff. If the runway is 2.5 x103 m
c. constant acceleration. long, what minimum average acceleration from rest is
d. constant kinetic energy. needed?
a. 0.040 m/s2
12. If friction is negligible, which of the following is true b. 2.0 m/s2
for the velocity components of projectiles? c. 4.0 m/s2
Horizontal Velocity Vertical Velocity d. 10 m/s2
Component Component
a. constant constant 19. Which of the following is a vector quantity?
b. constant changes a. work
c. changes constant b. speed
d. changes changes c. acceleration
d. kinetic energy
13. At what speed must a ball be thrown upwards to reach
a maximum height of 25 m? 20. Initial velocity vector νo and final velocity vector νf
a. 2.6 m/s are shown below.
b. 22 m/s
c. 2.5 x 102 m/s
d. 3.1 x 103 m/s
14. What is the frictional force due to air resistance on a
0.50 kg object falling vertically with an acceleration Which of the following represents the change in
of 8. 5 m/ s2 ? velocity ∆ν ?
a. 0.65 N a. c.
b. 4.3 N
c. 4.9 N
d. 9.2 N
15. Three masses connected by a light string are arranged
on frictionless surfaces, as shown in the diagram
below.
b. d
The strings pass over frictionless pulleys. Determine
the direction and magnitude of the acceleration of m1 . 21. A projectile is launched over level ground with a
Direction of m1 Acceleration (m/s2) speed of 240 m/s at 35° to the horizontal. If friction is
a. Up incline 0.20 negligible, what is the height of the projectile 17 s
b. Down incline 0.20 after launch?
c. Up incline 0.43 a. 9. 2 x 102
d. Down incline 0.43 b. 1. 9 x 103 m
c. 2.7 x 103 m
16. An object is sliding down a smooth incline. If friction d. 5. 5 x 103 m
is negligible, the object has
a. constant velocity.
b. constant momentum
c. constant acceleration.
d. constant displacement.
Version 2007 2-9- ©Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 2 Questions.doc
22. What minimum horizontal force F will just prevent 25. Which of the following is not a statement of one of
the 5.0 kg block from sliding if the coefficient of Newton’s laws of motion?
friction between the wall and the block is 0.65? a. For every action force, there is an equal and
opposite reaction force.
b. If no net force acts on an object, the object will
remain at rest, or continue to move at a constant
velocity.
c. The acceleration of freely falling objects is
proportional to their mass.
d. If a net force does act on an object, the object will
accelerate in the direction of the net force.
26. An object is launched at 65° to the horizontal with an
a. 6.4 N initial speed of 25 m s. What is the maximum height
b. 32 N reached by this object?
c. 49 N a. 5.7 m
d. 75 N b. 26 m
c. 32 m
23. A pendulum is swinging freely between points R and S d. 150 m
as shown in the diagram below.
27. Three blocks have masses 1.0 kg, 7.0 kg and 5.0 kg as
shown. The horizontal surface is frictionless.
Which of the following diagrams best represents the
forces acting on the pendulum bob at point R?
a. c.
What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the
system?
a. 3. 0 m/s 2
b. 3. 8 m/s 2
b. d. c. 6.5 m/s 2
d. 7.8 m/s 2
28. A 2.0 kg block is sliding down a 15° incline. The
coefficient of friction is 0.62. At some position the
block has a speed of 7. 0 m/s.
24. The projectile shown below has an acceleration which
is
Q
P
R
What distance d will this block move before coming to
rest?
a. zero.
a. 2.5 m
b. in the direction of P
b. 4.0 m
c. in the direction of Q.
c. 4.2 m
d. in the direction of R.
d. 7.4 m
Version 2007 2 - 10 - ©Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 2 Questions.doc
29. Which of the following statements concerning vector 31. Which list contains three vector quantities?
and scalar quantities is incorrect? a. force, mass, speed
a. All scalar quantities have direction. b. force, speed, velocity
b. All vector quantities have direction. c. acceleration, mass, velocity
c. All scalar quantities have magnitude. d. acceleration, momentum, velocity
d. All vector quantities have magnitude.
