Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ray 1 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Raman GoyalOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ray 1 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Raman GoyalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
(Paper-2) 13
PART – III : PHYSICS
Single Correct Choice Type
This Section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices a), b)
c) and d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct. (Marking Scheme : +6, – 2)
1. A concave convex lens has an index of refraction 1.5 and the radii of curvature of its
surfaces are 10 cm and 20 cm. The concave surface is upwards and it is filled with oil
= 1.6. Find the focal length of oil glass combination.
(a) 18.18 cm (b) 15 cm
(c) 22 cm (d) 17.5 cm
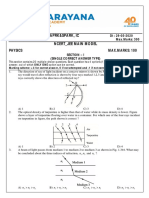
2. A concave mirror of focal length 2 cm is placed on a glass slab as shown in the figure. Then
the image of object O formed due to reflection at mirror and then refraction by the slab.
(a) will be virtual and will be at 2 cm from the pole of the concave mirror
(b) will be virtual and formed on the pole of the mirror
(c) will be virtual and on the object itself
(d) none of these
Space for Rough Work
Patiala Centre : TEL. 0175-5012029, 5012030
Lakshya Forum for Competitions Pvt. Ltd. Sangrur Centre : TEL. 01672-500136
TM www.lakshyainstitute.com Chandigarh Centre : TEL. 0172-4612029, 4622029
Forum for Competitions Panchkula Centre : TEL. 0172-4004028, 4005028
14 (Paper-2)
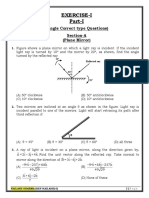
3. A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of incidence 45° as shown in the figure.
After reflection, the ray passes through a prism of refractive index 1.50, whose apex angle
is 4°. The angle through which the mirror should be rotated if the total deviation of the ray
is to be 90° is
(a) 1° clockwise (b) 1° anticlockwise
(c) 2° clockwise (d) 2° anticlockwise
4. The figure shows a ray incident at an angle i = /3. If the plot drawn shown the variation of
1
|r – i| versus k, (r = angle of refraction)
2
2
(a) the value of k1 is (b) the value of 1 = /3
3
(c) the value of 2 = /6 (d) the value of k2 is 1
Space for Rough Work
Patiala Centre : TEL. 0175-5012029, 5012030
Lakshya Forum for Competitions Pvt. Ltd. Sangrur Centre : TEL. 01672-500136
TM www.lakshyainstitute.com Chandigarh Centre : TEL. 0172-4612029, 4622029
Forum for Competitions Panchkula Centre : TEL. 0172-4004028, 4005028
(Paper-2) 15
5. If an object is placed at A (OA > f); Where f is the focal length of the lens the image is found
to be formed at B.A perpendicular is erected at O and C is chosen on it such that the angle
BCA is a right angle. Then the value of f will be
(a) AB/OC2 (b) (AC) (BC)/OC
(c) OC2/AB (d) (OC) (AB)/AC+BC
6. A beam of diameter ‘d’ is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature
of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to d, then the diameter of the beam at the
base of the hemisphere will be
3
(a) d (b) d
4
d 2
(c) (d) d
3 3
Space for Rough Work
Patiala Centre : TEL. 0175-5012029, 5012030
Lakshya Forum for Competitions Pvt. Ltd. Sangrur Centre : TEL. 01672-500136
TM www.lakshyainstitute.com Chandigarh Centre : TEL. 0172-4612029, 4622029
Forum for Competitions Panchkula Centre : TEL. 0172-4004028, 4005028
16 (Paper-2)
7. A flat glass slab of thickness 6 cm and index 1.5 is placed in front of a plane mirror. An
observer is standing behind the glass slab and looking at the mirror. The actual distance of
the observer from the mirror is 50 cm. The distance of his image from himself, as seen by
the observer is
(a) 94 cm (b) 96 cm (c) 98 cm (d) 100 cm
8. A concave-convex glass (index = 1.5) lens has radii of curvatures 60 cm and 40 cm
respectively. Its convex surface is silvered and it is placed on a horizontal table with concave
surface up. The concave surface is then filled with a liquid of index 2.0. The combination is
like a
(a) Concave mirror (b) Convex mirror
(c) Flat mirror (d) Convex lens
9. In the figure ABC is the cross section of a right angled prism and BCDE is the cross section
of a glass slab. The value of so that light incident normally on the face AB does not cross
the face BC is (given sin–1 (3/5) = 37°)
