Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
04-W-4 Chemistry
Hochgeladen von
zain IshaqOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
04-W-4 Chemistry
Hochgeladen von
zain IshaqCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
WORKSHEET-4
CHEMISTRY Chapter # 8
Worksheet-04
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons (Alkynes)
1. Alkynes can be reduced to cis-alkenes by hydrogenation USE THIS SPACE FOR
SCRATCH WORK
in the presence of:
A. Pd B. Anhydrous AlCl3
C. Lindlar’s Catalyst D. Raney Ni
2. When acetylene is passed through a copper tube at
300oC, it polymerizes to:
A. Polyacetylene B. Polyethylene
C. Benzene D. Chloroprene
3. Acetylene on reacting with ammonical silver nitrate
yield:
A. Silver metal B. Silver chloride
C. Silver mirror D. Silver acetylides
4. Which one of the following reagent distinguishes
ethylene from acetylene?
A. Cl2 dissolved in CCl4
B. Aqueous alkaline KMnO4
C. Ammonical Cu2Cl2
D. Conc. H2SO4
5. Benzene can be regarded as a polymer of:
A. Acetylene B. Ethylene
C. Ethane D. Methane
6. Acetylene is used in the manufacturing of:
A. Rubber B. Plastic
C. Ethyl alcohol D. All of these
7. When ethyne reacts with ammonia in the presence of
suitable catalyst the product obtained is?
A. Acetonitrile B. Acrylonitrile
C. Ethyl amide D. Both A and B
8. All the alkynes are colourless and odorless EXCEPT:
A. Acetylene B. Propyne
C. Butyne D. Pentyne
Your STEP Towards A Brighter Future! 726
CHEMISTRY Chapter # 8
9. Brick red precipitates are formed when ethyne reacts USE THIS SPACE FOR
with: SCRATCH WORK
A. Ammonical silver chloride
B. Ammonical cuprous chloride
C. Ammonical silver nitrate
D. All of these
10. HCN gives Acrylonitrile with acetylene in presence of
A. Silica B. Alumina
C. Phosphorous pentaoxide D. Nickel
11. Acetylene reacts with NH3 in the presence of Al2O3 to
produce:
A. Acetone B. Acetaldehyde
C. Acetonitrile D. Formaldehyde
12. Which of the following is not the use of ethyne?
A. Preparation of benzene
B. Welding
C. Ripening of fruits
D. Formation of mustard gas
13. Which of the following is the structural formula of vinyl
group?
A. H2C=CH– B. C6H5–
C. H2C=CH–CH2– D. C6H5–CH2–
14. Substitution reaction of acetylene (C2H2) is possible
when it is treated with:
A. Na metal B. NaNH2
C. Ammonical AgNO3 D. All of these
15. Which alkyne reacts with water to form aldehyde?
A. Ethyne B. Propyne
C. 1-Butyne D. 2-Butyne
16. Ethyne is used?
A. In the preparation of alcohols and acetic acid
B. In the manufacturing of polymers like PVC, PVA and
neoprene
C. For repining of fruits
D. All of these
Your STEP Towards A Brighter Future! 727
CHEMISTRY Chapter # 8
17. The end product (C) in the following sequence of USE THIS SPACE FOR
reactions starting from ethanol is: SCRATCH WORK
A B C alcohol
conc Br2
H2SO4 KOH
A. Propene B. Ethene
C. Butyne D. Butene
18. Vinyl acetylene reacts with HCl to form:
A. Chloroprene B. Neoprene
C. Isoprene D. Divinyl acetylene
19. Which one of the following gases is used in welding
purpose usually?
A. Methane B. Ethane
C. Ethene D. Acetylene
20. Acetylene polymerized in the presence of ammonium
chloride and cuprous chloride to form:
A. Benzene B. PVC
C. Polythene D. Divinyl acetylene
21. The correct name of the given structure according to
IUPAC is:
CH3
H 2 C C CH 2 C CH
A. 4-Methyl-1-pentyn-4-ene
B. 4-Methyl-4-penten-1-yne
C. 2-Methyl-1-penten-4-yne
D. 2-Methyl-2-penten-3-yne
22. The number of acidic hydrogen in 1-Butyne is:
A. 1 B. 2
C. 3 D. 4
23. Which one of the following reactions help us to
distinguish between alkene (e.g. ethene) and alkyne (e.g.
ethyne)?
