Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Analize Engleza PDF
Hochgeladen von
Alexandra CosmaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Analize Engleza PDF
Hochgeladen von
Alexandra CosmaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
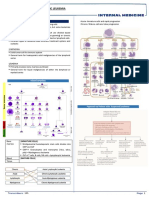
Blood Test Results: CBC Explained
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Definition: Measures essential components of the blood
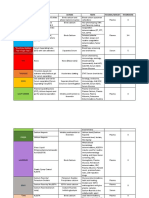
Substance What It Is Reference Ranges * What a Low Number May Mean What a High Number May Mean
USA UK/EU Australia/Canada
White blood cell count (WBC) Measures the total number of white blood cells, which defend the body 4,500-10,000 cells/mcL Autoimmune diseases, immunosuppression, bone marrow Infection, inflammation, leukemia, intense exercise, stress,
against infection; there are several different types of white blood cells: failure, chemotherapy, viral infections corticosteroids
lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
Lymphocytes, absolute (LY, abs) or Measures the number or percentage of lymphocytes, which are white 800-5,000 cells/mcL (abs) Immunosuppression, HIV-AIDS, bone marrow failure, Viral infections, leukemia, lymphoma
percentage (LY, pct) blood cells that include B-cells, T-cells, and natural killer cells 18-45 (pct) chemotherapy
Monocytes, absolute (MO, abs) or Measures the number or percentage of monocytes, which are white blood 400-1,000 cells/mcL (abs) Immunosuppression, bone marrow failure, chemotherapy Chronic infections, autoimmune diseases, leukemia
percentage (MO, pct) cells that move out of the circulating blood and into the tissues, where 1-10 (pct)
they mature into macrophages
Granulocytes, absolute (GR, abs) or Measures the number or percentage of white blood cells with granules in 1,800-8,300 cells/mcL (abs) Immunosuppression, bone marrow failure, chemotherapy Infection, inflammation, leukemia, intense exercise, stress,
percentage (GR, pct) their cytoplasm and two or more lobes in their nuclei; an inclusive term 45-75 (pct) corticosteroids
for neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils, although neutrophils are by far
the most abundant
Neutrophils, absolute (NE, abs) or Measures the number or percentage of neutrophils, which are normally 1,800-8,300 cells/mcL (abs) Immunosuppression, bone marrow failure, chemotherapy Infection, inflammation, leukemia, intense exercise, stress,
percentage (NE, pct) the most abundant circulating white blood cells and respond quickly to 45-75 (pct) corticosteroids
infection
Eosinophils, absolute (EOS, abs) or Measures the number or percentage of eosinophils, which combat 0-800 cells/mcL (abs) 0- Generally not a concern Parasitic infections
percentage (EOS, pct) parasitic infections and are involved in asthma or allergy responses 7 (pct)
Basophils, absolute (BAS, abs) or Measures the number or pecentage of basophils, which are involved in 0-100 cells/mcL (abs) 0- Generally not a concern Active allergic response
percentage (BAS, pct) allergy responses 0.5 (pct)
Red blood cell count (RBC) Measures the number of red blood cells, which pick up oxygen from the Male: 4.7-6.1 million/mcL Iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency; bone marrow damage; Dehydration, renal problems, pulmonary disease, congenital
blood and deliver it to tissues throughout the body Female: 4.2-5.4 million/mcL leukemia or lymphoma; acute or chronic blood loss; red blood heart disease, polycythemia vera
cell hemolysis
Reticulocytes Measures the percentage of circulating immature red blood cells 0.5-2.0% Generally not a concern Anemia, recent blood loss, red blood cell hemolysis
Hemoglobin (HgB) Oxygen-carrying pigment in red blood cells Male: 13.8-17.2 g/dL Iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency; bone marrow damage; Dehydration, renal problems, pulmonary disease, congenital
Female: 12.1-15.1 g/dL leukemia or lymphoma; acute or chronic blood loss; red blood heart disease, polycythemia vera
cell hemolysis
Hematocrit (HCT) The percentage of red blood cells Male: 40.7%-50.3% Iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency; bone marrow damage; Dehydration, renal problems, pulmonary disease, congenital
Female: 36.1%-44.3% leukemia or lymphoma; acute or chronic blood loss; red blood heart disease, polycythemia vera
cell hemolysis
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) Average size of red blood cells 80-95 fL Iron deficiency Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) The amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell 23-31 pg Iron deficiency Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin The average concentration of hemoglobin in a given volume of red blood 32-36 g/dL Iron deficiency Sickle cell disease, hereditary spherocytosis
concentration (MCHC) cells
