Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
02 Identifiying Stages of Group Work
Hochgeladen von
geovanefilhoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
02 Identifiying Stages of Group Work
Hochgeladen von
geovanefilhoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GOS5706 Gestão de Pessoas em Organizações de Saúde
Instrutor: Valdes Roberto Bollela
IDENTIFYING STAGES OF WORK GROUPS
High performing work groups don’t simply happen.
When people begin working on a project, they usually focus on the task — job needing done.
They often neglect team process/interactions/dynamics — social way people work together — or
fail to — that has a significant impact on the group’s effectiveness.
We increase effectiveness in getting tasks done by becoming sensitive to group dynamics.
Roles of Leader and Facilitator/Process Coach Change with Work Group Development
The leader and facilitator/process coach direct and set the stage in the beginning and gradually move to
the back set as the project progresses and the group members gain skills for self-managing.
ACTIVE LEADERSHIP BY LEADER AND FACILITATOR
Start of
Project
After
a few
meetings
End of
Project
ACTIVE LEADERSHIP BY MEMBERS
Attitudes and Behaviors of Group Members Change in Work Group Development
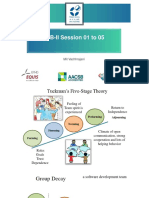
Various theorists have classified team development stages; we use Tuckman’s. As teams move through
the stages the amount of work performed gradually increases. Morale follows an up/down/up pattern.
FORM STORM NORM PERFORM
High
Amount ot work
Morale
Low
FAIMER Institute © 2013 All rights reserved. 1
GOS5706 Gestão de Pessoas em Organizações de Saúde
Instrutor: Valdes Roberto Bollela
Stages of Small Group Work
Stage 1 — Forming Dynamics
FO R M IN G
M ember
Typical Behaviors and Comments
M em ber M em ber
Wait for leader to initiate activity. May ask, “What
are we to do?”
Agreeable and obedient. “Whatever you say!”
Leader
M em ber M em ber Polite and formal.
F acilitato r
Negative feeling about the process are discussed at
breaks and after meetings privately.
M em ber M ember Leader focus: Directive; task focused
Facilitator/Process Coach focus: Self disclosure;
Member
openness; listening
Stage 2 — Storming Dynamics - transition from mild enthusiasm to conflict –
STORMING Typical Behaviors and Comments
Verbal and nonverbal frustration and
Member resistance.
Member Member Arguments and disagreements.
Challenges to roles, responsibilities, process,
agendas, etc.
Leader Self-oriented behavior: dominating, non-
Member Member participating, blocking, attention seeking.
Facilitator
Leader focus: High task AND high
relationship.
Member Member Facilitator/Process Coach focus: Providing
positive and negative feedback; creating safe
Member environment.
FAIMER Institute © 2013 All rights reserved. 2
GOS5706 Gestão de Pessoas em Organizações de Saúde
Instrutor: Valdes Roberto Bollela
Stage 3 — Norming Dynamics - Trust developing and cohesive group is forming.
Typical Behaviors and Comments NORMING
Personal sharing. Play instead of work. Facilitator
Member
Giving and receiving feedback.
“Either/or” statements are replaced with “both/and” Member Member
statements.
Typical behaviors include harmonizing, encouraging
and reconciling.
Member Leader Member
The pitfall may be desire to play (relief from storming)
and complacency.
Increasing responsibility and authority keeps the group
momentum growing. Member
Member
Leader focus: Low task and high relationship.
Facilitator/Process Coach focus: Exploring Member
differences; uncovering unspoken issues; encouraging
self-analysis.
Stage 4 — Performing Dynamics – work group functioning with self-confidence
Typical Behaviors and Comments PERFORMING
High energy focused on accomplishing the Facilitator
goal. Member Member
Interdependence. Sharing of tasks based
on each member's strengths and
weaknesses. Member Member
Task focused behaviors: information
giving and seeking, clarifying,
GOAL
summarizing, initiating, target keeping.
Member
Member
Leader focus: Low task and low
relationship (group functions by self). Member
Member
Facilitator/Process Coach function:
Leader
Encouraging group towards self-
intervention and self-management.
