Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
General Supplementary Notes in Science 8: Unbalanced Force
Hochgeladen von
KeannoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
General Supplementary Notes in Science 8: Unbalanced Force
Hochgeladen von
KeannoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
General Supplementary Notes in Science 8
Concepts of Force
Dynamics is a branch of mechanics that deals with the study of causes of changes in motion.
There are many philosophers/scientists have many several attempts to fully understand motion and the causes of
changes in motion.
Aristotle attempted to explain motion as the presence of an impetus; and the absence of this impetus means no
motion. While Galileo establish the fundamental concepts of accelerated motion and the concepts of inertia. And
finally, the famous Sir Isaac Newton found a way to describe changes in motion which he formulated the three laws
of motion were able to fully describe what force is.
Force is often qualitatively described as a push or pull. It is usually expressed in units called Newton (N).
Force are considered as vector quantities which expressed in both magnitude and direction.
Ex.: (500 N – magnitude) (to the right – direction)
Two types of forces:
Contact force have a direct touching or collision of the interacting objects is observed. Some examples are friction,
applied force, normal force, spring force, and buoyant force.
Non – contact force has not directly touching one another within an interacting objects. Some examples are
gravitational force, electromagnetic force, weak nuclear force, and strong nuclear force.
Net force is the sum of all the forces acting on an object.
Did you know that we need to understand and apply Cartesian coordinate plane by finding net force?
Cartesian coordinate plane was discovered by Rene Descartes. They
have a 2 lines intersect within each other. The horizontal line is the x
– axis and the vertical line is the y – axis.
An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends
to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction
unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
In the statement of Newton's first law, the unbalanced force refers
to that force that does not become completely balanced (or canceled)
by the other individual forces.
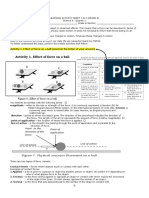
In each of the above situations, there is an unbalanced force. It is commonly said that in each situation there is
a net force acting upon the object. The net force is the vector sum of all the
forces that act upon an object. Observe the following examples of summing
two forces:
Fnet = Fx1 + Fx2
Observe in the diagram (on the left side) the addition of force vectors can
be done in the same manner in order to determine the net force (i.e., the
vector sum of all the individual forces).
By: Keanno Rod M. Peliña
General Supplementary Notes in Science 8
Take note:
Similar direction, you must need to add it!
Different direction, you will need to subtract on it!
(Tignan ang arrowhead kung saan papunta ang direction)
Consider the three situations below in which the net force is determined by summing the individual force vectors
that are acting upon the objects.
Free-body diagrams for four situations are shown below. For each situation, determine the net force acting upon the
object.
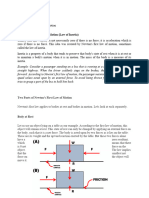
Situation 1. The net force is 0 N. All the individual forces balance each other (i.e., cancel each other out).
Situation 2. The net force is 5 N, left. The vertical forces balance each other (i.e., cancel each other out). The
leftward force (friction) remains unbalanced.
Situation 3. The net force is 0 Newton. All the individual forces balance each other (i.e., cancel each other out).
Situation 4. The net force is 15 N, upward. The upward force of air resistance is only partially balanced by the
downward force of gravity - 15 N of upward force remains unbalanced.
Note:
Kapag parehas kayong nagexert ng effort sa isa’t isa, at 0 N ang sagot, ibig sabihin naging balanced yung force nyo.
Parehas nyong binigay ang lahat ng best efforts nyo para maging balanse ang relasyon nyo! Hahahaha
At kapag hindi pantay o kahit isa sa inyo ay hindi binigay ang effort nyo sa isa’t isa (Let us say may value ang Net
Force mo within 1 N pataas) ibig sabihin naging unbalanced ang force nyo. Hindi nyo binigay ang best effort nyo para
ma - handle yung relationship nyo!
By: Keanno Rod M. Peliña
General Supplementary Notes in Science 8
Source of Reference:
https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/Lesson-2/Determining-the-Net-Force
Newton’s Law of Motion
1. Law of inertia states that a body at rest will remain at rest and a body in motion will move in a constant
speed in a straight line unless an external forces acts on it.
Inertia is the tendency of a body to stay at rest when it is initially at rest or stay in uniform motion in a
straight line when initially in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
Ex.
What happened to the coin if we flicked the card?
2. Law of Acceleration
The acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables, the net force acting upon an object and the
mass of the object.
The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object and inversely upon
the mass of the object.
