Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
20 Questions
Hochgeladen von
Aarohi Sood0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
480 Ansichten6 Seiten1. The document contains questions about aircraft systems and aerodynamics. It provides multiple choice answers to identify the correct response for each question.
2. Key topics covered include trim tabs, control surface flutter, differential ailerons, trailing edge flaps, ignition timing in 4-stroke engines, propeller design and function, magnetic compass errors, and aircraft stability and performance characteristics.
3. The questions assess understanding of how aircraft systems work individually and interact together to control the aircraft in flight.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1. The document contains questions about aircraft systems and aerodynamics. It provides multiple choice answers to identify the correct response for each question.
2. Key topics covered include trim tabs, control surface flutter, differential ailerons, trailing edge flaps, ignition timing in 4-stroke engines, propeller design and function, magnetic compass errors, and aircraft stability and performance characteristics.
3. The questions assess understanding of how aircraft systems work individually and interact together to control the aircraft in flight.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
480 Ansichten6 Seiten20 Questions
Hochgeladen von
Aarohi Sood1. The document contains questions about aircraft systems and aerodynamics. It provides multiple choice answers to identify the correct response for each question.
2. Key topics covered include trim tabs, control surface flutter, differential ailerons, trailing edge flaps, ignition timing in 4-stroke engines, propeller design and function, magnetic compass errors, and aircraft stability and performance characteristics.
3. The questions assess understanding of how aircraft systems work individually and interact together to control the aircraft in flight.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
1.
The trim tab:
A) increases hinge moment and reduces control surface
efficiency
B) increases hinge moment and control surface
efficiency
C) reduces hinge moment and increases control surface
efficiency
*D reduces hinge moment and control surface
) efficiency
2. Control surface flutter:
A) occurs at high angles of attack.
B) provides additional lift for take-off and landing in the event of
engine failure.
*C is a destructive vibration that must be damped out within the
) flight envelope.
D) is a means of predicting the critical safe life of the wing.
3. How do differential ailerons work?
A) equalise the lift on up going and down going wings.
*B increase drag on up going wing and decrease drag on down
) going wing.
C) equalise the drag on up going and down going wings.
D) Increase lift on down going wing and decrease lift on up
going wing.
4. Trailing edge flaps:
A) Reduce lift at a higher
AOA
B) Increase lift at a higher
AOA
C) Reduce lift at a lower
AOA
*D Increase lift at a lower
) AOA
5. The ignition occurs in each cylinder of an four-stroke engine (TDC=
Top Dead Center)
A) before TDC at each crankshaft revolution
*B before TDC at each second crankshaft
) revolution
C) behind TDC at each crankshaft revolution
D) behind TDC at each second crankshaft
revolution
6. In a four-stroke piston engine, the only "driving" stroke is:
A) compression
B) intake
*C firing-
) expansion
D) exhaust
7. When the magneto selector switch is set to "OFF" position, the
piston engine continues to run normally. The most probable cause of
this failure is that:
A) There are local hot points in the engine (probably due to
overheating of the cylinder heads)
*B On a magneto, a grounding wire is broken
)
C) A wire from the magneto is in contact with a metallic part of the
engine
D) There is a carbon deposit on the spark plugs electrodes
8. Valve overlap ensures that:
A Engine power is limited, at full power, to ambient conditions
)
B Engine oil system is always available for anti-icing
)
C Cylinder is efficiently scavenged of burnt gases during the
) exhaust stroke
D Ignition liming can be set accurately
)
9. Why is a propeller blade twisted?
A To reduce the tip speed
)
B To prevent the blade from fully feathering
)
C To even out the thrust force along the length of
) the blade
D To reduce the thrust at the root of the blade
)
10. The 'slipstream effect' of a propeller is most prominent at:
A high airspeeds with high power
) setting.
B low airspeeds with high power
) setting.
C low airspeeds with low power
) setting.
D high airspeeds with low power
) setting.
11. When descending through an isothermal layer at a constant
Calibrated Airspeed (CAS), the True Airspeed (TAS) will:
A increase
)
B decrease
)
C remain constant
)
D increase at a linear
) rate
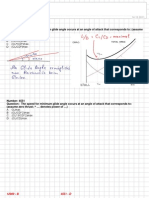
12. The Mach number is:
A) the ratio of the indicated airspeed to the sonic velocity at the
altitude considered.
B) a direct function of temperature ; it varies in proportion to the
square root of the absolute temperature.
*C the ratio of the aircraft true airspeed to the sonic velocity at the
) altitude considered.
D) the ratio of the aircraft conventional airspeed to the sonic velocity
at the altitude considered.
13. The heading read on the dial of a directional gyro is subject to
errors, one of which is due to the movement of the aircraft. This error...