Red cell distribution width (RDW) A measurement of the variation in red blood cell size 11-15% Generally not a concern Iron deficiency, vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, recent blood
loss
Platelet count (PLT) Measures the number of platelets, which are important for blood clotting 150-400 Thousand/mcL Bone marrow failure, chemotherapy, viral infections, lupus, Leukemia, myeloproliferative disorders (which cause blood cells
pernicious anemia (due to vitamin B12 deficiency), leukemia or to grow abnormally in bone marrow), inflammatory conditions
lymphoma, sequestration in the spleen, certain medications
Mean platelet volume (MPV) The average volume of a platelet; newer platelets tend to be larger than 7.0-11.0 fL Aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia Certain inherited disorders
older ones
* Reference ranges can vary by age, sex, methods of testing, and other factors. There are no KEY
nationally established reference ranges for CMP and CBC values; instead, each laboratory tests a mg: milligram g: gram mmol: millimole mEq: milliequivalent dL: deciliter
population and establishes its own reference ranges. Therefore, the reference ranges quoted are
IU: international unit L: liter mcL: microliter pg: picogram fL: femtoliter
only approximate.
m: meter mL: milliliter
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Understanding Acute and Chronic LeukemiaDokument10 SeitenUnderstanding Acute and Chronic LeukemiaKrisha BalorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decipher Your Labwork - CBC: Functional MedicineVon EverandDecipher Your Labwork - CBC: Functional MedicineBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE TESTDokument5 SeitenERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE TESTAliana RaymundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leukocytes Benign DisordersDokument3 SeitenLeukocytes Benign DisordersGerardLum100% (3)
- 100 Item Hematology Exam From DinglasanDokument6 Seiten100 Item Hematology Exam From DinglasanJaymih Santos Abasolo100% (1)
- S0850alug 1670953860959-SEU HDokument56 SeitenS0850alug 1670953860959-SEU HAziz KhwajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretasi Darah RutinDokument22 SeitenInterpretasi Darah Rutinboy jendri huluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology Review 2021-2Dokument142 SeitenHematology Review 2021-2Maram AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Tube Additives and TestsDokument3 SeitenBlood Tube Additives and TestsDanluidQMalintadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything You Need to Know About ThalassemiaDokument33 SeitenEverything You Need to Know About ThalassemiaMirzi Cuison100% (1)
- CBC InterpretationDokument6 SeitenCBC InterpretationKate Basa100% (1)
- Laboratory Investigations in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDokument187 SeitenLaboratory Investigations in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryTarun KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Test ResultsDokument1 SeiteBlood Test ResultsnindyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Modern Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 7th Edition Denise M HarmeningDokument12 SeitenTest Bank For Modern Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 7th Edition Denise M Harmeningkendrataylorygwedrfzcn100% (19)
- Fast Facts: CAR T-Cell Therapy in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A practical resource for nursesVon EverandFast Facts: CAR T-Cell Therapy in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A practical resource for nursesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haemogram RangesDokument3 SeitenHaemogram RangesMayra SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Blood Count Result Interpretation GuideDokument2 SeitenComplete Blood Count Result Interpretation GuideVet District Animal ClinicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attached in RBC, Color of The BloodDokument4 SeitenAttached in RBC, Color of The BloodAebee AlcarazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology: Complete Blood Count and Differential CountDokument12 SeitenHematology: Complete Blood Count and Differential CountimperiouxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete blood count guide for screening disordersDokument22 SeitenComplete blood count guide for screening disordersSerious LeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC and LFTDokument15 SeitenCBC and LFTAbdul SamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Physiology - WBC Cell Differential CountDokument1 SeiteAnimal Physiology - WBC Cell Differential CountIndah Rizka AprilianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC and LFTDokument14 SeitenCBC and LFTAbdul SamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Results MaleDokument5 SeitenLab Results MaleJb RosillosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC Test Results and InterpretationDokument9 SeitenCBC Test Results and InterpretationamiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Blood Count: Abdellatif Aly MohamedDokument81 SeitenComplete Blood Count: Abdellatif Aly MohamedGroup 11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Red blood cell production and functionDokument1 SeiteRed blood cell production and functionIsfahan MasulotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Laboratory Findings of AnemiaDokument6 SeitenEvaluation of Laboratory Findings of AnemiaSitha Medha ParamithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haematological Tests: Jhanvi Ka Patel Rool No. 09Dokument21 SeitenHaematological Tests: Jhanvi Ka Patel Rool No. 09Aditya PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Note Swelab Alfa Plus Analyzer Procedures For Optimized System Performance Tns 33228 2Dokument8 SeitenTech Note Swelab Alfa Plus Analyzer Procedures For Optimized System Performance Tns 33228 2Tholkappiyan Rajamanickam100% (1)
- Complete Blood Count: Performed To Provide An Overview of A Patient's General Health StatusDokument4 SeitenComplete Blood Count: Performed To Provide An Overview of A Patient's General Health StatusRaprnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Values Hema: All Values Varies With Age or Sex, or Ethnic SubgroupDokument9 SeitenLab Values Hema: All Values Varies With Age or Sex, or Ethnic SubgroupXerxyllXyreaneLinaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HematologyDokument42 SeitenHematologyFikadu GidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Full Blood Count by Group EightDokument15 SeitenPresentation On Full Blood Count by Group Eightmaxwell amponsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intepretasi Data KlinikDokument41 SeitenIntepretasi Data KlinikyohanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Blood CountDokument18 SeitenComplete Blood CountNazih MominNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 10 HivDokument40 SeitenCase 10 HivCeria Dorena Fe SeteraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Anemia and PolycythemiaDokument7 SeitenApproach To Anemia and PolycythemiaambutlangnimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of The Full Blood Count in Systemic Disease - A Guide For The PhysicianDokument6 SeitenInterpretation of The Full Blood Count in Systemic Disease - A Guide For The PhysicianKarthik SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common LabsDokument10 SeitenCommon Labsthevenue7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Full Blood Count by Group EightDokument15 SeitenPresentation On Full Blood Count by Group Eightmaxwell amponsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological Blood CountDokument4 SeitenPhysiological Blood CountRhea SaldanhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLS Unit 2 NotesDokument8 SeitenCLS Unit 2 NotesBailey EdwinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Interpret HEMATOLOGY Test ResultsDokument36 SeitenHow to Interpret HEMATOLOGY Test Resultssylvia haryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- XL22 - Basic HaematologyDokument18 SeitenXL22 - Basic HaematologyAdi TrisnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determine Your ANC with a CBC TestDokument1 SeiteDetermine Your ANC with a CBC TestRonanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology & UrinalysisDokument77 SeitenHematology & UrinalysismekuriawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aplastic and Hypoplastic Anemias Including Mylodysplastic SyndromeDokument47 SeitenAplastic and Hypoplastic Anemias Including Mylodysplastic SyndromeRahul Kumar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical InvestigationsDokument34 SeitenBiochemical InvestigationsPraneethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HematologyDokument38 SeitenHematologysultana alturkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout Basic HematologyDokument188 SeitenHandout Basic HematologymaikkadoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBC Count Guide Provides Definitions, Causes, and Diagnostic StepsDokument4 SeitenRBC Count Guide Provides Definitions, Causes, and Diagnostic StepsRaphael Joshua De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Policy Opportunities: Search Help?Dokument12 SeitenPolicy Opportunities: Search Help?Mj BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- N 5315 Advaned Pathophysiology Anemia TranscriptDokument9 SeitenN 5315 Advaned Pathophysiology Anemia TranscriptllukelawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Lect in Hem-2021-Dr - HazimDokument5 Seiten1st Lect in Hem-2021-Dr - HazimAnmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Far Eastern University Health Assessment TestsDokument4 SeitenFar Eastern University Health