Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
IDM-In Combating Blast Disease in Rice Crop in Temperate Environment
Hochgeladen von
Hasib UzzamanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IDM-In Combating Blast Disease in Rice Crop in Temperate Environment
Hochgeladen von
Hasib UzzamanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IDM- In Combating Blast Disease in Rice Crop in
Temperate Environment
T. Mubarak, M. A. Zarger and Z. A. Bhat
KrishiVigyan Kendra
Anantnag-192233 ( Jammu and Kashmir)
ABSTRACT
Integrated Disease Management ( IDM) is important for reducing threat to environment and
for sustaining higher yields. There is need to test and demonstrate IDM technique at farmers’
field for their wide adaptability. On-farm trials and frontline demonstrations were conducted by
Krishi-Vigyan-Kendra Anantnag to popularize IDM module to boost, rice production in blast
prone area of district Anantnag. Yield improved to the tune of 36 per cent by IDM module over
farmers practice plots. Net returns (Rs.47,952/ha) and benefit cost ratio (1.5) were also higher
in same practice. An additional income of Rs.16,589/ha was obtained over the farmer’s practice.
Key words: IDM, Rice, Blast.
INTRODUCTION ● Growing varieties which lack resistance
against Blast disease
Downloaded From IP - 122.173.244.76 on dated 1-Oct-2016
Indiscriminate use of agricultural chemicals
in general and pesticides in particular has become Farmer use varieties (Table 1) which are prone
to disease and if proper disease management
Members Copy, Not for Commercial Sale
a great concern. Emphasis is, therefore, being laid
www.IndianJournals.com
on Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for practices are not taken in time there always
environmental safety, good health and sustainable remains risk of crop being badly hit by blast
agriculture.. Technologies developed by SKUAST- disease particularly under fluctuating weather
Kashmir needs to be popularized among farming conditions as prevalent in the study area.
community to boost agricultural productivity and ● Imbalanced use of fertilizers
production. Since rice is a staple food of the Farmers have tendency towards using heavy
people of Kashmir valley and blast disease a doses of nitrogenous fertilizers without and a
major biologic threat to crop, an Integrated Disease small number of them apply Potassium
Management (IDM) module was needed to be supplying fertilizer. This makes plant tissues
tested at Farmers’ field to combat the menace of succulent and more prone to blast disease.
blast disease in district Anantnag. Krishi-Vigyan- Continuously use organic manures striking a
Kendra Anantnag (Pombay) conducted On-farm balance in the application of N and K
trials and Frontline Demonstrations to popularize fertilizer help some to escape severe disease
the IDM module in rice. attack. This signifies the importance of
balanced nutrient supply in IDM.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
● Lack of plant protection measures against
Analysis of Factors Responsible For the the disease
Outbreak of Disease Apple is the major fruit crop of the valley.
A joint survey was conducted by KVK Farmers pay much attention to their apple crop
scientist and the officers of agriculture in comparison to paddy. Though the
development department to identify hot spots of management technology for blast disease is
this disease. During survey it was found that the well established but unfortunately farmers do
microclimate of the area and farming practices, not follow the same resulting in considerable
were quite favourable for blast disease incidence. decline in crop yield due to the disease. Not a
single farmer even uses a simple technique of
Factors Which Favoured the Spread of Disease seed treatment against the disease.
Corresponding author e-mail: drtasneem.mubarak@gmail.com drtasneem_mubarak@rediffmail.com
Journal of Krishi Vigyan 27
Blast affected rice plant and Shalimar rice 1 plot Survey of Blast affected Plot of Jehlum rice
● Other causes WP and Hexaconazole 5 EC 0.15% each in
Poor water management, dense planting of cocktail was done as it has been found
seedlings with 5 to 14 seedlings per hill and effective against disease.
lack of coordination between farmers and the 4. Sowing time: Early sowing of the rice variety
line department at zonal level are some other SR-1 for timely maturation of the variety which
reasons which aggravated the situation. is essential for successful double cropping in
the valley.
