Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assignment FET 2
Hochgeladen von
shobanraj1995Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignment FET 2
Hochgeladen von
shobanraj1995Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SHOBANRAJ LETCHUMANAN
13561
MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING
ASSIGNMENT EEE133: ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT AND DEVICES
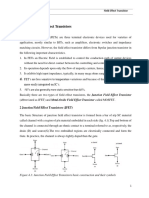
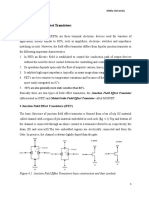
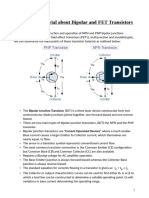
PART A: DESCRIPTION OF TRANSISTOR
Basis of operation of n-channel D-MOSFET
The basic construction of n-channel depletion type MOSFET is
provided in the figure shown above. The Depletion-mode
MOSFET, which is less common than the enhancement mode
types is normally switched “ON” (conducting) without the
application of a gate bias voltage. That is the channel conducts
when VGS = 0 making it a “normally-closed” device. The circuit
symbol shown above for a depletion MOS transistor uses a solid
channel line to signify a normally closed conductive channel.For the n-channel depletion MOS
transistor, a negative gate-source voltage, -VGS will deplete (hence its name) the conductive channel of
its free electrons switching the transistor “OFF”. Likewise for a p-channel depletion MOS transistor a
positive gate-source voltage, +VGS will deplete the channel of its free holes turning it “OFF”.In other
words, for an n-channel depletion mode MOSFET: +VGS means more electrons and more current. While
a -VGS means less electrons and less current. The opposite is also true for the p-channel types. Then
the depletion mode MOSFET is equivalent to a “normally-closed” switch. A slab of p-type material is
formed from a silicon base and is referred to as the substrate. It is the foundation upon which the
device will be constructed. In some cases, the substrate is internally connected to the source terminal.
The source and drain terminals are connected through metallic contacts to n-doped regions linked by
an n-channel . The fact that the SiO2 layer is an insulating layer reveals the following fact: There is no
direct electrical connection between the gate terminal and the channel of a MOSFET. It is the insulating
layer of SiO2 in the MOSFET construction that accounts for the very desirable high input impedance of
the device. In fact, the input resistance of a MOSFET is often that of the typical JFET, even though the
input impedance of most JFETs is sufficiently high for most applications. In the figure ,the gate-to-
source voltage is set to zero volts by the direct connection from one terminal to the other and a voltage
VDS is applied across the drain to source terminals. The result is an attraction for the positive potential
at the drain by the free electrons of the n-channel and a current similar to that established through the
channel of the JFET. In fact, the resulting current with VGS = 0 V continues to be labeled IDSS, as shown
in the characteristics of depletion type MOSFET figure.
Relation of D-MOSFET, E-MOSFET AND JFET in basic operation
(i) Induced channel in between of drain and source is required for both D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET.
(ii) The current,I flowing between drain and source channel corresponds the input voltage like in
JFET
(iii) Both D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET are voltage-controlled devices which is controlled by gate-
source voltage,VGS.
(iv) MOSFET has to be handled with precautions as the D-MOSFET is something similar to JFET
which has a very high input resistance that can accumulate numerous static charges.
Important parameters in characterizing the performance of the chosen FET.
(i) Drain-source voltage,VDS
(ii) Drain current,ID
(iii) Gate-source voltage,VGS
Related applications of the chosen FET.
(i) current sources,
(ii) solid-state relays,
(iii) telecom switches
(iv) Linear Voltage Regulator
PART B: DESCRIPTION OF CHOSEN ISSUE, PROBLEM, OR SITUATION
A depletion MOSFET can also be used as a pass transistor for a linear regulator. A
linear regulator circuit using a depletion MOSFET plus a Zener diode. In the circuit,
Q1 acts as a source follower where the source voltage follows the gate voltage
(VG) minus the gateto-source voltage. VGS increases with increasing drain current.
Thus, with a fixed gate voltage, the source voltage will drop with increasing load
current. For design purposes, VGS under saturation and cut-off conditions (0 V and
VGS(th), respectively) can be used. These values can be readily obtained from the datasheet, and Figure 11
shows the cut-off and saturation conditions of the Infineon BSS169. Bias current for the Zener diode is
determined by VGS/R. The Zener diode sets the gate voltage and should be selected to provide a source
voltage within the range determined, taking into account the variances of VGS with load.
