Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mathematical Models Control Systems
Hochgeladen von
12343567890Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mathematical Models Control Systems
Hochgeladen von
12343567890Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
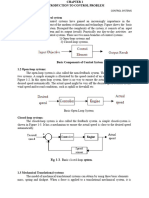
Mathematical Modelling In control System:
The control systems can be represented with a set of mathematical equations known as mathematical
model. These models are useful for analysis and design of control systems. Analysis of control system
means finding the output when we know the input and mathematical model. Design of control system
means finding the mathematical model when we know the input and the output.
The following mathematical models are mostly used.
Differential equation model
Transfer function model
State space model
Differential Equation Model
Differential equation model is a time domain mathematical model of control systems. Follow these steps
for differential equation model.
Apply basic laws to the given control system.
Get the differential equation in terms of input and output by eliminating the intermediate
variable(s).
Example
Consider the following electrical system as shown in the following figure. This circuit consists of
resistor, inductor and capacitor. All these electrical elements are connected in series. The input voltage
applied to this circuit is vi and the voltage across the capacitor is the output voltage vo
Mesh equation for this circuit is
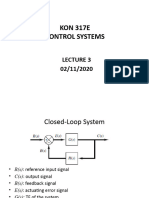
Transfer Function Model
Transfer function model is an s-domain mathematical model of control systems. The Transfer
function of a Linear Time Invariant (LTI) system is defined as the ratio of Laplace transform of output
and Laplace transform of input by assuming all the initial conditions are zero.
If x(t) and y(t) are the input and output of an LTI system, then the corresponding Laplace transforms are
X(s) and Y(s).
Therefore, the transfer function of LTI system is equal to the ratio of Y(s) and X(s)
The transfer function model of an LTI system is shown in the following figure.
Here, we represented an LTI system with a block having transfer function inside it. And this block has an
input X(s) & output Y(s).
Example
Previously, we got the differential equation of an electrical system as
Where,
Vi(s) is the Laplace transform of the input voltage vi
Vo(s) is the Laplace transform of the output voltage vo
The above equation is a transfer function of the second order electrical system. The transfer function
model of this system is shown below.
Here, we show a second order electrical system with a block having the transfer function inside it. And this
block has an input Vi(s) & an output Vo(s).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorVon EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlVon EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Modelling Electrical SystemsDokument3 SeitenModelling Electrical SystemsPandu KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Models of SystemsDokument45 SeitenMathematical Models of SystemsSaid Ahmed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide 2Dokument89 SeitenSlide 2EnesVSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TwoDokument32 SeitenChapter TwowabdushukurNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 3201 Week 3Dokument12 SeitenEEE 3201 Week 3harun or rashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-02-Mathematical ModelDokument4 SeitenL-02-Mathematical ModelMh RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Modeling: ESE439 - Chapter 2Dokument51 SeitenMathematical Modeling: ESE439 - Chapter 2norlelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling in The Time DomainDokument19 SeitenModeling in The Time DomainAnonymous 55cH67eIxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical ModellingDokument36 SeitenMathematical ModellingMohd Fazli100% (2)
- PidDokument2 SeitenPidOwais KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 3201: Control System I: Week 2: Lecture 1Dokument11 SeitenEEE 3201: Control System I: Week 2: Lecture 1harun or rashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is a SystemDokument6 SeitenWhat is a SystemRyan HiraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 State SpaceDokument57 SeitenUnit 1 State SpaceJoseph AgboglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Elements of Control SystemDokument36 SeitenBasic Elements of Control Systemeugeni madaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture (4) Mathematical Modeling in Mechanical and Electrical SystemDokument6 SeitenLecture (4) Mathematical Modeling in Mechanical and Electrical SystemAbdullah Mohammed AlsaadouniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemsDokument8 SeitenControl Systemsmohammed zaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3Dokument8 SeitenLec 3students answerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Control Unit LLDokument5 SeitenAutomated Control Unit LLRakgnar LodbrokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Synchronous Machine in Stability Study For Power SystemDokument6 SeitenSimulation of Synchronous Machine in Stability Study For Power SystemZawmin TunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Topic Covered in ECE408Dokument89 SeitenSummary of Topic Covered in ECE408Nishikata ManipolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Non Linear ControlDokument21 SeitenLecture 1 Non Linear ControlShivan BiradarNoch keine Bewertungen