Note:
Meron tayong equation na gagamitin (tanggapin natin na talagang magtropa talaga sina math at science but I
will allow you to use scientific calculator, pero kung wala kang calcu, mahihirapan at matatagalan kang
magsolve, kung hindi mo magets ang right process ng computation at hindi ka nakikinig sa klase ko, talaga nga
naming mahihirapan ka)
Paano kapag nawawala ang Force (F): F = ma
Paano kapag nawawala ang acceleration (a): a=F/m
By: Keanno Rod M. Peliña
General Supplementary Notes in Science 8
Paano kapag nawawala ang mass (m): m=F/a
3. Law of interaction: For every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction
By: Keanno Rod M. Peliña
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physics: Force and MotionDokument29 SeitenPhysics: Force and MotionGoce Totti KuzeskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons LaDokument9 SeitenNewtons La金 Abigail RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2keyconcepts 1Dokument4 SeitenUnit2keyconcepts 1ansonng16888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Basic Physics SEDokument15 SeitenChapter 7 Basic Physics SEtsoniffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion: Chapter - 00Dokument64 SeitenLaws of Motion: Chapter - 00aatishsubash9b35832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11 Physics Notes - Dynamics: Aaron G. KebedeDokument12 SeitenGrade 11 Physics Notes - Dynamics: Aaron G. KebedeAaron KebedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Newton'sLawsDokument61 SeitenL1 Newton'sLawsArafat AnikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 DynamicsDokument47 SeitenModule 2 DynamicsTaha Kafil-HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hit TerDokument29 SeitenHit TerSai-Min Thit-KoNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1 Quarter 1 - Week 4 SSLMDokument6 SeitenGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 1 - Week 4 SSLMCarmina Jane DomantayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons Laws of Motion PDFDokument26 SeitenNewtons Laws of Motion PDFRohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table of Elements ListDokument7 SeitenPeriodic Table of Elements ListMin YoongiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Newtons LawsDokument16 Seiten05 Newtons LawsLuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci.8 1 2 Las by Arnold and Mam JennyDokument7 SeitenSci.8 1 2 Las by Arnold and Mam JennyCherry Beth PagenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining The Net ForceDokument2 SeitenDetermining The Net ForceimanuelsukarnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stem BL - Gre RefugiaDokument6 SeitenStem BL - Gre RefugiaMichaela RefugiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of MotionDokument74 SeitenLaws of MotionRaichal P BijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDokument6 SeitenContact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesBethlehem CuradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactions and ForceDokument2 SeitenInteractions and Forcezhungjian586Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newton English1Dokument30 SeitenNewton English1Puspa LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDokument7 SeitenStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nkdievid 2Dokument10 SeitenNkdievid 2nik100% (2)
- Saanvi Shee XIB Roll 10 Physics Term 1 ProjectDokument27 SeitenSaanvi Shee XIB Roll 10 Physics Term 1 ProjectSing GyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Third Law: Contact Interactions (Normal, Frictional, Tensional, and Applied Forces Are Examples ofDokument4 SeitenNewton's Third Law: Contact Interactions (Normal, Frictional, Tensional, and Applied Forces Are Examples ofRayudu VVSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDDokument15 SeitenNewtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDApoorva TalankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and MotionDokument8 SeitenForce and MotionForsythe LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 Mechanics Part 2 2015-17Dokument92 SeitenTopic 2 Mechanics Part 2 2015-17Byron JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's First Law: Previous Chapter of StudyDokument5 SeitenNewton's First Law: Previous Chapter of StudyIrene QuiñonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons Laws of Motion1Dokument6 SeitenNewtons Laws of Motion1darlei byerotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Third Law of Motion: Sunil Kumar SinghDokument5 SeitenNewton's Third Law of Motion: Sunil Kumar SinghIekram RamiekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of MotionDokument22 SeitenLaws of MotionDebayanbasu.juNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec03-Newton's Laws of MotionDokument19 SeitenLec03-Newton's Laws of MotionpvriiscNoch keine Bewertungen