A is at its greatest value when the aircraft follows a meridional track
)
B shows itself by an apparent rotation of the horizontal axis of the
) gyroscope which seems to turn at 15° per hour to the right in the
northern hemisphere
C is, in spite of this, insignificant and may be neglected
)
D is dependent on the ground speed of the aircraft, its true track and
) the average latitude of the flight
14. A failed RMI rose is locked on 090° and the ADF pointer indicates
225°. The relative bearing to the station is:
A 225
) °
B 315
) °
C 045
) °
D 135
) °
15. Following 180° stabilized turn with a constant attitude and bank,
the artificial horizon indicates:
A too high pitch up and correct
) banking
B too high pitch-up and too low
) banking
C attitude and banking coorect
)
D too high pitch up and too high
) banking
16. A DGI has:
A one degree of freedom & a horizontal
) spin axis.
B two degrees of freedom & a vertical spin
) axis.
C one degree of freedom & a vertical spin
) axis.
D two degrees of freedom & a horizontal
) spin axis.
17. The quadrantal deviation of the magnetic compass is due to the
action of:
A the hard iron pieces influenced by the mild iron pieces
)
B the hard iron pieces influenced by the geomagnetic field
)
C the hard iron pieces and the soft iron pieces influenced by the
) hard iron pieces
D the soft iron pieces influenced by the geomagnetic field
)
18. The quadrantal deviation of the magnetic compass is due to the
action of:
A the hard iron pieces influenced by the mild iron pieces
)
B the hard iron pieces influenced by the geomagnetic field
)
C the hard iron pieces and the soft iron pieces influenced by the
) hard iron pieces
D the soft iron pieces influenced by the geomagnetic field
)
19. In a steep turn, the northerly turning error on a magnetic compass
on the northern hemisphere is:
A none on a 090° heading in a right turn
)
B equal to 180° on a 270° heading in a
) right turn
C equal to 180° on a 090° heading in a
) right turn
D none on a 270° heading in a left turn
)
20. Aircraft magnetism:
A does not vary with aircraft latitude but does vary with
) aircraft heading
B varies with latitude but does not vary with aircraft heading
)
C varies with aircraft heading and latitude
)
D does not vary with aircraft heading or latitude
)
21. A manifold pressure gauge of a piston engine measures:
A vacuum in the carburettor
)
B absolute airpressure entering the carburettor
)
C fuel pressure leaving the carburettor
)
D absolute pressure in intake system near the
) inlet valve
22. Dihedral of the wing:
A) decreases the static lateral stability
*B increases the static lateral stability
)
C) is only positive for aeroplanes with high
mounted wings
D) is the only way to increase the static lateral
stability
23. Asymmetric propeller blade effect is mainly induced by:
A large angles of climb.
)
B high speed.
)
C the inclination of the propeller axis to the
) relative airflow.
D large angles of yaw
)
24.The sweepback on a wing will:
A) reduce the possibility for the wing tip to
stall.
B) have no effect on the stall
characteristics.
C) cause the stall to occur at lower angles
of attack.
*D increase the possibility of a wing tip
) stall.
25.Fuel/air ratio is the ratio between the:
A volume of fuel and volume of air entering the
) carburetor
B mass of fuel and mass of air entering the
) carburetor
C mass of fuel and mass of air entering the
) cylinder
D volume of fuel and volume of air entering the
) cylinder
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Aerodynamics 2 Exam #1Dokument8 SeitenAerodynamics 2 Exam #1Kisna BhurtelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions ATA 51Dokument22 SeitenQuestions ATA 51Phạm PhátNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Weight and Balance PattsDokument20 SeitenReviewer Weight and Balance Pattsjesty0% (1)
- Agk AnswersDokument59 SeitenAgk AnswersblessedbuddhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aeroplane EssaysDokument12 SeitenAeroplane EssayscollinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation - Aeroplanes: 22.01. Flight InstrumentsDokument28 SeitenInstrumentation - Aeroplanes: 22.01. Flight InstrumentsVeena Divya Krishnappa100% (1)
- Caa Easa Mod 8Dokument4 SeitenCaa Easa Mod 8a_sharafiehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equal Time Point (ETP)Dokument2 SeitenEqual Time Point (ETP)gambit_zetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerodynamics DGCADokument19 SeitenAerodynamics DGCAIlhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ats Sample ExamDokument14 SeitenAts Sample ExamA320viatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latest Pilot Jobs - List AtplquestionbankquizDokument53 SeitenLatest Pilot Jobs - List AtplquestionbankquizmuratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 Airfoils Nomenclature NACA SeriesDokument38 SeitenLecture 5 Airfoils Nomenclature NACA Seriesraman palNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawaban PropulsiDokument35 SeitenJawaban PropulsiyandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Är Över Bättre Åvan FlygaDokument668 SeitenÄr Över Bättre Åvan Flygaerikjohansson91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operational-Procedure-Jaa Atpl QuestionsDokument131 SeitenOperational-Procedure-Jaa