A. Reaction with ammonical silver nitrate AgNO3
B. Reaction with alkaline KMnO4
C. Reaction with bromine / CCl4
D. Reaction with ozone
Your STEP Towards A Brighter Future! 728
CHEMISTRY Chapter # 8
24. Synthetic rubber is made by polymerization of: USE THIS SPACE FOR
SCRATCH WORK
A. Chloroform B. Acetylene
C. Divinyl acetylene D. Chloroprene
25. Propyne react with water in the presence of dil. H2SO4
and 10% HgSO4 forming:
A. Propyl alcohol B. Propionaldehyde
C. Propanoic acid D. Dimethyl ketone
Your STEP Towards A Brighter Future! 729
CHEMISTRY Chapter # 8
ANSWER KEY (Worksheet-04) 4. (C) Ammonical Cu2Cl2 gives red ppt. of
1 C 11 C 21 C copper acetylide with acetylene due to
2 C 12 D 22 A acidic hydrogen of acetylene and not with
ethylene.
3 D 13 A 23 A
4 C 14 D 24 D
5 A 15 A 25 D
6 D 16 D
7 A 17 B 5. (A) Benzene can be regarded as a polymer of
8 A 18 A acetylene.
9 B 19 D
10 B 20 D
ANSWER EXPLAINED
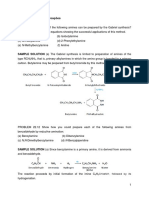
1. (C) The resulting mixture, known as
“Lindlar's catalyst” (Pd / BaSO4 / 6. (D) Acetylene is used in the manufacture of
Quinoline) after its inventor, is effective rubber, plastic and ethyl alcohol.
for the partial reduction of alkynes. Note 7. (A) When ethyne react with ammonia in the
the stereochemistry! Just as in presence of suitable catalyst the product
obtained is acetonitrile.
conventional alkene hydrogenation, both
hydrogen atoms are delivered in syn HC CH + NH3
Al2O3
300o C
CH3C N H2
fashion to provide us with the “cis”
alkene.” 8. (A) Pure acetylene is a colourless gas with an
ethereal smell. It is liquefied more easily
than ethylene or methane, and was first
obtained in the liquid state by Cailletet in
1877.
2. (C) Acetylene polymerizes to benzene on 9. (B) Brick red precipitates are formed when
ethyne reacts with ammonical cuprous
passing through Cu-tube at 300oC. chloride.
CH CH Cu 2Cl2 2NH 4OH
CuC CCu 2NH 4Cl 2H 2O
dicopper acetylide (red ppt.)
10. (B) HCN gives Acrylonitrile with acetylene
in presence of alumina.
HC CH+HCN
Cu 2 Cl2 /NH 4 Cl
Δ
CH 2 CH CN
3. (D) Acetylene reacts with ammonical silver
11. (C) Acetylene reacts with NH3 in the presence
nitrate to give a white ppt. of silver of Al2O3 and product is hydrolyzed to
acetylide. produce acetonitrile.
Your STEP Towards A Brighter Future! 730
CHEMISTRY Chapter # 8
12. (D) Ethyne is not used in the formation of 18. (A) Chloroprene is the common name for the
mustard gas. Sulfur mustard, commonly organic compound 2-chlorobuta-1,3-
known as mustard gas, is the prototypical
diene, which has the formula
substance of the sulfur-based family of
cytotoxic and vesicant chemical warfare CH2=CCl−CH=CH2. This colorless liquid
agents known as the sulfur mustards is the monomer for the production of the
which have the ability to form large polymer polychloroprene, a type of
blisters on exposed skin and in the lungs. synthetic rubber. Polychloroprene is
13. (A) Structural formula of vinyl group better known to the public as Neoprene,
H2C=CH–. the trade name.