- E101 - AgustinDokument21 SeitenE101 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- About: 4.2 Describe Contact and Non-Contact Force, Mass and WeightDokument6 SeitenAbout: 4.2 Describe Contact and Non-Contact Force, Mass and WeightNanzkie Andrei SamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch1 Newton MechanicsDokument16 SeitenCh1 Newton MechanicsRana JahanzaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of MotionDokument12 SeitenLaws of MotionMarc Angel ValeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of MotionDokument13 SeitenNewton's Laws of MotionChinmay SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Dynamics 23Dokument9 SeitenPhysics Dynamics 23Kirubel DessieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - 2Dokument25 SeitenChapter 5 - 2Qassem MohaidatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Summary NotesDokument7 SeitenDynamics Summary NotesArlo SeasenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces and Motion UpdatedDokument31 SeitenForces and Motion UpdatedIrvin GrabosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of MotionDokument43 SeitenNewton's Laws of MotionNasr UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wk6 GenPhys1 - 0926 30Dokument8 SeitenWk6 GenPhys1 - 0926 30JenRose Gadon SoliguenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws 2. Some Particular Forces 3. Applying Newton's LawsDokument67 SeitenNewton's Laws 2. Some Particular Forces 3. Applying Newton's LawsMario EscalonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- University Physics IDokument13 SeitenUniversity Physics IKenn SenadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter No 3 Dynamics Class 9thDokument53 SeitenChapter No 3 Dynamics Class 9thKaka KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Physics Note 1.Dokument6 SeitenGrade 12 Physics Note 1.babaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force, Mass and MomentumDokument24 SeitenForce, Mass and MomentumAhana100% (1)
- September General Physics 1Dokument12 SeitenSeptember General Physics 1bunso sernicilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lesson ReviewsDokument9 SeitenPhysics Lesson ReviewsРубабе ХалиловаNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 2Dokument11 SeitenLab Report 2Fida khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces and Motion Hs Study Guide KeyDokument2 SeitenForces and Motion Hs Study Guide Keyapi-325864985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 1011 - Dynamic NotesDokument10 SeitenPhys 1011 - Dynamic Notesnigusayele06Noch keine Bewertungen
- G9, 1.2 Forces and ShapeDokument5 SeitenG9, 1.2 Forces and ShapeKinmokusei MyoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons First Law of Motion - Balanced and Unbalanced ForcesDokument7 SeitenNewtons First Law of Motion - Balanced and Unbalanced ForcesDISTOR, JOSH GABRIEL100% (1)
- Newt 2Dokument3 SeitenNewt 2Tyro SpiedNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP1 - Q1 - Week 4Dokument5 SeitenGP1 - Q1 - Week 4Sathya CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of MotionDokument31 SeitenLaws of MotionManas ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER XI - Gene TherapyDokument4 SeitenCHAPTER XI - Gene TherapyKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of National Scientists of The Philippines - Official Gazette of The Republic of The Philippines PDFDokument3 SeitenList of National Scientists of The Philippines - Official Gazette of The Republic of The Philippines PDFKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LECTURES (Chapter II To Chapter XII)Dokument44 SeitenLECTURES (Chapter II To Chapter XII)KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER VIII - The Information Age (Gutenberg To Social Media)Dokument4 SeitenCHAPTER VIII - The Information Age (Gutenberg To Social Media)Keanno90% (21)
- CHAPTER V - The Good LifeDokument5 SeitenCHAPTER V - The Good LifeKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER III - Science and Technology and Nation BuildingDokument6 SeitenCHAPTER III - Science and Technology and Nation BuildingKeanno100% (1)
- CHAPTER X - The Nano WorldDokument4 SeitenCHAPTER X - The Nano WorldKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER V - The Good LifeDokument5 SeitenCHAPTER V - The Good LifeKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tentative Course Syllabus (BIOL 1)Dokument2 SeitenTentative Course Syllabus (BIOL 1)KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER VII - Why Does The Uture Do Not Need UsDokument3 SeitenCHAPTER VII - Why Does The Uture Do Not Need UsKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER IX - Biodiversity and The Healthy SocietyDokument11 SeitenCHAPTER IX - Biodiversity and The Healthy SocietyKeanno100% (1)
- CHAPTER IV - Technology and The Evolution of Human SocietyDokument4 SeitenCHAPTER IV - Technology and The Evolution of Human SocietyKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER VI - When Technology and Humanity CrossDokument5 SeitenCHAPTER VI - When Technology and Humanity CrossKeanno0% (1)
- CHAPTER III - Science and Technology and Nation BuildingDokument6 SeitenCHAPTER III - Science and Technology and Nation BuildingKeanno100% (1)
- CHAPTER IV - Technology and The Evolution of Human SocietyDokument4 SeitenCHAPTER IV - Technology and The Evolution of Human SocietyKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in PeroxisomeDokument8 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in PeroxisomeKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER VI - When Technology and Humanity CrossDokument5 SeitenCHAPTER VI - When Technology and Humanity CrossKeanno0% (1)
