Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pressure Transient Analysis: Orientation/Diagnostics
Hochgeladen von
Yaser RashedOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pressure Transient Analysis: Orientation/Diagnostics
Hochgeladen von
Yaser RashedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pressure Transient Analysis
Orientation/Diagnostics
Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U.
Department of Petroleum Engineering
Texas A&M University
College Station, TX 77843-3116
+1.979.845.2292 — t-blasingame@tamu.edu
Slide — 1
Pressure Transient Analysis: Philosophy/Objectives
Q. Issues with pressure transient analysis (PTA)?
A. Design → implementation → interpretation → analysis → review.
z Objectives of Pressure Transient Testing:
Evaluate reservoir pressure (initial or average pressure).
Evaluate reservoir fluid (fluid samples collected for lab study).
Estimate reservoir properties: k, S, xf, λ, ω, etc.
Estimate reservoir volumetrics: fluid-in-place, drainage area.
z Input Data:
BOTTOMHOLE pressure data (accurate to < 1 part in 10,000).
SURFACE flowrate data (often poorly measured/recorded).
Fluid properties: FVF, viscosity, compressibility, ...
Reservoir properties: h, φ, rw, cf, ...
z Results of PTA Interpretation:
Productive capacity of the WELL (damage/stimulation).
Productive capacity of the RESERVOIR (transmissibility).
Current average reservoir pressure.
Reservoir limits (for production to pseudosteady-state).
Well interference effects.
Well/Reservoir specific parameters: Cs, xf, λ, ω, Lfault, rcomp, kv/kh, ...
z Discussion: Pressure Transient Analysis — Philosophy/Objectives
Design/implementation issues? (prepare well for testing, model test)
Interpretation/analysis issues? (model uniqueness)
Slide — 2
Pressure Transient Analysis: Summary of Diagnostics
Q. Key elements of PTA diagnostics?
A. Utilize "regime-specific" data functions, use multiple data functions.
z Discussion: Pressure Transient Analysis — Summary of Diagnostics
Δp function (pressure drop)? (traditional diagnostic)
Δpd function (Bourdet derivative)? (primary diagnostic — IARF)
Δpβd function (β-derivative)? (new diagnostic — VF, NF, Hz, Faults, etc.)
Slide — 3
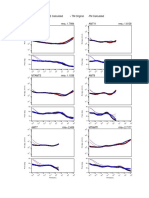
Diagnostic Plot: Infinite Acting Radial Flow
Type Curve for an Unfractured Well in an Infinite-Acting Homogeneous Reservoir
with Wellbore Storage and Skin Effects.
3
10
Legend: Radial Flow Type Curves
pD Solution
pDd Solution
100
pDβ d Solution 10 80
2
10 10 60
50 10
10 40
30 10
20 10
10 15
Wellbore Storage 10 10
8 10
Domination Region 104 106
1 10 3
10 1 10210
3 10 -2
3×10 1×10-2
pD, pDd and pDbd
100 2s -3
10 CDe =1×10
0
10
Radial Flow Region
2s -3
CDe =1×10 CDe =1×10
2s -3
-1 -3
10 3×10-2 3×10-2
-1 1 1×10
10
3 2 101 3
104 10
10 106 8
10 10
1015
20 10
10 10
30
-2 Wellbore Storage 40 50
10 10 10 60
Distortion Region 80 10
10
100
10
-3
10
-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
tD/CD
z Discussion: Diagnostic Plot — Infinite Acting Radial Flow
Δp function? ("hockey stick" behavior — WBS → IARF)