Action Plan
Downloaded From IP - 122.173.244.76 on dated 1-Oct-2016
5. Balanced dose of fertilizer: Use of balanced
All Important causes of outbreak of blast Fertilizers was demonstrated to the FLD
Members Copy, Not for Commercial Sale
disease in paddy were taken into consideration beneficiaries as per the package of practices.
www.IndianJournals.com
while framing a strategy to combat this disease They were advised to strictly follow the
and vis-à-vis to improve rice production. On-farm recommendations with regard to the dose
trials were conducted (Table 1) which revealed and time of fertilizer application. In some cases
that the disease incidence and severity was farmers were advised to reduce urea fertilizer
remarkably higher with farmers practice against dose owing to inherent nitrogen fertility/
improved technology. Yield was appreciably consistent use of organic manures in plenty.
higher in improved technology compared to the Emphasis was laid on the application of well
farmers practices. In view of these results, front decomposed Farmyard Manure.
line demonstration programme with following
6. Plant population: Farmers were given training
technical inputs were conducted in the area
programmes on raising of healthy rice
(Table1).
seedlings and at the same time were
1. Variety: Jehlum and K-39 varieties which lack instructed to transplant 2-3 healthy rice
resistance against the blast disease were seedling per hill with 35-45 Plants/sq.m.
replaced by Shalimar Rice -1(SR-1) which
7. Water management: Impounding of water
exhibits resistance to blast disease. This
(5cm) was advocated for the first 15 days
variety was released in 2005 for lower belts
after transplanting followed by intermitted
of the valley located up to an altitude of
irrigation to keep the soil saturated with
1600m MSL.
moisture.
2. Seed Treatment: Seed treated with the
chemical against paddy diseases( RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Mancozeb@ 2g + Carbendazim @1g per Kg Integrated disease management in rice against
of seed) was distributed free of cost among the menace of blast disease in demonstration plots
the farmers associated with the FLD gave excellent results compared to the farmers
progamme. practice. Yield ranged from 61 to 73 q/ha in
3. Seedbed treatment: Temperature fluctuation demonstration plots. Average yield was 66.6 q/ha
during nursery raising period may cause (Table 1) against the farmers’ practice (48.7 q/ha.).
rhizoctonia rot disease. Spray of Captan 50 Demonstration yield was 36 per cent higher than
28 Journal of Krishi Vigyan
Table 1. Performance of different rice cultivars against blast disease in the plains of district Anantnag.
Rice cultivar Disease incidence Disease severity(leaf blast) Grain yield(q/ha)
Leaf blast Neck blast
Jhelum 33 % 10.7 13.8 38
K-39 27.1% 6.3 8.3 41
Shalimar Rice -1 2% 0 0.1 63
Table 2. Summery of farmers’ practice and Technology demonstrated(FLD)
Parameter Farmers’ practice(Control) Technology demonstrated(FLD)
Variety K-39 , K-448 Shalimar Rice-1
Seed rate for one hectare >50 kg 60 Kg
Seed treatment/ Kg seed No seed treatment Seed treated with
Carbendazim (1g) + Mancozeb (2g)
Seed sowing 1st May-10th May Last week of April
Fertilizer dose(N,P2O5,K2O) Haphazard 120:60:20
Age of seedling at transplanting 35- 41 days 25-30 days
Plants per hill 5-14 2-3
Time of fertilizer application No knowledge ½ basal, ¼ at active tillering stage,
¼ at panicle initiation stage
Downloaded From IP - 122.173.244.76 on dated 1-Oct-2016
Water management Running water Intermitted irrigation
Crop yield/ha 48.7 q 66.6 q/ha
Members Copy, Not for Commercial Sale
Net returns /ha Rs.31363 Rs.47952
www.IndianJournals.com
B : C ratio 0.98 1.5
the yield realized in the control plots. Gross returns, reproductive phase to unfavourable weather
net profit and benefit cost ratio per hectare for conditions, resulting in increased sterility and
demonstration were Rs.79,900, Rs.47,952 and 1.5, chaffy grain.
respectively against Rs.58,444, Rs.31,363 and ● Inherent higher nitrogen status might be one
0.98 registered in the control. An additional of the reason.
income of Rs.16,589/ha was obtained with the
Early sowing preferably under protected
demonstrated technology over the farmers practice
nursery conditions, intermitted irrigation and
(control). Moreover SR-1 enhanced paddy straw
reduction in nitrogen dose was recommended for
production which is an important component of
such cases.
ration for cattle in the winter. Most important
aspect of the demonstrated technology was that Impact
not a single case of blast incidence was observed.