- Curr 21 For Educ 197Dokument10 SeitenCurr 21 For Educ 197KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science Review Notes PDFDokument9 SeitenEarth Science Review Notes PDFLigafel BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - Yr. and Section: - Date: - Exercise #10 Gas Laws Boyle's Law ProblemsDokument2 SeitenName: - Yr. and Section: - Date: - Exercise #10 Gas Laws Boyle's Law ProblemsKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Science ReviewerDokument76 SeitenBiological Science ReviewerhanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectures On BIOL 105 Parasitology 2018Dokument59 SeitenLectures On BIOL 105 Parasitology 2018KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tentative Course Syllabus (BIOL 1)Dokument2 SeitenTentative Course Syllabus (BIOL 1)KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam in Science 7Dokument5 SeitenFinal Exam in Science 7KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Multiple Choice. Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDokument3 SeitenI. Multiple Choice. Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise #14 Chemical Equillibrium: How Can We Combine The Reactions To Match The Last Reaction?Dokument1 SeiteExercise #14 Chemical Equillibrium: How Can We Combine The Reactions To Match The Last Reaction?KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise #13Dokument1 SeiteExercise #13KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Monthly Exam in Science 7Dokument3 Seiten3rd Monthly Exam in Science 7KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Periodical Exam in Science 7Dokument4 Seiten3rd Periodical Exam in Science 7KeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Multiple Choice. Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDokument3 SeitenI. Multiple Choice. Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerKeannoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particle KineticsDokument20 SeitenParticle Kineticsme2742700Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Exam OnlineDokument2 SeitenMid Exam OnlineShakeel Ahmad KasuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field ChseDokument13 SeitenMagnetic Field Chserifu91Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 04Dokument133 SeitenCH 04api-3699340Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics (Teachers)Dokument33 SeitenKinematics (Teachers)Rajiv BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab # 09Dokument8 SeitenLab # 09Muhammad WaqasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01 p001-011Dokument11 SeitenChapter 01 p001-011umamgis3304100% (3)
- Elementsofstatic00loneuoft 2Dokument326 SeitenElementsofstatic00loneuoft 2AakashParanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Coulombs Law Electric Field IntensityDokument36 SeitenA Coulombs Law Electric Field IntensityShaker HusienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hookes Law Practice Problems PDFDokument3 SeitenHookes Law Practice Problems PDFSyed JaffreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitors Workbook Solutions PDFDokument45 SeitenCapacitors Workbook Solutions PDFbrainx MagicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Physics 11se Ch04Dokument32 Seiten04 Physics 11se Ch04pecan_lisa38Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics II: Electricity and Magnetism: FIZ 102EDokument58 SeitenPhysics II: Electricity and Magnetism: FIZ 102EBarış UlukanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Session # 1 Objective: Apparatus: Schematic Diagram:: FlywheelDokument3 SeitenLab Session # 1 Objective: Apparatus: Schematic Diagram:: FlywheelMuhammad AshfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- How and Why Do Things FloatDokument25 SeitenHow and Why Do Things Floatswaglordswag123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 4 Conclusion and ApplicationsDokument2 SeitenExpt 4 Conclusion and ApplicationsW0% (2)
- 7 Magnetic Forces Materials InductanceDokument34 Seiten7 Magnetic Forces Materials InductanceVienNgocQuang100% (1)
- Std. IXth em ScienceDokument7 SeitenStd. IXth em ScienceManya JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitation WorksheetDokument1 SeiteGravitation WorksheetVishesh Kumar100% (1)
- Science 3 - Q1-W2 - Properties of MatterDokument36 SeitenScience 3 - Q1-W2 - Properties of Mattersteph ebonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shadan Zolghani - 9 Ag Displacement and VelocityDokument12 SeitenShadan Zolghani - 9 Ag Displacement and Velocityapi-531290004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Notes Year 7Dokument5 SeitenSummary Notes Year 7Cinara Rahimova100% (1)
- Physical Sciences P1 Nov 2022 EngDokument21 SeitenPhysical Sciences P1 Nov 2022 EngWilfried BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Physics FormulaDokument2 SeitenBasic Physics FormulaAdamu Ahmad100% (1)
- Mass Balance Benno Rahardyan2Dokument40 SeitenMass Balance Benno Rahardyan2rusdi100% (1)
- SSP 637 Audi Q7 Type 4M Occupant Protection and InfotainmentDokument72 SeitenSSP 637 Audi Q7 Type 4M Occupant Protection and Infotainmentpeter11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Mass SpectrometryDokument4 SeitenThesis Mass Spectrometryufagmcgld100% (2)
- Science Electricity Review Cheat Sheet: by ViaDokument2 SeitenScience Electricity Review Cheat Sheet: by ViaRadha RamineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q + NumericalsDokument17 SeitenQ + NumericalsVCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- My First Experience in A Badminton CompetitionDokument2 SeitenMy First Experience in A Badminton CompetitionŇel DanNoch keine Bewertungen