Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
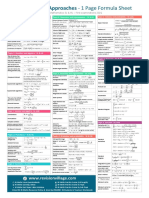
Applications & Interpretation - 1 Page Formula Sheet: IB Mathematics SL & HL - First Examinations 2021
Hochgeladen von
Zia SilverOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Applications & Interpretation - 1 Page Formula Sheet: IB Mathematics SL & HL - First Examinations 2021
Hochgeladen von
Zia SilverCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Applications & Interpretation - 1 Page Formula Sheet
IB Mathematics SL & HL – First examinations 2021
Prior Learning SL & HL Topic 3: Geometry and trigonometry – SL & HL Topic 4: Statistics and probability - SL & HL
Area: Parallelogram 𝐴 = 𝑏ℎ , 𝑏 = base, ℎ = height Distance between 2 points distance
(𝑑) = Interquartile range IQR = 𝑄3 − 𝑄1
1
𝐴 = 2 (𝑏ℎ) , 𝑏 = base, ℎ = height (𝒙𝟏 , 𝒚𝟏 , 𝒛𝟏 ) , (𝒙𝟐 , 𝒚𝟐 , 𝒛𝟐 ) √(𝑥1 − 𝑥2 )2 + (𝑦1 − 𝑦2 )2 + (𝑧1 − 𝑧2 )2 ∑𝑘
Area: Triangle 𝑖=1 𝑓𝑖 𝑥𝑖
Mean, ̅
𝒙 , of a set of data 𝑥̅ = , where 𝑛 = ∑𝑘𝑖=1 𝑓𝑖
1 𝑛
Area: Trapezoid 𝐴 = 2 (𝑎 + 𝑏)ℎ , 𝑎, 𝑏 = parallel sides, ℎ = height Coordinates of the 𝑥1 + 𝑥2 𝑦1 + 𝑦2 𝑧1 + 𝑧2 𝑛(𝐴)
midpoint with endpoints ( , , ) Probability of an event 𝑨 P(𝐴) =
Area: Circle 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟 2 , 𝑟 = radius (𝒙𝟏 , 𝒚𝟏 , 𝒛𝟏 ) , (𝒙𝟐 , 𝒚𝟐 , 𝒛𝟐 ) 2 2 2 𝑛(𝑢)
Circumference: Circle 𝐶 = 2𝜋𝑟, 𝑟 = radius 1 Complementary events P(𝐴) + P(𝐴′ ) = 1
Volume: Right-pyramid 𝑉 = 3 𝐴ℎ , 𝐴 = base area, ℎ = height
Volume: Cuboid 𝑉 = 𝑙𝑤ℎ , 𝑙 = length, 𝑤 = width, ℎ = height Combined events P(𝐴 ∪ 𝐵) = P(𝐴) + P(𝐵) − P(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵)
1
Volume: Right cone 𝑉 = 3 𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ , 𝑟= radius, ℎ = height P(𝐴 ∪ 𝐵) = P(𝐴) + P(𝐵)
Volume: Cylinder 𝑉 = 𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ , 𝑟 = radius, ℎ = height Mutually exclusive events
Volume: Prism 𝑉 = 𝐴ℎ , 𝐴 = cross-section area, ℎ = height Area: Cone curve 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟𝑙 , 𝑟= radius, 𝑙 = slant height P(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵)
Conditional probability P(𝐴|𝐵) =
P(𝐵)
Area: Cylinder curve 𝐴 = 2𝜋𝑟ℎ , 𝑟 = radius, ℎ = height Volume: Sphere
4 3
𝑉 = 3 𝜋𝑟 , 𝑟 = radius
Independent events P(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵) = P(𝐴)P(𝐵)
Distance between two
𝑑 = √(𝑥1 − 𝑥2 )2 + (𝑦1 − 𝑦2 )2 Surface area: Sphere 𝐴 = 4𝜋𝑟 2 , 𝑟 = radius Expected value of a
points (𝒙𝟏 , 𝒚𝟏 ) , (𝒙𝟐 , 𝒚𝟐 ) E(𝑋) = ∑ 𝑥 P(𝑋 = 𝑥)
discrete random variable X
𝑎 𝑏 𝑐
Coordinates of midpoint (
𝑥1+𝑥2 𝑦1 +𝑦2
, ), for endpoints (𝑥1 , 𝑦1), (𝑥2 , 𝑦2 ) Sine rule = = Binomial distribution 𝑋~B(𝑛, 𝑝)
2 2 sin𝐴 sin𝐵 sin𝐶
Mean ; Variance E(𝑋) = 𝑛𝑝 ; Var(𝑋) = 𝑛𝑝(1 − 𝑝)
Prior Learning HL only 𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏2 − 2𝑎𝑏 cos 𝐶
Solutions of a Cosine rule 𝑎2 + 𝑏2 − 𝑐 2 Topic 4: Statistics and probability – HL only
−𝑏 ± √𝑏2 − 4𝑎𝑐 cos 𝐶 =
quadratic equation in 𝑥= ,𝑎 ≠ 0 2𝑎𝑏 Linear transformation of a E(𝑎𝑋 + 𝑏) = 𝑎E(𝑋) + 𝑏
the form 𝒂𝒙𝟐 + 𝒃𝒙 + 𝒄 2𝑎
1 single random variable Var(𝑎𝑋 + 𝑏) = 𝑎2 Var(𝑋)
Area: Triangle 𝐴 = 𝑎𝑏 sin 𝐶
2 E(𝑎1 𝑋1 ± 𝑎2 𝑋2 ±. . . ±𝑎𝑛 𝑋𝑛 ) =
Topic 1: Number and algebra - SL & HL 𝜃 Linear combinations of 𝒏 𝑎1 E(𝑋1 ) ± 𝑎2 E(𝑋2 )± . . . ±𝑎𝑛 E(𝑋𝑛 )
𝑙= × 2𝜋𝑟