32. When a 2.0 kg rock is dropped from a cliff it hits the
30. Two forces act on an object as shown in the diagram. beach at 24 m/s. At what speed would a 4.0 kg rock,
dropped from the same cliff, hit the beach? Ignore
friction.
a. 12 m/s
b. 24 m/s
c. 34 m/s
d. 48 m/s
Which of the following best shows the resultant R of
these forces? 33. The 4.0 kg block shown accelerates across a
a. c. frictionless horizontal table at 1. 5 m/s 2 .
b. d.
Find the mass of object m1.
a. 0.61 kg
b. 0.72 kg
c. 6.0 kg
d. 26 kg
34. Pamela swims at 2.8 m/s relative to the water, heading
west. The current flows south at 1. 2 m/s .
Find Pamela’s resultant direction.
a. 23° S of W
b. 25° S of W
c. 23° N of W
d. 25° N of W
Written Portion:
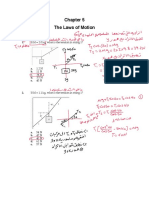
1. A 6.0 kg block is held at rest on a horizontal, frictionless air table. Two forces are pulling on this block in the directions
shown in the diagram below.
Table Viewed from Above
45 N
25 N
30˚ 40˚
6.0 kg
What will be the magnitude of the acceleration on the 6.0 kg block at the moment it is released?
Version 2007 2 - 11 - ©Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 2 Questions.doc
2. An 87 kg block slides down a 31° as shown in that diagram below. The coefficient of friction between the block and the
surface is 0.25.
µ = 0.25
31˚
What is the acceleration of the block?
3. The diagram shows a 4.4 kg mass connected by a string to an unknown mass over a frictionless pulley. The system
accelerates at 1.8 m/s2 in the direction shown.
a = 1.8 m/s2 a = 1.8 m/s2
m1 = 4.4 kg m2
a. Draw and label a free body diagram for the 4.4 kg mass.
b. Calculate the tension in the string
c. Find mass m2
4. In the diagram shown, the tension in the cord connecting the hanging mass and cart is 43 N.
a. Draw and label a free body diagram for the cart and the hanging mass.
b. Determine the mass of the cart.
5. Amanda exerts a horizontal force of 180 N on a piece of rope causing two blocks of mass 20 kg and 40 kg to accelerate.
Friction on the blocks is negligible.
a. Find the tension force at X in the rope joining the two blocks together.
Version 2007 2 - 12 - ©Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 2 Questions.doc
Bob exerts a force of equal magnitude in the opposite direction on an identical pair of blocks.
b. How does the tension force at X compare to the value in part a)? (Circle one.)
i) The tension force is the same.
ii) The tension force is greater than in a).
iii) The tension force is smaller than in a).
c. Using principles of physics, explain your answer to part b).
6. A student drags a 7.0 kg carton of apples across the floor by exerting a 45 N force in the direction shown. The coefficient of
friction between the carton and the floor is 0.52 .
a. What is the magnitude of the normal force acting on the carton?
b. What friction force acts on the carton?
7. The diagram shows two objects connected by a light string over a frictionless pulley. Object m2 is on a frictionless horizontal
table. The tension in the string is 24 N.
a. Find the acceleration of the system.
b. Find the mass of m2 .