Δpd function? (IARF — pDd = 1/2)
Δpβd function? (WBS Domination — pDβd = 1)
Slide — 4
Diagnostic Plot: Sealing Faults
Dimensionless Pressure Derivative Type Curves for Sealing Faults
(Inifinite-Acting Homogeneous Reservoir)
4
10
Legend: "Bourdet" Well Test Pressure Derivative
Single Fault Case
2 Perpendicular Faults (2 at 90 Degrees) 3 Perpendicular
2 Parallel Faults (2 at 180 Degrees) Faults
3
10 3 Perpendicular Faults (3 at 90 Degrees)
β-Pressure Derivative Function, pDβd = (tD/pD) d/dtD(pD )
"Bourdet" Well Test Pressure Derivative, pDd = tD dpD/dtD
2 Parallel
Faults
2
10
pDd = tD dpD/dtD
1
10 2 Perpendicular
Faults
Undistorted
Single
Radial Flow Behavior
0 Fault
10
3 Perpendicular 2 Parallel 2 Perpendicular
Faults Faults Faults
-1
10
pDβ d = (tD/pD) dpD/dtD Single
Fault
-2 Legend: β -Pressure Derivative Function
10
Single Fault Case
2 Perpendicular Faults (2 at 90 Degrees)
2 Parallel Faults (2 at 180 Degrees)
3 Perpendicular Faults (3 at 90 Degrees)
-3
10
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
2
tD/LD (LD = Lfault/rw)
z Discussion: Diagnostic Plot — Sealing Faults
Δp function? (not included in this plot)
Δpd function? (IARF — pDd = 1/2; single/2-perpendicular faults = constant)
Δpβd function? (2-parallel/3-perpendicular faults = constant)
Slide — 5
Diagnostic Plot: Fractured Well (no WBS)
Type Curve for a Well with a Finite Conductivity Vertical
Fractured in an Infinite-Acting Homogeneous Reservoir
(CfD = (wkf)/(kxf) = 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, 10000)
1
10
CfD=0.25
0.5 1
0
10 4
CfD=1×10 5 Radial Flow Region
pD, pDd and pDβd
3
1×10 500
2
1
0.5
-1 1 CfD=0.25
10 2
-2
10
Legend:
pD Solution
pDd Solution
4
CfD=1×10 pDβd Solution
-3
10
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
tDxf
z Discussion: Diagnostic Plot — Fractured Well (no WBS)
Δp function? (BLF: pD = 1/4 slope, FLF: pD = 1/2 slope)
Δpd function? (BLF: pDd = 1/4 slope, FLF: pDd = 1/2 slope, IARF: pDd = 1/2)
Δpβd function? (BLF: pDβd = 1/4, FLF: pDβd = 1/2)
Slide — 6
Diagnostic Plot: Fractured Well (w/WBS)
Type Curve for a Well with Finite Conductivity Vertical Fracture in an Infinite-Acting
Homogeneous Reservoir with Wellbore Storage Effects CfD = (wkf)/(kxf)= 10
1
10
2 0
Legend: CfD = (wkf)/(kxf)= 10 1×10 1
1×10
1×10
pD Solution -1 1×10
-2
1×10
pDβd Solution -3
2 1×10
0 1×10
10
-3
1×10 1×10
-5 -4
Wellbore Storage 1×10
-6
Domination Region CDf=1×10
-2
1×10
-1 -4 0
10 1×10 1×10
1 1×10
pD and pDβd
2
-5 1×10
1×10
-6
CDf=1×10
-2
10
Radial Flow Region
-3 Wellbore Storage
10
Distortion Region
-4
10
-4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
tDxf/CDf
z Discussion: Diagnostic Plot — Fractured Well (w/WBS) (THIS CASE)
Δp function? (WBS: pD = 1 slope, BLF: pD = 1/4 slope)
Δpd function? (not included on this plot)
Δpβd function? (WBS: pDβd = 1, BLF: pDβd = 1/4)
Slide — 7
Diagnostic Plot: Horizontal Well (no WBS)
Type Curve for a Infinite Conductivity Horizontal Well in an Infinite-Acting
Homogeneous Reservoir (LD= 0.1, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100).
2
10
LD= 0.1
0.125
1
10
0.25
0.5 1
LD= 0.1
pD, pDd and pDβd
0.125
0
Infinite Conductivity
10 0.25
Vertical Fracture
0.5
5 100
10 5
10 25
50
-1
10 1
25
0.5
50
0.25
100
-2 25
Legend: 0.125
10 L=0.1
pD Solution
50 Infinite Conductivity pDd Solution
Vertical Fracture
pDβ d Solution
-3
10
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
tDL
z Discussion: Diagnostic Plot — Horizontal Well (no WBS) (THIS CASE)
Δp function? (FLF: pD = 1/2 slope)
Δpd function? (FLF: pDd = 1/2 slope, IARF: pDd = 1/2)
Δpβd function? (FLF: pDβd = 1/2)
Slide — 8
Diagnostic Plot: Horizontal Well (w/WBS)
Type Curve for an Infinite Conductivity Horizontal Well in an Infinite-Acting
Homogeneous Reservoir with Wellbore Storage Effects (LD = 100).
2
10
Legend: LD = 100
pD Solution Radial Flow Region
1
pDβ d Solution
10 2
1×10 1 -1
1×10
Wellbore Storage 1 1×10
-2
Domination Region 1×10 1×10
-3
1×10
-4
-6
0 CDL=1×10
pD and pDβd
10 -5
1×10
-6
-5
CDL=1×10
1×10
-4
-3 1×10
-1 1×10
10 1
-1
-2
1×10
1 1×10
1×10
2
1×10
-2
10
Wellbore Storage
Distortion Region
-3
10
-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
tDL/CDL
z Discussion: Diagnostic Plot — Horizontal Well (w/WBS) (THIS CASE)
Δp function? (WBS: pD = 1 slope, FLF: pD = 1/2 slope)
Δpd function? (not included on this plot)
Δpβd function? (WBS: pDβd = 1, FLF: pDβd = 1/2)
Slide — 9
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Stable Region: Fig. 6 D-Partition Boundary For Current Controller Design For Absolute StabilityDokument2 SeitenA Stable Region: Fig. 6 D-Partition Boundary For Current Controller Design For Absolute StabilityDr. Nitin LangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagram GaDokument2 SeitenDiagram GaDr. Nitin LangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Stable Region: Fig. 6 D-Partition Boundary For Current Controller Design For Absolute StabilityDokument2 SeitenA Stable Region: Fig. 6 D-Partition Boundary For Current Controller Design For Absolute StabilityDr. Nitin LangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- FFT DiagramDokument2 SeitenFFT DiagramDr. Nitin LangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI UnitsDokument2 SeitenSI UnitsStephen FrazierNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Conventional Water TreatmentDokument80 Seiten03 Conventional Water Treatmentbksri1239561Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pcm2ba A BodyDokument1 SeitePcm2ba A BodyJubayer SabujNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mia Lead TabDokument11 SeitenMia Lead TablinkindouchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concentration Analyte Concentration: Aoac O A (2016) G S RDokument1 SeiteConcentration Analyte Concentration: Aoac O A (2016) G S RVăn MyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Richie Kotzen LicksDokument23 SeitenRichie Kotzen LicksPaco D100% (1)
- Science Acids Bases Salts Part 2 PDF 82Dokument5 SeitenScience Acids Bases Salts Part 2 PDF 82Shreya chaureNoch keine Bewertungen
- TE Original TE Calculated TM Original TM Calculated: Period (Sec) Period (Sec)Dokument2 SeitenTE Original TE Calculated TM Original TM Calculated: Period (Sec) Period (Sec)Aryono AdhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LR1 - Statistics and Probability - LESSON 3 4Dokument5 SeitenLR1 - Statistics and Probability - LESSON 3 4Leanne HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 未完成交響曲Dokument7 Seiten未完成交響曲nice IceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allspect v5Dokument1 SeiteAllspect v5Alvaro Alex Osorio HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 Borderou BacDokument1 Seite0 Borderou BacMarcela EmanuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allspect v5Dokument1 SeiteAllspect v5Alvaro Alex Osorio HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Kurt J. Lester, 2018) Pressure Measurement Technical NotesDokument5 Seiten(Kurt J. Lester, 2018) Pressure Measurement Technical NotesLucelly Muñoz AmarilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Other BSM Searches at The LHC: D.Bourilkov (For The ATLAS and CMS Collaborations)Dokument9 SeitenOther BSM Searches at The LHC: D.Bourilkov (For The ATLAS and CMS Collaborations)bourilkovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pseudo Section2Dokument1 SeitePseudo Section2M Rizky YudhaprasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diving Into Mastery (DiM) - Vertical Format - Representing NumbersDokument3 SeitenDiving Into Mastery (DiM) - Vertical Format - Representing Numberstabac_alinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantity TR AR MR: Price 10Dokument2 SeitenQuantity TR AR MR: Price 10Blossom KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Borderou EN8Dokument1 SeiteBorderou EN8dabitzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 12Dokument1 SeiteZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 12Pierre-Cécil KönigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ranges of Validity of Some Distribution Functions For Blast-Fragmented RockDokument27 SeitenRanges of Validity of Some Distribution Functions For Blast-Fragmented RockAlvaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iec 62305 1 7Dokument7 SeitenIec 62305 1 7Hamza AHMED SAADINoch keine Bewertungen
- Theology 8 The Laity and The Christian Family Quizzes Hands-On PerformanceDokument13 SeitenTheology 8 The Laity and The Christian Family Quizzes Hands-On PerformanceRexson TagubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OmniPop200 1Dokument282 SeitenOmniPop200 1Demetrio BenitezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 12 - Regresi Multi-LinierDokument22 SeitenLec 12 - Regresi Multi-LinierAsal ReviewNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC531 - Minutes of Meeting Assessment FormDokument2 SeitenMEC531 - Minutes of Meeting Assessment Formkhairi_mohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Confidence and WeatherDokument1 SeiteConsumer Confidence and WeatherJaphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOSFET Overview: Paul HaslerDokument14 SeitenMOSFET Overview: Paul HaslerBiju ChackoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communications UnderwaterDokument18 SeitenCommunications UnderwaterDamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabaq With Tang Band 4Dokument4 SeitenTabaq With Tang Band 4Lmute MedioliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foto Diodo Infrarrojo Receptor 5mmDokument1 SeiteFoto Diodo Infrarrojo Receptor 5mmcreative_26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coba 2Dokument1 SeiteCoba 2Annisa Trisnia SNoch keine Bewertungen
- bt cad cơ bảnDokument21 Seitenbt cad cơ bảnVõ Huỳnh Hữu NghịNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abe Construction Chemicals Flooring Conversion TablesDokument4 SeitenAbe Construction Chemicals Flooring Conversion TablesPrashant PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sma d2023Dokument1 SeiteSma d2023Mik VlogsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math DemoDokument9 SeitenMath DemoJohn PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wall Panel - Plywood T 18mm - Finish Cat Duco List Profil Wall Panel - Plywood T 18mm - Finish Cat DucoDokument1 SeiteWall Panel - Plywood T 18mm - Finish Cat Duco List Profil Wall Panel - Plywood T 18mm - Finish Cat DucoRatih WulandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outsourcing MatrixDokument2 SeitenOutsourcing MatrixKordasti EnglishNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Dancin' Shoes in C - PerformanceDokument3 Seiten7 Dancin' Shoes in C - PerformanceL. ZemnickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Lab Research Lab For Environmental For Environmental Nanotechnology NanotechnologyDokument10 SeitenResearch Lab Research Lab For Environmental For Environmental Nanotechnology NanotechnologyChih-Hsiang LiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1: Response Spectrum For Zeta 0.02Dokument1 SeiteFigure 1: Response Spectrum For Zeta 0.02Yash DhabaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforcement Column D1 Reinforcement Column D2 Reinforcement Column D5 Reinforcement Column D6Dokument1 SeiteReinforcement Column D1 Reinforcement Column D2 Reinforcement Column D5 Reinforcement Column D6Nae GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double - Indexing - Multiplex - Sequencing 6Dokument1 SeiteDouble - Indexing - Multiplex - Sequencing 6BobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Corrosion Rate of The Carbon Steel in Atmospheric ExposureDokument4 SeitenDetermination of Corrosion Rate of The Carbon Steel in Atmospheric ExposureForood TorabianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 88p PDFDokument26 Seiten88p PDFEduardo Raúl Roque CasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Нулевой Вариант - 2023-2024Dokument5 SeitenНулевой Вариант - 2023-2024АСЫЛБЕК СаматовNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pseudo SectionDokument1 SeitePseudo SectionM Rizky YudhaprasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milena Araya Araya 15785243-4 CBCT Reporte Maxilar Dte. 2.1Dokument1 SeiteMilena Araya Araya 15785243-4 CBCT Reporte Maxilar Dte. 2.1milenaaraya20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hold Back The River TABDokument1 SeiteHold Back The River TABmastrodommyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE Class Record 1Dokument16 SeitenPE Class Record 1SHERRIE MAE BIJASANoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Half, Five-Tenths, and Fifty Hundredths: e EmemberDokument9 SeitenOne-Half, Five-Tenths, and Fifty Hundredths: e EmemberRukmani VenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tornado IlDokument1 SeiteTornado IlHspetrocrusosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tornado Il PDFDokument1 SeiteTornado Il PDFHspetrocrusosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dusty in The Wind - Violão 1 (A)Dokument2 SeitenDusty in The Wind - Violão 1 (A)Victor MatosNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE Online Education Informational SlidesDokument6 SeitenSPE Online Education Informational SlidesYaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE Ementoring ProgramDokument1 SeiteSPE Ementoring ProgramYaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Career Pathways FairDokument1 SeiteVirtual Career Pathways FairYaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE Bookstore Program FinalDokument1 SeiteSPE Bookstore Program FinalYaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE Global Training ProgramDokument1 SeiteSPE Global Training ProgramYaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Pressure Drawdown Test Analysis: (Lee Text (1st Edition), Example 3.2)Dokument5 SeitenExample Pressure Drawdown Test Analysis: (Lee Text (1st Edition), Example 3.2)Yaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusivity Equation: 13 February 2008Dokument17 SeitenDiffusivity Equation: 13 February 2008Yaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petroleum Engineering 324 - Well Performance Syllabus and Administrative Procedures Spring 2009Dokument13 SeitenPetroleum Engineering 324 - Well Performance Syllabus and Administrative Procedures Spring 2009Yaser Rashed100% (1)
- P324 08A Exam 01 KeyDokument36 SeitenP324 08A Exam 01 KeyYaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- T3 - Building A Model For A Saturated Reservoir Using CMG - IMEX Simulator (Blackoil Model)Dokument35 SeitenT3 - Building A Model For A Saturated Reservoir Using CMG - IMEX Simulator (Blackoil Model)Yaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5: Fluid SaturationDokument5 SeitenChapter 5: Fluid SaturationYaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6: Permeability Measurement: H H L KA QDokument9 SeitenChapter 6: Permeability Measurement: H H L KA QYaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- T2 - Modeling Hydraulic Fractured Gas Wells Using CMG Using CMG - IMEX Simulator (Blackoil Model)Dokument31 SeitenT2 - Modeling Hydraulic Fractured Gas Wells Using CMG Using CMG - IMEX Simulator (Blackoil Model)Yaser RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- T1 - Building A Model For A Tight Sand Gas Reservoir Using CMG - IMEX Simulator (Blackoil Model)Dokument37 SeitenT1 - Building A Model For A Tight Sand Gas Reservoir Using CMG - IMEX Simulator (Blackoil Model)Yaser Rashed100% (1)
- ADDIE - Model - For - E-Learning - Sinteza2017 - Corr-With-Cover-Page-V2 (New)Dokument6 SeitenADDIE - Model - For - E-Learning - Sinteza2017 - Corr-With-Cover-Page-V2 (New)arief m.fNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalki ProjectDokument3 SeitenKalki ProjectMandar SohoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership PaperDokument6 SeitenLeadership PaperSTANCIU VALENTINNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShakespeareDokument12 SeitenShakespeareapi-510189551Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management - Risk and Return Assignment 2 - Abdullah Bin Amir - Section ADokument3 SeitenFinancial Management - Risk and Return Assignment 2 - Abdullah Bin Amir - Section AAbdullah AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Position Paper On Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity and Expression (SOGIE)Dokument3 SeitenPosition Paper On Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity and Expression (SOGIE)SYDNEY MARASIGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- b8c2 PDFDokument193 Seitenb8c2 PDFRhIdho POetraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTRC FInal Report 558 Development of Performance-Based Specifications For Louisiana Asphalt MixturesDokument149 SeitenLTRC FInal Report 558 Development of Performance-Based Specifications For Louisiana Asphalt MixtureswalaywanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GALVEZ Vs CADokument2 SeitenGALVEZ Vs CARyannCabañeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- (2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiDokument11 Seiten(2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiFajar HatmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average and Instantaneous AccelerationDokument35 SeitenAverage and Instantaneous AccelerationaraneyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Template - 2018-2020Dokument2 SeitenCV Template - 2018-2020Rahul AbhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heirs of Candelaria V RomeroDokument2 SeitenHeirs of Candelaria V Romeromoniquehadjirul100% (1)
- Mécanisme de La Physionomie HumaineDokument2 SeitenMécanisme de La Physionomie HumainebopufouriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child Development Assessment Tools in Low-Income and Middle-Income CountriesDokument9 SeitenChild Development Assessment Tools in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countriesalibaba1888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Filters SlideDokument17 SeitenFilters SlideEmmanuel OkoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- N Advocates Act 1961 Ankita218074 Nujsedu 20221008 230429 1 107Dokument107 SeitenN Advocates Act 1961 Ankita218074 Nujsedu 20221008 230429 1 107ANKITA BISWASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Στέργος Νεκτάριος-Μικκιος-CVDokument4 SeitenΣτέργος Νεκτάριος-Μικκιος-CVNektarios MikkiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling Strategies For Heterogeneous WastesDokument18 SeitenSampling Strategies For Heterogeneous Wastesmohammed karasnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO - Config Sap Top JobsDokument81 SeitenCO - Config Sap Top JobsAditya PakalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Step by Step Approach To The Modeling of Chemical Engineering Processes, Using Excel For Simulation (2018)Dokument182 SeitenA Step by Step Approach To The Modeling of Chemical Engineering Processes, Using Excel For Simulation (2018)Anonymous NxpnI6jC100% (7)
- Liquid Holdup in Large-Diameter Horizontal Multiphase PipelinesDokument8 SeitenLiquid Holdup in Large-Diameter Horizontal Multiphase PipelinessaifoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agvan DorzhievDokument7 SeitenAgvan DorzhievMichael FelicianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Q1 PDFDokument29 SeitenJurnal Q1 PDFSepti DamayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric Data Science 1 150Dokument150 SeitenFabric Data Science 1 150pascalburumeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ruchika Project ReportDokument28 SeitenRuchika Project Reportnavdeep2309Noch keine Bewertungen
- Law of Conservation of MassDokument7 SeitenLaw of Conservation of Massحمائل سجادNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project RealDokument4 SeitenProject RealKenneth Jay BagandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Consumer Behavior: by Dr. Kevin Lance JonesDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To Consumer Behavior: by Dr. Kevin Lance JonesCorey PageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why We're Still Learning New Things About The JFK AssassinationDokument8 SeitenWhy We're Still Learning New Things About The JFK AssassinationNolan SNoch keine Bewertungen