The 𝒏th term of an Length of an arc 360 independent random Var(𝑎1 𝑋1 ± 𝑎2 𝑋2 ±. . . ±𝑎𝑛 𝑋𝑛 ) =
𝑢𝑛 = 𝑢1 + (𝑛 − 1)𝑑 𝜃 = angle in degrees, 𝑟 = radius variables, 𝑿𝟏 , 𝑿𝟐 , … . 𝑿𝒏
arithmetic sequence 𝑎1 2 Var(𝑋1 ) + 𝑎2 2 Var(𝑋2 ) + ⋯ +
Sum of 𝒏 terms of an 𝑛 𝑛 𝜃 𝑎𝑛 2 Var(𝑋𝑛 )
𝑠𝑛 = (2𝑢1 + (𝑛 − 1)𝑑) = (𝑢1 + 𝑢𝑛 ) 𝐴= × 𝜋𝑟 2
arithmetic sequence 2 2 Area of a sector 360 Unbiased estimate of 2
𝑛
𝑠𝑛−1 = 𝑠2 Sample statistics
The 𝒏th term of a 𝜃 = angle in degrees, 𝑟 = radius population variance 𝑛−1 𝑛
𝑢𝑛 = 𝑢1 𝑟 𝑛−1
𝑋~Po(𝑚)
geometric sequence
Topic 3: Geometry and trigonometry – HL only Poisson distribution
Sum of 𝒏 terms of a 𝑢1 (𝑟 𝑛 − 1) 𝑢1 (1 − 𝑟 𝑛 ) Mean ; Variance E(𝑋) = 𝑚 ; Var(𝑋) = 𝑚
𝑠𝑛 = = ,𝑟 ≠ 1 𝑙 = 𝑟𝜃
finite geometric seq. 𝑟−1 1−𝑟 Length of an arc Transition matrices 𝑻𝑛 𝒔0 = 𝒔𝑛 , where 𝒔0 is the initial state
𝑟 = radius, 𝜃 = angle in radians
𝑟 𝑘𝑛
𝐹𝑉 = 𝑃𝑉 × (1 + ) 1
100𝑘 𝐴 = 𝑟2 𝜃 Topic 5: Calculus - SL & HL
Area of a sector 2
Compound interest 𝐹𝑉 is future value, 𝑃𝑉 is present value, 𝑛 Derivative of 𝒙𝒏
𝑟 = radius, 𝜃 = angle in radians 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 𝑛 → 𝑓′(𝑥) = 𝑛𝑥 𝑛−1
is the number of years, 𝑘 is the number of
cos 2 𝜃 + sin2 𝜃 = 1 𝑥 𝑛+1
compounding periods per year, 𝑟% is the Integral of 𝒙 𝒏
∫ 𝑥 𝑛 𝑑𝑥 = + 𝐶 , 𝑛 ≠ −1
nominal annual rate of interest Identities sin 𝜃 𝑛+1
tan 𝜃 = 𝑏
cos 𝜃 Area enclosed by a
Exponents & logarithms 𝑎 𝑥 = 𝑏 ↔ 𝑥 = log 𝑎 𝑏 , 𝑎, 𝑏 > 0, 𝑎 ≠ 1 𝐴 = ∫ 𝑦 𝑑𝑥 , where 𝑓(𝑥) > 0
cos 2𝜃 sin 2𝜃 curve and the 𝒙-axis 𝑎
𝑣𝐴 − 𝑣𝐸 ( )
𝜀=| | × 100% sin 2𝜃 −cos 2𝜃 𝑏
Percentage error 𝑣𝐸 ∫ 𝑦 𝑑𝑥 ≈
reflection in the line 𝑦 = (tan 𝜃)𝑥 The trapezoidal rule
𝑣𝐴 = approximate value, 𝑣𝐸 = exact value 𝑏−𝑎
𝑎
𝑘 0 where ℎ = 1
( ) 𝑛
ℎ((𝑦0 + 𝑦𝑛 ) + 2(𝑦1 + 𝑦2 +. . . +𝑦𝑛−1 ))
Topic 1: Number and algebra - HL only 0 1 2
horizontal stretch by scale factor of 𝑘
log 𝑎 𝑥𝑦 = log 𝑎 𝑥 + log 𝑎 𝑦 Topic 5: Calculus – HL only
𝑥 1 0
log 𝑎 = log 𝑎 𝑥 − log 𝑎 𝑦 ( ) Derivative of 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = sin 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) = cos 𝑥
Laws of logarithms 𝑦 0 𝑘
log 𝑎 𝑥 𝑚 = 𝑚 log 𝑎 𝑥 Transformation vertical stretch with scale factor of 𝑘 Derivative of 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = cos 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) = − sin 𝑥
for 𝑎, 𝑥, 𝑦 > 0 matrices 𝑘 0 1
( ) centre (0,0) Derivative of 𝐭𝐚𝐧 𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = tan 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) =
The sum of an infinite 𝑢1 0 𝑘 cos 2 𝑥
𝑠∞ = , |𝑟| < 1 enlargement with scale factor of 𝑘 Derivative of 𝒆𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑒 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) = 𝑒 𝑥
geometric sequence 1−𝑟
𝑧 = 𝑎 + 𝑏𝑖 cos 𝜃 − sin 𝜃 1
Complex numbers ( ) , anticlockwise rotation Derivative of 𝐥𝐧 𝒙 𝑓(𝑥) = ln 𝑥 → 𝑓′(𝑥) =
sin 𝜃 cos 𝜃 𝑥
Discriminant ∆ = 𝑏2 − 4𝑎𝑐 of angle 𝜃 about the origin (𝜃 > 0) 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑢
Modulus-argument cos 𝜃 sin 𝜃
Chain rule 𝑦 = 𝑔(𝑢) , 𝑢 = 𝑓(𝑥) → = ×
( ) , clockwise rotation 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑥
(polar) & Exponential 𝑧 = 𝑟(cos 𝜃 + 𝑖 sin 𝜃) = 𝑟𝑒 𝑖𝜃 = 𝑟cis𝜃 −sin 𝜃 cos 𝜃 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑣 𝑑𝑢