Atpl QuestionsAnita MukulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruments 1Dokument32 SeitenInstruments 1Jehan IchhaporiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General TechnicalDokument7 SeitenGeneral TechnicalMoumita ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A320Dokument6 SeitenA320Atharav Ansil ChowdharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Mass & Balance and PerformanceDokument109 Seiten1 Mass & Balance and PerformanceFahim HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Which Group Does Use The Largest Power in AircraftDokument11 SeitenWhich Group Does Use The Largest Power in AircraftNgân LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal TestDokument15 SeitenInternal TestbaknedicemNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATC Clearances Quiz With AnswersDokument11 SeitenATC Clearances Quiz With AnswersAaron GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flight Performance Planning PDFDokument9 SeitenFlight Performance Planning PDFvimuktiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine Essay - My SummaryDokument12 SeitenGas Turbine Essay - My Summaryjames kuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aeroplane Aerodynamics, Structures & SystemsDokument389 SeitenAeroplane Aerodynamics, Structures & Systemsadityarana531Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scheduled Performance of Multi-Engine Transport AircraftDokument30 SeitenScheduled Performance of Multi-Engine Transport AircraftAyush KmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EFISDokument9 SeitenEFISsangeetamanishkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNA Phraseology Radiotelephony GlossaryDokument4 SeitenUNA Phraseology Radiotelephony GlossaryJackson XavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- FlpanDokument8 SeitenFlpanRaveendran Sukumaran PareshnathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type Ratting CessnaDokument7 SeitenType Ratting CessnaAzuma Cenation AzraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - ATPL Questions AGK2-Electricity - ElectonicsDokument94 Seiten3 - ATPL Questions AGK2-Electricity - ElectonicsTanvir HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of Flights PDFDokument167 SeitenPrinciple of Flights PDFNirja oza100% (1)
- Fragen - Principles of FlightDokument313 SeitenFragen - Principles of FlightTomasz Kurdziel50% (2)
- ATM The Pilots EnvironmentDokument25 SeitenATM The Pilots EnvironmentNick TsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icao Annexes and Others PDFDokument7 SeitenIcao Annexes and Others PDFRealyn LabaynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.initial ClimbDokument26 Seiten4.initial Climbchhetribharat08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reg qns1Dokument15 SeitenReg qns1Hardik MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical General PDFDokument11 SeitenTechnical General PDFSumit PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrics Revision QuestionsDokument5 SeitenElectrics Revision QuestionsIludiran KolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 8 JcarcDokument11 SeitenModule 8 JcarcKHAIREDDIN BUSINESS100% (1)
- Exam Compilation Module 11aDokument18 SeitenExam Compilation Module 11aMohamad Nor ImanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions ATA 51Dokument22 SeitenQuestions ATA 51huynhnhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airbus Vs BoeingDokument5 SeitenAirbus Vs BoeingFlorin Anton100% (1)
- Piper Seneca Pa-34 Questions by Capt JP SharmaDokument10 SeitenPiper Seneca Pa-34 Questions by Capt JP SharmaOxygen SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Bus 330Dokument28 SeitenAir Bus 330Putu RobedNoch keine Bewertungen
- A) B) C) D) : Level A (Multiple Choice Question)Dokument5 SeitenA) B) C) D) : Level A (Multiple Choice Question)Tran Trong TienNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Speed AerodynamicsDokument92 SeitenHigh Speed AerodynamicsKunal Patel100% (1)
- Question For ExaminationDokument6 SeitenQuestion For ExaminationVo DanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary StallsDokument3 SeitenSecondary StallsMike Aguirre100% (1)
- Jar Ops Minimums On Jeppesen ChartsDokument10 SeitenJar Ops Minimums On Jeppesen ChartsEce TuğrulözNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airbus320 Non Formal NotesDokument114 SeitenAirbus320 Non Formal NotesReggie JoshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Gen Knowledge 4 150questions Answered PDFDokument26 SeitenAC Gen Knowledge 4 150questions Answered PDFmoik ojooNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPL Flight Planning ManualDokument94 SeitenCPL Flight Planning ManualChina LalaukhadkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument30 SeitenUntitledKayla MilneNoch keine Bewertungen
