Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Yearly Lesson Plan Science Year 6: Semester 1 Week Learning Objective Learning Outcome Investigating Living Things
Hochgeladen von
mrkanjopangOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Yearly Lesson Plan Science Year 6: Semester 1 Week Learning Objective Learning Outcome Investigating Living Things
Hochgeladen von
mrkanjopangCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
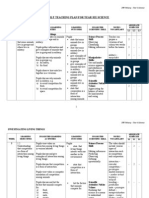
YEARLY LESSON PLAN
SCIENCE YEAR 6
SEMESTER 1
Week Learning Objective Learning Outcome
1 Investigating Pupils
03/01/11 Living Things • state that some animals live in groups.
To 1. Interaction • state that some animals live in solitary.
07/01/11 among living things • give examples of animals that live in
1.1 Understanding that groups.
some animals live in • give examples of animals that live in
groups and others live solitary.
in solitary • explain why animals live in groups.
• explain why animals live in solitary.
• state that cooperation is a form of
interaction among animals.
2 1.2 Understanding that Pupils
10/01/11 competition is a form • state that living things
To of interaction among interact with one another in the
14/01/11 living things environment
• state that competition is a form of
interaction.
• list the factors that animals compete for.
• give reasons why animals compete.
3 1.2 Understanding that • list factors that plants compete for.
17/01/11 competition is a form • give reasons why plants compete with
To of interaction among each other.
21/01/11 living things
4 1.3 Understanding the Pupils
24/01/11 responsibility of human • give examples of extinct animal.
To beings in protecting • give examples of endangered animal.
28/01/11 endangered species • give examples of endangered plant.
5 1.3 Understanding the • explain why certain animals or plants are
31/01/11 responsibility of human facing the threat of extinction.
To beings in protecting • suggest ways to prevent animals and
02/02/11 endangered species plants from extinction.
6 1.4 Knowing the Pupils
07/01/11 impact of human • give examples of environmental
To activities on destruction caused by human.
11/02/11 environment • explain how human activities cause
environmental destruction.
• predict what will happen to the Earth if
human activities are not controlled.
8 Investigating Pupils
21/01/11 Force and Energy • state that push and pull are forces.
To 1. Force • state that force cannot be seen but its
effects can be observed.
25/02/11 1.1 Understanding that
push and pull are
forces Pupils
• state that a force can move a stationary
1.2 Understanding the object.
effects of a force • state that a force can change the motion
of an object.
• state that a force can change the shape
of an object.
9 1.3 Analysing friction Pupils
28/02/11 • state that friction is a type of force.
To • describe the effects of friction.
04/03/11 • describe ways to reduce friction.
• describe ways to increase friction.
• state the advantages of friction.
• state the disadvantages of friction.
• conclude that friction occurs when two
surfaces are in contact.
10 1.3 Analysing friction • design a fair test to find out how different
07/03/11 types of surfaces affect the distance a
To trolley moves by deciding what to change,
11/03/11 what to keep the same and what to
measure.
14/0 3/ 1 1 Το 18/03/1 1
11 ΦΙΡΣΤ ΤΕΡΜ ΣΧΗΟΟΛ ΗΟΛΙ∆ΑΨ
12 2. Movement 2.1 Understanding speed
21/03/11 2.1 Understanding Pupils
To speed • state that an object which moves faster
25/03/11 travels a longer distance in a given time.
• state that an object which moves faster
takes a shorter time to travel a given
distance.
• state what speed is.
• solve problems using the formula.
13 Investigating Pupils
28/03/11 Materials • describe what spoilt food is.
To 1. Food • identify characteristics of spoilt food.
01/04/11 preservation • state that microorganisms can spoil
1.1 Understanding food.
food spoilage • state the conditions for microorganisms
to grow.
14 1.2 Synthesisng the Pupils
04/04/11 concept of food • describe ways to preserve food.
To preservation • give examples of food for each type of
08/04/11 food preservation.
• give reasons why each way of food
preservation is used.
• state what food preservation is.
• design and carry out a project to
preserve a given food.
Pupils
1.3 Realising the • give reasons why we need to preserve
importance of food.
preserving food
15 2. Waste Pupils
11/04/11 management • identify types of waste in the
To 2.1 Understanding the environment.
15/04/11 effects of improper • identify sources of waste.
disposal of waste on • state the improper ways of waste
the environment disposal.