(Euler) form of angle 𝜃 about the origin (𝜃 > 0) Product rule 𝑦 = 𝑢𝑣 → =𝑢 +𝑣
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥
Determinant of a 𝑎 𝑏 𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑣
𝑨=( ) → det 𝑨 = |𝑨| = 𝑎𝑑 − 𝑏𝑐 Magnitude of a vector |𝒗| = √𝑣1 2 + 𝑣2 2 + 𝑣3 2 𝑢 𝑑𝑦 𝑣 𝑑𝑥 − 𝑢 𝑑𝑥
2×2 matrix 𝑐 𝑑 Quotient rule 𝑦= → =
𝑣 𝑑𝑥 𝑣2
Inverse of a 𝑎 𝑏 1 𝑑 −𝑏 Vector equ. of a line 𝒓 = 𝒂 + 𝜆𝒃
𝑨=( ) → 𝑨−1 = ( ) 1
2×2 matrix 𝑐 𝑑 det 𝑨 −𝑐 𝑎 ∫ 𝑑𝑥 = ln|𝑥| + 𝐶
Parametric form of the 𝑥
𝑴𝑛 = 𝑷𝑫𝑛 𝑷−1 , where 𝑷 is the matrix of 𝑥 = 𝑥0 + 𝜆𝑙, 𝑦 = 𝑦0 + 𝜆𝑚, 𝑧 = 𝑧0 + 𝜆𝑛
Power formula for a equation of a line ∫ sin 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = − cos 𝑥 + 𝐶
eigenvectors and 𝑫 is the diagonal matrix
matrix
of eigenvalues 𝒗 ∙ 𝒘 = 𝑣1 𝑤1 + 𝑣2 𝑤2 + 𝑣3 𝑤3
Standard integrals ∫ cos 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = sin 𝑥 + 𝐶
Scalar product 𝒗 ∙ 𝒘 = |𝒗||𝒘| cos 𝜃
Topic 2: Functions – SL & HL where 𝜃 is the angle between 𝒗 and 𝒘 ∫
1
𝑑𝑥 = tan 𝑥 + 𝐶
cos 2 𝑥
Equations of a 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐 ; 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑦 + 𝑑 = 0 ; Angle between two 𝑣1 𝑤1 + 𝑣2 𝑤2 + 𝑣3 𝑤3
cos 𝜃 = ∫ 𝑒 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑒 𝑥 + 𝐶
straight line 𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 ) vectors |𝒗||𝒘|
𝑦2 − 𝑦1 𝑣2 𝑤3 − 𝑣3 𝑤2 𝑏 𝑏
𝑚= Area enclosed by a
Gradient formula
𝑥2 − 𝑥1 𝐴 = ∫ |𝑦| 𝑑𝑥 or 𝐴 = ∫ |𝑥| 𝑑𝑦
𝒗 × 𝒘 = (𝑣3 𝑤1 − 𝑣1 𝑤3 ) curve and 𝒙 or 𝒚-axes 𝑎 𝑎
𝑏 𝑣1 𝑤2 − 𝑣2 𝑤1
Axis of symmetry of a Vector product 𝑏 𝑏
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 → 𝑥 = − |𝒗 × 𝒘| = |𝒗||𝒘| sin 𝜃
Volume of revolution
𝑉 = ∫ 𝜋𝑦 2 𝑑𝑥 or 𝑉 = ∫ 𝜋𝑥 2 𝑑𝑦
quadratic function 2𝑎 about 𝒙 or 𝒚-axes 𝑎 𝑎
Topic 2: Functions – HL only where 𝜃 is the angle between 𝒗 and 𝒘
d𝑣 d2 𝑠 d𝑣
Acceleration 𝑎= = =𝑣
𝐿 Area of a 𝐴 = |𝒗 × 𝒘| , where 𝒗 and 𝒘 form two d𝑡 d𝑡 2 d𝑠
Logistic function 𝑓(𝑥) = , 𝐿, 𝑘, 𝐶 > 0
1 + 𝐶𝑒 −𝑘𝑥 parallelogram adjacent sides of a parallelogram Distance; Displacement 𝑡 𝑡
dist = ∫𝑡 2|𝑣(𝑡)| 𝑑𝑡 ; disp = ∫𝑡 2 𝑣(𝑡) 𝑑𝑡
travelled from 𝒕𝟏 to 𝒕𝟐 1 1
𝑦𝑛+1 = 𝑦𝑛 + ℎ × 𝑓(𝑥𝑛 , 𝑦𝑛 ); 𝑥𝑛+1 = 𝑥𝑛 + ℎ
Euler’s method
www.revisionvillage.com where ℎ is a constant (step length)
𝑥𝑛+1 = 𝑥𝑛 + ℎ × 𝑓1 (𝑥𝑛 , 𝑦𝑛 , 𝑡𝑛 )
IB Maths Exam Questionbanks IB Maths Practice Exams (Full Length) Euler’s method for 𝑦𝑛+1 = 𝑦𝑛 + ℎ × 𝑓2 (𝑥𝑛 , 𝑦𝑛 , 𝑡𝑛 )
IB Maths Learning Videos IB Maths Practice Exams by Topic coupled systems 𝑡𝑛+1 = 𝑡𝑛 + ℎ
where ℎ is a constant (step length)
IB Maths Past Paper Video Solutions IB Maths Practice Exams by Sub-Topic
Exact solution for
Voted #1 IB Maths Resource Online & Used by 250,000+ IB Students & Teachers Worldwide coupled linear 𝒙 = 𝐴𝑒 𝜆1 𝑡 𝒑1 + 𝐵𝑒 𝜆2𝑡 𝒑2
differential equations
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetDokument1 SeiteAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetFN6012021 RAVICHANDRAN GOKULNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.3Dokument1 SeiteAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.3Chantal TockeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetDokument1 SeiteAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula SheetAmanda PoetirayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDokument37 SeitenWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizEdal SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sequences IBDokument15 SeitenSequences IBEjaz AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Maths IADokument20 SeitenIB Maths IAMilla RamnebroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Theorems PDFDokument13 SeitenGeometry Theorems PDFmandeep singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus - Differentiation 1Dokument69 SeitenCalculus - Differentiation 1Amina Rakha HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 - Question BankDokument677 SeitenPaper 2 - Question BankRingo ChungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Dokument1 SeiteFormula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Roberto DiscutidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus Review Packet NovemberDokument23 SeitenCalculus Review Packet NovemberagwenexusNoch keine Bewertungen
- HL Year 1 Random Trig Practice ProblemsDokument6 SeitenHL Year 1 Random Trig Practice ProblemslilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet On Derivatives 3Dokument8 SeitenWorksheet On Derivatives 3Darshana Madushanka100% (1)
- Math HL (Part 1)Dokument17 SeitenMath HL (Part 1)Chirag HablaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trig Equations for Modelling ProblemsDokument5 SeitenTrig Equations for Modelling ProblemsRita LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Paper 1 TZ1 SL PDFDokument12 SeitenMathematics Paper 1 TZ1 SL PDFvikusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test1 HL Seq Series Bin THM v1Dokument2 SeitenTest1 HL Seq Series Bin THM v1priyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math IB Revision Differentiation BasicsDokument3 SeitenMath IB Revision Differentiation Basicsmykiri79100% (1)
- Mathematics Ia CompDokument19 SeitenMathematics Ia CompAnonymous umm8CDYcpMNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBSL Circular Functions and Trig QsDokument6 SeitenIBSL Circular Functions and Trig QsJashkirat VirdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MYP 5 - Looping Back Revision SheetDokument17 SeitenMYP 5 - Looping Back Revision SheetridhimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Mathematics AA: 2020-2022Dokument3 SeitenIB Mathematics AA: 2020-2022min LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.4 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, Sum and Product of The Zeros of PolynomialsDokument4 Seiten3.4 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, Sum and Product of The Zeros of PolynomialsAryan WaghdhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCT MC (T + 273) : IB Chemistry SL Topic 5 Questions 1. 5. 9Dokument16 SeitenMCT MC (T + 273) : IB Chemistry SL Topic 5 Questions 1. 5. 9MiriamNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Math Probability Practice(b) 11/36(C2Dokument13 SeitenIB Math Probability Practice(b) 11/36(C2Abdullah AmbusaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39Von EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39Noch keine Bewertungen