- EASA 66 Test ExamDokument9 SeitenEASA 66 Test ExammarcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Question Chapter 12Dokument12 SeitenRevision Question Chapter 12Sealtiel1020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Fly-by-Wire Flight Control Systems: The professional pilot’s guide to understanding modern aircraft controlsVon EverandIntroduction to Fly-by-Wire Flight Control Systems: The professional pilot’s guide to understanding modern aircraft controlsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseVon EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbulences: Remeiniscences of of an Airline PilotVon EverandTurbulences: Remeiniscences of of an Airline PilotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Jetskey B200GT SpecDokument6 SeitenAir Jetskey B200GT SpecAarohi SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Conditions in Which MAYDAY & PANPAN Call Should Be Made: May Day Pan PanDokument1 SeiteList of Conditions in Which MAYDAY & PANPAN Call Should Be Made: May Day Pan PanAarohi SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flight Deck Crew Application: Captain First Officer Ab-InitioDokument4 SeitenFlight Deck Crew Application: Captain First Officer Ab-InitioAarohi SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pilot Exam FormDokument2 SeitenPilot Exam Formtiger402092900% (1)
- A320 Induction With AnswersDokument13 SeitenA320 Induction With AnswersAarohi Sood79% (19)
- 28aug2010Dokument1 Seite28aug2010Aarohi SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intel Core - WikipediaDokument16 SeitenIntel Core - WikipediaEEBB0% (1)
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDokument18 SeitenUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unclaimed Abandoned Vehicles Feb 2022Dokument66 SeitenUnclaimed Abandoned Vehicles Feb 2022kumar himanshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cages With Various Infill Pattern For 3D Printing ApplicationDokument7 SeitenDesign of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cages With Various Infill Pattern For 3D Printing ApplicationdhazliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incident Log - TemplateDokument10 SeitenIncident Log - TemplateRajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCMCHistoryDokument18 SeitenMCMCHistoryAli S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp.1 (Screening) Group1Dokument16 SeitenExp.1 (Screening) Group1itokki otoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonus 6 - Mastering ASP - NET Core SecurityDokument147 SeitenBonus 6 - Mastering ASP - NET Core SecurityDark Shadow100% (1)
- NO.76 Method Statement for Chemical Anchoring of Rebars on Piles - Rev.0第一次Dokument5 SeitenNO.76 Method Statement for Chemical Anchoring of Rebars on Piles - Rev.0第一次Amila Priyadarshana DissanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude Palm OilDokument4 SeitenCrude Palm OilpalmoilanalyticsNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRB 301 Ma Operating Instructions Safety-Monitoring ModulesDokument6 SeitenSRB 301 Ma Operating Instructions Safety-Monitoring ModulesMustafa EranpurwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Repair Overhaul: Safely To New Horizons Ensuring Your Aircraft Is Ready Whenever Duty CallsDokument10 SeitenMaintenance Repair Overhaul: Safely To New Horizons Ensuring Your Aircraft Is Ready Whenever Duty CallsSuryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spice Board BBLDokument24 SeitenSpice Board BBLvenkatpficoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Worksheet: 6.1A MeanDokument7 SeitenLesson Worksheet: 6.1A Meanwaiman fuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lease Contract AddendumDokument1 SeiteLease Contract AddendumjasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harrod-Domar ModelDokument13 SeitenHarrod-Domar ModelsupriyatnoyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUF-2000M User Manual PDFDokument56 SeitenTUF-2000M User Manual PDFreinaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fernbetätigte Armaturen: Remote Controlled Valve SystemsDokument14 SeitenFernbetätigte Armaturen: Remote Controlled Valve SystemslequangNoch keine Bewertungen
- EIV Operation ManualDokument339 SeitenEIV Operation ManualJJSNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO - PowerpointDokument16 SeitenIMO - PowerpointMahen Fernando100% (3)
- FIN323 Project 2021-2022Dokument6 SeitenFIN323 Project 2021-2022saleem razaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ColgateDokument32 SeitenColgategargatworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slid e 4-1Dokument67 SeitenSlid e 4-1Rashe FasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAU 2022 - Prostate CancerDokument229 SeitenEAU 2022 - Prostate Cancerpablo penguinNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Radio Network Design Guideline (FDD)Dokument33 SeitenLTE Radio Network Design Guideline (FDD)Tri Frida NingrumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Industrial Relation of BDDokument12 SeitenAssignment On Industrial Relation of BDKh Fahad Koushik50% (6)
- Tugas Moneter CH 4 - Dewi Lucky Aryanti Sinaga F1119025Dokument4 SeitenTugas Moneter CH 4 - Dewi Lucky Aryanti Sinaga F1119025Scream InungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etpm Mód 3 Assignment 2.1 Grammar and Use of English SkillsDokument3 SeitenEtpm Mód 3 Assignment 2.1 Grammar and Use of English SkillsLourdes LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autodesk Inventor Practice Part DrawingsDokument25 SeitenAutodesk Inventor Practice Part DrawingsCiprian Fratila100% (1)
- Bảo MậtDokument2 SeitenBảo MậtMinh Nghia PhamNoch keine Bewertungen