Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pharmacology Long Exam 1 2 Yr - 2 Sem 2016: ND ND
Hochgeladen von
Carlos NiñoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pharmacology Long Exam 1 2 Yr - 2 Sem 2016: ND ND
Hochgeladen von
Carlos NiñoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
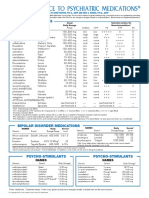
PHARMACOLOGY 29 felbamate - aplastic
LONG EXAM 1
30 phenytoin - gingival
2nd yr – 2nd sem 2016
31 valproic - neural tube
1 phenytoin - na
2 carba - na 32 valproic - 50-100
3 pheno - gaba 33 carba – 5-15 (but should be 4-12)
4 vigabatrin - gaba transaminase
5 lamotigrine - na 34 phenytoin - 20-50 (10-20)
6 lithium - gsk 35 phenobarb - 5-10 (10-40)
7 chlorpromazine - dopa blocker 36 succinylcholine - depo
8 haloperidol - dopa blocker 37 tubocurarine - nondepo
9 clozapine- dopa blocker ----- 38 atracurium - nondepo
10 fluoxetine - ssri 39 vero - nondepo
11 amitriptyline - TCA 40 rocu - nondepo
12 tranylcypromine - MAOI 41 cyp inh - cimetidine
13 ergot deriv receptor agonist - bromocriptine 42 long acting - clorazepate
14 parkinson etiology - all (idiopathic, acquired, 43 selegiline + SSRI - serotonin sydrome
hereditary) 44 alcohol + tca - sedation
15 naloxone - antag 45 - depression
16 fentanyl - agonist 46 serotonin agonist - buspirone
17 nalbuphine - mixed 47 alcohol resembles - tca
18 meperidine - agonist 48 same with gaba (K receptor) - serotonin
19 lidocaine - amide local 49 alcohol tox – all ( toxic psychosis, ____, ____)
20 bupivacaine - amide local 50 pt coma, chronic alcoholic - wernicke
21 tetracaine - ester local 51 increased tendency to sleep - hypnosis
22 propofol - gen iv 52 phenobarb effect in hypnosis - dec latency of
23 halothane - gen inh sleep
24 mc ae antiparkinsonism - tremor? 53 total cost - cost
25 cardinal feature - resting tremor 54. Parkinsons disease- amyloid deposit
26 parkinsonism - all of the above (slow mvt, 55 Mirtazipine - wt gain/sedation
stiffness, tremors) 56 venlafaxine - sedation
27 pheno - hyperactivity in children 57 clomipramine- hypotension
28 carba - aplastic 58 nefazodone- hypotension
59 cause inh - cl channels activated 75 In what circumstances will they need to
come earlier – D
I. define the dx
76 active subs and dosage form –
II. specify the therapeutic objective
77 std dosage schedule –
III. inventory of effective groups of
drugs 78 std duration of tx –
IV. choose an effective group accdg to 79 successful outcome – parkinsons
criteria
80 parkinsons – loss of neurons from structure
V. choose P drug of the basal ganglia
VI. give complete information 81 _________ - neurons
60. mechanism of bacteria – I 82 neurodegenerative d/o – neuronal
degeneration in anatomically or functionally
61 S/Sx of the pt – I
related regions
62 pneumonia – I
83 alzheimers – loss of hippocampal and
63 advised the pt on vit C – II cortical neurons – impaired memory and
cognitive ability
64 give antibacterial – II or III?
