Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Control Structures in Java
Hochgeladen von
Nina Canares0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
321 Ansichten2 SeitenControl structures in Java allow programmers to control the flow and order of program execution. There are decision control structures like if/else that allow selecting code blocks based on conditions, repetition control structures like while and for that repeat code execution, and branching statements like break and continue that change the flow of loops. Common control structures are if/else for conditional execution, while/for loops for repetitive execution, and switch for selecting blocks based on multiple conditions.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenControl structures in Java allow programmers to control the flow and order of program execution. There are decision control structures like if/else that allow selecting code blocks based on conditions, repetition control structures like while and for that repeat code execution, and branching statements like break and continue that change the flow of loops. Common control structures are if/else for conditional execution, while/for loops for repetitive execution, and switch for selecting blocks based on multiple conditions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
321 Ansichten2 SeitenControl Structures in Java
Hochgeladen von
Nina CanaresControl structures in Java allow programmers to control the flow and order of program execution. There are decision control structures like if/else that allow selecting code blocks based on conditions, repetition control structures like while and for that repeat code execution, and branching statements like break and continue that change the flow of loops. Common control structures are if/else for conditional execution, while/for loops for repetitive execution, and switch for selecting blocks based on multiple conditions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
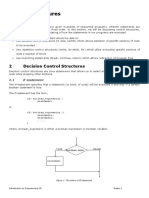
Control Structures in Java
- allow us to change the ordering of how the statements in our programs are executed
● Decision Control Structures - which allow selection of specific sections of code to be executed
- if
- if-else
- if - else if
- switch
● Repetition Control Structures – which allow executing specific sections of code a number of
times
- while
- do-while
- for
● Branching Statements – which allow redirection of program flow
- break
- continue
- return
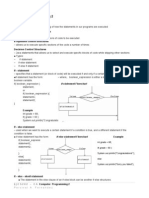
Syntax and Examples
if-statement has the form:
if ( boolean_expression ) statement; or
if ( boolean_expression )
{statement 1;statement 2;}
-where: boolean _expression is either a boolean expression or boolean variable
Ex:
int grade = 68;if ( grade > 60 )
System.out.println ("Congratulations! ") ;
if-else statement has the form:
if ( boolean_expression )
{statement 1;statement 2;. . .}
else
{statement 3;statement 4;. . .}
Ex:
int grade = 68; if ( grade > 60 )
System.out.println ("Congratulations! ");
Else System.out.println ("Sorry you failed") ;
if-else-if statement has the form:
if ( boolean_expression1 )statement 1;
else if ( boolean_expression2 )statement 2;
else statement 3;
Ex:
int grade = 68;if ( grade > 90 )
{System. out. println ("Very good! ") ;}
else if ( grade > 60 )
{System. out. println ("Very good! ") ;}
else
{System. out. println ("Sorry you failed") ;}
switch statement has the form:
switch( switch_expression )
{case case_selector1:
statement1;//
statement2;//block 1
break;
case case_selector2:
statement1;//
statement2;//block2
break;
:
default:
statement1;//statement2;//block n}
-where: switch _expression - is an integer or character expression
case_selector1, case_selector2 and so on - are unique integer or character constants.
Ex:
public class Grade { publicstatic void main( String[] args )
{ int grade = 92;5
switch(grade)
{ case 100: System.out.println( "Excellent!" ); break;
case 90: System.out.println("Good job!" );break;
case 80: System.out.println("Study harder!");
break;
default: System.out.println("Sorry, you failed."); } }}
while loop has the form:
while ( boolean_expression )
{statement 1;statement 2;. . .}
Ex:
Int x = 0;while (x<10)
{System. out. println (x) ;x++;}
do-while loop has the form:
do {statement 1;statement 2;. . .}
while ( boolean_expression ) ;
Ex:
int x = 0;
do {System. out. println (x) ;x++;}
while (x<10) ;
for loop has the form:
for(InitializationExpression;LoopCondition;StepExpression)
{statement1;statement2;. . .}
-where: InitializationExpression -initializes the loop variable
LoopCondition - compares the loop variable to some limit value
StepExpression - updates the loop variable.