Version 2007 2 - 13 - ©Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Physics 12: Unit 2 Questions.doc
Answers to Vector Dynamic Study Pack
Multiple Choice
1. a 12. b 23. a
2. d 13. b 24. d
3. a 14. a 25. c
4. a 15. a 26. b
5. b 16. c 27. a
6. d 17. a 28. d
7. d 18. b 29. a
8. a 19. c 30. c
9. b 20. b 31. d
10. d 21. a 32. b
11. c 22. d 33. b
34. a
Written Response
1. 7.2 m/s2
2. 2.9 m/s2
3a) Ft b) 51.0 N c) 6.38 kg
Fg
Fn 43 N
4a) b) 16 kg
Ft
60 N
Fg
5a) Ft = 120 N b) iii
c) In both situations the total mass is the same so both systems accelerate at the same rate. In b) the tension must accelerate a
smaller mass at the same rate hence, from Newton’s second law, F = ma, a smaller tension force will cause this
6a) FN = 50.3 N b) FF = 26.2 N c) a = 2.1 m/s2
7a) a = 1.8 m/s2 b) m2 = 13.3 kg
Version 2007 2 - 14 - ©Lockwood, Murray and Bracken
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Kinematics and DynamicsDokument16 SeitenKinematics and DynamicsmartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Physics Exam ReviewDokument3 SeitenWeekly Physics Exam ReviewgiophilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech ADokument5 SeitenMech AJanine Jade SetiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proficiency Test 13 Ans (April 2023)Dokument3 SeitenProficiency Test 13 Ans (April 2023)Justin GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tsu m17 Practice Problems Statics of Rigid BodiesDokument2 SeitenTsu m17 Practice Problems Statics of Rigid BodiesMark Lester ValdozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Physics Exam: Final Temp of Water Mixed at 20CDokument1 SeiteTech Physics Exam: Final Temp of Water Mixed at 20CAron BalinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Exit Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument4 SeitenPhysics Exit Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsrickiegasparNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS APTITUDE TEST WORK POWER AND ENERGYDokument9 SeitenPHYSICS APTITUDE TEST WORK POWER AND ENERGYKomalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tryout 1.0 IUP ITB - OctDokument7 SeitenTryout 1.0 IUP ITB - Octsyafr.e.424Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physic Eng Mech StremaDokument9 SeitenPhysic Eng Mech StremaAllyssa ErcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems v1Dokument2 SeitenPractice Problems v1Gerrard PantopioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Theory Refresher Set PDFDokument6 SeitenStructural Theory Refresher Set PDFezer joseph bacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Unit 3 Practice Test Dynamics5Dokument5 SeitenPhysics Unit 3 Practice Test Dynamics5StephanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Wizard Practice ExamDokument2 SeitenDynamics Wizard Practice ExamMatthew MlacedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion Chapter 4 ReviewDokument18 SeitenLaws of Motion Chapter 4 ReviewHaw-ChyunNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsDokument10 SeitenPHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsAaisha SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pretest Physics For EngineersDokument10 SeitenPretest Physics For EngineersIrish NaragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aller EC Anica Ctubre DEDokument4 SeitenAller EC Anica Ctubre DEjonatan felipe leon pardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsDokument20 SeitenDAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsJM De Guzman TuzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 82 - Engineering Mechanics Refresher SetDokument6 Seiten82 - Engineering Mechanics Refresher Setdevilene nayazakoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preboard Problems FinalDokument5 SeitenPreboard Problems FinalAngel MarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Energy and PowerDokument13 SeitenWork Energy and PowermartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corre CeDokument29 SeitenCorre CeKim VeneracionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector and Kinematics Problems AnswersDokument14 SeitenVector and Kinematics Problems AnswersAhmed aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENERAL PHYSICS 1 GRADE 12 Q1 Summative Test 1 5Dokument5 SeitenGENERAL PHYSICS 1 GRADE 12 Q1 Summative Test 1 5kurtwilliamtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1575286840Dokument12 Seiten1575286840Rloofy namiNoch keine Bewertungen
- F3 Phy 1Dokument12 SeitenF3 Phy 1BUKENYA BEEE-2026Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Engineering and Construction November 2017 KEYDokument5 SeitenStructural Engineering and Construction November 2017 KEYBenjie MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 105 Exam ReviewDokument5 SeitenPhysics 105 Exam ReviewjessieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion ExplainedDokument52 SeitenLaws of Motion ExplainedAmeen ShaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 2Dokument5 SeitenQuiz 2Nurul AinNoch keine Bewertungen
- File 1582710448 PDFDokument5 SeitenFile 1582710448 PDFNatasha Marie MallareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 11 Mock Exam Answers PDFDokument11 SeitenPhysics 11 Mock Exam Answers PDFMichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 105 Exam ReviewDokument5 SeitenPhysics 105 Exam ReviewMona Mohamed SafwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal EnergyDokument8 SeitenThermal EnergyRBNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceDokument8 SeitenThe Laws of Motion: Multiple Choicealiya mNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Mary's College Tagum pre-finals exam questionsDokument1 SeiteSt. Mary's College Tagum pre-finals exam questionsJefferson Kevin LerioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyd - 6Dokument2 SeitenHyd - 6SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPYQ NEET Level Practice Test-1 for JEE Main & NEET AspirantsDokument6 SeitenDPYQ NEET Level Practice Test-1 for JEE Main & NEET Aspirantsairs primeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST Joseph'S International College: Physics (AS) Multiple Choice: Practice Test - March, 2023 - Grade 12Dokument6 SeitenST Joseph'S International College: Physics (AS) Multiple Choice: Practice Test - March, 2023 - Grade 12brought to inspire - faith silvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- USTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 SolutionDokument10 SeitenUSTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 Solutionabcvn67Noch keine Bewertungen
- Keieiie TQMCorrelation DesignDokument5 SeitenKeieiie TQMCorrelation DesignJeth Verdejo RiveroNoch keine Bewertungen
- DefaultDokument4 SeitenDefaultfeynmanwannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jamb Phy Questions 6 10Dokument47 SeitenJamb Phy Questions 6 10pillardesigns9Noch keine Bewertungen
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review CenterDokument3 SeitenF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Centermateojullieanne100% (1)
- STRUCTURAL THEORY REFRESHER SETDokument6 SeitenSTRUCTURAL THEORY REFRESHER SETLa BeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0711ph PDokument39 Seiten0711ph PRana HazemNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Chapter5Dokument18 SeitenTB Chapter5Jerry HuntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hge Pre-Board QuestionnaireDokument3 SeitenHge Pre-Board QuestionnairegregNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jamb Physics 16 20Dokument48 SeitenJamb Physics 16 20timothyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1Dokument8 SeitenPhysics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1abdiasfaw7152Noch keine Bewertungen
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDokument7 SeitenUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice-Problems-11_Dynamics-Part-2Dokument1 SeitePractice-Problems-11_Dynamics-Part-2Jayve BasconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium TorquesDokument14 SeitenEquilibrium TorquesmartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- USTH Final Fundamental Physic 1ADokument6 SeitenUSTH Final Fundamental Physic 1AHà Nguyễn Thị ViệtNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY440 - Assignment 2 - Sept 2016 - Jan 2017Dokument4 SeitenPHY440 - Assignment 2 - Sept 2016 - Jan 2017Ainaa NadhirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Dokument3 SeitenRasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Greg Rasco, REE, RMPNoch keine Bewertungen
- BPhO Round 1 2017-2018 S2 PDFDokument12 SeitenBPhO Round 1 2017-2018 S2 PDFWWTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toys for OrphanageDokument7 SeitenToys for OrphanageMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 2 Study Pack 1 and Answer SheetDokument7 SeitenClass 2 Study Pack 1 and Answer SheetMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitor Pretest ReviewDokument4 SeitenCapacitor Pretest ReviewKiros HagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 QuestionsDokument7 SeitenUnit 6 QuestionsAnalyn EnsanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mother Teresa - The Angel of MercyDokument2 SeitenMother Teresa - The Angel of MercyMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsDokument7 SeitenMultiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Portion: Unit 7: Electric CircuitsDokument6 SeitenMultiple Choice Portion: Unit 7: Electric CircuitsMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave Transmission Lines