84 ALS – muscle weakness
65 ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin – III
85 etiology: haloperidol, thorazine, etc –
66 Rx writing – V? parkinsons
67 choose a drug – V 86 dopamine aagonist SE – hallucinosis
68 ….. – IV 87 levodopa combined with – carbidopa
88 cholinergic agonist – bethanecol
a. effects of the drug 89 sedative-hyp excretion – kidney
b. instructions 90
c. warnings
d. future consultations
69 w/c s/sx of the pt will disappear – A
70 when will the effect of the drug expected to
start – A
71 how/when should it be taken – B
72 what are we going to do w left over drugs –
B
73 when should the drug not be taken – C
74 maximum dose of the drug – C
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- (Mebooksfree Net) Bd&Cha&Hum&Ana&Vol4&7thDokument215 Seiten(Mebooksfree Net) Bd&Cha&Hum&Ana&Vol4&7thElias Răduță100% (2)
- Jason Edward Cafer MD, Julianna Link PA-C - Cafer's Antipsychotics - Visualize To Memorize (2020, Independently Published) - Libgen - LiDokument74 SeitenJason Edward Cafer MD, Julianna Link PA-C - Cafer's Antipsychotics - Visualize To Memorize (2020, Independently Published) - Libgen - LiElectric Amoeba100% (2)
- Example Personal StatementsDokument22 SeitenExample Personal Statementsstarblue265100% (1)
- Herbal Medication HandbookDokument125 SeitenHerbal Medication Handbooktracey younge83% (6)
- Drug Interaction Chart for Antidepressants and PsychedelicsDokument3 SeitenDrug Interaction Chart for Antidepressants and PsychedelicsFred The Nomad100% (2)
- Paul D. Purves, George J. Klein, Peter Leong-Sit, Raymond Yee, Lorne J. Gula, Andrew D. Krahn-Cardiac Electrophysiology - A Visual Guide For Nurses, Techs, and Fellows-Cardiotext Publishing (2011)Dokument161 SeitenPaul D. Purves, George J. Klein, Peter Leong-Sit, Raymond Yee, Lorne J. Gula, Andrew D. Krahn-Cardiac Electrophysiology - A Visual Guide For Nurses, Techs, and Fellows-Cardiotext Publishing (2011)Mario Josipović100% (1)
- 1 Ep PDFDokument35 Seiten1 Ep PDFMiguel LizarragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSIO Prelims SamplexDokument11 SeitenPHYSIO Prelims SamplexCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Reference BWDokument2 SeitenQuick Reference BWmcbermudezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFDokument2 SeitenQuick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFAaron ShokarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrofisiologia Cardiaca Guia Viasual 1 PDFDokument80 SeitenElectrofisiologia Cardiaca Guia Viasual 1 PDFMiguel LizarragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Neurotransmitters and Their Role in Psychiatric DisordersDokument70 SeitenMajor Neurotransmitters and Their Role in Psychiatric DisordersVlad Si Camelia RachieruNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE STUDY Bronchial AsthmaDokument6 SeitenCASE STUDY Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de Castro86% (22)
- Neuro Board Exam StrategiesDokument8 SeitenNeuro Board Exam StrategiesshanuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glasgow Coma ScaleDokument2 SeitenGlasgow Coma Scalejean thereseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laurie Lundy-Ekman-Neuroscience - Fundamentals For Rehabilitation-Saunders (2007) (Trashed 2016-03-14 10-21-35) (Trashed 2019-05-29 09-55-40)Dokument645 SeitenLaurie Lundy-Ekman-Neuroscience - Fundamentals For Rehabilitation-Saunders (2007) (Trashed 2016-03-14 10-21-35) (Trashed 2019-05-29 09-55-40)Razvan Cde100% (1)
- SURFING National Biology 4 Maitaing Internal Sample PDFDokument21 SeitenSURFING National Biology 4 Maitaing Internal Sample PDFelamNoch keine Bewertungen
- neurotransmittersNSlectures HDokument67 SeitenneurotransmittersNSlectures Hapi-3784483Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plab2 Stations Topics New Old PDFDokument6 SeitenPlab2 Stations Topics New Old PDFBeaulahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plab2 Stations Topics New Old PDFDokument6 SeitenPlab2 Stations Topics New Old PDFBeaulahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertensive DietDokument6 SeitenHypertensive DietCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertensive DietDokument6 SeitenHypertensive DietCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyDokument23 Seiten14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyCandilicious10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medicament classification by category and commercial nameDokument2 SeitenMedicament classification by category and commercial nameAhmet Burak Canefendiç100% (1)
- AntiepilepticiDokument29 SeitenAntiepilepticiIskraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BY2201 Colm Basic NeurochemOct11Dokument96 SeitenBY2201 Colm Basic NeurochemOct11Rhys DunneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azam IndexDokument7 SeitenAzam IndexBiswajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurotransmitters and receptorsDokument8 SeitenNeurotransmitters and receptorsmahambaqaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Finals ReviewDokument2 SeitenPharmacology Finals ReviewVince CabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPM6A Research PaperDokument7 SeitenGPM6A Research PaperRida ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev. SystDokument101 SeitenRev. Systdr.israquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity NURS13 BSN3Dokument4 SeitenActivity NURS13 BSN3Danica Liah PanlilioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histophysiology of Synapses and Neurosecretion: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesVon EverandHistophysiology of Synapses and Neurosecretion: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- General PharmacologyDokument6 SeitenGeneral PharmacologyLaureece Salm ApduhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor ModulatorsDokument41 SeitenNicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor ModulatorsQi JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Pharma 1445 PHT 272 Activity 2Dokument6 SeitenNursing Pharma 1445 PHT 272 Activity 2rory06363Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sessionwise Topics List Sure Shot 150 Dr. NikitaDokument6 SeitenSessionwise Topics List Sure Shot 150 Dr. NikitaShashi100% (1)
- Clinical Chemistry IDokument8 SeitenClinical Chemistry IMariel AbatayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital's Drug Formulary (2nd Edition)Dokument96 SeitenHospital's Drug Formulary (2nd Edition)henry omacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- PG 0005Dokument1 SeitePG 0005m7876Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic Nervous System FunctionsDokument25 SeitenAutonomic Nervous System FunctionsLisa KangNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Central and Peripheral Nertvous SystemDokument5 SeitenGeneral Central and Peripheral Nertvous SystemSubramaniam KrishnamoorthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echidnas: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyVon EverandEchidnas: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mirtazapina + ZincDokument6 SeitenMirtazapina + ZincPablo Maldonado MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrument and Drug ListDokument4 SeitenInstrument and Drug ListAaditya GadhviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Points of Antipsychotics and AntidepressantsDokument51 SeitenPractical Points of Antipsychotics and AntidepressantsHayaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nsaids: Dr.B.M.Purohit Assistant Professor (Pharmacology) P.D.U.Medical College, Rajkot (GUJARAT) - 360001Dokument83 SeitenNsaids: Dr.B.M.Purohit Assistant Professor (Pharmacology) P.D.U.Medical College, Rajkot (GUJARAT) - 360001Masali MacdonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDokument4 SeitenEVikash KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Elektroakupunktur For Pain (Nyeri)Dokument52 SeitenA. Elektroakupunktur For Pain (Nyeri)effiekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To CNS PharmacologyDokument49 SeitenIntroduction To CNS Pharmacologymatchees-gone rogueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahanr 3 Ftambahkohen 2002Dokument10 SeitenBahanr 3 Ftambahkohen 2002Fitri anaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biophysics of Action Potential & Synapse: Ivan PoliačekDokument40 SeitenBiophysics of Action Potential & Synapse: Ivan PoliačekRam RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap Psychology - Unit 2 - Biopsych' Terms: Bloodstream Flight Hormones, AdrenalineDokument2 SeitenAp Psychology - Unit 2 - Biopsych' Terms: Bloodstream Flight Hormones, Adrenalineapi-421695293Noch keine Bewertungen
- DECYSYM - Paper - The Endocannabinoid System Is Present in Rod Outer Segments From Retina and Is Modulated by LightDokument12 SeitenDECYSYM - Paper - The Endocannabinoid System Is Present in Rod Outer Segments From Retina and Is Modulated by LightLucianoIgnacioMudryjNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOUDIDokument10 SeitenDOUDIToufik QlfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hsp70 and Hsp40 Chaperone Activities in The Cytoplasm and The Nucleus of Mammalian CellsDokument39 SeitenHsp70 and Hsp40 Chaperone Activities in The Cytoplasm and The Nucleus of Mammalian CellsjojonsharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week4 PCR Detailed StrategyDokument6 SeitenWeek4 PCR Detailed StrategyArjun BujjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDokument42 SeitenThe Autonomic Nervous SystemArkene LevyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ain NeuroanatomyDokument5 SeitenAin NeuroanatomyLabana LabanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Van Gogh's Epilepsy and CreativityDokument30 SeitenVan Gogh's Epilepsy and CreativityAndreea RalucaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMP 3564Dokument10 SeitenTMP 3564FrontiersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cis-Trans Isomeric Carotenoids, Vitamins A and ArylpolyenesVon EverandCis-Trans Isomeric Carotenoids, Vitamins A and ArylpolyenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Nikita's NEETPG 2021 RECALL - All 200Q - FinalDokument14 SeitenDr. Nikita's NEETPG 2021 RECALL - All 200Q - FinalDheeraj GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs - Group Wise and InstrumentsDokument1 SeiteDrugs - Group Wise and InstrumentsAaditya GadhviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caregiving Practicum Medical Terminology ReviewDokument3 SeitenCaregiving Practicum Medical Terminology ReviewJan Marielle CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Monitoring Sept 2020Dokument112 SeitenDrug Monitoring Sept 2020aleksme88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topicslist Sure Shot 150 Dr. NikitaDokument6 SeitenTopicslist Sure Shot 150 Dr. NikitaShashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManualDokument113 SeitenManualJose PototskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of SynapsesDokument17 SeitenDisorders of Synapsessana1994Noch keine Bewertungen
- 244 IndexDokument2 Seiten244 IndexVasilii LentitchiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Cortisol Suppresses Pituitary and Hypothalamic Peptide Message Expression in Pigtailed MacaquesDokument6 SeitenChronic Cortisol Suppresses Pituitary and Hypothalamic Peptide Message Expression in Pigtailed MacaquesFrontiersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to Pediatric Physical Exam: Gen Survey, Vital Signs, Anthropometry & Skin InspectionDokument9 SeitenGuide to Pediatric Physical Exam: Gen Survey, Vital Signs, Anthropometry & Skin InspectionCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Protocol - BechaydaDokument9 SeitenCase Protocol - BechaydaCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lumbar Tap - Procedure, Indications, Contraindications - Analysis of Normal CSF ResultsDokument4 SeitenLumbar Tap - Procedure, Indications, Contraindications - Analysis of Normal CSF ResultsCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypoglycemic Effect of Catharantus Roseus (Tsitsirika) Against Albino RabbitsDokument2 SeitenHypoglycemic Effect of Catharantus Roseus (Tsitsirika) Against Albino RabbitsCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Severe Headache: Clinical Manifestations: LOC, GCS 3, Anisocoric Pupils, Very Minimal Eyelid Movements To CornealDokument1 SeiteSevere Headache: Clinical Manifestations: LOC, GCS 3, Anisocoric Pupils, Very Minimal Eyelid Movements To CornealCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGD For NCD and Disease Occurrence: MD1-1 Group 4Dokument4 SeitenSGD For NCD and Disease Occurrence: MD1-1 Group 4Carlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Long Exam 1 2 Yr - 2 Sem 2016: ND NDDokument2 SeitenPharmacology Long Exam 1 2 Yr - 2 Sem 2016: ND NDCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innate Immune Response: Defensins - Most Abundant Antimicrobial Peptides That Kill Bacteria (G+ andDokument5 SeitenInnate Immune Response: Defensins - Most Abundant Antimicrobial Peptides That Kill Bacteria (G+ andCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gross Anats Presem ReviewDokument14 SeitenGross Anats Presem ReviewCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypoglycemic Effect of Catharantus Roseus (Tsitsirika) Against Albino RabbitsDokument2 SeitenHypoglycemic Effect of Catharantus Roseus (Tsitsirika) Against Albino RabbitsCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Officinale) Which Exhibited Its Anti-Angiogenic Property by Decreasing The CAMDokument2 SeitenOfficinale) Which Exhibited Its Anti-Angiogenic Property by Decreasing The CAMCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carlos D. Achondo Jr. 2MD-1Dokument4 SeitenCarlos D. Achondo Jr. 2MD-1Carlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RespiDokument3 SeitenRespiCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Officinale) Which Exhibited Its Anti-Angiogenic Property by Decreasing The CAMDokument2 SeitenOfficinale) Which Exhibited Its Anti-Angiogenic Property by Decreasing The CAMCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem3 Amino AcidsDokument3 SeitenBiochem3 Amino AcidsCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart, Blood and Lymph NodesDokument12 SeitenHeart, Blood and Lymph NodesCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabi For Basic PharmacologyDokument1 SeiteSyllabi For Basic PharmacologyCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Le Ga 1Dokument15 SeitenLe Ga 1Carlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Higher Cortical FunctionsDokument2 SeitenHigher Cortical FunctionsCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histo Path PUDDokument1 SeiteHisto Path PUDCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gross Anats Presem ReviewDokument14 SeitenGross Anats Presem ReviewCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Schools Needed Say CampaignersDokument11 SeitenIn Schools Needed Say CampaignersCarlos NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tools AssistDokument5 SeitenTools AssistAGRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Dopamine Receptors: 1 S 2 I 2A 2C 2C 2ADokument2 SeitenDopamine Receptors: 1 S 2 I 2A 2C 2C 2AMike GNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG-ABUSE-WPS-Office (Grade 9-Report)Dokument11 SeitenDRUG-ABUSE-WPS-Office (Grade 9-Report)Ailyn UmlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug AbuseDokument13 SeitenDrug AbuseLydah Trina RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antidepressant MCQs Group 2Dokument4 SeitenAntidepressant MCQs Group 2Ayesha AyeshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TC in 200 Pages PDFDokument195 SeitenTC in 200 Pages PDFWaleed MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UT Dallas Syllabus For nsc4363.001.08s Taught by Lucien Thompson (Tres)Dokument3 SeitenUT Dallas Syllabus For nsc4363.001.08s Taught by Lucien Thompson (Tres)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caplan, Michael J-Reference Module in Biomedical Research-Elsevier (2014)Dokument17 SeitenCaplan, Michael J-Reference Module in Biomedical Research-Elsevier (2014)Muhammad IkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument5 SeitenDrugsJessica GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS Acting Drugs and Their MechanismsDokument84 SeitenCNS Acting Drugs and Their MechanismsAishwarya PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacy Endorsement LetterDokument2 SeitenPharmacy Endorsement LetterShielo Marie CabañeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dangerous DrugsDokument13 SeitenDangerous Drugsjames van naronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit One Vocabulary: 'prɔvidәntDokument53 SeitenUnit One Vocabulary: 'prɔvidәntKhanh Chi NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs FOR Psychiatric & Neurologic Disorders: Clonazepam (Klonopin, Rivotril) Midazolam (Versed, Dormicum)Dokument5 SeitenDrugs FOR Psychiatric & Neurologic Disorders: Clonazepam (Klonopin, Rivotril) Midazolam (Versed, Dormicum)Noriko MatsumotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychotropic Medications by Trade and Generic NameDokument9 SeitenPsychotropic Medications by Trade and Generic NameSyed BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS 3075593948Dokument3 SeitenCS 3075593948DantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bản Sao Tóm Tắt Các ThuốcDokument10 SeitenBản Sao Tóm Tắt Các ThuốcHan NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Types of DrugsDokument8 SeitenCommon Types of DrugsFELIX Mary Ann G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Question Bank AnsDokument36 SeitenPharmacology Question Bank AnsNeelam RamanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGDokument13 SeitenDRUGReniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article4Archives32021 3509Dokument7 SeitenArticle4Archives32021 3509Slobodna DalmacijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chupp's Herb 3000mg Berry - BT 345 12278Dokument1 SeiteChupp's Herb 3000mg Berry - BT 345 12278CJ PetersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Classifications and the Six Types of Drugs of AbuseDokument8 SeitenDrug Classifications and the Six Types of Drugs of AbuseRizalyn GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PENGGOLONGAN OBAT PSIKOTROPIK DAN SEDIAAN OBAT ANTI-PSIKOSISDokument18 SeitenPENGGOLONGAN OBAT PSIKOTROPIK DAN SEDIAAN OBAT ANTI-PSIKOSISMirzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Med Card PregabalinDokument1 SeiteMed Card PregabalinTaylor NicholNoch keine Bewertungen