- 102 Transformation of GraphsDokument8 Seiten102 Transformation of GraphsJoel GrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathHL QB3 T2Dokument25 SeitenMathHL QB3 T2Nikola PetrovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Analytic GeometryDokument15 SeitenApplications of Analytic GeometrydaniloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Math Studies Unit 3 Review NotesDokument8 SeitenIb Math Studies Unit 3 Review Notesapi-262324064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Aa SL MathsDokument9 SeitenIb Aa SL MathsAbhipsa PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions Practice ProblemsDokument4 SeitenFunctions Practice ProblemstaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venn Diagram Probability ProblemsDokument40 SeitenVenn Diagram Probability Problemstaimoor2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Higher Level Paper 2: Instructions To CandidatesDokument12 SeitenMathematics Higher Level Paper 2: Instructions To CandidatesРуддщNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test3 - Complex Numbers: W Z W Z in Its Simplest FormDokument11 SeitenTest3 - Complex Numbers: W Z W Z in Its Simplest FormOrisa THANAJARONoch keine Bewertungen
- 13-3 Volume of SphereDokument18 Seiten13-3 Volume of SphereMr. AulisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic EquationDokument1 SeiteQuadratic EquationEmyRaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations On MatricesDokument2 SeitenOperations On MatricesAngelinaGuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Trigonometric EquationsDokument3 SeitenSolving Trigonometric EquationsjamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Quadratic Equations PDFDokument4 SeitenSolving Quadratic Equations PDFMario CalderonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exponential and Logarithmic Functions ReviewDokument19 SeitenExponential and Logarithmic Functions ReviewPaco WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB REVIEW - Integration 2012Dokument6 SeitenIB REVIEW - Integration 2012makunjapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsDokument4 SeitenVectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsJasmine YimNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Diploma Math Repayment QuestionsDokument4 SeitenIB Diploma Math Repayment QuestionsVishal Gadhiya0% (1)
- Logarithms and Exponets Worksheet Exam Style PDFDokument2 SeitenLogarithms and Exponets Worksheet Exam Style PDFYuan CuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- G Force Tolerance IB Math Portfolio Maths IA SL Course Work G Force ToleranceDokument1 SeiteG Force Tolerance IB Math Portfolio Maths IA SL Course Work G Force ToleranceIb IaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Math SL Statistics ReviewDokument11 SeitenIB Math SL Statistics ReviewJorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Level Permutation and Combination, Probability QuestionsDokument4 SeitenCAT Level Permutation and Combination, Probability QuestionsKshitija Sahani100% (1)