FAIMER Institute © 2013 All rights reserved. 3
GOS5706 Gestão de Pessoas em Organizações de Saúde
Instrutor: Valdes Roberto Bollela
Stage 5 Adjourning for the Next Phase
Completely adjourning groups is rare in academia. However, there are punctuations for:
terminating the current set of tasks
disengagement from relationships, when a group member leaves or new member arrives
This process should be planned and include:
celebration of the group’s achievements and members' contributions
good-byes to members leaving and welcomes to new members.
And with these changes, it is important to acknowledge that the ‘new’ group is likely to revisit the
various stages of group development – forming, storming, and norming before the previous level of
performing is reached again!
Unsuccessful Team Successful Team
FAIMER Institute © 2013 All rights reserved. 4
GOS5706 Gestão de Pessoas em Organizações de Saúde
Instrutor: Valdes Roberto Bollela
FAIMER Institute © 2013 All rights reserved. 5
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Leadership and ManagementDokument24 SeitenLeadership and Managementansh2195100% (2)
- Unit 2 Organisational CultureDokument28 SeitenUnit 2 Organisational CultureJesica MaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iraq-A New Dawn: Mena Oil Research - July 2021Dokument29 SeitenIraq-A New Dawn: Mena Oil Research - July 2021Beatriz RosenburgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relativity of ContractsDokument7 SeitenRelativity of ContractsCristy C. Bangayan100% (1)
- Implementation of Brigada EskwelaDokument9 SeitenImplementation of Brigada EskwelaJerel John Calanao90% (10)
- P119 - Module 4Dokument6 SeitenP119 - Module 4Mariella MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Situational and Behavioral Theories of LeadershipDokument19 SeitenSituational and Behavioral Theories of LeadershipmalayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyadic Leadership: Ashish Bagla-1020807 Donald Brian-1020809 Jacob Vergese-1020811Dokument24 SeitenDyadic Leadership: Ashish Bagla-1020807 Donald Brian-1020809 Jacob Vergese-1020811rajeevforyouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Servant Leadership 2 14 22Dokument4 SeitenServant Leadership 2 14 22Al MarzolNoch keine Bewertungen
- En 10083 3 Technical Delivery Conditions For Alloy Steels SummaryDokument10 SeitenEn 10083 3 Technical Delivery Conditions For Alloy Steels SummaryEngineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 TeamworkDokument17 SeitenChapter 6 TeamworkBerk TekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leader-Follower RelationshipDokument24 SeitenLeader-Follower RelationshipUwais UwaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stages in Group CounselingDokument16 SeitenStages in Group Counselingwhirly101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To OBDokument25 SeitenIntroduction To OBGuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Chap 1 LeadershipDokument4 SeitenLeadership Chap 1 LeadershipSophia Marie BesorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEADERSHIP ConceptsDokument6 SeitenLEADERSHIP ConceptsJulie Ann GernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument8 SeitenUntitledAswini NalluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Styles Final Report VipulDokument23 SeitenLeadership Styles Final Report VipulVipul75% (8)
- Matched Leadership GuideDokument2 SeitenMatched Leadership Guidegersymann.subscriptionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 Contingency Leadership TheoriesDokument47 SeitenTopic 5 Contingency Leadership TheoriesSyarifah SulaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2Dokument26 SeitenCH 2soul12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership: Chapter 4 - Style ApproachDokument20 SeitenLeadership: Chapter 4 - Style ApproachMochamadAliHaidarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 Development of Leadership TheoryDokument22 SeitenWeek 1 Development of Leadership Theoryagung prawiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument17 SeitenChapter 7Ahmad Z. SultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership and Theories of LeadershipDokument26 SeitenLeadership and Theories of Leadershipritz rawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015-2016 Leadership For Food Services StaffDokument25 Seiten2015-2016 Leadership For Food Services StaffTotdi AicragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership: and Its TheoriesDokument14 SeitenLeadership: and Its TheoriesShruti SumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Outline VER22Dokument55 SeitenLeadership Outline VER22rj cornejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSTPDokument7 SeitenNSTPCecilia Afinidad100% (1)