Results also show that in few cases the crop Successful demonstration of SR-1 paddy
maturity delayed beyond normal which reduced variety and related technology has highly
yield of the crop. Analysis of such cases revealed convinced the other farmers of the area to adopt
that the reason for delay were; the technology at much greater speed. Higher
yield potential , more recovery percentage and
● Late sowing and transplanting of the crop
resistance against blast disease makes SR-1
compared to recommended one due to one or
versatile paddy variety. Interaction with farmers
the other reason.
and the officers of Development Department
● Some plots were situated near to the irrigation confirm that more than 50 per cent farmers used
source(canal) with lower water temperature. the same technology next year. Adaptation was
Some farmers follow traditional system of dramatic in villages most severely hit by blast
irrigation through running water which disease. Exchange of seed among farmers paved
prolongs the vegetative phase and pushes the way for speedy spread of the technology.
Journal of Krishi Vigyan 29
CONCLUSION pressure on a crop not only reduced cost of
Jhelum, no doubt is an excellent rice variety cultivation by curtailment in expenditure on
but under the microclimatic conditions which pesticide purchase and labour but also increases
favour blast disease adopting recommended farm income through improvement in crop yield.
management practice against the disease becomes This approach is environmentally safe and farmers
essential. Under the situation when farmer fails friendly. It promises higher yield and at the same
to execute the disease management practices in time minimizes threat to the environment. In IDM
time, there always remains a risk of crop being approach, development and adaptation of disease
damaged by diseases. Moreover, Integrated resistant/ tolerant high yielding crop variety plays
Disease Management (IDM) which is a well a pivotal role.
established technology to reduce the disease
Downloaded From IP - 122.173.244.76 on dated 1-Oct-2016
Members Copy, Not for Commercial Sale
www.IndianJournals.com
30 Journal of Krishi Vigyan
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Monday HaufDokument6 SeitenMonday HaufNational Press FoundationNoch keine Bewertungen
- MccconDokument1 SeiteMccconarrow.silver021995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Profile of Dermatological Disorders Among Workers.5Dokument7 SeitenProfile of Dermatological Disorders Among Workers.5Sankita SandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tillage, herbicides impact weed density and yields cotton, maizeDokument8 SeitenTillage, herbicides impact weed density and yields cotton, maizedarwin alfonso castilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Project Report On Agro Chemical Industry by Thatawale Babasaheb - Pesticide - Insecticide222Dokument1 SeiteSummer Project Report On Agro Chemical Industry by Thatawale Babasaheb - Pesticide - Insecticide222sharadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organically - Grown Mango ProductionDokument2 SeitenOrganically - Grown Mango ProductionCynthia MilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project SPGDokument2 SeitenProject SPGRyell CabunacanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incidence_of_basal_stem_rot_disease_of_oil_palm_inDokument8 SeitenIncidence_of_basal_stem_rot_disease_of_oil_palm_inFranky zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Is Ipm Important?: Food Demand Increase Yields Global PopulationDokument2 SeitenWhy Is Ipm Important?: Food Demand Increase Yields Global PopulationPrince CharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Agrochemicals Industry: Insights and Outlook: February, 2019 I Industry ResearchDokument17 SeitenIndian Agrochemicals Industry: Insights and Outlook: February, 2019 I Industry ResearchVenkatram PailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferreira y Musumeci 2021Dokument17 SeitenFerreira y Musumeci 2021Wenceslao Aboite “WencesAc”Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima YojanaDokument4 SeitenPradhan Mantri Fasal Bima YojanaShantanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real-time Weed Identification in Oil Palm Using Machine LearningDokument9 SeitenReal-time Weed Identification in Oil Palm Using Machine Learningerick firmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adams Et Al (2019) Financial Analysis of Small Scale Mango Chips Processing in Ghana PDFDokument17 SeitenAdams Et Al (2019) Financial Analysis of Small Scale Mango Chips Processing in Ghana PDFFanegha Oro LaminadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (19437714 - HortTechnology) Comparative Cost Analyses of Conventional, Integrated Crop Management, and Organic MethodsDokument9 Seiten(19437714 - HortTechnology) Comparative Cost Analyses of Conventional, Integrated Crop Management, and Organic MethodsJuan Carlos TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 - Meilin Et Al - IOP - Conf. - Ser. - Earth - Environ. - Sci. - 752 - 012008Dokument7 Seiten2021 - Meilin Et Al - IOP - Conf. - Ser. - Earth - Environ. - Sci. - 752 - 012008ratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vegetable Production Doubling Farmers IncomeDokument6 SeitenVegetable Production Doubling Farmers IncomeShaqena ZamriNoch keine Bewertungen
- DESIGN AND MANAGEMENT NOTESDokument50 SeitenDESIGN AND MANAGEMENT NOTESRyza MartizanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postharvest Handling in Asia 1. Rice: Keywords: Bulk Systems, Drying, Losses, Mechanization, Milling, Post-Harvest, RiceDokument12 SeitenPostharvest Handling in Asia 1. Rice: Keywords: Bulk Systems, Drying, Losses, Mechanization, Milling, Post-Harvest, RiceAgustinus Wahyu Adi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02d07025-02d05012 - It-625 - Agricultural Insurance in IndiaDokument19 Seiten02d07025-02d05012 - It-625 - Agricultural Insurance in IndiapmanikNoch keine Bewertungen
- FertilizantesDokument8 SeitenFertilizantesLeonardo EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2._Maize_Journal_Vol._7_2__Oct__2018__pp_56-63Dokument8 Seiten2._Maize_Journal_Vol._7_2__Oct__2018__pp_56-63hasu9749Noch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Evaluation and Risk Analysis ofDokument21 SeitenEconomic Evaluation and Risk Analysis ofAlvin RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fa 3 STS Group 4Dokument11 SeitenFa 3 STS Group 4Samantha Lauren BinuyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CombinationfungicideDokument7 SeitenCombinationfungicideRaghavendra SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Importance of Personal Protective Equipment in Pesticide App 2018Dokument4 SeitenThe Importance of Personal Protective Equipment in Pesticide App 2018Anees MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- (2018 - IJASET) Kumbalep&Devaraju - Awareness & Perceptions About Crop InsuranceDokument5 Seiten(2018 - IJASET) Kumbalep&Devaraju - Awareness & Perceptions About Crop InsuranceMarkus WidodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Shikha FMC Internship Report - Docx - 20240308 - 123616 - 0000Dokument10 SeitenDeep Shikha FMC Internship Report - Docx - 20240308 - 123616 - 0000Sabrm Rpcau PusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dhanuka Apoorva-CompressedDokument24 SeitenDhanuka Apoorva-CompressedSabrm Rpcau PusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial Biosynthesis and Applications of Gentamicin: A Critical AppraisalDokument40 SeitenMicrobial Biosynthesis and Applications of Gentamicin: A Critical AppraisalMANUELANoch keine Bewertungen
- Siganex PDFDokument3 SeitenSiganex PDFGerry CainNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Generation Fungicides in Disease Management of Horticultural CropsDokument8 SeitenNew Generation Fungicides in Disease Management of Horticultural CropsVishnuvardhan RavichandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- BT Brinjal and Alternatives 2.0Dokument27 SeitenBT Brinjal and Alternatives 2.0ramoo.csaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article - 02 Vol - XXIVDokument18 SeitenArticle - 02 Vol - XXIVKrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 PA Alametal MechanicaldryingofpaddyusingBAU STRdryerforreducingdryinglossinBangladeshDokument10 Seiten2019 PA Alametal MechanicaldryingofpaddyusingBAU STRdryerforreducingdryinglossinBangladeshShankar AcharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost-Effectiveness of Greenhouse Gases Mitigation Measures in Andean AgricultureDokument2 SeitenCost-Effectiveness of Greenhouse Gases Mitigation Measures in Andean AgricultureJhenny CayambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contracted AgricultureDokument6 SeitenContracted AgriculturesudamailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Agrochemicals Industry: Insights and Outlook: February, 2019 I Industry ResearchDokument24 SeitenIndian Agrochemicals Industry: Insights and Outlook: February, 2019 I Industry ResearchSurajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agriculture Product Training-4Dokument37 SeitenAgriculture Product Training-4Abhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GM