- Maths Ai Study GuideDokument77 SeitenMaths Ai Study GuideNaomi BoesonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Approaches Standard May 2021 Paper 1 TZDokument12 SeitenAnalysis and Approaches Standard May 2021 Paper 1 TZJailani AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- (9660) Outline Schemes of WorkDokument10 Seiten(9660) Outline Schemes of WorkNovanolo Christovori ZebuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Extension Exam Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenMath Extension Exam Cheat SheetRishineel SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Specialist 3C3D Calc Assumed Ratified Marking Key 2015Dokument26 SeitenMathematics Specialist 3C3D Calc Assumed Ratified Marking Key 2015Dark LordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patterns From Complex Numbers IB Math Portfolio Maths IA HL Course Work Patterns From Complex NumbersDokument1 SeitePatterns From Complex Numbers IB Math Portfolio Maths IA HL Course Work Patterns From Complex NumbersIb Ia50% (2)
- 11.1 The Area Between Two Curves 12 PDFDokument12 Seiten11.1 The Area Between Two Curves 12 PDFHin Wa LeungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Theorem Cheat SheetDokument4 SeitenGeometry Theorem Cheat Sheetsaksham50% (2)
- GCSE Trigonometry Revision Cards: SohcahtoaDokument5 SeitenGCSE Trigonometry Revision Cards: SohcahtoaboostoberoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics HL Paper 1 TZ1 PDFDokument15 SeitenMathematics HL Paper 1 TZ1 PDFMary LuNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBDP Arithmetic Sequence WorksheetDokument3 SeitenIBDP Arithmetic Sequence WorksheetbalajibabutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications and Interpretation 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.1Dokument1 SeiteApplications and Interpretation 1 Page Formula Sheet V1.1talahamayel07Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 YISS - Beginning Korean Language IDokument3 Seiten2020 YISS - Beginning Korean Language IZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 YISS - 4 Week - KOREAN (1) - Dongsook KimDokument2 Seiten2020 YISS - 4 Week - KOREAN (1) - Dongsook KimZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0580 w14 Ms 12Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 12Haider Ali50% (2)
- 0580 w14 Ms 21Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 21Haider Ali100% (1)
- 2020 YISS - Beginning Korean Language IDokument3 Seiten2020 YISS - Beginning Korean Language IZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0580 w14 Ms 22Dokument5 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 22Haider Ali50% (2)
- Math HL Formula Booklet 2015 VersionDokument15 SeitenMath HL Formula Booklet 2015 VersionChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 YISS - Beginning Korean Language IIDokument3 Seiten2020 YISS - Beginning Korean Language IIZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 YISS - 4 Week - KOREAN (1) - Dongsook KimDokument2 Seiten2020 YISS - 4 Week - KOREAN (1) - Dongsook KimZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silabus Sekolah UI - UXDokument9 SeitenSilabus Sekolah UI - UXMochamad IbnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0580 w14 Ms 12Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 12Haider Ali50% (2)
- 0580 w14 Ms 23Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 23Haider Ali100% (3)
- 0580 w14 Ms 21Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 21Haider Ali100% (1)
- 0580 w14 Ms 23Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 23Haider Ali100% (3)