PART C: EXPLANATION ON THE ENVIRONMENTAL, ECONOMIC, AND SOCIAL IMPACTS – CONSIDERING
THE STAKEHOLDERS
Low total cost of Linear Voltage Regulator accounted for about 67% of sales market share in total. Fast
development in most Chinese domestic industrial technologies, Linear Voltage are in progressed to be more
advanced and eco-friendly. Less complex it makes less pollution.
No Stakeholder Impact
Positive Negative
(Provide explanation) (Provide explanation)
1 Electronic industry manufacturers Organize more electronic Can be only used as step down
product due to the advanced voltage which needs greater
operating current, droupoud voltage hence more heat wastage
voltage, noise and packaging
2 consumer Lesser cost and noise Efficiency is in between low
and medium
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Unit 01Dokument21 SeitenUnit 01mathanstar77Noch keine Bewertungen
- ElectronicsDokument22 SeitenElectronicsVARSHITH REDDY JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power MosfetsDokument11 SeitenPower MosfetsSoudip KUNDUNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 To 5 ManualDokument30 Seiten1 To 5 ManualRoshan DodiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Module2 (FET Part) Basic Electronics 22BBEE203Dokument12 SeitenNotes Module2 (FET Part) Basic Electronics 22BBEE203Hani MNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Mosfets (Prepared) 1Dokument75 SeitenOn Mosfets (Prepared) 1Ankit RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEC Lab ManualDokument75 SeitenAEC Lab Manualphalanetra100% (1)
- Mosfet Differential AmplifierDokument7 SeitenMosfet Differential AmplifierSunil PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trafo PulsoDokument132 SeitenTrafo PulsoNestor FonteneleNoch keine Bewertungen
- AN-478A TextDokument12 SeitenAN-478A TextAl BenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlled Devices FET, BJT, IGBTDokument51 SeitenControlled Devices FET, BJT, IGBTHolloGramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Ii: BY Professor Omotosho T. Victor & DR Akinwumi SayoDokument46 SeitenElectronics Ii: BY Professor Omotosho T. Victor & DR Akinwumi SayoOmotosho Temidayo VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jfet MosfetDokument25 SeitenJfet Mosfethrishabhraj710Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Chapter 4Dokument16 SeitenElectronics Chapter 4YidnekachewNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFDokument21 SeitenEI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFsartpgitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 IntroductionDokument61 Seiten1 Introductionfiraol temesgenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Note AN-1084: Power MOSFET BasicsDokument13 SeitenApplication Note AN-1084: Power MOSFET Basicshardcore18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power MOSFET BasicsDokument13 SeitenPower MOSFET BasicsTim PriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece-Research Work 1Dokument10 SeitenEce-Research Work 1Peale ObiedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog and Digital Electronics (Subject Code: 17CS32) Lecturer NotesDokument59 SeitenAnalog and Digital Electronics (Subject Code: 17CS32) Lecturer NotesKarthik v BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Cmos Multistage High Gain Differential Amplifier Using CadenceDokument4 SeitenDesign of Cmos Multistage High Gain Differential Amplifier Using CadenceAbdulrahman behiryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 FET MOSFETDokument23 SeitenModule 4 FET MOSFETsenthilnathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RESEARCH of Communications Research No. 2Dokument19 SeitenRESEARCH of Communications Research No. 2Princess EsmejardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsDokument5 SeitenEEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsFaria SharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit3 Mosfet Diode TransistorDokument45 SeitenUnit3 Mosfet Diode TransistorPriyanshu yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- REN An7244 APN 19980812Dokument5 SeitenREN An7244 APN 19980812Jeff PalaganasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument16 SeitenChapter 4firomsaguteta12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resonant Converter Topologies: Application NoteDokument5 SeitenResonant Converter Topologies: Application Notesatyam swarup dubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab No. 01: TitleDokument10 SeitenLab No. 01: TitleArbab AslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsDokument5 SeitenExperiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsManikandan P Engineering EEE100% (1)
- Power ElectronicDokument17 SeitenPower ElectronicHAMID SULIAMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poer ElectronicDokument17 SeitenPoer ElectronicHAMID SULIAMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.1 S06L05-FieldEffectTransistors-MOSFETs - PDF - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Dokument19 Seiten8.1 S06L05-FieldEffectTransistors-MOSFETs - PDF - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)yotopia horoor gameNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 1 - FET - WatermarkDokument16 SeitenMODULE 1 - FET - WatermarkAnupama MohananNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-PPT MosfetDokument28 Seiten3-PPT MosfetVaibhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Effect Transistor, Ujt, SCR, Triac: Scope of The ChapterDokument8 SeitenField Effect Transistor, Ujt, SCR, Triac: Scope of The ChapterAkhilesh PandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power BJTDokument14 SeitenPower BJTJahangeer SoomroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorDokument21 SeitenElectronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorGawrav BaishyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecler Pam2000 Pam2600 Power Amplifier Service ManualDokument107 SeitenEcler Pam2000 Pam2600 Power Amplifier Service Manuallluissb92% (12)