14. (D) Substitution reaction of acetylene:
Na + C C Na + H 2
HC CH + 2Na
HC CH + 2AgNO3 +2NH4OH
AgC CAg+2NH4 NO3 +2H2O
15. (A) When ethyne reacts with water it form
19. (D) Acetylene is used in welding purpose
aldehyde (ethanal).
usually.
20. (D) Acetylene polymerized in the presence of
ammonium chloride and cuprous chloride
to form divinyl acetylene.
2HC CH Cu 2 Cl2
NH 4 Cl
CH 2 = CH-C CH
HC CH
CH 2 = CH-C CH = CH 2
16. (D) Ethyne is used: divinyl acetylene
For the preparation of alcohols and 21. (C) The correct name of the given structure
acetic acid according to IUPAC is
B. For the manufacture of polymers 2-Methyl-1-penten-4-yne.
like PVC, PVA and neoprene
C. For repining of fruits CH3
1 2 3 4 5
H 2 C C CH 2 C CH
17. (B) The end product is ethene in the
following sequence of reactions starting 22. (A) In 1-Butyne only one acidic hydrogen is
from ethanol. present
CH3CH2OH
Conc
CH2 = CH2
Br2
C2 H5Br
KOH
CH 2 = CH 2
CH3 CH2 C CH
H2SO4 Alcoholic
Your STEP Towards A Brighter Future! 731
CHEMISTRY Chapter # 8
23. (A)
CH CH Cu 2Cl2 2NH 4OH
CuC CCu 2NH 4Cl 2H 2O
dicopper acetylide (red ppt.)
HC CH 2AgNO3 +2NH 4OH
Ag C- C-Ag + 2NH 4 NO3 2H 2O
+
disilver acetylide (white ppt.)
24. (D) Synthetic rubbers (neoprene) are complex
chemical compounds built by means of
polymerization of monomers (chloroprene).
These are then treated by polymerization
using catalyst and process steam to form
chains of polymers which finally results
in rubber substances. These substances
are then processed to rubber products by
vulcanization.
25. (D) All other alkynes give ketones:
Your STEP Towards A Brighter Future! 732
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Alkyne and AromaticDokument3 SeitenAlkyne and AromaticJayanth KNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Chemistry Unit-10 (Student Copy)Dokument4 Seiten04 Chemistry Unit-10 (Student Copy)Kamran ShabbirNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDCAT 2022 HydrocarbonsDokument41 SeitenMDCAT 2022 Hydrocarbonszaka ullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ChemistryDokument2 SeitenOrganic ChemistryKim SeungminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etea Chem W 3Dokument9 SeitenEtea Chem W 3rashid1986100% (1)
- Success Point Science Academy: Chemistry Time: 1.00 HR Marks: 100Dokument4 SeitenSuccess Point Science Academy: Chemistry Time: 1.00 HR Marks: 100Brahmanand TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Chemistry CH-15MCQsDokument4 Seiten12th Chemistry CH-15MCQsRana DugNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th CHMDokument1 Seite10th CHMzeeshanhameedz1996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet-02-Chem (2021) STEP PDFDokument11 SeitenWorksheet-02-Chem (2021) STEP PDFHallo KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JAMB Chemistry Past Question 1983 2004Dokument119 SeitenJAMB Chemistry Past Question 1983 2004iamprecious2allNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Nmdcat: Uhs Topic Wise Test (Unit-10)Dokument4 SeitenChemistry Nmdcat: Uhs Topic Wise Test (Unit-10)Saad Arsalan100% (1)
- Competency Exam in Organic ChemistryDokument4 SeitenCompetency Exam in Organic ChemistryRaymond Yabut100% (1)
- Chemistry PDFDokument70 SeitenChemistry PDFJacob AyoolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument70 SeitenChemistryOguntona GloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry MCQ (For Exam)Dokument2 SeitenOrganic Chemistry MCQ (For Exam)Ismail HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkenes SummaryDokument2 SeitenAlkenes SummarySeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec. 2Dokument46 SeitenLec. 