- W EE 418 - Lecture 2 ModelingDokument20 SeitenW EE 418 - Lecture 2 ModelingGGAP LASTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer Function & Block Diagram Algebra: M. Azharul Haque Dept. of EEE PAUDokument69 SeitenTransfer Function & Block Diagram Algebra: M. Azharul Haque Dept. of EEE PAUShazidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter ThreeDokument13 SeitenChapter ThreeGetahun tuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Models: Module - 2Dokument13 SeitenMathematical Models: Module - 2Rajath UpadhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- State SpaceDokument101 SeitenState SpaceShivam AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Chapter Objectives: Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 4: Systems and Network TheoremsDokument42 SeitenIntroduction and Chapter Objectives: Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 4: Systems and Network TheoremskrajasekarantutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Feedback Linearization Based Control Strategy For VSC-HVDC Transmission ConvertersDokument10 SeitenA Feedback Linearization Based Control Strategy For VSC-HVDC Transmission ConvertersĐỗ TrườngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems: Lecture Notes of ME 862Dokument9 SeitenModeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems: Lecture Notes of ME 862RajrdbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 1 Lab KendaliDokument31 SeitenModul 1 Lab KendaliSyukran0% (1)
- Control System Engineering 2 MarksDokument18 SeitenControl System Engineering 2 MarksSeenu CnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer Functions and Block Diagrams PDFDokument21 SeitenTransfer Functions and Block Diagrams PDFJuliana NepembeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1. Chapter 1_Transfer FunctionDokument52 Seiten1. Chapter 1_Transfer FunctionNahome NigussieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Automatic Control System Modeling and RepresentationDokument55 Seiten01 Automatic Control System Modeling and RepresentationPaul BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Modeling of Electrical Systems: Nader SadeghDokument10 SeitenMathematical Modeling of Electrical Systems: Nader SadeghAmr BalbolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Two MarksDokument7 SeitenCS Two MarkssivaeinfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Modeling of Quasi-Resonant Converters Extension of State-Space Averaging To Model non-PWM SwitchesDokument36 SeitenAC Modeling of Quasi-Resonant Converters Extension of State-Space Averaging To Model non-PWM Switchessiddhartha_anirbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 505-Lec 09 PDFDokument19 Seiten505-Lec 09 PDFUdara DissanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic SystemDokument56 SeitenChapter 2 Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic SystemAmanuel AsfawNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCC Mini ProjetDokument5 SeitenMCC Mini ProjetMohammed Amine SayehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Controls PDFDokument24 SeitenModule 2 Controls PDFPrincess LutivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp01 EEE318Dokument7 SeitenExp01 EEE318Abid AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Flow Analysis of Unbalanced Multiphase Radial Distribution SystemsDokument11 SeitenPower Flow Analysis of Unbalanced Multiphase Radial Distribution SystemsneripereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - 2Dokument42 SeitenLecture 3 - 2faruktokuslu16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling of The State Transition Equations of Power Systems With Non-Continuously Operating Elements by The RCF MethodDokument6 SeitenModeling of The State Transition Equations of Power Systems With Non-Continuously Operating Elements by The RCF Methodkanda71Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Electric Machinery and Power Electronics InterfacingDokument6 SeitenSimulation of Electric Machinery and Power Electronics Interfacingadilo7780Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mecht 4Dokument6 SeitenMecht 4YoungneticNoch keine Bewertungen
- State Space AnalysisDokument73 SeitenState Space AnalysisDevaki V DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week3 5Dokument22 SeitenWeek3 5Abdullah MahsudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diff Eqn and State Variable Analysis 18 March 23Dokument70 SeitenDiff Eqn and State Variable Analysis 18 March 23Md Nazmus Sadat ShadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 45 - 70685 - EE411 - 2013 - 1 - 1 - 1 - Control System I-State SpaceDokument84 Seiten45 - 70685 - EE411 - 2013 - 1 - 1 - 1 - Control System I-State SpaceSwifty SpotNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDokument19 SeitenSchool of Electrical and Computer EngineeringSurafel TadesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCW - Control Systems - I (EE 503) - AY 2016-17 - 2017-18 PDFDokument100 SeitenOCW - Control Systems - I (EE 503) - AY 2016-17 - 2017-18 PDFCiczmockingbird TsvkAdm100% (1)
- IC6501 CONTROL SYSTEMSDokument67 SeitenIC6501 CONTROL SYSTEMSK.Sushita VISTASNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLECS-piece-wise Linear Electrical Circuit Simulation For SimulinkDokument6 SeitenPLECS-piece-wise Linear Electrical Circuit Simulation For Simulink曾乙申Noch keine Bewertungen
- EC2255 Control Systems Question BankDokument62 SeitenEC2255 Control Systems Question BankreporterrajiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Engineering ME - 4012: Instructor Muhammad Rizwan SiddiquiDokument23 SeitenControl Engineering ME - 4012: Instructor Muhammad Rizwan SiddiquiTalha JalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetVon EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Operation & Service Manual: POSDION Co., LTDDokument75 SeitenOperation & Service Manual: POSDION Co., LTD12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- FFMedicalDevicesRules2017Notifiedon16 01 2018Dokument93 SeitenFFMedicalDevicesRules2017Notifiedon16 01 2018Anonymous dukfCrCBdnNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual Geratherm DesktopDokument17 SeitenUser Manual Geratherm Desktop12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument3 SeitenUntitled12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- DENTAL CHAIR OPERATING INSTRUCTIONSDokument48 SeitenDENTAL CHAIR OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Publications: Dental Delivery Unit Operation ManualDokument38 SeitenTechnical Publications: Dental Delivery Unit Operation Manual12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual: September 2014, QS4 631 v.1Dokument47 SeitenUser Manual: September 2014, QS4 631 v.1Ali SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Discrete-Time Fourier Transform: Solutions To Recommended ProblemsDokument10 Seiten11 Discrete-Time Fourier Transform: Solutions To Recommended ProblemsShivansh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attachment 4Dokument4 SeitenAttachment 412343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6 7 × User's ManualDokument16 Seiten6 7 × User's Manual12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculator of CPD PointsDokument1 SeiteCalculator of CPD PointsFahad ZulfiqarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hiob Thesis FinalDokument70 SeitenHiob Thesis Final12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication and Characteriation of P-N Junction DiodeDokument11 SeitenFabrication and Characteriation of P-N Junction Diode12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- William RaveisDokument3 SeitenWilliam Raveis12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fiverr Design BriefDokument3 SeitenFiverr Design Brief12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Integrated CircuitsDokument10 SeitenLinear Integrated Circuits123435678900% (1)
- 1.7 Resistance Levels: Variation in Diode Characteristics With Temperature ChangeDokument7 Seiten1.7 Resistance Levels: Variation in Diode Characteristics With Temperature Change12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 8th Maths PaperDokument1 SeiteClass 8th Maths Paper12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8086 Microprocessor Signal DescriptionDokument17 Seiten8086 Microprocessor Signal Description12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hands-On Exercise No. 3 Batch-08 Wordpress Total Marks: 10 Due Date: 03/12/2020Dokument3 SeitenHands-On Exercise No. 3 Batch-08 Wordpress Total Marks: 10 Due Date: 03/12/202012343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded C Programming For 8051 Using KeilDokument12 SeitenEmbedded C Programming For 8051 Using KeilNishant MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hands-On Exercise No. 1 Batch-08 Wordpress Total Marks: 10 Due Date: 29/10/2020Dokument3 SeitenHands-On Exercise No. 1 Batch-08 Wordpress Total Marks: 10 Due Date: 29/10/202012343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Water PollutionDokument18 SeitenWater PollutionСаманати СоринNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year Physics Complete NotesDokument133 Seiten2nd Year Physics Complete Notes12343567890100% (1)
- 8051 C Programming Guide for BeginnersDokument16 Seiten8051 C Programming Guide for Beginners12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Time Response of Second Order SystemDokument6 SeitenTime Response of Second Order System12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- MICROCONTROLLER-8051 Features & ApplicationsDokument94 SeitenMICROCONTROLLER-8051 Features & Applications12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic school bell system replaces manual operationDokument26 SeitenAutomatic school bell system replaces manual operationKoshy Geoji86% (7)
- Multiple Choice Questions Section: Examination Department, Saudi Commission For Health SpecialtiesDokument2 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions Section: Examination Department, Saudi Commission For Health Specialties12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Processor Architectures and Programming: Conference PaperDokument5 SeitenDigital Signal Processor Architectures and Programming: Conference Paper12343567890Noch keine Bewertungen