Crops Fail to Deliver Promised BenefitsDokument40 SeitenGM Crops Fail to Deliver Promised BenefitsamiiasalikhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Histories of Different IPM Programs On Vegetable CropsDokument18 SeitenCase Histories of Different IPM Programs On Vegetable CropsPratyus BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of in Situ Mechanical Weed Control Vs Chemical Weed Control For Better Growth and Yield of MaizeDokument8 SeitenComparison of in Situ Mechanical Weed Control Vs Chemical Weed Control For Better Growth and Yield of MaizeSaboor OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.5 Research Paper - Machinery Mechanization - Harvesting and Threshing MachineDokument29 Seiten2.5 Research Paper - Machinery Mechanization - Harvesting and Threshing MachineArman RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real-Time Machine-Learning Based Crop Weed Detection and Classification For Variable-Rate Spraying in Precision AgricultureDokument8 SeitenReal-Time Machine-Learning Based Crop Weed Detection and Classification For Variable-Rate Spraying in Precision AgricultureGökçe yılmazNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICMSSC2016 Assisetal.Dokument7 SeitenICMSSC2016 Assisetal.Shawon MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30565-Article Text-57330-1-10-20200914Dokument11 Seiten30565-Article Text-57330-1-10-20200914nishan khatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growing Cotton: in A Better, Farmer Friendly WayDokument12 SeitenGrowing Cotton: in A Better, Farmer Friendly WayV VishalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Botanical Pesticides in Controlling SitophiDokument5 SeitenUse of Botanical Pesticides in Controlling SitophiOjo DamilolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Mahendra SharmaDokument39 SeitenDR Mahendra Sharmasumana86_ghoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starting A Cassava FarmDokument12 SeitenStarting A Cassava Farmoecox10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ajol File Journals - 608 - Articles - 244192 - Submission - Proof - 244192 7156 586518 1 10 20230322Dokument18 SeitenAjol File Journals - 608 - Articles - 244192 - Submission - Proof - 244192 7156 586518 1 10 20230322c82878992Noch keine Bewertungen
- Umiyati, U. D. Kurniadie D. Widayat I. Abdurrahim: Fimbristylis Miliaceae, Ludwigia Adscendes, Cyperus DifformisDokument7 SeitenUmiyati, U. D. Kurniadie D. Widayat I. Abdurrahim: Fimbristylis Miliaceae, Ludwigia Adscendes, Cyperus DifformisJuniver CapriatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural FarmingDokument14 SeitenNatural FarmingSri VNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - 2018 - IEEE - Robotics For Sugarcane Cultivation Analysis of Billet Quality Using Computer VisionDokument8 Seiten01 - 2018 - IEEE - Robotics For Sugarcane Cultivation Analysis of Billet Quality Using Computer VisionaryoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bifenthrin in The Tropical Sugarcane Ecosystem: Persistence and Environmental Risk AssessmentDokument9 SeitenBifenthrin in The Tropical Sugarcane Ecosystem: Persistence and Environmental Risk AssessmentninnakhairinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Operatedsmall ScalereaperDokument8 SeitenBattery Operatedsmall ScalereaperAbdulrasheed AbdulrazaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Pest Management (Ipm) : Role of The Plant Science IndustryDokument2 SeitenIntegrated Pest Management (Ipm) : Role of The Plant Science IndustryKitty van VuurenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agr 182 Case Study Nur Sofea Alanis BT ZulkifliDokument8 SeitenAgr 182 Case Study Nur Sofea Alanis BT ZulkifliNur Sofea AlanisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) farmer Field School (FFS): A Guide for Facilitators of FFS on Maize with Special Emphasis on Fall ArmywormVon EverandIntegrated Pest Management (IPM) farmer Field School (FFS): A Guide for Facilitators of FFS on Maize with Special Emphasis on Fall ArmywormNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Presentation On: Study Tour 2020Dokument13 SeitenA Presentation On: Study Tour 2020Hasib UzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
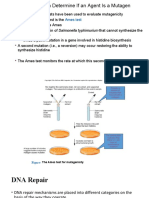
- Mutation 2 - Ames Test and Biological RepairDokument14 SeitenMutation 2 - Ames Test and Biological RepairHasib UzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vinegar: An Introduction and Inustrial ProductionDokument27 SeitenVinegar: An Introduction and Inustrial ProductionHasib UzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fermentation Allows The Production of A Small Amount of ATP Without OxygenDokument7 SeitenFermentation Allows The Production of A Small Amount of ATP Without OxygenHasib UzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JMB Pharma-Draft MOUDokument20 SeitenJMB Pharma-Draft MOUAndrianus Emank JeniusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Right to Food in India Analyzed Through Constitutional InterpretationDokument10 SeitenRight to Food in India Analyzed Through Constitutional Interpretationsruti chandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mattice-Mault Compaint Paperwork (256222)Dokument21 SeitenMattice-Mault Compaint Paperwork (256222)News 8 WROCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialogue V Mchugh: A Charter of Rights in NSWDokument10 SeitenDialogue V Mchugh: A Charter of Rights in NSWSeanGongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 - PWKDokument4 SeitenWeek 3 - PWKhalo akufikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muhammad Haseeb Tabassum (LMS)Dokument105 SeitenMuhammad Haseeb Tabassum (LMS)Saleiha SharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adolescent Alcohol AbuseDokument11 SeitenAdolescent Alcohol Abuse4-5 Raquyah MitchellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Case AssignmentDokument3 SeitenTax Case AssignmentChugsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet of Things Based Intelligent Drowsiness Alert SystemDokument5 SeitenInternet of Things Based Intelligent Drowsiness Alert SystemFlavio CarvalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSDRDokument1 SeiteCSDRbrijeshnarainsaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Management System: Shaurya Cement Industries Private LimitedDokument2 SeitenIntegrated Management System: Shaurya Cement Industries Private LimitedMechanical ShauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lindale Abrameit Hines Aff Michigan Debate Tournament Round1Dokument31 SeitenLindale Abrameit Hines Aff Michigan Debate Tournament Round1IanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily RoutineDokument1 SeiteDaily Routineapi-361779682Noch keine Bewertungen
- Five Models of Staff DevelopmentDokument34 SeitenFive Models of Staff DevelopmentZulaiha Abdul Rahman100% (3)
- The Science of Handwriting AnalysisDokument1 SeiteThe Science of Handwriting Analysisrajesh mehlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torren - NDDC LetterDokument2 SeitenTorren - NDDC LetterZobia1348Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Transformation StrategyDokument7 SeitenDigital Transformation StrategyMa10centNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Train Radio CommunicationDokument8 SeitenMobile Train Radio CommunicationMadhumitha ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overspeed Verification TestDokument2 SeitenOverspeed Verification TestRichard ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Media and Its Impact On Personal Development NewDokument2 SeitenSocial Media and Its Impact On Personal Development NewRanti HarviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Career ObjectiveDokument1 SeiteCareer ObjectiveNitin MahawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Quality Kings Fund February 2016Dokument38 SeitenImproving Quality Kings Fund February 2016Robert CoffinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notice: Environmental Statements Availability, Etc.: New England Fishery Management CouncilDokument2 SeitenNotice: Environmental Statements Availability, Etc.: New England Fishery Management CouncilJustia.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wftda Statsbook Full Us LetterDokument58 SeitenWftda Statsbook Full Us Lettermariana jaquelineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bengson vs. Cruz GR NO 142840Dokument2 SeitenBengson vs. Cruz GR NO 142840Atheena Marie PalomariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andover Swim LessonsDokument7 SeitenAndover Swim LessonsIola IolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication: Siti Azilah AtanDokument22 SeitenCommunication: Siti Azilah AtanIslahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guia Mun Pueblos IndigenasDokument25 SeitenGuia Mun Pueblos IndigenasRoberto ValladaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methodology in Accounting & Finance, SY BCAF, Sem IV, SAMPLEDokument10 SeitenResearch Methodology in Accounting & Finance, SY BCAF, Sem IV, SAMPLEPrathamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPTXDokument23 SeitenPPTXherrajohnNoch keine Bewertungen