AssignmentDokument2 SeitenMicrowave Transmission Lines AssignmentMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave Engineering Assignment - 1 Issue: 28/08/2017 Submission: 02/09/2017 Set1Dokument4 SeitenMicrowave Engineering Assignment - 1 Issue: 28/08/2017 Submission: 02/09/2017 Set1Mr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Review 1528317655806 SCDokument18 SeitenFinal Exam Review 1528317655806 SCAdil KhurshaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Portion 1.: Unit 8: ElectromagnetismDokument6 SeitenMultiple Choice Portion 1.: Unit 8: ElectromagnetismMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Theory Objective Type Questions PDFDokument50 SeitenElectromagnetic Theory Objective Type Questions PDFManojDhage100% (1)
- 15.microwave TheorySampleDokument23 Seiten15.microwave TheorySampleMr saifan and Mr shehzad0% (1)
- Multiple Choice Portion: Unit 7: Electric CircuitsDokument6 SeitenMultiple Choice Portion: Unit 7: Electric CircuitsMr saifan and Mr shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Paper On Future of Antigravity and Antigravity PropulsionDokument6 SeitenReview Paper On Future of Antigravity and Antigravity PropulsionIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems Set1Dokument21 SeitenPractice Problems Set1Adalric LeungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat Sheet Unit 3 MotionDokument1 SeiteCheat Sheet Unit 3 MotionkerrevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casio Edifice 5069 PDFDokument3 SeitenCasio Edifice 5069 PDFrbp_Noch keine Bewertungen
- AIAA Agnew WarpDrive Final PDFDokument15 SeitenAIAA Agnew WarpDrive Final PDFmisterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Axis TheoremDokument3 SeitenParallel Axis TheoremKareem Ibrahim Mohamed NasrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Higher Mechanics Unit 2 Notes COMPLETEDokument6 SeitenAdvanced Higher Mechanics Unit 2 Notes COMPLETERyan_Hoyle95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Draft-Black HolesDokument13 SeitenFinal Draft-Black Holesapi-466395170Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational KinematicsDokument28 SeitenRotational KinematicsKnightmare98710% (1)
- CAIE A Level Physics 3E SAMPLE PDFDokument16 SeitenCAIE A Level Physics 3E SAMPLE PDFJimmy Teh0% (1)
- Phy FormulaDokument1 SeitePhy FormulaCarlos Albert MeguizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toy Car Motion Lab GraphsDokument2 SeitenToy Car Motion Lab Graphspixelhobo33% (3)
- Bucio - Projectile WS 1Dokument3 SeitenBucio - Projectile WS 1ZhaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy of Time TravelDokument20 SeitenPhilosophy of Time TraveltomruttleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13.simple Harmonic MotionDokument54 Seiten13.simple Harmonic MotionAman KeltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Connectors in ABAQUS/Explicit to Simulate Dynamic Motion Along a Curved PathDokument15 SeitenUse of Connectors in ABAQUS/Explicit to Simulate Dynamic Motion Along a Curved PathTina LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Physics Rotational ProblemsDokument4 SeitenExtra Physics Rotational ProblemsjohnnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jackson Problem Solution 6 17Dokument2 SeitenJackson Problem Solution 6 17mohammadi1360100% (3)
- Davis Basil S The Basic Physics of Quantum TheoryDokument220 SeitenDavis Basil S The Basic Physics of Quantum TheoryStrahinja Donic100% (2)
- HPhys Unit 02 BFPM Packet 2013Dokument16 SeitenHPhys Unit 02 BFPM Packet 2013Kelly O'Shea100% (2)
- Rigid Body DynamicsDokument55 SeitenRigid Body DynamicsKenn ConsueloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics 11111Dokument67 SeitenKinematics 11111Pankaj K DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parachute Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenParachute Lab ReportNathan T. Cheung100% (2)
- Particle Kinem Circ Motion Ex Prob 3Dokument6 SeitenParticle Kinem Circ Motion Ex Prob 3dssrwrtgwtgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior General Physics 1 q1 Module 3Dokument26 SeitenSenior General Physics 1 q1 Module 3arcyeliefaithcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morning To Afternoon Choghadiya: Sunset SunriseDokument1 SeiteMorning To Afternoon Choghadiya: Sunset Sunriserashmi chauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of ForceDokument14 SeitenNature of ForceShiela CarabidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion in Two and Three DimensionsDokument29 SeitenMotion in Two and Three Dimensionssmart.engineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centripetal Force and Rotating Frames of ReferenceDokument5 SeitenCentripetal Force and Rotating Frames of ReferenceAyman HalimeNoch keine Bewertungen