Assessment TestsMayls Sevilla CalizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematologic DisorderDokument63 SeitenHematologic DisorderjvaccinatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretive Summary: Nucleated RBCDokument2 SeitenInterpretive Summary: Nucleated RBCWael SafwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Lymphoid Leukemia (Airway Management)Dokument48 SeitenAcute Lymphoid Leukemia (Airway Management)Ankita SamantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C B C I: Omplete Lood Ount NterpretationsDokument44 SeitenC B C I: Omplete Lood Ount NterpretationsridhoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBCDokument15 SeitenCBCUlicer CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBC count and anemia tests explainedDokument6 SeitenRBC count and anemia tests explainedSharmaine Grace FlorigNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Qualitative Estimation of BCR-ABL Transcript: An In-Lab Procedural Study on Leukemia PatientsVon EverandThe Qualitative Estimation of BCR-ABL Transcript: An In-Lab Procedural Study on Leukemia PatientsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBSDokument72 SeitenPBSKavi KaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thromboelastography Guide Trans 0413 p127 132Dokument6 SeitenThromboelastography Guide Trans 0413 p127 132MarcelliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NHLBI OSPEEC YourGuidetoAnemia Booklet RELEASE 508Dokument44 SeitenNHLBI OSPEEC YourGuidetoAnemia Booklet RELEASE 508bnvjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Von Willebrand Disease Types and TreatmentDokument4 SeitenVon Willebrand Disease Types and TreatmentJohannah DaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warfarin Initiation and Dosage Adjustments GuideDokument9 SeitenWarfarin Initiation and Dosage Adjustments Guidemarto langNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBC Abnormalities in Morphology: HematologyDokument6 SeitenRBC Abnormalities in Morphology: HematologyCarlo SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Bank Data Collection FormDokument3 SeitenBlood Bank Data Collection Formpbta punjab100% (1)
- CI-08 - Others Critical Illness (Lain-Lain Jenis Penyakit Kritikal)Dokument2 SeitenCI-08 - Others Critical Illness (Lain-Lain Jenis Penyakit Kritikal)nur'afeefa binti hamdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Pustaka: Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. 6 Ed. Philadelphia, PADokument3 SeitenDaftar Pustaka: Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. 6 Ed. Philadelphia, PAAhmad Agus PurwantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lana Adila SGD Modul 6 LBM 2 Step 7Dokument42 SeitenLana Adila SGD Modul 6 LBM 2 Step 7adhillaagniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfusion ReactionsDokument36 SeitenTransfusion Reactionsmarky203Noch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Erythrocyte1Dokument4 SeitenNormal Erythrocyte1RonyArtoKapidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pendekatan Diagnosis AnemiaDokument7 SeitenPendekatan Diagnosis AnemiaFerry GhifariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemolytic Disease of The Fetus and NewbornDokument6 SeitenHemolytic Disease of The Fetus and NewbornCj CCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinian Ibu Hamil Kurang Energi Kronik (KEK) Dan AnemiaDokument8 SeitenDeterminian Ibu Hamil Kurang Energi Kronik (KEK) Dan Anemiagirinawasena8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autologous - OmaDokument55 SeitenAutologous - OmaOmprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia in Pregnancy: Causes, Effects and TreatmentDokument6 SeitenAnemia in Pregnancy: Causes, Effects and TreatmentLeroy LoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erba Protime LSDokument2 SeitenErba Protime LSthinh.ho2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Blood Picture: Test Name Value Units Reference Range 3.44 7.4 76 22 28.5Dokument107 SeitenComplete Blood Picture: Test Name Value Units Reference Range 3.44 7.4 76 22 28.5anil tanankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Hematology Lab ObjectivesDokument7 SeitenAdvanced Hematology Lab ObjectivesoyadieyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quyet Dinh 921 QD Byt Bo y Te PDFDokument27 SeitenQuyet Dinh 921 QD Byt Bo y Te PDFNgọc DungNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Blood Typing StudentDokument21 Seiten1 Blood Typing Studentapi-217623200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Donation PDFDokument1 SeiteBlood Donation PDFNitesh Kumar PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Anemia and ClassificationDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To Anemia and ClassificationDarien LiewNoch keine Bewertungen
- DapusDokument4 SeitenDapusRuth VeraulinaNoch keine Bewertungen