2Abdullah AmjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- AttachmentDokument71 SeitenAttachmentAhmad ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbon 1Dokument6 SeitenHydrocarbon 1VK CREATIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Questions On U-12, 13 & 14Dokument12 SeitenModel Questions On U-12, 13 & 14kadedoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbons Q 2Dokument3 SeitenHydrocarbons Q 2REJA MUKIB KHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry CT 3 22-23Dokument6 SeitenChemistry CT 3 22-23Sancia SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDokument23 Seiten12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsBedosi Bidita PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem-Class12th Resend-Up Paper-2Dokument2 SeitenChem-Class12th Resend-Up Paper-2tahir zamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Mid ExamDokument4 SeitenChemistry Mid ExamKidu GideyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbon - Practice SheetDokument3 SeitenHydrocarbon - Practice SheetAbhishek PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Practice Test 2B: 10 Items - 15 MinutesDokument1 SeiteOrganic Chemistry Practice Test 2B: 10 Items - 15 MinutesJelo LacernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 2Dokument12 SeitenChemistry 2kahguaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3B-HYDROCARBON Assignment - FinalDokument49 Seiten3B-HYDROCARBON Assignment - Finalkraken monsterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Examination Organic ChemistryDokument4 SeitenMidterm Examination Organic ChemistryMichael Padilla EsmallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Org 2Dokument9 SeitenOrg 2Chandan SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AminesDokument3 SeitenAminesgarvitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 2014Dokument17 SeitenChemistry 2014Agatha chilesheNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10X SOE - D - Carbon and Its Compounds (Sol)Dokument6 Seiten10X SOE - D - Carbon and Its Compounds (Sol)sarayu vishwanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tick The Correct Option.: Chemistry Entry Test MCAT By: Sagheer Ahmad Gudara M.Phill ChemistryDokument4 SeitenTick The Correct Option.: Chemistry Entry Test MCAT By: Sagheer Ahmad Gudara M.Phill ChemistrykamranNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEP-W1 ChemDokument10 SeitenSTEP-W1 Chemz kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Mock Exam (ANSWER KEY)Dokument7 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Mock Exam (ANSWER KEY)k.talle039Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Model Paper XIIDokument10 SeitenChemistry Model Paper XIImoonmehar2240Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9 11Dokument1 Seite9 11hassan tariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Problemas Sobre AminasDokument4 Seiten2 Problemas Sobre AminasmarianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Form5Dokument9 SeitenChapter 2 Form5Zulkifli Bin Pari100% (1)
- 01 - Carbonyl Compound (Aldehyde & Ketone) (Level) Module-5Dokument19 Seiten01 - Carbonyl Compound (Aldehyde & Ketone) (Level) Module-5Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Colleges of Northern PhilippinesDokument8 SeitenMedical Colleges of Northern PhilippinesJerrypol Casil PalmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Q) - P3 STPM 2017 (JPNT)Dokument9 Seiten(Q) - P3 STPM 2017 (JPNT)NorNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEM 3 UPPP Ke 2 2016 (Johor-Smk Taman Johor Jaya 1)Dokument7 SeitenSEM 3 UPPP Ke 2 2016 (Johor-Smk Taman Johor Jaya 1)Chan Yek FungNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Year Chemistry Up To 2018 PDFDokument37 SeitenAll Year Chemistry Up To 2018 PDFAGAH LUCKYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melaka (GBS) S3 2020Dokument16 SeitenMelaka (GBS) S3 2020Keertana SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Chemistry CH-3MCQsDokument4 Seiten12th Chemistry CH-3MCQskirabankai5Noch keine Bewertungen
- PCT MCQ With AnswerDokument22 SeitenPCT MCQ With AnswerswapnilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test No-4 Hydrocarbon - Key PDFDokument3 SeitenTest No-4 Hydrocarbon - Key PDFNaveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year 1st HalfDokument3 Seiten2nd Year 1st HalfBilal SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ChemistryDokument36 SeitenOrganic ChemistryPepy PeachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chennai Public School: Anna NagarDokument4 SeitenChennai Public School: Anna Nagar11F10 RUCHITA MAARANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohols (Multiple Choice) QP With ANSWERS NewDokument9 SeitenAlcohols (Multiple Choice) QP With ANSWERS NewApollonas Marios SofroniouNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSSC II Chemistry AKU-EB June 2021Dokument11 SeitenHSSC II Chemistry AKU-EB June 2021Shahid Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Questions and ProblemsDokument6 SeitenReview Questions and Problemsmache dumadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem PaperDokument4 SeitenChem PaperKeertana SN100% (1)
- ACS Review 18 Enols and EnolatesDokument11 SeitenACS Review 18 Enols and EnolatesJana BazziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Q&ADokument9 SeitenAlcohols, Phenols & Ethers Q&AGaurav nayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM Lab TitelDokument1 SeiteFM Lab Titelzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Transportation EngineeringDokument17 SeitenIntroduction To Transportation Engineeringzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- TP 2Dokument1 SeiteTP 2zain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marshall Stability Test: (ASTM D-1663-73, ASTM D-1559-75)Dokument24 SeitenMarshall Stability Test: (ASTM D-1663-73, ASTM D-1559-75)zain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOQ HouseDokument2 SeitenBOQ Housezain Ishaq100% (1)
- Lab PDC AgingDokument27 SeitenLab PDC Agingzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pavement Design and Construction: Dynamic Shear RheometerDokument36 SeitenPavement Design and Construction: Dynamic Shear Rheometerzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Graphics and VisualizationDokument35 SeitenEngineering Graphics and Visualizationzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Graphics and Visualization: Lecture - Unit 10Dokument11 SeitenEngineering Graphics and Visualization: Lecture - Unit 10zain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Transportation Engineering TEM 141: Engr. Hina Saleemi Assistant ProfessorDokument17 SeitenIntroduction To Transportation Engineering TEM 141: Engr. Hina Saleemi Assistant Professorzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab PDC BBRDokument26 SeitenLab PDC BBRzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 To Study 5 Second Theodolite: 1.1 Least CountDokument51 SeitenChapter 1 To Study 5 Second Theodolite: 1.1 Least Countzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 6 Prismatc CompassDokument10 SeitenLec 6 Prismatc Compasszain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotech-1-Soil InvestigationDokument97 SeitenGeotech-1-Soil Investigationzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Paper SolutionDokument7 SeitenHydro Paper Solutionzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- B R E A K Fre e Free Free FreeDokument1 SeiteB R E A K Fre e Free Free Freezain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Engineering-1: Course Code - CE-221Dokument14 SeitenGeotechnical Engineering-1: Course Code - CE-221zain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1 Introduction To GeoTech Engg ADokument62 SeitenLec 1 Introduction To GeoTech Engg Azain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Engineering-1: Course Code - CE-221Dokument36 SeitenGeotechnical Engineering-1: Course Code - CE-221zain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying & Levelling: Lecture # 3 Theodolite TraversingDokument11 SeitenSurveying & Levelling: Lecture # 3 Theodolite Traversingzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photogrammetry: Ced, Uet LahoreDokument55 SeitenPhotogrammetry: Ced, Uet Lahorezain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying & Levelling: Lecture # 1Dokument37 SeitenSurveying & Levelling: Lecture # 1zain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying & Levelling: Civil Engineering DeptDokument25 SeitenSurveying & Levelling: Civil Engineering Deptzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrology L 1Dokument26 SeitenHydrology L 1zain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrographic and Tunnel SurveyingDokument21 SeitenHydrographic and Tunnel Surveyingzain Ishaq100% (1)
- 04-W-4 Math PDFDokument11 Seiten04-W-4 Math PDFzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geographic Information System: Ced, Uet LahoreDokument69 SeitenGeographic Information System: Ced, Uet Lahorezain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04-W-4 ComputerDokument5 Seiten04-W-4 Computerzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04-W-4 EnglishDokument6 Seiten04-W-4 Englishzain IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 12 17 - Parenting in America - FINALDokument105 Seiten2015 12 17 - Parenting in America - FINALKeaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tackling Food Inflation: Ashwinkumar Kokku - 67 Malcolm Pinto - 89 Samir Vele - Nitin JadhavDokument9 SeitenTackling Food Inflation: Ashwinkumar Kokku - 67 Malcolm Pinto - 89 Samir Vele - Nitin JadhavMalcolm PintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Removing Eyelid LesionsDokument4 SeitenRemoving Eyelid LesionsMohammad Abdullah BawtagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Quality Index Determination of Malathalli LakeDokument16 SeitenWater Quality Index Determination of Malathalli Lakeajay kumar hrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Stress TheoryDokument10 SeitenFamily Stress TheoryKarina Megasari WinahyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standerdised Tools of EducationDokument25 SeitenStanderdised Tools of Educationeskays30100% (11)
- Cis MSCMDokument15 SeitenCis MSCMOliver DimailigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational Safety and Health Procedures, Practices and RegulationsDokument20 SeitenOperational Safety and Health Procedures, Practices and RegulationsDionisa ErnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1: Basic Design of Fluidized-Bed ReactorDokument3 SeitenFigure 1: Basic Design of Fluidized-Bed ReactorElany Whishaw0% (1)
- Acuson P10Dokument2 SeitenAcuson P10anon-259218Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Categories of Lipids: FunctionsDokument3 Seiten8 Categories of Lipids: FunctionsCaryl Alvarado SilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Harn v1 2Dokument17 SeitenGeology Harn v1 2vze100% (1)
- White Vaseline: Safety Data SheetDokument9 SeitenWhite Vaseline: Safety Data SheetHilmi FauziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variance AnalysisDokument22 SeitenVariance AnalysisFrederick GbliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Field Summary NotesDokument11 SeitenElectric Field Summary NotesVoyce Xavier PehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dryer Regenerative Blower Purge DBP 02250195 405 R00 PDFDokument84 SeitenDryer Regenerative Blower Purge DBP 02250195 405 R00 PDFjennyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE R10 Certification Guide-Edition 1.3Dokument33 SeitenECE R10 Certification Guide-Edition 1.3Ôm Pŕâkẵsh PẵñdêýNoch keine Bewertungen
- TherabandDokument1 SeiteTherabandsuviacesoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constantino V MendezDokument3 SeitenConstantino V MendezNīc CādīgālNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Cell City AnswersDokument5 SeitenBiology - Cell City AnswersDaisy be100% (1)
- BV DSG eDokument18 SeitenBV DSG eIulianIonutRaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faraz Chem ProjectDokument13 SeitenFaraz Chem ProjectFaraz AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm B633Dokument5 SeitenAstm B633nisha_khan100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram For Pharmaceutical Water System 1652323261Dokument1 SeiteSchematic Diagram For Pharmaceutical Water System 1652323261Ankit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiếng AnhDokument250 SeitenTiếng AnhĐinh TrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desigo PX SeriesDokument10 SeitenDesigo PX SeriestemamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literary Portraiture & Modern Spain: Dr. Rebecca M. Bender (Dokument6 SeitenLiterary Portraiture & Modern Spain: Dr. Rebecca M. Bender (Pedro PorbénNoch keine Bewertungen
- AA-036322-001 - Anchor Bolt DetailsDokument1 SeiteAA-036322-001 - Anchor Bolt DetailsGaurav BedseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4EVC800802-LFEN DCwallbox 5 19Dokument2 Seiten4EVC800802-LFEN DCwallbox 5 19michael esoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doingwell Coaching ServicesDokument4 SeitenDoingwell Coaching ServicesPaweł PawełNoch keine Bewertungen