- 0580 w14 Ms 21Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 21Haider Ali100% (1)
- 0580 w14 Ms 12Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 12Haider Ali50% (2)
- Applications & Interpretation - 1 Page Formula Sheet: IB Mathematics SL & HL - First Examinations 2021Dokument1 SeiteApplications & Interpretation - 1 Page Formula Sheet: IB Mathematics SL & HL - First Examinations 2021Zia Silver100% (1)
- 0580 w14 Ms 23Dokument4 Seiten0580 w14 Ms 23Haider Ali100% (3)
- Analysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDFDokument1 SeiteAnalysis and Approaches 1 Page Formula Sheet PDFZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 2019: Online SampleDokument1 SeiteMathematics 2019: Online SampleZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utah Math Graduate Bulletin 2013-2014Dokument68 SeitenUtah Math Graduate Bulletin 2013-2014Zia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Natural Sciences Test-421Dokument14 Seiten2012 Natural Sciences Test-421amandashn96Noch keine Bewertungen
- FT MBA Questionnaire Young Leader Scholarship 2014Dokument1 SeiteFT MBA Questionnaire Young Leader Scholarship 2014Zia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO2015SLDokument83 SeitenIMO2015SLHimansu Mookherjee100% (1)
- Practice Test E Section 2 Structure and Written ExpressionDokument8 SeitenPractice Test E Section 2 Structure and Written ExpressionZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bali - Bps.go - Id Series Data Tampil Data SeriesDokument7 SeitenBali - Bps.go - Id Series Data Tampil Data SeriesZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form Surat Dan Absen CutiDokument1 SeiteForm Surat Dan Absen CutiZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Year Global MBA at World's Largest Business SchoolDokument64 SeitenOne-Year Global MBA at World's Largest Business SchoolZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Text DocumentDokument1 SeiteNew Text DocumentZia SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 The Power MethodDokument6 Seiten6 The Power MethodAnonymous pMVR77x1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exam11 MAM202 (Paper2)Dokument9 SeitenExam11 MAM202 (Paper2)rowmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-1 Syllabus R23 - CSE & DSDokument10 Seiten1-1 Syllabus R23 - CSE & DSSatish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 4883Dokument50 SeitenEx 4883Arya Mp YaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AHP Expert Survey InstructionsDokument6 SeitenAHP Expert Survey InstructionsRyan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Construction and Topological Classification of Crystalline Flat BandsDokument7 SeitenGeneral Construction and Topological Classification of Crystalline Flat BandsluoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscillation Theorems For Second-Order Nonhomogeneous Linear Differential EquationsDokument4 SeitenOscillation Theorems For Second-Order Nonhomogeneous Linear Differential Equationsiatrakisg8671Noch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of EngineeringDokument206 SeitenPrinciple of EngineeringbmhshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Analysis II - With MATLABDokument53 SeitenCircuit Analysis II - With MATLABAaron Vergara100% (1)