(a) 37° (b) > 37°
(c) 53° (d) < 53°
10. A point object is moving with velocity 10 m/s along the principal axis of a stationary lens.
The lens is free to move along its axis. The mass of the object and the lens is same. There
are no external forces on the system of object and the lens. If the collision is elastic then just
after the collision the speed of the image relative to ground will be
(a) zero, only if the lens is converging (b) zero, only if the lens is diverging
(c) zero, for any type of lens (d) 20 m/s, for any type of lens.
Space for Rough Work
Patiala Centre : TEL. 0175-5012029, 5012030
Lakshya Forum for Competitions Pvt. Ltd. Sangrur Centre : TEL. 01672-500136
TM www.lakshyainstitute.com Chandigarh Centre : TEL. 0172-4612029, 4622029
Forum for Competitions Panchkula Centre : TEL. 0172-4004028, 4005028
(Paper-2) 17
Multiple Correct Choice Type
This Section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices a), b) c)
and d) out of which ONE OR MORE may be correct. (Marking Scheme : +4, 0)
11. Two refracting media are separated by a spherical interface as shown in the figure. PP’ is
the principal axis, 1 and 2 are the refractive indices of medium of incidence and medium of
refraction respectively. Then
P P'
(a) if 2 > 1, then there cannot be a real image of real object.
(b) if 2 > 1, then there cannot be a real image of virtual object.
(c) if 1 > 2, then there cannot be a virtual image of virtual object.
(d) if 1 > 2, then there cannot be a real image of real object.
12. A cubical block of glass of refractive index n1 is in contact with the surface of water of
refractive index n2. A beam of light is incident on vertical face of the block (see figure).
After refraction, a total internal reflection at the base and refraction at the opposite vertical
face, the ray emerges out at an angle . The value of is given by
(a) sin n12 n 22 (b) tan n12 n 22
1 1
(c) sin (d) tan
n12 n 22 n12 n 22
Space for Rough Work
Patiala Centre : TEL. 0175-5012029, 5012030
Lakshya Forum for Competitions Pvt. Ltd. Sangrur Centre : TEL. 01672-500136
TM www.lakshyainstitute.com Chandigarh Centre : TEL. 0172-4612029, 4622029
Forum for Competitions Panchkula Centre : TEL. 0172-4004028, 4005028
18 (Paper-2)
13. There are three optical media 1, 2, and 3 with their refractive indices 1 > 2 > 3. (TIR
total internal reflection)
(a) when a ray of light travels from 3 to 1 no TIR will take place
(b) critical angle between 1 and 2 is less than the critical angle between 1 and 3
(c) critical angle between 1 and 2 is more than the critical angle between 1 and 3
(d) chances of TIR are more when ray of light travels from 1 to 3 as compared to the case
when it travels from 1 to 2
14. Parallel rays of light are falling on convex spherical surface of radius of curvature R = 20
cm as shown. Refractive index of the medium is = 1.5. After refraction from the spherical
surface parallel rays
(a) actually meet at some point
(b) appears to meet after extending the refracted rays backwards
(c) meet (or appears to meet) at a distance of 30 cm from the spherical surface
(d) meet (or appears to meet) at a distance of 60 cm from the spherical surface
15. Focal length of a lens in air is f. Refractive index of the lens is . Focal length changes to f1
if lens is immersed in a liquid of refractive index and it becomes f2 if the lens is immersed
2
in a liquid of refractive index 2. Then
f
(a) f1 (b) f2 = – 2f
2
3f
(c) f 2 (d) Data is insufficient
2
Space for Rough Work
Patiala Centre : TEL. 0175-5012029, 5012030
Lakshya Forum for Competitions Pvt. Ltd. Sangrur Centre : TEL. 01672-500136
TM www.lakshyainstitute.com Chandigarh Centre : TEL. 0172-4612029, 4622029
Forum for Competitions Panchkula Centre : TEL. 0172-4004028, 4005028
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Part - Iii: PhysicsDokument9 SeitenPart - Iii: PhysicsRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half Yearly Revision AssignmentDokument28 SeitenHalf Yearly Revision AssignmentSidra QueenNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP-3 Geo Ques p65Dokument2 SeitenDPP-3 Geo Ques p65Maddala NagendrakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioiogyDokument8 SeitenBioiogyAmjid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 OpticsDokument7 Seiten17 OpticssinghashubhadeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half Yearly Revision Assignment For Grade X 2022Dokument7 SeitenHalf Yearly Revision Assignment For Grade X 2022Anabella NavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 39 DTW NX QBTJ TBXs Wi Ip 8Dokument8 Seiten39 DTW NX QBTJ TBXs Wi Ip 8Movie mania tricksNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR - Iit - Incomming-Cosaprk&Spark, Ic Ncert - Jee Main Model: Physics MAX - MARKS: 100Dokument8 SeitenSR - Iit - Incomming-Cosaprk&Spark, Ic Ncert - Jee Main Model: Physics MAX - MARKS: 100Yogy YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surprise Test (Physics)Dokument5 SeitenSurprise Test (Physics)sara DaphneNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAY OPTICS MCQsDokument5 SeitenRAY OPTICS MCQsaryaadarshsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics - Refraction at Plane Surfaces: Test Time: 30 MinsDokument2 SeitenOptics - Refraction at Plane Surfaces: Test Time: 30 MinsHarsh TyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII - Revision Sheet - 2 - PhysicsDokument2 SeitenXII - Revision Sheet - 2 - PhysicsVipin VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kssirs12thsheet01 GeometricalopticsDokument66 SeitenKssirs12thsheet01 GeometricalopticsAshutosh TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics AssignmentDokument9 SeitenOptics AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics MCQDokument8 SeitenRay Optics MCQVamsi Vangara100% (1)
- (Ch-9) Ray DPP 7Dokument9 Seiten(Ch-9) Ray DPP 7Rijak KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Optics 1Dokument4 SeitenTest Optics 1Anant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics CP23 - Ray Optics & Optical InstrumentsDokument9 SeitenPhysics CP23 - Ray Optics & Optical InstrumentsKumaranRamu100% (1)
- MCQ Ray OpticsDokument4 SeitenMCQ Ray OpticsDikshant SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vmts Jee Part Test 6Dokument14 SeitenVmts Jee Part Test 6harshit pandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resonance INJSO Full Test - 5Dokument18 SeitenResonance INJSO Full Test - 58134 Ashwin RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247Dokument4 SeitenDPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247gaurankkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics XII Ray OpticsDokument19 SeitenPhysics XII Ray OpticsKartik YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy - Dpp-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDokument10 SeitenPhy - Dpp-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsSrusti Srujanika100% (1)
- Refraction of Light at Curved SurfaceDokument12 SeitenRefraction of Light at Curved Surfacenavrosepreetsingh8a4hhps14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asif Insight Physics OpticsDokument14 SeitenAsif Insight Physics OpticsMOHAMMED ASIF67% (3)
- Revision QP Set ADokument5 SeitenRevision QP Set Aimraan smNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometricaloptics 2 31Dokument30 SeitenGeometricaloptics 2 31Harshit RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ks Sirs 12th Sheet 01 Geometrical Optics 1664891760221 1Dokument65 SeitenKs Sirs 12th Sheet 01 Geometrical Optics 1664891760221 1Shubham BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class - X (Going To XI) Duration: 2 Hrs. - Maximum Marks: 180Dokument11 SeitenClass - X (Going To XI) Duration: 2 Hrs. - Maximum Marks: 180shubhamsuresh2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resilience: Er. Gaurav AgarwalDokument6 SeitenResilience: Er. Gaurav AgarwalRati SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XDokument4 SeitenSainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XBornil Bikash BhuyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Class 10 LightDokument8 SeitenMCQ Class 10 LightRithika GoruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan 03 Sep 2020Dokument14 SeitenAdobe Scan 03 Sep 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit PCB (NEET) 29.03.2020 For AmitDokument14 SeitenUnit PCB (NEET) 29.03.2020 For Amitinglesarvesh10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics (Ques Bank)Dokument7 SeitenRay Optics (Ques Bank)Om GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekend Test - 2: GRADE:-12 Subject:-Physics DATE:-12/08/22 Time: - 90 MinsDokument4 SeitenWeekend Test - 2: GRADE:-12 Subject:-Physics DATE:-12/08/22 Time: - 90 MinsKrishna ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 OpticsDokument46 Seiten12 OpticsSivakumar SarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL 10 CH Light Obj 1Dokument29 SeitenCL 10 CH Light Obj 1Harshavardhan RajaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)Dokument4 SeitenPHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)shylaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics & Optical Instruments, Home Work Sheet-1: Plane Mirror 1Dokument60 SeitenRay Optics & Optical Instruments, Home Work Sheet-1: Plane Mirror 1venkat krishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Ray OpticsDokument4 SeitenTest Ray OpticsSarvesh Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: ReflectionDokument20 SeitenPhysics: Reflectionhemal mitreshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50Q - Ray OpticsDokument10 Seiten50Q - Ray Opticskabir singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics Entrance Questions HannDokument4 SeitenRay Optics Entrance Questions HannPHYSCO BOT GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Geometrical OpticsDokument40 Seiten18 Geometrical OpticsSamsul BahriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On YoutubeDokument2 SeitenHysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On YoutubeAbhishek jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Test 6: (Optics)Dokument6 SeitenUnit Test 6: (Optics)padhi8480Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise-01: MCQ (Single Choice Correct)Dokument5 SeitenExercise-01: MCQ (Single Choice Correct)Abhishek jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics Mcq1Dokument7 SeitenOptics Mcq1Manash SinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phylight 1594463562136Dokument22 SeitenPhylight 1594463562136akshat goyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDokument8 SeitenRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsKoyal GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ace of PACE Medical Sample PaperDokument7 SeitenAce of PACE Medical Sample PaperHiten Tjs100% (1)
- Mock Test 17-5-2020Dokument16 SeitenMock Test 17-5-2020childicuNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main Level Practice Test-16: For JEE & NEET AspirantsDokument6 SeitenJEE Main Level Practice Test-16: For JEE & NEET AspirantsJeet GovindNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEETTest Paper - Physics - 27-4-2020Dokument4 SeitenNEETTest Paper - Physics - 27-4-2020Chandrika VeerareddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course: Geometrical Optics: Presented by Kailash SharmaDokument70 SeitenCourse: Geometrical Optics: Presented by Kailash SharmaIITCracke JyothirNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMI Mains PDFDokument4 SeitenEMI Mains PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEOC, Magnetism, WPEC, CM PDFDokument4 SeitenMEOC, Magnetism, WPEC, CM PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP PDFDokument2 SeitenMP PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective Questions: Section (A) : Measurement and Calculation of PressureDokument8 SeitenObjective Questions: Section (A) : Measurement and Calculation of PressureRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Opitics Disha Solns PDFDokument5 SeitenRay Opitics Disha Solns PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FXNS, RLNS, Sets, ITF, S&S, Log PDFDokument3 SeitenFXNS, RLNS, Sets, ITF, S&S, Log PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- KTG, Thermo - IITJEE Adv Test PDFDokument16 SeitenKTG, Thermo - IITJEE Adv Test PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics Ans PDFDokument1 SeiteRay Optics Ans PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat PDFDokument20 SeitenHeat PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Opitics Disha PDFDokument4 SeitenRay Opitics Disha PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEOC, Magnetism, WPEC, CM PDFDokument4 SeitenMEOC, Magnetism, WPEC, CM PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP - Daily Practice Problems: Name: DateDokument8 SeitenDPP - Daily Practice Problems: Name: DateRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids PDFDokument7 SeitenFluids PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Solutions PDFDokument7 SeitenHeat Transfer Solutions PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics Final Test JA 1.5 Hrs PDFDokument4 SeitenRay Optics Final Test JA 1.5 Hrs PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Test PDFDokument2 SeitenCE Test PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation of Centre of MassDokument14 SeitenPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation of Centre of MassRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics Ans PDFDokument1 SeiteRay Optics Ans PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eastern Europe 9 Getting StartedDokument14 SeitenEastern Europe 9 Getting StartedRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Series: Test - 9 (Objective) : PhysicsDokument4 SeitenTest Series: Test - 9 (Objective) : PhysicsRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- cHEM kINETICS, sURFACE CHEM PDFDokument2 SeitencHEM kINETICS, sURFACE CHEM PDFRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ics 2013Dokument883 SeitenIcs 2013Raman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eastern Europe 9 IndexDokument7 SeitenEastern Europe 9 IndexRaman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eastern Europe Czech Republic v1 m56577569830516526Dokument33 SeitenEastern Europe Czech Republic v1 m56577569830516526Raman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eastern Europe Bosnia Hercegovina v1 m56577569830516521Dokument18 SeitenEastern Europe Bosnia Hercegovina v1 m56577569830516521Raman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eastern Europe 9 ContentsDokument9 SeitenEastern Europe 9 ContentsRaman Goyal0% (1)
- Eastern Europe Bulgaria v1 m56577569830516522Dokument29 SeitenEastern Europe Bulgaria v1 m56577569830516522Raman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Character QuestionsDokument3 SeitenCharacter QuestionsAaron FarmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Big Table of Quantum AIDokument7 SeitenThe Big Table of Quantum AIAbu Mohammad Omar Shehab Uddin AyubNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUMBAI ConsultantsDokument43 SeitenMUMBAI ConsultantsER RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test 3.1 Math 10Dokument2 SeitenSummative Test 3.1 Math 10Christian DecenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Activity Sheet in Science-9: Week 7-Quarter 3Dokument5 SeitenLearning Activity Sheet in Science-9: Week 7-Quarter 3theinvaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2-Translation Practice MarkDokument3 SeitenUnit 2-Translation Practice MarkHương ThảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Surge NewDokument65 SeitenMind Surge NewmazzagraNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-04 Analysis and Design of Two-Way Slab With Beams (Coloured)Dokument63 SeitenL-04 Analysis and Design of Two-Way Slab With Beams (Coloured)Hidayat Ullah100% (3)
- 31 The Emergence of Social GerontologyDokument9 Seiten31 The Emergence of Social GerontologygiacomobarnigeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UK TV StreamingDokument22 SeitenUK TV StreamingSuhanto KastaredjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supg NS 2DDokument15 SeitenSupg NS 2DruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prima Magistra:: Wulan Rahayu Syachtiyani, Novi TrisnawatiDokument12 SeitenPrima Magistra:: Wulan Rahayu Syachtiyani, Novi TrisnawatiGita GloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dumisani Maths Prac AssignmentDokument6 SeitenDumisani Maths Prac AssignmentDumisani Tawanda DubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Pts GSL 8 - Inggris - JWBNDokument9 SeitenSoal Pts GSL 8 - Inggris - JWBNRindah Tiara SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Seminar Report CV94Dokument62 SeitenTechnical Seminar Report CV941MS19CV053 KARTHIK B SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Task 315Dokument9 SeitenBasic Task 315gaikwadamitag1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Czujniki Temperatury MOTOMETERDokument7 SeitenCzujniki Temperatury MOTOMETERhelp3rNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.Space-Activity BookDokument21 Seiten3.Space-Activity BookRania FarranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vocabulary Placement TestDokument3 SeitenVocabulary Placement TestMonica Vergara MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Mango Cultivation ProjectDokument40 SeitenReport On Mango Cultivation Projectkmilind007100% (1)
- Prompt by NikistDokument4 SeitenPrompt by NikistMãnoj MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sepction - 3Dokument3 SeitenSepction - 3k koradiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSO Digital Storage Oscilloscope: ApplicationDokument2 SeitenDSO Digital Storage Oscilloscope: ApplicationmsequipmentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cold-Formed Steel Portal Frame Moment-Resisting Joints Behaviour Capacity and DesignDokument13 SeitenCold-Formed Steel Portal Frame Moment-Resisting Joints Behaviour Capacity and DesignAhmed MoniemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collaboration Proposal FormDokument4 SeitenCollaboration Proposal FormGabriel TecuceanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding SymbolDokument8 SeitenWelding SymbolMuhammad Cahya Adi PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Office Phone Number Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh (A.p.)Dokument11 SeitenCurrent Office Phone Number Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh (A.p.)Manoj Digi Loans100% (1)
- TUYA ManualDokument2 SeitenTUYA ManualMagandang MallNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09-Hispec DespecDokument51 Seiten09-Hispec DespecHyungon KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proper Storage of Instruments2Dokument20 SeitenProper Storage of Instruments2Pierre Vincent PorrasNoch keine Bewertungen