• state the proper ways of waste
disposal.
• describe the harmful effects of
improper waste disposal.
• describe how waste is disposed in a
local area.
• suggest ways to improve waste
disposal.
16 2.2 Understanding that Pupils
18/04/11 some waste can decay • state that certain waste can decay.
To • give examples of waste that can decay.
21/04/11 • give examples of waste that do not
decay.
• state that microorganisms can cause
waste materials to decay.
• state the advantages of waste decaying.
• state the disadvantages of waste
decaying.
• predict what will happen to human and
the environment if waste do not decay.
17 Investigating The Pupils
25/04/11 Earth and The • state what eclipse of the moon is.
To Universe • state the position of the Moon, the Earth
29/04/11 1. Eclipses and the Sun during the eclipse of the
1.1 Understanding the moon.
eclipse of the moon • explain why eclipse of the moon occurs
1.2 Understanding the Pupils
eclipse of the sun • state what eclipse of the sun is.
• state the position of the Moon, the Earth
and the Sun during the eclipse of the sun.
• explain why eclipse of the sun occurs.
• predict the scenario on the Earth during
the eclipse of the sun.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2011Dokument20 SeitenYearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2011Syahida IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kontrak SC Yr 6Dokument9 SeitenKontrak SC Yr 6Shafinaz SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 0 7 First SemesterDokument9 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 0 7 First SemesterzakitamsirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Tahun 6 - Sem 1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Tahun 6 - Sem 1Mismah Binti Tassa YanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Dokument13 SeitenYearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008ff_fadzli275Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.interaction Among Living ThingsDokument4 Seiten1.interaction Among Living ThingsRain KipliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science Syllabus For Primary SchoolsDokument12 SeitenPrimary Science Syllabus For Primary SchoolsMadeleine Agius CarbonaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Year6 2012Dokument21 SeitenYearly Plan Year6 2012Hasliza HasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Dokument9 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Annie GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Som Mai EmaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Dokument12 SeitenYearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Wan Shahlan FatimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Yr 6Dokument18 SeitenYearly Plan Science Yr 6Joe SabriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science Syllabus For Primary SchoolsDokument12 SeitenPrimary Science Syllabus For Primary SchoolsMary ZuzuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 2011Dokument8 SeitenLesson Plan Biology Form 4 2011FidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 1 LODokument4 SeitenGrade 1 LOSarah ZaheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Scheme of Work Yr6 (New)Dokument17 SeitenYearly Scheme of Work Yr6 (New)HairulIzhamIshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Lesson Plan Science Form 1Dokument9 SeitenAnnual Lesson Plan Science Form 1Rodzila GhadziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 4Dokument127 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 4Satia KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggested Yearly Plan / Please Change or Edit Based On Your School CalendarDokument16 SeitenSuggested Yearly Plan / Please Change or Edit Based On Your School CalendarMuhamad Hamadi IthninNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated ScienceDokument6 SeitenIntegrated Scienceiteachclassroom100% (2)
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterDokument10 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterRaffie MuksinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Year 6 2012Dokument12 SeitenScience Year 6 2012Hirdawati Abdul HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan Year 6Dokument16 SeitenScience Yearly Plan Year 6shaharinsulongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 3 2010 Week Date Learning Area / Learning Objectives / Learning Outcomes NotesDokument6 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 3 2010 Week Date Learning Area / Learning Objectives / Learning Outcomes NotesAnonymous 7NXXd87sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science TM Grade 4Dokument20 SeitenScience TM Grade 4Bhawna KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Revision Booklet Term 3 - 2023Dokument14 SeitenLife Sciences Grade 12 Revision Booklet Term 3 - 2023Babazile HlongwaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekolah Rendah Agama Integrasi: Tengku Ampuan Fatimah, Batu BelahDokument23 SeitenSekolah Rendah Agama Integrasi: Tengku Ampuan Fatimah, Batu BelahMohd HafizanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 1: Solid Butter Ice CubeDokument26 SeitenScience Form 1: Solid