- Lanz, K. (2013) - The Art of Self-Awareness. Training Journal, 65-69Dokument6 SeitenLanz, K. (2013) - The Art of Self-Awareness. Training Journal, 65-69seattlechazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Training NSTP - PowerPointDokument33 SeitenLeadership Training NSTP - PowerPointAngelie Jalandoni100% (5)
- Chapter Fourteen: LeadershipDokument22 SeitenChapter Fourteen: LeadershipTanmay PednekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10 - Situational Leadership StylesDokument31 SeitenLecture 10 - Situational Leadership StylesThanh HằngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Groups and TeamsDokument9 SeitenGroups and TeamsDarlene TigcalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liderazgo Program CompletoDokument23 SeitenLiderazgo Program Completodiosaegipcia8626Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Process of Influencing and Supporting Others To Work EnthusiasticallyDokument26 SeitenThe Process of Influencing and Supporting Others To Work EnthusiasticallydnyanniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Style Approach NPTEL 2020 - WatermarkDokument21 SeitenStyle Approach NPTEL 2020 - WatermarkSumalatha BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership: Ami Amaliah Fitria Nur Cahyati Visdha Ersita Rinjani Ayu RizkiaDokument38 SeitenLeadership: Ami Amaliah Fitria Nur Cahyati Visdha Ersita Rinjani Ayu RizkiaWita ramadhiantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBO (Chapter 5: Leadership and Its Changing Development in Organizations)Dokument7 SeitenHBO (Chapter 5: Leadership and Its Changing Development in Organizations)Soojoo HongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leader: Define and Compare The Different Roles and Characteristics of A Leader and A ManagerDokument7 SeitenLeader: Define and Compare The Different Roles and Characteristics of A Leader and A ManagerOnelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4 Leadership CH 4 Style ApproachDokument25 SeitenWeek 4 Leadership CH 4 Style Approachshah gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership - Traits & Theories (Main)Dokument125 SeitenLeadership - Traits & Theories (Main)SarfarazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Management Assignment Slide V1.1Dokument19 SeitenBusiness Management Assignment Slide V1.1akhinesoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership TrainingDokument111 SeitenLeadership TrainingAmy VSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Role and Qualities: LessonDokument5 SeitenLeadership Role and Qualities: LessonDaisy Mae Cañete PingcasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 01-05Dokument27 SeitenSession 01-05RISHAB DAS PGP 2020 BatchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership in Customer ServiceDokument32 SeitenLeadership in Customer ServicePeter WekesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership 1Dokument43 SeitenLeadership 1AmaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTIONDokument4 SeitenINTRODUCTIONmohamed110Noch keine Bewertungen
- LeadershipDokument22 SeitenLeadershipAnubhav WaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout 6 LeadershipDokument4 SeitenHandout 6 LeadershipRifatVanPersieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transactional and Transformational LeadershipDokument37 SeitenTransactional and Transformational LeadershipRoy Garing100% (1)
- Leadership Erika (0218101098) Sekar Indah Utami (0218101107) Sabila Nailah Najjah (0218101108) Group 6 Class ODokument21 SeitenLeadership Erika (0218101098) Sekar Indah Utami (0218101107) Sabila Nailah Najjah (0218101108) Group 6 Class OSekar Indah UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By:: Lib P. Uyaco, DVM Veterinarian I During TheDokument47 SeitenPresented By:: Lib P. Uyaco, DVM Veterinarian I During TheLib PalmaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Introduction To LeadershipDokument6 Seiten1 - Introduction To LeadershipJuwita Merlinda100% (1)
- 12 Leadership 2Dokument54 Seiten12 Leadership 2danielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 11 - Leadership, Morale and ProductivityDokument28 SeitenLesson 11 - Leadership, Morale and ProductivitySheenly CordovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1-Ch 1Dokument48 SeitenLec 1-Ch 1yaser abdelrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective LeadershipDokument5 SeitenEffective LeadershipNuton ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership & Teamwork in Social Care: I.A.S.C.E. Annual Conference 16/17 OCTOBER 2003Dokument11 SeitenLeadership & Teamwork in Social Care: I.A.S.C.E. Annual Conference 16/17 OCTOBER 2003gbmayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEADERSHIPDokument64 SeitenLEADERSHIPAzeli SiquianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership and FollowershipDokument43 SeitenLeadership and FollowershipNishant AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BDM 202 Chapter 3Dokument22 SeitenBDM 202 Chapter 3siti sapikahwanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artigo HughesDokument11 SeitenArtigo HughesgeovanefilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boudreau e Ramstad, 2005Dokument8 SeitenBoudreau e Ramstad, 2005geovanefilho100% (1)
- Constructing Career Through Narrative: Charles BujoldDokument15 SeitenConstructing Career Through Narrative: Charles BujoldgeovanefilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Constructionism in The Study of Career: Accessing The Parts That Other Approaches Cannot ReachDokument16 SeitenSocial Constructionism in The Study of Career: Accessing The Parts That Other Approaches Cannot ReachgeovanefilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hughes Award: Michael B. ArthurDokument24 SeitenThe Hughes Award: Michael B. ArthurgeovanefilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Prelim ExamDokument6 Seiten2nd Prelim Exammechille lagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocampo - v. - Arcaya-ChuaDokument42 SeitenOcampo - v. - Arcaya-ChuaChristie Joy BuctonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linking Social Science Theories/Models To EducationDokument2 SeitenLinking Social Science Theories/Models To EducationAlexa GandioncoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OECD - AI Workgroup (2022)Dokument4 SeitenOECD - AI Workgroup (2022)Pam BlueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Martin, BrianDokument3 SeitenMartin, Brianapi-3727889Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gouri MohammadDokument3 SeitenGouri MohammadMizana KabeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hatch Waxman Act OverviewDokument7 SeitenHatch Waxman Act OverviewPallavi PriyadarsiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satisfaction On Localized Services: A Basis of The Citizen-Driven Priority Action PlanDokument9 SeitenSatisfaction On Localized Services: A Basis of The Citizen-Driven Priority Action PlanMary Rose Bragais OgayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Fundamentals of Thermodynamics 6th Edition Sonntag Solutions ManualDokument20 SeitenFull Download Fundamentals of Thermodynamics 6th Edition Sonntag Solutions Manualadenose.helveo0mvl100% (39)
- I'M NOT A SKET - I Just Grew Up With Them (Chapter 4 & 5)Dokument13 SeitenI'M NOT A SKET - I Just Grew Up With Them (Chapter 4 & 5)Chantel100% (3)
- People vs. PinlacDokument7 SeitenPeople vs. PinlacGeenea VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Strategy: MarketingDokument14 SeitenRetail Strategy: MarketingANVESHI SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On "Buying Behaviour: of Gold With Regards ToDokument77 SeitenProject Report On "Buying Behaviour: of Gold With Regards ToAbhishek MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Product and Service CostingDokument28 SeitenFundamentals of Product and Service CostingPetronella AyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Study GuideDokument3 SeitenChapter 6 Study GuidejoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ModernismDokument4 SeitenModernismSiya SunilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authors & Abstract Guideline V-ASMIUA 2020Dokument8 SeitenAuthors & Abstract Guideline V-ASMIUA 2020tiopanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hudson Legal CV Interview GuideDokument16 SeitenHudson Legal CV Interview GuideDanielMead100% (1)
- WOREL Q2 Week 2Dokument8 SeitenWOREL Q2 Week 2Pearl CuarteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A#2 8612 SehrishDokument16 SeitenA#2 8612 SehrishMehvish raniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muhammad Naseem KhanDokument2 SeitenMuhammad Naseem KhanNasim KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Us and China Trade WarDokument2 SeitenUs and China Trade WarMifta Dian Pratiwi100% (1)
- Ethical Dilemma Notes KiitDokument4 SeitenEthical Dilemma Notes KiitAritra MahatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baseball Stadium Financing SummaryDokument1 SeiteBaseball Stadium Financing SummarypotomacstreetNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEBI Management Summary SheetsDokument398 SeitenSEBI Management Summary SheetsPriyanka ChandakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Penal LawsDokument14 SeitenSpecial Penal LawsBrenna ColinaNoch keine Bewertungen