- Cc201-N-Engineering Mathematics - IiDokument4 SeitenCc201-N-Engineering Mathematics - IiDev OzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Algebra Lecture on Linear TransformationsDokument22 SeitenLinear Algebra Lecture on Linear Transformationsamar BaroniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study The Effects of Seismic and Wind Loads On Hyperbolic Cooling TowerDokument95 SeitenStudy The Effects of Seismic and Wind Loads On Hyperbolic Cooling TowerRkkodi100% (5)
- Damping Optimization PDFDokument11 SeitenDamping Optimization PDFFredy PicaulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stability of Castellated Beam WebsDokument142 SeitenStability of Castellated Beam WebsLuiz Flávio Vieira BrantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage and Power Stability of HVDC Systems - Emerging Issues and New Analytical MethodologiesDokument10 SeitenVoltage and Power Stability of HVDC Systems - Emerging Issues and New Analytical MethodologiesscdScdNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Guide PDFDokument183 SeitenUser Guide PDFchandi sasmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block Lms AlgorithmDokument15 SeitenBlock Lms AlgorithmSumanta BhattacharyyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copy PastaDokument2 SeitenCopy PastaStefanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pca and t-SNE Dimensionality ReductionDokument3 SeitenPca and t-SNE Dimensionality ReductionИван РадоновNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cold Magneto PlasmaDokument12 SeitenCold Magneto PlasmaJulia HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics in Chemical EngineeringDokument148 SeitenMathematics in Chemical EngineeringNelson Miguel VézuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LS-dyna Implicit Users GuideDokument62 SeitenLS-dyna Implicit Users GuidenoussnoussaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical & Statistical Anylysis For Cheme's Part1Dokument72 SeitenNumerical & Statistical Anylysis For Cheme's Part1Fug azNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes On Nonlinear Vibrations CoDokument153 SeitenLecture Notes On Nonlinear Vibrations CoGerson CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Mathematical Modelling - Theory and Applications 10) C. Rocşoreanu, A. Georgescu, N. Giurgiţeanu (Auth.) - The FitzHugh-Nagumo Model - Bifurcation and Dynamics-Springer Netherlands (2000)Dokument244 Seiten(Mathematical Modelling - Theory and Applications 10) C. Rocşoreanu, A. Georgescu, N. Giurgiţeanu (Auth.) - The FitzHugh-Nagumo Model - Bifurcation and Dynamics-Springer Netherlands (2000)neel1237Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Statistics Syl Lab UsDokument29 SeitenMSC Statistics Syl Lab UssaniljayamohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greens FunctionsDokument56 SeitenGreens FunctionsCarolina BouvierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fe LTB Manual en PDFDokument126 SeitenFe LTB Manual en PDFStefan NaricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematica As A CalculatorDokument73 SeitenMathematica As A CalculatorZafar IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen