Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Basic Electronics Questions
Hochgeladen von
Reddyvari Venugopal0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
536 Ansichten15 SeitenThe document provides definitions and explanations of basic electronics concepts including voltage and current sources, Ohm's law, semiconductor theory, diodes, transistors, and more. It contains multiple choice questions with answers on these topics. An ideal voltage source is defined as having zero internal resistance while an ideal current source has infinite internal resistance. Practical sources have small/large but non-zero/infinite internal resistance. Semiconductors like silicon have 4 valence electrons and conductivity depends on temperature. Doping introduces free electrons or holes for n-type or p-type materials. Diodes allow current in one direction due to a p-n junction barrier. Transistors have two p-n junctions and current gain.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Basic Electronics Questions.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document provides definitions and explanations of basic electronics concepts including voltage and current sources, Ohm's law, semiconductor theory, diodes, transistors, and more. It contains multiple choice questions with answers on these topics. An ideal voltage source is defined as having zero internal resistance while an ideal current source has infinite internal resistance. Practical sources have small/large but non-zero/infinite internal resistance. Semiconductors like silicon have 4 valence electrons and conductivity depends on temperature. Doping introduces free electrons or holes for n-type or p-type materials. Diodes allow current in one direction due to a p-n junction barrier. Transistors have two p-n junctions and current gain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
536 Ansichten15 SeitenBasic Electronics Questions
Hochgeladen von
Reddyvari VenugopalThe document provides definitions and explanations of basic electronics concepts including voltage and current sources, Ohm's law, semiconductor theory, diodes, transistors, and more. It contains multiple choice questions with answers on these topics. An ideal voltage source is defined as having zero internal resistance while an ideal current source has infinite internal resistance. Practical sources have small/large but non-zero/infinite internal resistance. Semiconductors like silicon have 4 valence electrons and conductivity depends on temperature. Doping introduces free electrons or holes for n-type or p-type materials. Diodes allow current in one direction due to a p-n junction barrier. Transistors have two p-n junctions and current gain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 15
Basic Introduction Questions
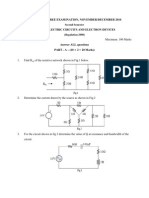
1. What is an ideal voltage source?
Answer: A device with zero internal resistance.
2. What is an ideal current source?
Answer: A device with infinite internal resistance.
3. What is a practical voltage source?
Answer: A device with small internal resistance.
4. What is a practical current source?
Answer: A device with large internal resistance.
5. The voltage out of an ideal voltage source is
A. Zero
B. Constant
C. Load resistance dependent
D. Internal resistance dependent
Answer: B
6. The current out of an ideal current source is
A. Zero
B. Constant
C. Load resistance dependent
D. Internal resistance dependent
Answer: B
7. The path between two points along which an electrical current can
be carried is called
A. A network
B. A relay
C. A circuit
D. A loop
Answer: C
8. The formula for current as per Ohm’s Law is
A. Voltage / Resistance
B. Resistance * Voltage
C. Voltage + Resistance
D. Resistance / Voltage
Answer: A
9. The unit of electrical resistance is
A. Volt
B. Amp
C. Ohm
D. Coulomb
Answer: C
10. In a constant voltage DC circuit, when the resistance increases,
the current will
A. Decrease
B. Stop
C. Increase
D. Remains constant
Answer: A
Basic Semiconductor Theory Questions
1. Number of valence electrons in a silicon atom are
A. 1
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
Answer: B
2. The most commonly used semiconductor element is
A. Silicon
B. Germanium
C. Gallium
D. Carbon
Answer: A
3. Copper is a
A. Insulator
B. Conductor
C. Semiconductor
D. Super Conductor
Answer: B
4. Number of protons in the nucleus of a silicon atom are
A. 4
B. 14
C. 29
D. 32
Answer: B
5. The valence electron of a conductor are also called as
A. Bound electron
B. Free electron
C. Nucleus
D. Proton
Answer: B
6. An intrinsic semiconductor at room temperature has
A. A few free electrons and holes
B. Many holes
C. Many free electrons
D. No holes
Answer: A
7. At room temperature, an intrinsic semiconductor has some holes in
it due to
A. Doping
B. Free electrons
C. Thermal energy
D. Valence electrons
Answer: C
8. The number of holes in an intrinsic semiconductor is
A. Equal to number of free electrons
B. Greater than number of free electrons
C. Less than number of free electrons
D. None of the above
Answer: A
9. Holes act as
A. Atoms
B. Crystals
C. Negative charges
D. Positive charges
Answer: D
10. Pick the odd one in the group
A. Conductor
B. Semiconductor
C. Four valence electrons
D. Crystal structure
Answer: A
11. To produce P-type semiconductors, you need to add
A. Trivalent impurity
B. Carbon
C. Pentavalent impurity
D. Silicon
Answer: A
12. Electrons are the minority carriers in
A. Extrinsic Semiconductors
B. p-type Semiconductors
C. Intrinsic Semiconductors
D. n-type Semiconductors
Answer: D
13. A p-type semiconductor contains
A. Holes and Negative ions
B. Holes and Positive ions
C. Holes and Pentavalent atoms
D. Holes and Donor atoms
Answer: A
14. How many electrons does pentavalent atoms have?
A. 1
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer: D
15. Negative ions are
A. Atoms that obtained a proton
B. Atoms that lost a proton
C. Atoms that obtained an electron
D. Atoms that lost an electron
Answer: C
Basic Semiconductor Diode Questions
1. Depletion layer is caused by
A. Doping
B. Recombination
C. Barrier potential
D. Ions
Answer: B
2. The reverse current in a diode is usually
A. Very small
B. Very large
C. Zero
D. In the breakdown region
Answer: A
3. Avalanche in Diode occurs at
A. Barrier potential
B. Depletion layer
C. Knee voltage
D. Breakdown voltage
Answer: D
4. The potential barrier of a silicon diode is
A. 0.3 V
B. 0.7 V
C. 1 V
D. 5V
Answer: B
5. The reverse saturation current in a Silicon Diode is _____ than that
of Germanium Diode
A. Equal
B. Higher
C. Lower
D. Depends on temperature
Answer: C
6. A Diode is a
A. Bilateral Device
B. Nonlinear Device
C. Linear Device
D. Unipolar Device
Answer: C
7. The diode current is large for which condition
A. Forward Bias
B. Inverse Bias
C. Poor Bias
D. Reverse Bias
Answer: A
8. The output voltage signal of a bridge rectifier is
A. Half-wave
B. Full-wave
C. Bridge-rectified signal
D. Sine wave
Answer: B
9. If the maximum DC current rating of diodes in Bridge Rectifier is
1A, what is the maximum DC load current?
A. 1A
B. 2A
C. 4A
D. 8A
Answer: B
10. Voltage multipliers produce
A. Low voltage and low current
B. Low voltage and high current
C. High voltage and low current
D. High voltage and high current
Answer: C
11. What is a Clipper?
Answer: A circuit that removes a part (positive or negative) of a waveform
so that it doesn’t exceed a certain voltage level.
12. What is a Clamper?
Answer: A circuit that adds a DC voltage (positive or negative) to a wave.
13. Zener diode can be described as
A. A rectifier diode.
B. A device with constant – voltage.
C. A device with constant – current.
D. A device that works in the forward region.
Answer: B
14. If the Zener Diode is connected in wrong polarity, the voltage
across the load is
A. 0.7 V
B. 10 V
C. 14 V
D. 18 V
Answer: A
Basic Transistor Questions
1. Number of PN Junctions in a Transistor
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
Answer: B
2. The doping concentration of Base in NPN Transistor is
A. Lightly Doped
B. Moderately Doped
C. Heavily Doped
D. Not Doped
Answer: A
3. The Base – Emitter Diode (Base – Emitter Junction) in an NPN
Transistor is
A. Doesn’t conduct
B. Forward Biased
C. Reverse Biased
D. Operates in breakdown region
Answer: B
4. The size comparison between Base, Emitter and Collector is
A. Base > Collector > Emitter
B. Emitter > Collector > Base
C. Collector > Emitter > Base
D. All are equal
Answer: C
5. The Base – Collector Diode (Base Collector Junction) is usually
A. Reverse Biased
B. Forward Biased
C. Breakdown Region
D. No Conduction
Answer: A
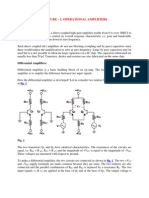
6. The DC Current Gain of a Transistor is
A. Ratio of Emitter Current to Collector Current
B. Ratio of Base Current to Emitter Current
C. Ratio of Collector Current to Base Current
D. Ratio of Base Current to Collector Current
Answer: C
7. If base current is 100µA and current gain is 100, then collector
current is
A. 1A
B. 10A
C. 1mA
D. 10mA
Answer: D
8. The majority carriers in NPN and PNP Transistors are
A. Holes and Electrons
B. Electrons and Holes
C. Acceptor Ions and Donor Ions
D. None
Answer: B
9. A Transistor acts as a
A. Voltage Source and a Current Source
B. Current Source and a Resistor
C. Diode and Current Source
D. Diode and Power Supply
Answer: C
10. The relation between Base Current IB, Emitter Current IE and
Collector Current IC is
A. IE = IB + IC
B. IB = IC + IE
C. IE = IB – IC
D. IC = IB + IE
Answer: A
11. The total power dissipated by a transistor is a product of collector
current and
A. Supply Voltage
B. 0.7V
C. Collector – Emitter Voltage
D. Base – Emitter Voltage
Answer: C
12. The input impedance of Common Emitter Configuration is
A. Low
B. High
C. Zero
D. Very High
Answer: A
13. The output impedance of Common Emitter Configuration is
A. Low
B. Very Low
C. High
D. Zero
Answer: C
14. The current gain in Common Base configuration (α) is
A. Ratio of Base Current to Emitter Current (IB/IE)
B. Ratio of Collector Current to Emitter Current (IC/IE)
C. Ratio of Collector Current to Base Current (IC/IB)
D. None
Answer: B
15. Relation between α and ß is
A. α = ß / (ß + 1)
B. ß = α / (1 – α)
C. α = ß * (ß + 1)
D. α = ß / (ß – 1)
Answer: Both A and B
Q1. A semiconductor is formed by ……… bonds.
1. Covalent
2. Electrovalent
3. Co-ordinate
4. None of the above
Answer : 1
Q2. A semiconductor has ………… temperature coefficient of resistance.
1. Positive
2. Zero
3. Negative
4. None of the above
Answer : 3
Q3. The most commonly used semiconductor is ………..
1. Germanium
2. Silicon
3. Carbon
4. Sulphur
Answer : 2
Q4. A semiconductor has generally ……………… valence electrons.
1. 2
2. 3
3. 6
4. 4
Answer : 4
Q5. The resistivity of pure germanium under standard conditions is
about ……….
1. 6 x 104
2. Ω cm
3. 60
4. Ω cm
5. 3 x 106
6. Ω cm
7. 6 x 10-4
8. Ω cm
Answer : 2
Q6. The resistivity of a pure silicon is about ……………
1. 100 Ω cm
2. 6000 Ω cm
3. 3 x 105 Ω m
4. 6 x 10-8 Ω cm
Answer : 2
Q7. When a pure semiconductor is heated, its resistance …………..
1. Goes up
2. Goes down
3. Remains the same
4. Can’t say
Answer : 2
Q8. The strength of a semiconductor crystal comes from ……..
1. Forces between nuclei
2. Forces between protons
3. Electron-pair bonds
4. None of the above
Answer : 3
Q9. When a pentavalent impurity is added to a pure semiconductor, it
becomes ………
1. An insulator
2. An intrinsic semiconductor
3. p-type semiconductor
4. n-type semiconductor
Answer : 4
Q10. Addition of pentavalent impurity to a semiconductor creates many
……..
1. Free electrons
2. Holes
3. Valence electrons
4. Bound electrons
Answer : 1
Q11. A pentavalent impurity has ………. Valence electrons
1. 3
2. 5
3. 4
4. 6
Answer : 2
A12. An n-type semiconductor is ………
1. Positively charged
2. Negatively charged
3. Electrically neutral
4. None of the above
Answer : 3
Q13. A trivalent impurity has ….. valence electrons
1. 4
2. 5
3. 6
4. 3
Answer : 4
A14. Addition of trivalent impurity to a semiconductor creates many
……..
1. Holes
2. Free electrons
3. Valence electrons
4. Bound electrons
Answer : 1
Q15. A hole in a semiconductor is defined as …………….
1. A free electron
2. The incomplete part of an electron pair bond
3. A free proton
4. A free neutron
Answer : 2
Q16. The impurity level in an extrinsic semiconductor is about ….. of
pure semiconductor.
1. 10 atoms for 108 atoms
2. 1 atom for 108 atoms
3. 1 atom for 104 atoms
4. 1 atom for 100 atoms
Answer : 2
Q17. As the doping to a pure semiconductor increases, the bulk
resistance of the semiconductor ………..
1. Remains the same
2. Increases
3. Decreases
4. None of the above
Answer : 3
Q18. A hole and electron in close proximity would tend to ……….
1. Repel each other
2. Attract each other
3. Have no effect on each other
4. None of the above
Answer : 2
Q19. In a semiconductor, current conduction is due to ……..
1. Only holes
2. Only free electrons
3. Holes and free electrons
4. None of the above
Answer : 3
Q20. The random motion of holes and free electrons due to thermal
agitation is called ……….
1. Diffusion
2. Pressure
3. Ionisation
4. None of the above
Answer : 1
Q21. A forward biased pn junction diode has a resistance of the order of
1. Ω
2. kΩ
3. MΩ
4. None of the above
Answer : 1
Q22. The battery connections required to forward bias a pn junction are
……
1. +ve terminal to p and –ve terminal to n
2. -ve terminal to p and +ve terminal to n
3. -ve terminal to p and –ve terminal to n
4. None of the above
Answer : 1
Q23. The barrier voltage at a pn junction for germanium is about
………
3. 5 V
4. 3 V
5. Zero
6. 3 V
Answer : 4
Q24. In the depletion region of a pn junction, there is a shortage of ……..
1. Acceptor ions
2. Holes and electrons
3. Donor ions
4. None of the above
Answer : 2
Q25. A reverse bias pn junction has …………
1. Very narrow depletion layer
2. Almost no current
3. Very low resistance
4. Large current flow
Answer : 2
Q26. A pn junction acts as a ……….
1. Controlled switch
2. Bidirectional switch
3. Unidirectional switch
4. None of the above
Answer : 3
Q27. A reverse biased pn junction has resistance of the order of
1. Ω
2. kΩ
3. MΩ
4. None of the above
Answer : 3
Q28. The leakage current across a pn junction is due to …………..
1. Minority carriers
2. Majority carriers
3. Junction capacitance
4. None of the above
Answer : 1
Q29. When the temperature of an extrinsic semiconductor is increased,
the pronounced effect is on……
1. Junction capacitance
2. Minority carriers
3. Majority carriers
4. None of the above
Answer : 2
Q30. With forward bias to a pn junction , the width of depletion layer
………
1. Decreases
2. Increases
3. Remains the same
4. None of the above
Answer : 1
Q31. The leakage current in a pn junction is of the order of
1. Aa
2. mA
3. kA
4. µA
Answer : 4
Q32. In an intrinsic semiconductor, the number of free electrons ………
1. Equals the number of holes
2. Is greater than the number of holes
3. Is less than the number of holes
4. None of the above
Answer : 1
Q33. At room temperature, an intrinsic semiconductor has ……….
1. Many holes only
2. A few free electrons and holes
3. Many free electrons only
4. No holes or free electrons
Answer : 2
Q34. At absolute temperature, an intrinsic semiconductor has ……….
1. A few free electrons
2. Many holes
3. Many free electrons
4. No holes or free electrons
Answer : 4
Q35. At room temperature, an intrinsic silicon crystal acts
approximately as ……
1. A battery
2. A conductor
3. An insulator
4. A piece of copper wire
Answer : 3
Q36. Under normal conditions a diode conducts current when it is
……………
1. reverse biased
2. forward biased
3. avalanched
4. saturated
Answer : 2
Q37. The term bias in electronics usually means ……….
1. the value of ac voltage in the signal.
2. the condition of current through a pn junction.
3. the value of dc voltages for the device to operate properly.
4. the status of the diode.
Answer : 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Maintenance Manual: Models 7200/7300/7310 Reach-Fork TrucksDokument441 SeitenMaintenance Manual: Models 7200/7300/7310 Reach-Fork TrucksMigue Angel Rodríguez Castro100% (2)
- Solid State DevicesDokument42 SeitenSolid State Devicesmonirba48Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital to Analogue Converter Circuits LabDokument6 SeitenDigital to Analogue Converter Circuits LabAbdul Aziz ZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSD MCQs Semiconductor Devices QuestionsDokument10 SeitenSSD MCQs Semiconductor Devices QuestionsKimberly TaboraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs Transistor Biasing Op-AmpDokument96 SeitenMCQs Transistor Biasing Op-AmpReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs Transistor Biasing Op-AmpDokument96 SeitenMCQs Transistor Biasing Op-AmpReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bondek Design & Construct ManualDokument131 SeitenBondek Design & Construct ManualAkuma.Gokai7328100% (12)
- Transistors and Applications PDFDokument28 SeitenTransistors and Applications PDFLeticia MelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics Objective Type QuestionsDokument3 SeitenBasic Electronics Objective Type QuestionsParames WaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Electrics Question BankDokument40 SeitenDC Electrics Question Bankgaurav aryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - SemiconductorDokument49 SeitenChapter 3 - SemiconductorBalqis yasin100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: Basic Electronics 1 Year Subject Code: 3110016Dokument4 SeitenGujarat Technological University: Basic Electronics 1 Year Subject Code: 3110016Ayush PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductors: Materials that enable modern electronicsDokument58 SeitenSemiconductors: Materials that enable modern electronicsadi_risingsun0% (1)
- Electrical Upgrading Course Review for Master ElectriciansDokument3 SeitenElectrical Upgrading Course Review for Master ElectriciansMark John DrilonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cebu Technological University: AST 111 Fundamentals of Electrical and ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenCebu Technological University: AST 111 Fundamentals of Electrical and ElectronicsDominic Libradilla100% (1)
- ELE 115 Basic Electricity SyllabusDokument2 SeitenELE 115 Basic Electricity SyllabusGalvez ChaCha100% (2)
- 2 Lecture 2 Diode B Stad - CH - 01Dokument66 Seiten2 Lecture 2 Diode B Stad - CH - 01peter brownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boylestad IRM TIFDokument163 SeitenBoylestad IRM TIFEngr. Ronell B. SolijonNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC BIASING - BJTs: Key ConceptsDokument44 SeitenDC BIASING - BJTs: Key ConceptsUgeswran ThamalinggamNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLE REVIEWER ELECTRICITY BASICSDokument5 SeitenTLE REVIEWER ELECTRICITY BASICSDaphnie DelantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated CircuitDokument51 SeitenIntegrated Circuitparthos100% (1)
- DiodesDokument91 SeitenDiodesMohammad Gulam AhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Gates Explained: Types, Truth Tables & ApplicationsDokument9 SeitenLogic Gates Explained: Types, Truth Tables & ApplicationsEdzai Nyasha TarupiwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ElectronicsDokument7 SeitenBasic ElectronicsGlenn TotzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics Lab Manual for III Semester B.Tech (ECEDokument57 SeitenDigital Electronics Lab Manual for III Semester B.Tech (ECEAravind BalasundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- UJTDokument9 SeitenUJTdheeraj rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC Syllabus OverviewDokument2 SeitenEDC Syllabus Overviewghftyftfhfhg50% (4)
- Power Diode CharacteristicsDokument23 SeitenPower Diode Characteristicsunity123d deewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics Objective Type QuestionsDokument18 SeitenBasic Electronics Objective Type Questionsimranaftab1069Noch keine Bewertungen
- TLE ELECTRONICS With AnswersDokument1 SeiteTLE ELECTRONICS With AnswersCOA DSWD7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Questions On DiodesDokument40 SeitenQuestions On Diodeskibrom atsbha100% (1)
- ECE Workshop Practicals Exp No.4Dokument6 SeitenECE Workshop Practicals Exp No.4oxygen oxygenNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC DC Power SupplyDokument26 SeitenAC DC Power SupplyNathaniel RogeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNTLDokument31 SeitenCNTLAkanksha DixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- EX.3 Small Signal Analysis of Diode PDFDokument17 SeitenEX.3 Small Signal Analysis of Diode PDFram charanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Majorship TLE ElectronicsDokument12 SeitenMajorship TLE ElectronicsAnonymous gijMJlwS6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ohm's Law PPT by Somya and AtharvDokument17 SeitenOhm's Law PPT by Somya and AtharvSomya KulshresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode CharacteristicsDokument12 SeitenDiode CharacteristicsAhmedElsiddiegA.AbdallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI2353-Digital System DesignDokument13 SeitenEI2353-Digital System DesignSanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Electric Circuits Objective QuestionsDokument35 SeitenApplied Electric Circuits Objective QuestionsGanesan KandasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applicatio To Short AntennasDokument4 SeitenApplicatio To Short Antennasbchaitanya55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Raghu Institute of Technology ECE Lab ManualDokument150 SeitenRaghu Institute of Technology ECE Lab ManualMad DamnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limitations of Ohm's Law, KCL & KVLDokument2 SeitenLimitations of Ohm's Law, KCL & KVLAhsan Sial AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational Amplifiers: Key Concepts and ConfigurationsDokument39 SeitenOperational Amplifiers: Key Concepts and ConfigurationsJani SkNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC Question-Papers Complete SetDokument13 SeitenEDC Question-Papers Complete Setselvi04120% (1)
- Experiment 5Dokument6 SeitenExperiment 5Sittha WajadeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Digital Electronics - Unit 1Dokument12 SeitenBasic Digital Electronics - Unit 1Soni Mishra TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to read resistor color codesDokument11 SeitenHow to read resistor color codesAndro Mar Maceda BagadiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cmos Analog Ic Design Course Plan NewDokument9 SeitenCmos Analog Ic Design Course Plan Newjim2001Noch keine Bewertungen
- DIACDokument15 SeitenDIACTanmay WalkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Registers and CountersDokument6 SeitenRegisters and CountersgeethajeganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Report Lab 7Dokument15 SeitenLong Report Lab 7Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report of Induction ProgramDokument23 SeitenReport of Induction ProgramDhruv Chunawala100% (1)
- Electrical Machines Quiz QuestionsDokument13 SeitenElectrical Machines Quiz Questionskarthi100% (1)
- Power Electronics Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenPower Electronics Lesson PlanViswa NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec13 BJTDokument25 SeitenLec13 BJTnisanth123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Introduction Questions: AnswerDokument9 SeitenBasic Introduction Questions: AnswerPaula Mohsen BotrossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics HUB: Basic Electronics Questions For InterviewDokument22 SeitenElectronics HUB: Basic Electronics Questions For Interviewkonguart08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics ObjectivesDokument33 SeitenBasic Electronics ObjectivesKARTHIK LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Start Practice Exam Test Questions Part 1 of The SeriesDokument155 SeitenStart Practice Exam Test Questions Part 1 of The SeriesNida Bagoyboy NatichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - I Electronic Components & Signals: 22225 BEC MCQ (Basic Electronics) Chapter-WiseDokument9 SeitenUnit - I Electronic Components & Signals: 22225 BEC MCQ (Basic Electronics) Chapter-WiseShobhit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ideal Voltage Sources vs Real Voltage SourcesDokument66 SeitenIdeal Voltage Sources vs Real Voltage SourcesC_VhonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malvino Questions (Electronics)Dokument12 SeitenMalvino Questions (Electronics)Mikz Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsVon EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- 1) What Is An Electric Potential?: AB A BDokument24 Seiten1) What Is An Electric Potential?: AB A BReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankDokument3 SeitenB.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Degree College, Mahabubabad Physics:: Paper VIIIA:: Basic ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenGovernment Degree College, Mahabubabad Physics:: Paper VIIIA:: Basic ElectronicsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. V Semester Physics:: Paper VI (A) Solid State Physics:: Imp QuestionsDokument2 SeitenB.Sc. V Semester Physics:: Paper VI (A) Solid State Physics:: Imp QuestionsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. V Semester Physics:: Paper VI (A) Solid State Physics:: Imp QuestionsDokument2 SeitenB.Sc. V Semester Physics:: Paper VI (A) Solid State Physics:: Imp QuestionsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics QuestionsDokument15 SeitenBasic Electronics QuestionsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) What Is An Electric Potential?: AB A BDokument24 Seiten1) What Is An Electric Potential?: AB A BReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. II Semester Physics:: Paper II Thermal Physics:: Imp QuestionsDokument2 SeitenB.Sc. II Semester Physics:: Paper II Thermal Physics:: Imp QuestionsReddyvari Venugopal100% (1)
- B.Sc. I Semester Physics:: Paper I Mechanics and Oscillations:: Imp QuestionsDokument2 SeitenB.Sc. I Semester Physics:: Paper I Mechanics and Oscillations:: Imp QuestionsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Govt - Degree College, Mahabubabad:: Department of Physics Electromagnetism:: Question BankDokument1 SeiteGovt - Degree College, Mahabubabad:: Department of Physics Electromagnetism:: Question BankReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. II Semester Physics:: Paper II Thermal Physics:: Imp QuestionsDokument2 SeitenB.Sc. II Semester Physics:: Paper II Thermal Physics:: Imp QuestionsReddyvari Venugopal100% (1)
- B.Sc. I Semester Physics:: Paper I Mechanics and Oscillations:: Imp QuestionsDokument2 SeitenB.Sc. I Semester Physics:: Paper I Mechanics and Oscillations:: Imp QuestionsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Govt - Degree College, Mahabubabad:: Department of Physics Electromagnetism:: Question BankDokument1 SeiteGovt - Degree College, Mahabubabad:: Department of Physics Electromagnetism:: Question BankReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Degree College, Mahabubabad Physics:: Paper VIIIA:: Basic ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenGovernment Degree College, Mahabubabad Physics:: Paper VIIIA:: Basic ElectronicsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Source MATLAB Substitute - Xcos GuideDokument4 SeitenOpen Source MATLAB Substitute - Xcos GuideReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankDokument3 SeitenB.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- "SCILAB - An Open Source Substitute For MATLAB": Basic Level Introduction To ScilabDokument1 Seite"SCILAB - An Open Source Substitute For MATLAB": Basic Level Introduction To ScilabReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankDokument3 SeitenB.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicol PrismDokument4 SeitenNicol PrismDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankDokument3 SeitenB.Sc. VI Semester Physics:: Paper VII Modern Physics:: Question BankReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Amazingly Dedicated Indian Civil ServantsDokument4 Seiten11 Amazingly Dedicated Indian Civil ServantsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Healthy HabitsDokument1 Seite15 Healthy HabitsReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBCS Structure For UG Programs 2018-19Dokument6 SeitenCBCS Structure For UG Programs 2018-19Reddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVPE Syllabus of Ist Year & IInd Year Degree StudentsDokument5 SeitenHVPE Syllabus of Ist Year & IInd Year Degree StudentsReddyvari Venugopal0% (1)
- Photo Transistor 1Dokument5 SeitenPhoto Transistor 1kriitkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photo Transistor 1Dokument5 SeitenPhoto Transistor 1kriitkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QlikView Business Intelligence Tool OverviewDokument11 SeitenQlikView Business Intelligence Tool OverviewMithun LayekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Heat ExchangersDokument88 Seiten02 - Heat ExchangerssanjaysyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic Revision DocumentsDokument7 SeitenThermodynamic Revision DocumentshakimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3 One Way Slab Design-SS, Cant, ContinuousDokument54 Seiten2.3 One Way Slab Design-SS, Cant, ContinuousAhmed SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Tech.Dokument31 SeitenEnvironmental Tech.csyena28225Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acetylated Castor Oil - Preparation and Thermal DecompositionDokument7 SeitenAcetylated Castor Oil - Preparation and Thermal DecompositionPee Hai NingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tivizen Iplug Greek GuideDokument13 SeitenTivizen Iplug Greek GuideDenexoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical VolumeDokument162 SeitenTechnical Volumeiamskg63891583Noch keine Bewertungen
- TUGAS BAHASA INGGRIS Cahaya Karisma Wilani Faturrachman Rengga Wisnu Resza Bunga Nisa POLITEKNIK NEGERI JAKARTA JURUSAN KONSTRUKSI BANGUNAN SIPILDokument4 SeitenTUGAS BAHASA INGGRIS Cahaya Karisma Wilani Faturrachman Rengga Wisnu Resza Bunga Nisa POLITEKNIK NEGERI JAKARTA JURUSAN KONSTRUKSI BANGUNAN SIPILFaturrachman Nanu Rengga WisnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerodrome Controller (ADC) ExamDokument5 SeitenAerodrome Controller (ADC) ExamaxnpicturesNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC F18 Super Hornet - Manual v2.0Dokument13 SeitenRC F18 Super Hornet - Manual v2.0Darren-Edward O'NeillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project-BOQ - (Excluding VUP, LVUP)Dokument127 SeitenProject-BOQ - (Excluding VUP, LVUP)Shivendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Partes y Operación de Trituradora Vsi Canica Modelo 65Dokument105 SeitenManual de Partes y Operación de Trituradora Vsi Canica Modelo 65Jose AlfaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaspardo MAESTRA 2004-02 (19530520)Dokument78 SeitenGaspardo MAESTRA 2004-02 (19530520)costelchelariuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NHA 2430 Design Analysis Reporting FEADokument7 SeitenNHA 2430 Design Analysis Reporting FEAASIM RIAZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lincoln FC ElectrodesDokument44 SeitenLincoln FC ElectrodeszmcgainNoch keine Bewertungen
- FANUC Robot R-2000iB SeriesDokument4 SeitenFANUC Robot R-2000iB SeriesChandan KanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aniosyme DD1 SDSDokument6 SeitenAniosyme DD1 SDSSherwin CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Stress: DR Atul JAIN Mechanical Engineering Department Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDokument57 SeitenConcept of Stress: DR Atul JAIN Mechanical Engineering Department Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpursneha KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSOFTX3000 BICC Data Configuration 20090227 B 1 0Dokument52 SeitenMSOFTX3000 BICC Data Configuration 20090227 B 1 0Amjad VtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasmon CD-R ReviewDokument11 SeitenPlasmon CD-R Reviewgrudva2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To CAL ProgrammingDokument198 SeitenIntroduction To CAL ProgrammingSalam Mohamed RiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Sentry Guardian-BreathersDokument14 SeitenAir Sentry Guardian-BreathersNelson PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Silicone Chemistry P 1Dokument21 SeitenBasic Silicone Chemistry P 1Rahul Yadav100% (1)
- Mohr's Circle Analysis of Rock Failure Under StressDokument26 SeitenMohr's Circle Analysis of Rock Failure Under StressNitishNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPTC 12029 Selection Criteria For Artificial Lift Technique in Bokor FieldDokument13 SeitenIPTC 12029 Selection Criteria For Artificial Lift Technique in Bokor FieldJean Carlos100% (1)
- Mousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeDokument1 SeiteMousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeMorteza AtaeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB 2 Free N Force VibrationDokument8 SeitenLAB 2 Free N Force Vibrationmohdanis53yahoocomNoch keine Bewertungen