Ex:
int i;
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{System. out. println (i) ;}
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- BE EXPERT IN JAVA Part- 2: Learn Java programming and become expertVon EverandBE EXPERT IN JAVA Part- 2: Learn Java programming and become expertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control StructuresDokument18 SeitenControl StructuresloidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- If and LoopDokument9 SeitenIf and LooploreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PresentCh03 - Decision and Repetition StatementsDokument16 SeitenPresentCh03 - Decision and Repetition StatementsGebreigziabher M. AbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Flow StatementsDokument19 SeitenControl Flow StatementsSay The NameNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Control StructuresDokument9 Seiten6 Control StructuresMay-ann NoricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 05Dokument24 SeitenLecture 05Mʌ ɭɩĸNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEDI Slides Intro1 Chapter06 Control StructuresDokument38 SeitenJEDI Slides Intro1 Chapter06 Control Structuresbawbawbiscuit6282Noch keine Bewertungen
- Java Control Statements PPTDokument51 SeitenJava Control Statements PPTEkta Singh100% (1)
- BMS 201 C++ Control Structures 2021Dokument41 SeitenBMS 201 C++ Control Structures 2021Brian MutuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Structures: Introduction To Programming 1Dokument39 SeitenControl Structures: Introduction To Programming 1Janelle CalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-5. Control StatementsDokument27 SeitenLecture-5. Control StatementsMinhaz Uddin MirazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 JavacontrolDokument54 Seiten5 Javacontrolapi-3748699Noch keine Bewertungen
- Java Control StructureDokument34 SeitenJava Control StructureAiza SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEDI Slides Intro1 Chapter06 Control StructuresDokument52 SeitenJEDI Slides Intro1 Chapter06 Control Structuresredbutterfly100% (2)
- Flow ControlsDokument35 SeitenFlow ControlsImaya SenuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Chapter 4Dokument36 SeitenJava Chapter 4Manu KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Making Statements in JavaDokument10 SeitenDecision Making Statements in JavaSrinivas TNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSC 201-Lecture 3Dokument39 SeitenCSC 201-Lecture 3pavanilNoch keine Bewertungen
- JavaDokument9 SeitenJavaXxenttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-8 Control StatementsDokument6 SeitenLecture-8 Control StatementsAkshay Anjali Kalidas ShelkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java-Control Flow StatementsDokument69 SeitenJava-Control Flow StatementsMacon Suarez-VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-2-Basic JavaDokument40 SeitenChapter-2-Basic JavaEden AdmasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- LoopsDokument17 SeitenLoopsAnikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes4 Control StructuresDokument13 SeitenNotes4 Control Structuresseniorhigh LISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three OopDokument13 SeitenChapter Three OopHaymanot MatebieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Making and LoopingDokument24 SeitenDecision Making and LoopingPramod kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Flow, Arrays - DocDokument34 SeitenControl Flow, Arrays - DocHARIBABU N SEC 2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 part-I:Control Flow Statements: A. The Selection StatementDokument13 SeitenChapter 2 part-I:Control Flow Statements: A. The Selection Statementabel bahiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Control Structures - PPSXDokument43 Seiten03 Control Structures - PPSXJamaico GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control StatementsDokument7 SeitenControl StatementsVASUDEVAN N (RC2113003011006)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Programming Fundamentals (COMP1112) Selection StructureDokument19 SeitenProgramming Fundamentals (COMP1112) Selection StructureAbdul HafeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture2 Control Structures-1Dokument52 SeitenLecture2 Control Structures-1Samuel NDATIMANANoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Flow StatementsDokument23 SeitenControl Flow StatementsMuhammad AbdurrehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Programming Tools and Techniques-I: Lecture 4: Control StructuresDokument38 SeitenModern Programming Tools and Techniques-I: Lecture 4: Control StructuresVinay PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java 2Dokument12 SeitenJava 2saimond linNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Structure: The Statement(s) To Be Executed.) For ExampleDokument4 SeitenControl Structure: The Statement(s) To Be Executed.) For ExampleVictor OrdoñezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect8 JavaDokument8 SeitenLect8 JavaMahir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect02 - OperationsDokument9 SeitenLect02 - Operations2151150038Noch keine Bewertungen
- Program Control Structures - Part 1Dokument37 SeitenProgram Control Structures - Part 1Thinagaran MahendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs202 - Compo2 - Part 2Dokument2 SeitenCs202 - Compo2 - Part 2rayden22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Control Structures: 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All Rights ReservedDokument82 SeitenChapter 2 - Control Structures: 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All Rights ReservedMahesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Control Structures: 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All Rights ReservedDokument82 SeitenChapter 2 - Control Structures: 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All Rights ReservedSukhwinder Singh GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Structures / Control Flow StatementsDokument13 SeitenControl Structures / Control Flow StatementsMarlon TugweteNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ ChaDokument15 SeitenC++ ChaYE' JEMBRU Lige EshetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Structure in JavaDokument64 SeitenControl Structure in JavaJozef PortilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- OOPadditional CH 2Dokument14 SeitenOOPadditional CH 2amaredemise21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oop JavaDokument49 SeitenOop JavaAdrian TurcanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 22Dokument10 SeitenPractical 22Rani PowarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation3 - Control StatementsDokument18 SeitenPresentation3 - Control StatementsKavitha SundararajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Structures (Part 1) : Java Control Structures Decision Control Structures If If-Else If-Else-If SwitchDokument14 SeitenControl Structures (Part 1) : Java Control Structures Decision Control Structures If If-Else If-Else-If SwitchGelo DurandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPROG2 Assignment1 EscribaJanineDokument8 SeitenCOMPROG2 Assignment1 EscribaJanineIzaya Kun OriharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Flow and Statement: Assignment Statement Compound Statement Control Statement Standard I/ODokument22 SeitenControl Flow and Statement: Assignment Statement Compound Statement Control Statement Standard I/OSaurabh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estructuras de Control CDokument4 SeitenEstructuras de Control CByron FelipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programming Fundamentals: Academic Year 2014-2015 Yusra A.SalihDokument18 SeitenProgramming Fundamentals: Academic Year 2014-2015 Yusra A.SalihMhamad NasihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java and Software Design: Introduction ToDokument60 SeitenJava and Software Design: Introduction ToJayendra N KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 - Flow ControlDokument42 SeitenModule 4 - Flow Controlapi-19796528Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVon EverandAdvanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2. Review of Related Literature and StudiesDokument1 SeiteChapter 2. Review of Related Literature and StudiesNina CanaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Array in JavaDokument1 SeiteArray in JavaNina CanaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. The Problem and Its BackgroundDokument3 SeitenChapter 1. The Problem and Its BackgroundNina CanaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical TheoriesDokument1 SeiteEthical TheoriesNina CanaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book ReportDokument2 SeitenBook ReportNina CanaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recognition Day Program ScriptDokument4 SeitenRecognition Day Program ScriptNina Canares95% (272)
- 12 OlympiansDokument8 Seiten12 OlympiansNina Canares100% (1)
- Project in EnglishDokument7 SeitenProject in EnglishNina CanaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Causes and Effects of Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent DiseaseDokument35 SeitenThe Causes and Effects of Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent DiseaseNina Canares100% (2)
- Zenon Pestaño Niña S. Cañares Jo-Sha Borja Remjen Francisco JannicaDokument11 SeitenZenon Pestaño Niña S. Cañares Jo-Sha Borja Remjen Francisco JannicaNina Canares100% (1)
- Vxworks For Pentium Architecture Supplement PDFDokument40 SeitenVxworks For Pentium Architecture Supplement PDFNitesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process ConceptsDokument79 SeitenProcess Concepts21PC12 - GOKUL DNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSP ArchitectureDokument2 SeitenJSP ArchitectureNigam PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Urimaps, Pipelines and Webservices For CICS100407Dokument75 SeitenUnderstanding Urimaps, Pipelines and Webservices For CICS100407Sabariram KandasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheduling Algorithms IDokument5 SeitenScheduling Algorithms IksajjNoch keine Bewertungen
- VBA Excel BOOKDokument131 SeitenVBA Excel BOOKSokol100% (8)
- Essential C - Nick ParlanteDokument45 SeitenEssential C - Nick ParlantePetru AgapiNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Rules of The Tower of Hanoi: Iterative SolutionDokument8 SeitenI. Rules of The Tower of Hanoi: Iterative SolutionDon J AsuncionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interacting With Generative MusicDokument14 SeitenInteracting With Generative Musicdavidoggit100% (1)
- Bachelor of Science in Computer Science (BSCS) : First YearDokument17 SeitenBachelor of Science in Computer Science (BSCS) : First YearTheo Aquino GorospeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20210501-ML Question BankDokument1 Seite20210501-ML Question BankRajachandra VoodigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Guid": "Islistable": "Ownerguid": "Type"Dokument20 Seiten"Guid": "Islistable": "Ownerguid": "Type"nguyen congoanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQLCODES For DB2Dokument43 SeitenSQLCODES For DB2sxdasgu100% (1)
- Pega OwnDokument102 SeitenPega OwnNag ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- P PP PDokument9 SeitenP PP PNikita SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Odoo DevelopmentDokument137 SeitenOdoo DevelopmentTiago CássioNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPFX e BookDokument106 SeitenSPFX e BookSyaiful AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refactoring Erlang ProgramsDokument24 SeitenRefactoring Erlang Programsciukes100% (1)
- Mikroc ManualDokument391 SeitenMikroc ManualtoredaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week-04Assignment MCQDokument5 SeitenWeek-04Assignment MCQPawan NaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS202-Ch1Dokument85 SeitenCS202-Ch1naaz_pinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISSUE Tracking DocumentDokument64 SeitenISSUE Tracking DocumentAishwarya SairamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 TH Computer Science Python Unit-1 NotesDokument75 Seiten12 TH Computer Science Python Unit-1 NotesR. GopinathNoch keine Bewertungen
- R-30ia Karel Reference Manual (Ver.7.30) (Marrcrlrf04071e Rev.b)Dokument947 SeitenR-30ia Karel Reference Manual (Ver.7.30) (Marrcrlrf04071e Rev.b)anonomail100% (6)
- Time Sharing OptionDokument13 SeitenTime Sharing Optionapi-3829326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Write A Function: Amity International School PRACTICAL LIST 2021-22 (Final) Class Xii Computer ScienceDokument7 SeitenWrite A Function: Amity International School PRACTICAL LIST 2021-22 (Final) Class Xii Computer ScienceShail Singh0% (1)
- Structured Web Documents in XML: Grigoris Antoniou Frank Van HarmelenDokument109 SeitenStructured Web Documents in XML: Grigoris Antoniou Frank Van HarmelenKainat AnsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DB Managment Ch5Dokument4 SeitenDB Managment Ch5Juan Manuel Garcia NoguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workflow Editor IdeasDokument17 SeitenWorkflow Editor IdeasFloriNaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument38 SeitenLecture 1walaba06100% (2)