- Project 1: Power Electronics IDokument10 SeitenProject 1: Power Electronics ISaratul AkmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Cmos BufferDokument5 SeitenDesign of Cmos BufferVarunKaradesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEXFETs Power MOSFETsDokument22 SeitenHEXFETs Power MOSFETsMiguel PenarandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter ForDokument17 SeitenChapter Forbelacheweshetu222Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power BJT & MOSFETDokument7 SeitenPower BJT & MOSFETAsha DurafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADC Unit 2 LM MOSFET BJTDokument37 SeitenADC Unit 2 LM MOSFET BJTKeerthi SadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor Tutorial: Bipolar vs FETDokument4 SeitenTransistor Tutorial: Bipolar vs FETlosmilzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Observations: Experimental ValuesDokument7 SeitenObservations: Experimental ValuesShibeshwar MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture10 MOS Field Effect Transistors v1Dokument33 SeitenLecture10 MOS Field Effect Transistors v1Dr-Suraj Kumar SawNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC Unit-4Dokument23 SeitenEDC Unit-4laxmanabcdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mosfet PDFDokument13 SeitenMosfet PDFTad-electronics TadelectronicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of JFETDokument13 SeitenApplication of JFETtalha2905100% (10)
- Chapter 1 Micro Electronics Circuit NotesDokument59 SeitenChapter 1 Micro Electronics Circuit NotesswamySLR100% (1)
- Field Effect Transistors (FET) : Comparison Between BJT and FETDokument9 SeitenField Effect Transistors (FET) : Comparison Between BJT and FETpranavraikar1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesVon EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (7)
- FYP Seminar Series II 2019-2020 - Abstract - Introduction ZD PDFDokument27 SeitenFYP Seminar Series II 2019-2020 - Abstract - Introduction ZD PDFshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Light ComponentsDokument14 SeitenTraffic Light Componentsshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- FYP Final Report Preparation 2019-2020 - MKMJ PDFDokument10 SeitenFYP Final Report Preparation 2019-2020 - MKMJ PDFshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- FYP Seminar Series 2019-2020 RMM - Chapter 4 - 5 PDFDokument33 SeitenFYP Seminar Series 2019-2020 RMM - Chapter 4 - 5 PDFshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fun and Games With Pi: Calculating Area and PerimeterDokument5 SeitenFun and Games With Pi: Calculating Area and Perimetershobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scanned by CamscannerDokument16 SeitenScanned by Camscannershobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile bill detailsDokument4 SeitenMobile bill detailsshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- FYP Seminar Series II 2019-2020 - LITERATURE REVIEW NMM PDFDokument46 SeitenFYP Seminar Series II 2019-2020 - LITERATURE REVIEW NMM PDFshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- FYP Seminar Series II 2019-2020 - Methodology AAADokument20 SeitenFYP Seminar Series II 2019-2020 - Methodology AAAshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eee133 Electronic Devices and Circuits AssignmentDokument2 SeitenEee133 Electronic Devices and Circuits Assignmentshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coursework Marks EEE355 PDFDokument1 SeiteCoursework Marks EEE355 PDFshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- EEM348 Principles of Intelligent SystemsDokument2 SeitenEEM348 Principles of Intelligent Systemsshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- TIMELINE FOR FINAL YEAR PROJECT 2019-2020 - Student Covid19 RevDokument2 SeitenTIMELINE FOR FINAL YEAR PROJECT 2019-2020 - Student Covid19 Revshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Agricultural Arduino Controlled Pick and Place Robotic ArmDokument10 SeitenAgricultural Arduino Controlled Pick and Place Robotic Armshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instrument 1718Dokument17 SeitenInstrument 1718shobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial MagneticDokument6 SeitenTutorial Magneticshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLC Control of Assembly Unit with Pneumatic ComponentsDokument1 SeitePLC Control of Assembly Unit with Pneumatic Componentsshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- EEK373 Group Simulation Report - 3 Phase AC RectifierDokument1 SeiteEEK373 Group Simulation Report - 3 Phase AC Rectifiershobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- EEK373 Advance Power Electronics AssignmentDokument6 SeitenEEK373 Advance Power Electronics Assignmentshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- EEM253Assignments2V2 2020Dokument1 SeiteEEM253Assignments2V2 2020shobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Light ComponentsDokument14 SeitenTraffic Light Componentsshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- EEM348 201718 GAAssignmentsDokument1 SeiteEEM348 201718 GAAssignmentsshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vehicle Tracking System Using GPS and Android OSDokument5 SeitenVehicle Tracking System Using GPS and Android OSshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Vehicle Tracking Application: Information TechnologyDokument32 SeitenSmart Vehicle Tracking Application: Information Technologyshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Android App Based Vehicle Tracking Using GPS and GSM: AbstractDokument6 SeitenAndroid App Based Vehicle Tracking Using GPS and GSM: AbstractManoharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix DDokument31 SeitenAppendix Dshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Android Vehicle Tracking Application: Microsoft Windows Microsoft SQL Server Visual Studio Android SDKDokument2 SeitenAndroid Vehicle Tracking Application: Microsoft Windows Microsoft SQL Server Visual Studio Android SDKshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix B..Dokument3 SeitenAppendix B..shobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Contents:: Chapter One INTRODUCTION: .2Dokument4 SeitenTable of Contents:: Chapter One INTRODUCTION: .2shobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Canterburytales-No Fear PrologueDokument10 SeitenCanterburytales-No Fear Prologueapi-261452312Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trishasti Shalaka Purusa Caritra 4 PDFDokument448 SeitenTrishasti Shalaka Purusa Caritra 4 PDFPratik ChhedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WBC Study Reveals God's NatureDokument11 SeitenWBC Study Reveals God's NatureSherwin Castillo DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVADokument7 SeitenRecent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVAcal2_uniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPSS-TEST Survey QuestionnaireDokument2 SeitenSPSS-TEST Survey QuestionnaireAkshay PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual EDokument12 SeitenManual EKrum KashavarovNoch keine Bewertungen
- War, Rivalry An State Building in Latin AmericaDokument16 SeitenWar, Rivalry An State Building in Latin AmericaPablo Andrés Garrido GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Oven and Sun Dry Meat and ProduceDokument12 SeitenHow To Oven and Sun Dry Meat and ProduceLes BennettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horizontal Vertical MarketDokument4 SeitenHorizontal Vertical MarketVikasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Seven Kings of Revelation 17Dokument9 SeitenThe Seven Kings of Revelation 17rojelio100% (1)
- SAP SD Course Content PDFDokument4 SeitenSAP SD Course Content PDFshuku03Noch keine Bewertungen
- C++ NotesDokument129 SeitenC++ NotesNikhil Kant Saxena100% (4)
- So You Want To Be A NeurosugeonDokument10 SeitenSo You Want To Be A NeurosugeonColby TimmNoch keine Bewertungen
- T Cells & Autoimmunity, s3Dokument21 SeitenT Cells & Autoimmunity, s3LiaAriestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Web 2014Dokument40 SeitenScience Web 2014Saif Shahriar0% (1)
- 2.7.3 Lab Use Steganography To Hide Data Answer KeyDokument3 Seiten2.7.3 Lab Use Steganography To Hide Data Answer KeyVivek GaonkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elective Course (2) - Composite Materials MET 443Dokument16 SeitenElective Course (2) - Composite Materials MET 443يوسف عادل حسانينNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Con LouvresDokument1 SeiteAir Con LouvresChung May LynnNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM385Dokument14 SeitenLM385vandocardosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reasons Why Coca Cola Has A Large Market Share in Kenya and The WorldDokument9 SeitenReasons Why Coca Cola Has A Large Market Share in Kenya and The WorldAludahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Download 12,000 Shed PlansDokument27 SeitenDownload 12,000 Shed PlansRadu_IS100% (2)
- Lazo v. Judge TiongDokument9 SeitenLazo v. Judge TiongKing BadongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Politics Concepts ExplainedDokument3 SeitenPhilippine Politics Concepts ExplainedAngel Lyn A Lacerna100% (1)
- Rock Laboratory PricelistDokument1 SeiteRock Laboratory PricelistHerbakti Dimas PerdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProSteel Connect EditionDokument2 SeitenProSteel Connect EditionInfrasys StructuralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeDokument5 SeitenProcess of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeSantosh Kumar MahtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Discontinuous Puf Panels Using Cyclopentane As A Blowing AgentDokument6 SeitenProject Report On Discontinuous Puf Panels Using Cyclopentane As A Blowing AgentEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 2maxamed0% (1)
- EINC ChecklistDokument3 SeitenEINC ChecklistMARK JEFTE BRIONESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutritional support through feeding tubesDokument76 SeitenNutritional support through feeding tubesKryzza LeizellNoch keine Bewertungen