Butter Ice CubeRidzuan MihatNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 - 3 - Additional - Lesson 2Dokument4 SeitenM1 - 3 - Additional - Lesson 2Paul Victor TamuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Grade Science Goals and ObjectivesDokument2 Seiten1st Grade Science Goals and ObjectivesShane A. ChasteauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3 ScienceDokument40 SeitenGrade 3 ScienceLovely CarbonelNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 - 3 - Additional - Lesson 5Dokument4 SeitenM1 - 3 - Additional - Lesson 5Paul Victor TamuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 5 - Taechers - T1Dokument20 SeitenScience 5 - Taechers - T1marypazochoa923Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Grade Animal Adaptations Final VersionDokument78 Seiten4th Grade Animal Adaptations Final VersionTGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 2 LODokument4 SeitenGrade 2 LOSarah ZaheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- LS3 WLL Perimeter 1Dokument8 SeitenLS3 WLL Perimeter 1alsginaeneroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physcience 3-5Dokument9 SeitenPhyscience 3-5Sangsang BartoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Year 4 2008: Wee K Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning OutcomeDokument13 SeitenScience Year 4 2008: Wee K Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning OutcomeSopi Abd HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan GR 9 SS Geography T3 W1-2Dokument8 SeitenLesson Plan GR 9 SS Geography T3 W1-2Bismark kofi Baafi BaafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smk. Saint Andrew, Muar. Science Form Two Yearly Lesson Plan 2015Dokument12 SeitenSmk. Saint Andrew, Muar. Science Form Two Yearly Lesson Plan 2015aikanazirfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Con 6Dokument16 SeitenTeaching Con 6alyasserbinmdisa82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kecukupan Latihan YEAR 6Dokument23 SeitenKecukupan Latihan YEAR 6Asnal KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marina International School: Science Scheme of WorkDokument13 SeitenMarina International School: Science Scheme of WorkMariama KanyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan: Year 6 2013Dokument14 SeitenScience Yearly Plan: Year 6 2013Rajesware GovindasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science3 Teachers T1Dokument20 SeitenScience3 Teachers T1marypazochoa923Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smith Lessonplan1Dokument6 SeitenSmith Lessonplan1api-548452244Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year Planner SC Yr 6Dokument8 SeitenYear Planner SC Yr 6ccqwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCNJ Lesson Plan: Living V Nonliving: WormsDokument3 SeitenTCNJ Lesson Plan: Living V Nonliving: Wormsapi-358126166Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 2.1 Issues in The OceansDokument21 SeitenYear 8 2.1 Issues in The Oceansmaya.a.shaker.1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Esc 100Dokument8 SeitenEsc 100khngoccNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1 PowerPoint With LinkDokument22 SeitenCH 1 PowerPoint With LinkBlezzie BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 4 SequenceDokument5 SeitenGrade 4 SequenceSarah ZaheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 59Dokument6 SeitenLesson 59Janina Aira VisitacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidences of EvolutionDokument31 SeitenEvidences of Evolutionljsgarcia25Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Sci 9Dokument219 SeitenNCERT Sci 9devagandivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week Learning Objectives and Outcomes Learning ActivitiesDokument13 SeitenWeek Learning Objectives and Outcomes Learning ActivitiesNorazla MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Vole Field Signs and Habitat Assessment: A Practical Guide to Water Vole SurveysVon EverandWater Vole Field Signs and Habitat Assessment: A Practical Guide to Water Vole SurveysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategies for Survival: Cultural Behavior in an Ecological ContextVon EverandStrategies for Survival: Cultural Behavior in an Ecological ContextNoch keine Bewertungen
- WDH 20240101Dokument2 SeitenWDH 20240101mrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- GuruDokument27 SeitenGurumrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Takwim Penggal 2017Dokument2 SeitenTakwim Penggal 2017Nurul AyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tanda NamaDokument1 SeiteTanda NamamrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ithink Final Test AnswerDokument15 SeitenIthink Final Test AnswermrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCNJDL ZK'VDFKVMCDokument1 SeiteMCNJDL ZK'VDFKVMCmrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- January February March AprilDokument4 SeitenJanuary February March AprilmrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tahun 6Dokument6 SeitenTahun 6mrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calender 2015 Edit2Dokument1 SeiteCalender 2015 Edit2mrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hei KaweanDokument1 SeiteHei KaweanmrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- RgsqetjtkDokument1 SeiteRgsqetjtkmrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Kahirol Mohd SallehDokument6 Seiten06 Kahirol Mohd SallehmrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To - Get On The Internet..Dokument2 SeitenHow To - Get On The Internet..mrkanjopangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 4Dokument140 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 4bviazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dexter Quilisadio-Tanzo BSA-2 Unit-1 Quiz-1: OPMATQM-490Dokument1 SeiteDexter Quilisadio-Tanzo BSA-2 Unit-1 Quiz-1: OPMATQM-490Red AriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security and Azure SQL Database White PaperDokument15 SeitenSecurity and Azure SQL Database White PaperSteve SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria SymptomsDokument3 SeitenMalaria SymptomsShaula de OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novel Synthesis of BarbituratesDokument3 SeitenNovel Synthesis of BarbituratesRafaella Ferreira100% (2)
- Minimum Structural Properties and Test Procedure For TG20 Compliant Prefabricated Structural Transom UnitsDokument16 SeitenMinimum Structural Properties and Test Procedure For TG20 Compliant Prefabricated Structural Transom UnitsPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bnblist3559 PDFDokument430 SeitenBnblist3559 PDFJagroopSinghBalhraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical Remarks On The Semantic Approach PDFDokument34 SeitenLogical Remarks On The Semantic Approach PDFFelipe SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guoyin Shen, Ho-Kwang Mao and Russell J. Hemley - Laser-Heated Diamond Anvil Cell Technique: Double-Sided Heating With Multimode Nd:YAG LaserDokument5 SeitenGuoyin Shen, Ho-Kwang Mao and Russell J. Hemley - Laser-Heated Diamond Anvil Cell Technique: Double-Sided Heating With Multimode Nd:YAG LaserDeez34PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment in Legal CounselingDokument4 SeitenAssignment in Legal CounselingEmmagine E EyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pi 100 Book ReviewDokument10 SeitenPi 100 Book ReviewBianca CacnioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emcee - Graduation DayDokument5 SeitenEmcee - Graduation DayBharanisri VeerendiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The American New CriticsDokument5 SeitenThe American New CriticsSattigul KharakozhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 ActivityDokument3 Seiten8 ActivityNICOOR YOWWNoch keine Bewertungen
- HotsDokument74 SeitenHotsgecko195Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sigmund Freud 1Dokument3 SeitenSigmund Freud 1sharoff saakshiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swimming Pool - PWTAG CodeofPractice1.13v5 - 000Dokument58 SeitenSwimming Pool - PWTAG CodeofPractice1.13v5 - 000Vin BdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Most Common Punctuation Errors Made English and Tefl Majors Najah National University - 0 PDFDokument24 SeitenMost Common Punctuation Errors Made English and Tefl Majors Najah National University - 0 PDFDiawara MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Statistics For Business AnalyticsDokument15 SeitenBasic Statistics For Business AnalyticsNeil Churchill AniñonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elc650 Ws Guidelines (250219)Dokument3 SeitenElc650 Ws Guidelines (250219)panda_yien100% (1)
- 1 Patient Assessment Form.Dokument3 Seiten1 Patient Assessment Form.Aina HaravataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tips On Being A Successful StudentDokument2 SeitenTips On Being A Successful Studentshimbir100% (3)
- Football Trading StrategyDokument27 SeitenFootball Trading StrategyChem100% (2)
- Plate Tectonics QuizDokument6 SeitenPlate Tectonics QuizJordan Santos100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Biochemical Engineering Dutta Solution ManualDokument6 SeitenFundamentals of Biochemical Engineering Dutta Solution Manualhimanshu18% (22)
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Key Drawings and Animation BreakdownsDokument6 SeitenSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Key Drawings and Animation BreakdownsRUFINO MEDICONoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Draft Basel II DissertationDokument110 SeitenFinal Draft Basel II DissertationWilliam Weru80% (5)
- Amy Kelaidis Resume Indigeous Education 2015 FinalDokument3 SeitenAmy Kelaidis Resume Indigeous Education 2015 Finalapi-292414807Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Academy: ESE Conventional Revision TEST - IDokument8 SeitenEngineering Academy: ESE Conventional Revision TEST - Ividya chakitwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop BayesDokument534 SeitenWorkshop Bayesapi-27836396Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gamma Ray Interaction With Matter: A) Primary InteractionsDokument10 SeitenGamma Ray Interaction With Matter: A) Primary InteractionsDr-naser MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen